PHAR100 exam
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
acetaminophen
Tylenol
MOA: inhibits the hypothalamic heat regulating center, has analgesic effects due to activation of descending inhibitory pathways in CNS
classification: antipyretic, non opioid analgesic
indications: fever, mild-moderate pain
contraindications: hypersensitivity, acute liver disease, severe hepatic impairment
adult dose PO: 975-1000mg to max of 4g a day, PR: 650mg q 4h no repeat
activated charcoal
MOA: absorbs toxic substances to prevent GI absorption
indications: acute poison ingestion
contraindications: GI obstruction, vomiting or unprotected airway, uncooperative patient, caustic ingestion
adverse reactions: GI; ABD distension, N/V, dental, and fecal discoloration, GI obstruction
dosage is 1g/kg to max of 50g
hydroxocobalamin
cyanokit
MOA: binds to cyanine ions and converts them to non-toxic forms for excretion
indications: cyanide poisoning
adverse reactions: increased BP, bradycardia, red urine, red skin and mucous membranes
adult dose: 5g over 15 minutes, IV infusion
acetylsalicylic acid
aspirin
MOA: inhibits COX1 and 2 to decrease prostaglandin precursors which inhibits platelet aggregation
drug interactions: thrombolytics, avoid aspirin for 24 hours
indications: acute coronary syndrome/chest pain with cardiac features
contraindications: hypersensitivity to NSAID’s
adverse reactions: bleeding, worsening of active GI ulcer
adult dosage: 160mg chewed and swallowed
dextrose
MOA: source of calories and fluid
classification: antidote, monosaccharide
indications: hypoglycemia
contraindications: hypersensitivity to corn products, hyperglycemia
adverse reactions: phlebitis, hyperglycemia, dehydration
adult dose: 25 grams q 10 min prn PO, 0.5g/kg or 10 grams reassess BGL to a max of 25 grams IV/IO
dimenhydrinate
gravol
MOA: competes with histamine for H1 receptor sites in GI tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract
classification: H1 antagonist, antiemetic
drug interactions: may potentiate CNS depressant effects of opiates, barbiturates, ethanol and other sedatives. may potentiate the effects of tricyclic antidepressants
indications: motion sickness, N/V, vertigo
contraindications: hypersensitivity, MOA inhibitors within 14 days, prostatic hypertrophy, children < 2
adverse reactions: tachycardia, dizziness, drowsiness, excitation
adult dose: 1mg/kg to max of 50 mg over 2-3 min dilute in 10ml SIVP, 50mg in mini bag over 20 minutes infusion
epinephrine
adrenaline
MOA: stimulates alpha1 and beta 1 and 2 adrenergic receptors to relax muscle of bronchial tree, stimulate cardiac output, large dosage may produce constriction of skeletal and vascular smooth muscle
indications: cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, severe asthma, croup, symptomatic bradycardia, hypotensive shock refractory to fluid resuscitation
adverse reactions: cardiac arrythmias, hypertension, nausea, vomiting
drug interactions: incompatible - sodium bicarbonate
glucagon
MOA: stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver, raising blood glucose levels. Extra effects include the relaxation of the smooth muscle of the stomach, duodenum, small bowel, and colon
classification: antidote, antihyperglycemic agent
indications: hyperglycemia, beta/calcium channel blocker OD
contraindication: hypersensitivity, pheochromocytoma
adverse reactions: nausea, increased BP, hypoglycemia
adult dosage: 1mg q 15 min max 3mg IM/SC, 2.10mg bolus IV
ibuprofen
MOA: reversibly inhibits COX1 and 2 enzymes, decreasing formation of prostaglandin precursors, also antipyretic properties
classification: analgesic, nonopioid, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory NSAID
indications: mild to moderate pain, fever
adverse reactions: decreased hemoglobin, epigastric pain, heartburn, increased bleeding time, dizziness
