Chemistry S3 HL
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry of organic compunds can cause fragmentation of molecules
Fragmentation pattern
The molecules are vaporised and then bombarded with a beam of high-speed electrons shot from an electron gun. The collisions between the electrons and the molecule are so high that they cause the molecule to break up into molecular ions
The detected ions produce a mass spectrum. The peak with the highest m/z value is the molecular ion (M+ ) peak. This gives the molecular mass of the compound.
Infrared spectroscopy
It can be used to identify the type of bond present in a molecule
Wavenumber
The frequency of infrared radiation is measured as the number of waves per cm
absorption of infrared
If an organic molecule is irradiated with infra-red energy that matches the natural vibration frequency of its bonds, it absorbs some of that energy and the amplitude of vibration increases
This is known as resonance
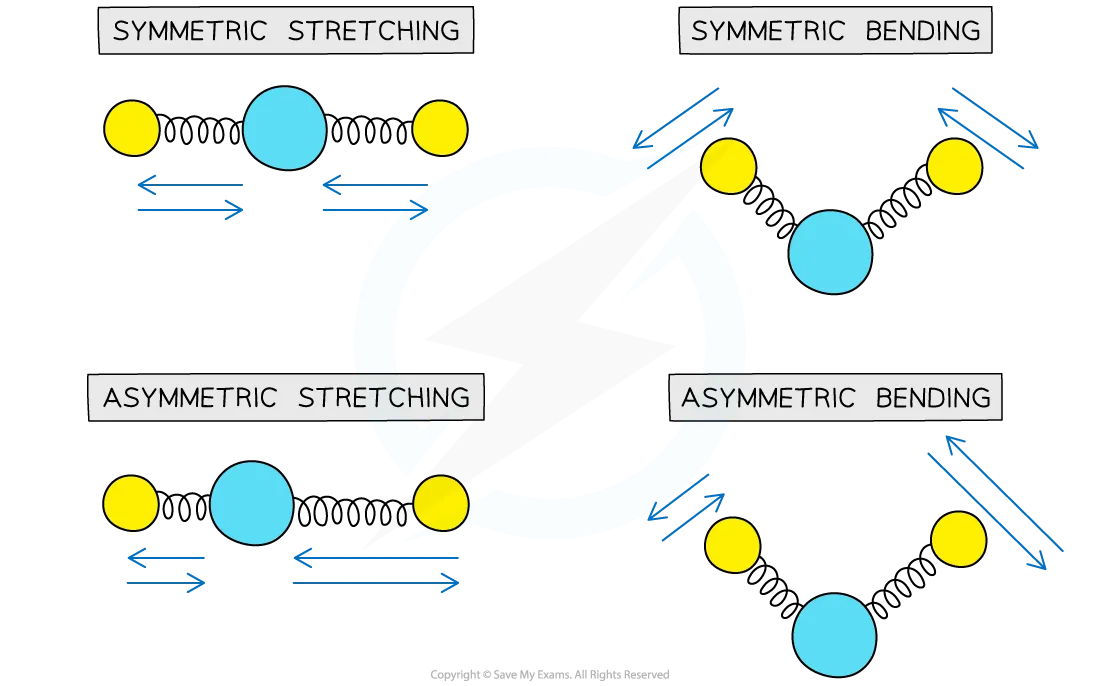
modes of vibration
symmetric or asymmetric stretching
symmetric or asymmetric bending
These vibrations have a unique wavelength and frequency, which is used to identify the functional group
condition for IR absorption
A molecule must have a permanent dipole
Symmetric molecules like H2 and O2 are IR inactive
uses of IR spectroscopy
Pollution
Infrared spectroscopy is used to identify pollutants in vehicle emissions in the air
Sensors detect and measure the amount of pollutants such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and unburnt hydrocarbons
This commonly occurs on motorways and in busy town centres to monitor localised pollution
Breathalysers
Infrared spectroscopy can be used to measure alcohol levels using roadside breathalysers
A ray of infrared radiation is passed through the breath that is exhaled into the breathalyser chamber
The characteristic bonds of ethanol are detected and measured - the higher the absorbance of infrared radiation, the more ethanol in the person's breath
Greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases such as CO2, H2O, and CH4 absorb infrared radiation due to the vibrations of their polar bonds
This absorption contributes to the greenhouse effect, as the energy is re-emitted and trapped in the Earth's atmosphere
The effectiveness of a greenhouse gas depends on the type of bonds it contains and how strongly they absorb infrared radiation
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (HNMR) spectroscopy gives information on the different chemical environments of hydrogen atoms in a molecule