patho lab final
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
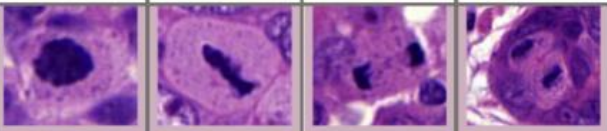
Normal Mitosis
Normal Mitosis

normal mitosis
normal mitosis

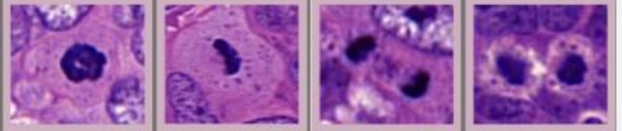
Abnormal mitosis
Normal mitosis
Abnormal mitosis

Psudostratified columinar epithelium
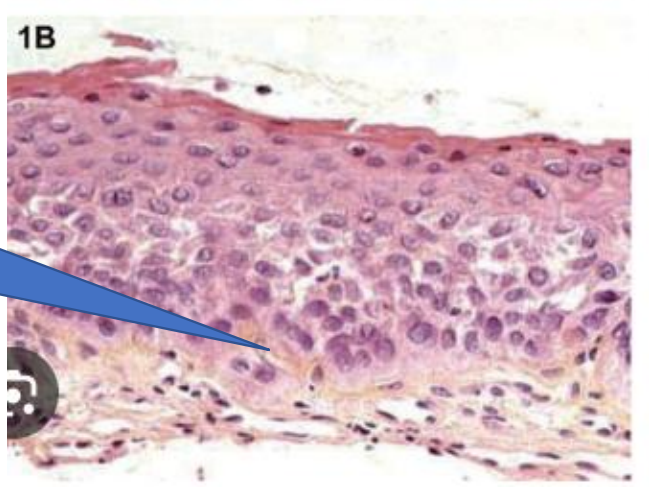
Metaplasia of stratified squamous epithelium
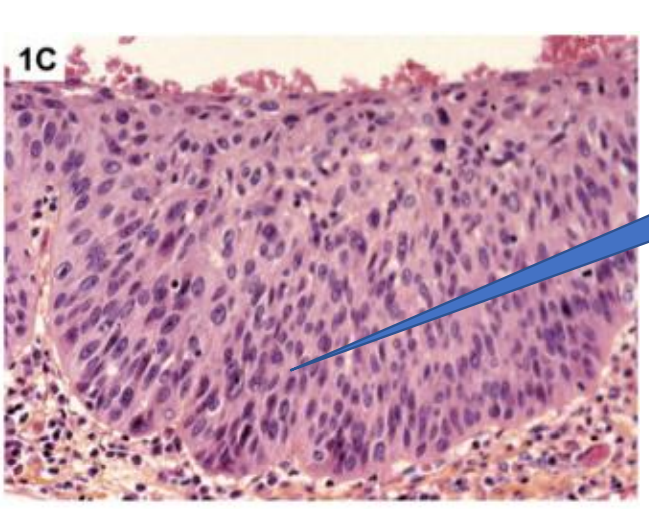
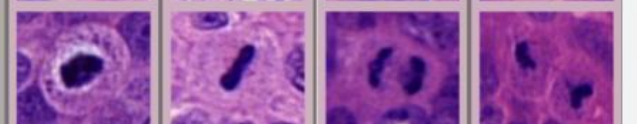
Dysplasia
Dysplastic features:
Irregular stratification
loss of polarity
hyperchromasia
nuclear and cellular pleomorphism
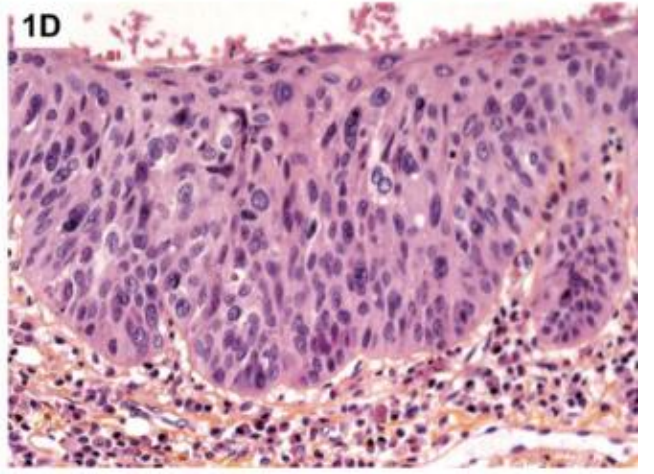
Dysplasia
Dysplastic signs:
Irregular stratification
loss of polarity
hyperchromasia
nucleaur and cellular pleomorphism
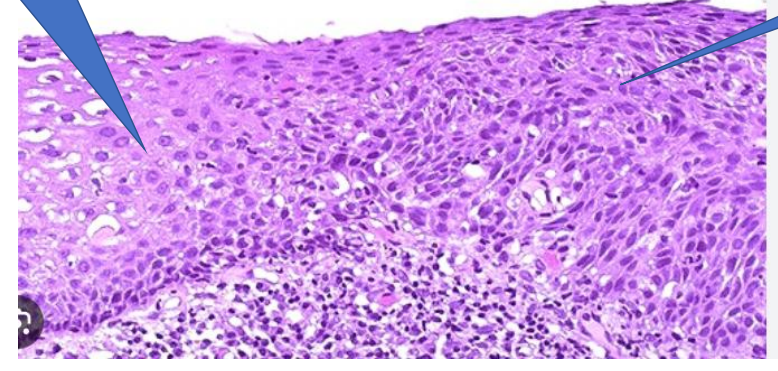
Dysplasia
—> normal stratified squamous epithelium
—> Dysplasia
Dysplastic signs
irregular stratification
nuclear and cellular pleomorphism
hyperchromasia
loss of polarity