adult dose: 200-400 mg q 4-6 hours up to 3200mg PO/PR
drug interactions: aminoglycosides, caffeine, digoxin and vancomycin clearance may be reduced, corticosteroids may increase risk of intestinal perforation
ipratropium bromide
MOA: blocks the action of acetylcholine at the parasympathetic sites in bronchial smooth muscle
classification: bronchodilator, anticholinergic
indications: asthma exacerbation, COPD with bronchospasm
contraindications: hypersensitivity
adverse reactions: headache, nausea, dizziness
ketorolac
Toradol
MOA: decreases the formation of prostaglandins by inhibiting COX 1 and 2 enzymes, has antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory properties
classification: analgesic, nonopioid, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory NSAID
indications: moderate - severe pain
contraindications: hypersensitivity, active GI bleeding, severe hepatic impairment, hyperkalemia, serious bleeding
adverse reactions: headache, GI pain, indigestion and nausea, burning at injection site
adult dose: 10-15mg IM/IV
drug interactions: anticoagulants, heparin , diuretics, ACE inhibitors< selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors all may increase bleeding risks
naloxone
narcan
MOA: competes and displaces opioids at the opioids receptor site
classification: antidote, opioid antagonist
indications: respiratory depression associated with opioid OD
adverse reactions: agitation, body pain, irritability, shivering
adult dosage: 0.1-0.4mg titrate to effect IV/IO, 0.4-2mg IM, 1-2mg IN
nitroglycerin
nitrostat
MOA: reduces cardiac oxygen demand by decreasing payload; may reduce afterload; dilate coronary arteries and improves collateral flow to ischemic regions
classification: antianginal, vasodilator
indications: ACS and acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
contraindications: hypersensitivity, systolic BP <90mmHg, HR <50bpm, recent use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors
adverse reactions: headache, dizziness, hypotension, syncope
dose: 0.4mg q 3-5min titrate to effect SL
nitrous oxide
nitronox
MOA: general CNS depressant action
indications: pain
contraindications: hypersensitivity, inability to follow commands, intoxication, chest trauma
adverse reactions: dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting
dose: PRN titrate to effect inhaled
drug interactions: may potentiate effects of other CNS depressants such as opioids
may not work in low temps, monitor SpO2
ondansetron
MOA: blocks serotonin on vagal nerve terminals and in chemoreceptor trigger zone
classification: antiemetic, selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist
indications: acute, sever nausea and/or vomiting
adverse reactions: headache, burning at site drowsiness
adult dose: 4mg SIVP over 2-5 min every 4-6 hrs max 8mg dilute in 10ml IV, 4mg, max 8mg IM
ECG monitoring recommended in patient with electrolyte abnormalities, CHF, or bradycardia arrythmias, crosses placental barrier
oral glucose
MOA: source of calories and fluid
classification: antidote, monosaccharide
indication: hypoglycemia
contraindications: hypersensitivity to corn products, hyperglycemia
adverse reactions: electrolyte imbalances, hyperglycemia, local pain at site
oxygen
MOA: reverses hypoxemia, necessary for cellular metabolism
class: gas
indications: hypoxia, signs of inadequate tissue perfusion
adverse reactions: drying of mucus membranes
dose: 2-15 ppm titrate to effect
pharmacokinetics: onset immediate, lasts less than 2 min
oxytocin
MOA: stimulates uterine contraction by activating G-protein-coupled receptors that trigger increases in intracellular calcium levels in uterine myofibrils. decreases local prostaglandin precursors which stimulates uterine contraction.
class: uterotonic, oxytocic agent
indications: postpartum hemorrhage, to produce uterine contractions during third stage of labour
contraindications: hypersensitivity, second fetus, uterine inversion placenta previa, abrupto placenta
adverse reactions: tachycardia, premature ventricular contractions, nausea/vomiting
dose: 10 units I, 20 units in 1000mml NS or LR IV infusion then 500ml bolus titrate drip to control bleeding IV (ACP)
pharmacokinetics: onset 3-5 min, duration 2-3 hours IM
drug interactions: concurrent use of dinoprostone
methoxyflurane
penthrox
MOA: effects on substance P and beta-endorphin
classification: analgesic, non opioid
indications: pain
contraindications: hypersensitivity, renal failure, hemodynamics instability, respiratory impairment, altered LOC, malignant hyperthermia
adverse reactions: dizziness, headache, drowsiness
dose: 3ml max 6ml per day
drug interactions: may potentiate CNS depressants such as opioids or ethanol
pharmacokinetics: onset <5min, duration 60 minutes intermittent inhalation
MUST BE ABLE TO SELF ADMINISTER
salbutamol
Ventolin
MOA: relaxes bronchial smooth muscle by action on beta2 receptors with little effect on HR. redistributes and induces a transcellular shift of K
classification: bronchodilator, beta2 agonist
indications: bronchospasm, hyperkalemia
contraindications: hypersensitivity, tachyarrythmias
adverse reactions: excitement, nervousness, tremor, tachycardia
dose: 5mg titrate to effect PRN nebulized, 10 inhalations with aero chamber PRN MDI
pharmacokinetics: onset <5 min, duration 3-6 hours
drug interactions: MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants: effect on vascular system may be potentiated
use with caution in patients with glaucoma
six rights of medication
right patient, medication, dose, route, time, PCR
percutaneous, enteral, and parenteral
percutaneous: applied and absorbed through skin or mucous membranes; transdermal, sublingual, buccal, pulmonary
enteral: GI tract, usually oral; oral, per rectum
parenteral: everything else; IV, IO, IM, SQ
solid drug forms
extract: drug in solution and evaporating excess solvent
powder: pulverized form
capsule: gelatin container enclosing dose of medication
pulvule: non gelatin capsule
tablet: powdered drug pressed into small disk
suppository: drug in firm base designed to melt at body temp
ointment: semisolid designed for external application
patch: medication on the surface of a patch
liquid drug forms
solution: one or more chemicals dissolved in water
suspension: supplied as powder add water
fluid extract: concentrated drug from dissolving drug in fluid
tincture: dilute alcoholic. extract of a drug
spirits: volatile substance dissolved in alcohol
milk: aqueous suspension of insoluble drug
emulsion: one liquid dispersed in another
liniments: lotion for external use
clinical trials phases
animal testing occurs before; testing in at least 2 species is required by law
phase I: drug tested in healthy volunteers to compare with animal results
phase II: trials are performed in homogenous groups of patients and one group receives a placebo to determine safety, efficacy, and dosage
phase III: drug is made available to a larger group of patients
phase IV: drug company submits new drug submission to the HPFB for marketing approval
controlled drugs and substances act
schedule I: narcotics
schedule II: cannabis
schedule III: stimulants and hallucinogens
schedule IV: anabolic steroids, barbiturates, benzodiazepines
schedule V: phenylpropanolamine
schedule VI: precursors that can be converted into controlled substances
schedule VII: limits associated with application of cannabis - related penalties, cannabis 3kg
schedule VIII: defines limits with application of cannabis - related penalties, cannabis 30kg
canadian food and drugs act
three major classifications of drugs: non prescription, prescription, restricted
allows the government to withdraw drugs that are found to be toxic
regulation of over the counter drugs
absorption and factors
the transfer of a medication from its site of administration to specific target organ or tissue
factors affecting rate of absorption: solubility, concentration, pH of body, site, surface area of site, blood supply to site, bioavailability (how much of med is active upon reaching target)
distribution
how a drug moves through the body, its form and its concentration in the tissues influences the effect it will have. Adequate blood circulation is required.
Plasma protein binding is an important mechanism of distribution. Drugs are bound in variable degrees to proteins or become stored in fatty tissues. These are referred to as bound drug. Only those drug particles that are not bound can be active in the cells. These are referred to as free drug.