abnormal mitotic features

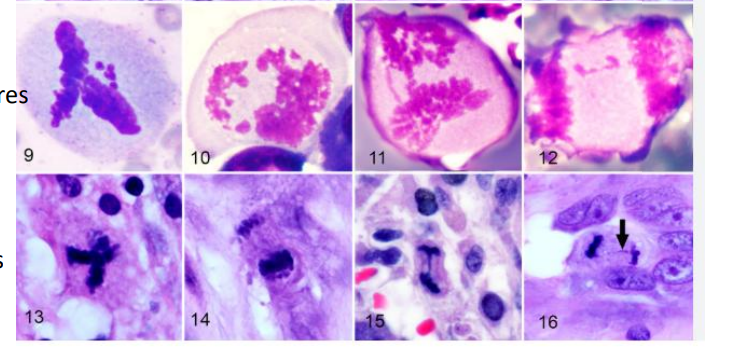
abnormal mitosis
arrow= normal
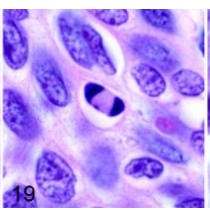
abnormal mitosis

abnormal mitosis
down= normal
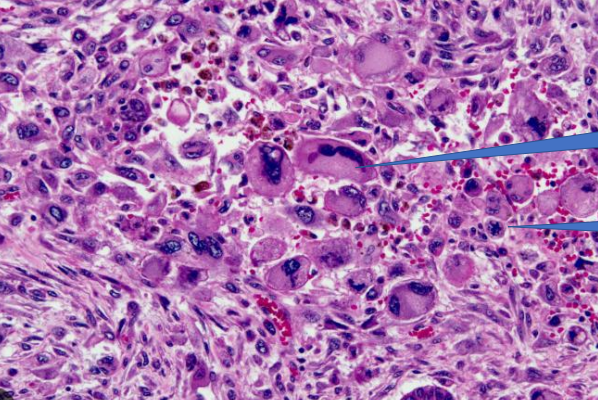
cellular and nuclear pleomorphism
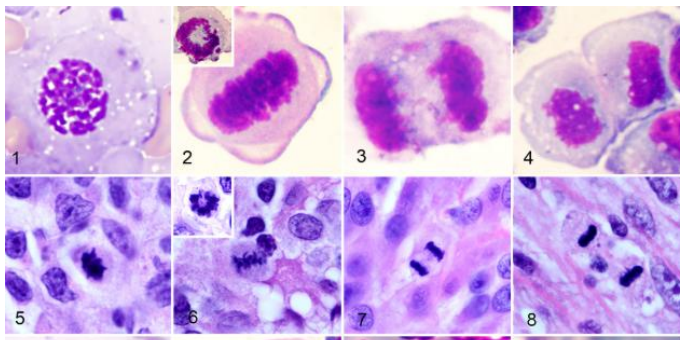
abnormal mitotic figures
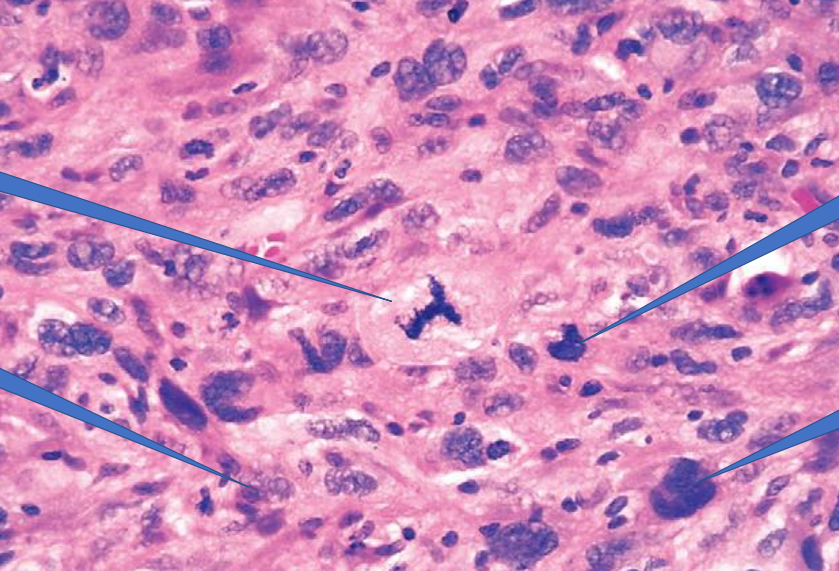
1- abnormal mitotic figure
2- chromatin clumping
3- nuclear pleomorphism
4- increased nuclear cytoplasmic ratio