Drugs can also be stored in other body tissues such as fat and muscle for gradual release
albumin
plasma protein that is too large to diffuse out of the bloodstream which binds to meds making them ineffective
biotransformation (metabolism)
takes place mostly in liver, how the body metabolizes meds
occurs in 2 ways: transforming med into a metabolite or by making med more water soluble
only free drugs can be biotransformed
phase 1: liver enzymes oxidize the drug or bind it with oxygen molecules. may also hydrolyze it either way its more water soluble
phase 2: medication molecules combine with chemical found in body to form conjugates that are more easily excreted
excretion
occurs primarily through the kidneys in three ways:
glomerular filtration: passive process where blood flows through glomeruli of kidneys, forcing waste into a capsule where it is transported for excretion via urine
tubular secretion: active transport process where medications are bound to transporters who aid in their elimination
partial reabsorption: some amount of the drug is reabsorbed after being filtered
four mechanisms of medication action
bind to receptor site
change physical properties of cells
chemically combine with other chemicals
alter normal metabolic pathway
agonist vs antagonist
agonist stimulates as normal
antagonist blocks receptor or inhibits its action
partial agonists produce only a moderate effect
therapeutic index
ratio of a drugs lethal dose for 50% pop to its effective dose for 50% pop
unpredictable med responses
idiosyncrasy: rare unique response for a specific person
tachyphylaxis: rapid development of tolerance to med
iatrogenic response: adverse condition inadvertently induced in a patient by treatment given (UT infection after catheter)
accumulative vs summation vs synergism vs potentiation
accumulative: increased effect from several successive doses
summation: additive effect, two medications give combined effect equal to the sum of their individual effects
synergism: combined effect greater than sum of individual effects
potentiation: when one med enhances the effect of another
ADME process
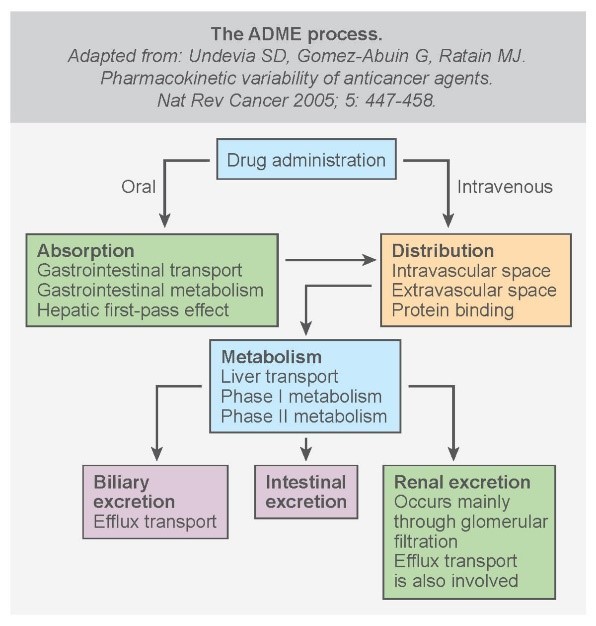
pharmacodynamics vs pharmacokinetics
pharmacodynamics is study of the drugs effects
pharmacokinetics is the study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
how many sites need to match for a cell to be receptive
3
efficacy vs potency
efficacy is the maximal effect a drug produces irrespective of concentration (dose)
potency is the amount needed to produce an effect
preganglionic vs postganglionic
preganglionic neurons originate in the CNS, through spinal cord, and synapse in ganglia. release acetylcholine
postganglionic neurons innervate target organs. primarily release norepinephrine, sometimes ACh
sympathetic nervous system (meds)
sympathetic nerves have origins in thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord
primary chemical messengers are norepinephrine and epinephrine and catecholamines
two types of receptors:
adrenergic
alpha1
alpha2
beta1
beta2
dopaminergic (cause renal, coronary, and cerebral artery dilation)
sympatholytic: interfering or inhibiting the effect of impulses from SNS
sympathomimetic: stimulates adrenergic receptors
parasympathetic nervous system (meds)
principle neurotransmitter is acetylcholine; cholinergic receptors (nicotinic and muscarinic)
parasympathetic nerves have origins in the brainstem and sacral segments of spinal cord. nerves from brainstem pass through 4 of the cranial nerves: ocularmotor III, facial VII, pharyngeal IX, and vagus X
cholinergic receptors
ound in CNS and PNS nicotinic are triggered by ACh but opened by nicotine. nicotinic effects are the same as sympathetic overactivity; tachycardia, hypertension, dilated pupils. muscle twitching, muscle weakness
found in CNS and ANS muscarinic are triggered by ACh and muscarine. muscarinic effects result in parasympathetic overactivity; bradycardia, miosis, sweating, blurred vision, excessive lacrimation, excessive bronchial secretions, wheezing, SOB, urinary and fecal incompetence. atropine reverses effects of muscarinic overstimulation.
alpha beta 1 and 2
1 heart
2 lungs
A B C D
ac: alpha constricts
bd: beta dilates
alpha 1: located on peripheral blood vessels
peripheral vasoconstriction
mild bronchoconstriction
increased metabolism
sweat glands
alpha 2: located on nerve endings
control release of neurotransmitters
beta 1: located in cardiovascular system
increased HR
increased conduction
increased contraction
beta 2: located on bronchial smooth muscle
bronchodilation
peripheral vasodilation
analgesics
affect CNS
medications that relieve pain
most common are opioid agonists which bind to opiate receptors preventing pain signals
nonopioid analgesics alter the production of prostaglandins and COX
salicylates
NSAIDS
para-aminophenol derivatives
opioid antagonists reverse the effects of opioids (narcan)
opioid agonist-antagonists have agonistic and antagonistic properties. are preferred because decrease pain without diminishing respiratory system or leading to dependence or addiction
anaesthetics
affect CNS
medications intended to induce loss of sensation to touch or pain
systemic anaesthesia is usually done via inhalation and is used for operating room
regional anaesthesia focuses on a particular portion of the body
local anaesthesia focuses at a specific spot on the body where a procedure is about to take place
can slow the functioning of the respiratory system, CNS and cardiovascular system
anti anxiety, sedative, and hypnotic medications
affect CNS
benzodiazepines are sedatives most commonly used to prepare for invasive procedures. they enhance the affinity of GABA binding sites which causes brain activity to slow
barbiturates: increase the affinity between receptor sites and GABA as well however they have significant side effects
nonbarbituate hypnotics: also the same MOA, less side effects
anticonvulsants
affect CNS
work by inhibiting the influx of sodium into cells, enhancing GABA A system, reducing excitatory glutaminergic neurotransmission, and reducing activity in calcium channels
opioid antagonists
affect CNS
MOA: attach to opioid receptors and displace the narcotic
pure: competitive, occupy receptor so narcotic cannot
partial: bind with receptor sites and produce weak narcotic like effects
may cause worsening of respiratory depression
non narcotic analgesics
affect CNS
MOA: provide analgesia by blocking prostaglandin stimulation in CNS, fever reduction by affecting hypothalamic center, increase sweating and peripheral blood flow to increase heat loss. some can reduce inflammation by stabilizing cell membranes
inhalation anesthetics stage 1-4
affect CNS
stage 1: analgesia. cerebral cortex is inhibited, decreased response to pain, euphoria, unconsciousness
stage 2: involuntary movement. cerebral cortex completely depressed, hypothalamus takes over, absence in sympathetic tone cause increased HR, BP, resp, and muscle tone
stage 3: surgical anesthesia: hypothalamus is depressed, cardiac and respiratory function return to normal, spinal reflexes blocked, muscles relax
stage 4: medullary paralysis. medulla is paralyzed, cardiac and respiratory centres are effected, death may occur
cholinergic medications
affect PSNS
stimulate cholinergic receptors of the PNS
excessive cholinergics can cause SLUDGEM
anticholinergic medications
affect parasympathetic NS
work in opposition to the parasympathetic NS by blocking cholinergic receptors
muscarinic cholinergic antagonists: block ACh at the muscarinic receptors
nicotinic cholinergic antagonists: block ACh at nicotinic receptors which disables the ANS so they are almost never used
neuromuscular blocking agents
bind to to somatic ACh receptors at neuromuscular junction
depolarizing: stimulate depolarization of muscle cells (causes muscle twitches) then produces continuous stimulation of the muscle cell
nondepolarizing: bind in a competitive but nonstimulatory manner to part of ACh receptor (no muscle twitches), but have long onset and DOA
sympathomimetics/adrenergic agonists
stimulate adrenal medulla to release epinephrine and norepinephrine
stimulation of dopaminergic receptors: dilation of renal, coronary, cerebral arteries
adrenergic receptors: cause various effects alpha beta 1 and 2
non selective adrenergic agonists stimulate both A and B receptors
bronchodilators
b2 agonists
act on sympathetic NS
fit and act at b2 receptors in lungs
bronchodilation, decreased resp secretions
short acting <12hrs, long acting >12hrs
anticholinergics
act on parasympathetic NS
block action of ACh on bronchial smooth muscle
brinchodilation, decreased resp secretions
best treatment for COPD
xanthines
act directly on respiratory muscle
most commonly oral
narrow therapeutic range
antianginal agents
nitrates: relax smooth vascular muscle, vasodilation results in decreased preload, after load, and work meaning less oxygen is required
prevent angina attacks
decrease BP
nitroglycerin
alcohol potentiates
beta blockers: block beta 1 receptors in heart decreasing HR and contractility reducing oxygen demand
post myocardial infarction
bradycardia, reduced AV conduction, reduced contractility
calcium channel blockers: block calcium channels in arterioles which causes arteriolar dilation
angina
can cause hypotension and tachycardia
anticoagulants and platelet inhibitors
anticoagulants: prevent production of fibrin by disrupting the coagulation cascade
can cause bleeding gums, nosebleeds, easy bruising
platelet inhibitors: decrease the ability of platelets to stick together by inhibiting TXA2 or ADP
effective for preventing arterial thrombosis
ASA
prevention of myocardial infarction, thrombotic stroke
increases risk of bleeding
uterotonics
stimulate uterine contractions and compression of maternal blood vessels at rheumatoid arthritis placental site to induce labor and control postpartum hemorrhage
oxytocin
ergometrine is contraindicated by hypertension, pre-eclampsia or heart disease
vitamins
vit A: enables retinal rods to adapt to dim light
vit D: regulates serum calcium levels as well as parathormone and calcitonin
vit E: grevants formation of toxic metabolites, maintenance of RBC membranes
vit K: synthesis of blood clotting factors
vit B: cell reproduction and maturation
vit C: formation of catecholamines, steroids, and conversion reactions
antihypoglycemic agents
either
break down glycogen stores from liver
supply usable glucose to bloodstream
used for hypoglycemia
antimicrobials
antibiotics: prevent cell wall synthesis (penicillins), block synthesis of folic acid (sulphonamides), interfere with protein syntheses (tetracycline, macrolydes, amnuglycosides) interfere with DNA synthesis (quinolones)
can cause bacteria to become resistant
antivirals: prevent the virus from replicating, inhibit revers transcriptase used by RNA viruses, inhibit protease used by RNA viruses, prevent virus from incorporating into host cells
treats herpes
decrease HIV virus production
can cause nausea, headache, dizziness, drowsiness
antifungals: inhibit ergosterol synthesis in fungal cell membranes inhibiting fungal cell membrane synthesis
antidotes and neutralizing agents
they:
compete and displace drug from receptor sites
use different cellular mechanism to overcome poison
prevent biotransformation
bind and inactivate the poison
antiemetics
5-HT3 receptor antagonist: blocks the effects of serotonin
most effective in controlling N/V with simulation of the CTZ
H1 histamine antagonists: blocks the effects of H1 histamine and blunts vestibular inputs
effective in treating N/V with stimulation of vestibular system
iv formuler
V x S = T x R
vestibular
immediate transfusion reactions
acute hemolytic transfusion reactions: usually due to incompatible blood, fever, chills. hypotension, hemoglobin in urine, flank pain, SOB. discontinue and keep open with saline
febrile reactions: fever during transfusion due to
destruction of RBCs or WBCs
bacterial contamination of blood
reaction to proteins
discontinue and keep open with saline
allergic reactions: urticaria (hives) are not serious unless accompanied by other signs of anaphylaxis. discontinue and keep open with saline. when anaphylaxis occurs, discontinue, keep open, provide high flow 02
transfusion associated circulatory overload: fluid overload and pulmonary edema. causes SOB, hypertension, dyspnea, lumbar pain. discontinue and keep open, high flow O2, sitting position
chills and hypothermia: discontinue and keep open with saline
delayed transfusion reactions
include hepatitis, sepsis, iron overload, delayed hemolytic reaction, post transfusion purpura, transfusion associated graft-versus-host disease
rights of transfusion
patient, product, amount, rate, time
blood product monitoring guidelines
patient must be stable for 30 min before transport
reassess vitals after 15 minutes of initiation
repeat vitals every 30 min wth temp
only normal saline can be infused via same line as blood
tubing must changed every 2-4 units of blood
needle sizes
SQ: 24-26 gauge, 1.27-2.5cm needle
IM: 21 or 22 gauge, 2.5cm or 5cm
rates of absorption
oral 30-90 minutes
rectal very rapid
subcutaneous slow onset and prolonged duration
intramuscular is faster than SQ
intravenous: fastest onset
endotracheal/inhalation: 2-3 minutes
transdermal: slow, sustained release
sublingual/buccal: very rapid
alarm system infusion pump
end of infusion
occlusion (blockage)
air in line
battery low
bad tubing
excessive pressure
signs of dehydration and over hydration
dehydration: decreased LOC, tachypnea, dry mucus membranes, tachycardia, poor skin turgor, flushed dry skin
over hydration: SOB, puffy eyelids, edema, polyuria (excessive urination), moist crackles, acute weight gain
electrolytes
sodium: water regulation, nerve and muscle function. high levels: edema, lethargy, weakness. low levels: pulmonary or cerebral edema
potassium: nerve and muscle function. low levels: decreased skeletal muscle function, GI disturbances, arrhythmia. high levels: hyperstimulation of neural cell transmission leading to arrhythmias and cardiac arrest
calcium: bone formation, heart function, nerve transmission, blood clotting. too low: muscle cramps, abdominal cramps, hypotension, vasoconstriction. high levels: weakness, lethargy, lack of coordination, cardiac arrhythmia, vasodilation, flushed skin
magnesium: metabolism of protein and carbs, neuromuscular activity, myocardial function. low levels: weakness, irritability, tetany, delirium, convulsions, anorexia, nausea, emesis, cardiac arrhythmia. high levels: hypotension, weakness, N/V, altered mental functioning
bicarbonate: determine acidosis or alkalosis in body
chloride: strongly liked to sodium, formation of stomach acids, fluid balance, Ph. low levels: muscle spasms, metabolic acidosis, shallow respiration, hypotension, tetany. high levels: lethargy weakness, metabolic acidosis, rapid deep breathing
phosphorus: component of ATP
macro vs micro drip set
macro: 10, 15 or 20 gtts/ml
micro: 60 gets/ml
IV fluids
D5W: 5% dextrose in 100ml of water. not used for fluid replacement
ringers lactate: isotonic solution containing chloride, lactate, potassium, and calcium that remains in the vascular space. good for trauma patients. volume expander
normal saline: isotonic solution of 0.9 sodium chloride. close to body fluid in density and osmotic pressure. good for hemorrhage, fluid loss due to burns, peritonitis, or diarrhea. volume expander
local IV site reactions
infiltration: escape of fluid unto surrounding tissue causing edema, cold skin. discontinue, apply cold packs early, hot packs later, re-establish IV at another site, physician
thrombophlebitis: inflammation of the vein due to the presence of a clot, red skin, swelling, palpable cord along course of vein. discontinue, war packs, physician
phlebitis: inflammation of the vein, edema, redness, hot skin. discontinue, apply warm packs, notify physician
occlusion: physical blockage of vein or catheter.
vein irritation: observe closely for allergic reaction, discontinue and reestablish in another extremity
hematoma: accumulation of blood in surrounding tissue. discontinue and apply pressure
systemic IV reactions
circulatory overload: too much fluid in the intravascular compartment, rapid pulse, venous distension, increased BP, coughing, SOB, increased resp, syncope, shock, pulmonary edema - dyspnea, cyanosis. slow to TKO, administer O2, sitting position, physician
air embolism/catheter embolus: air or a piece of the catheter enter the circulatory system causing shock, chest pain, cyanosis, tachycardia, resp distress, rapid loss of consciousness. close adjustment valve, clamp off tubing, patient on left side with head down, administer O2, initiate IV, physician
discontinuing IV
shut off flow valve
remove tape
hold cotton swab or 4×4 above entry site
remove catheter, check its in tact while applying pressure
apply band aid
document