1- Nuclear pleomorphism
2- abnormal mitotic figure
3- tumor giant cell
4- tumor giant cell
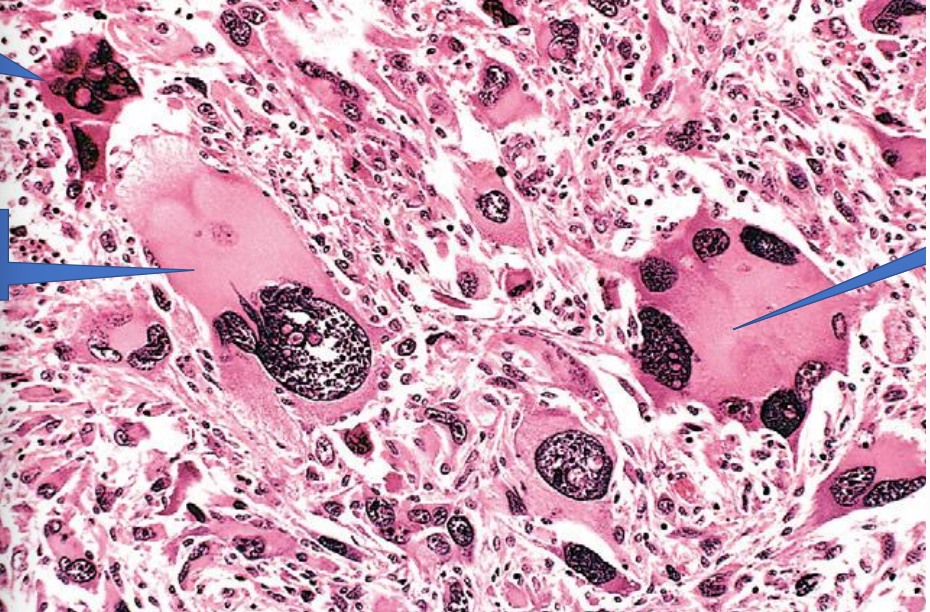
1- Tumor giant cell
2- Cellular and nuclear pleomorphism
3- Tumor giant cell
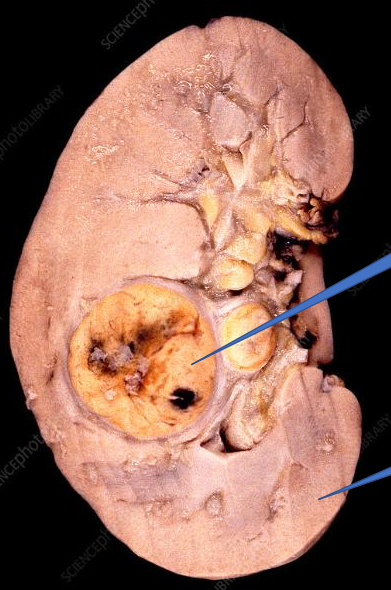
1- renal tumor
2- Normal kidney
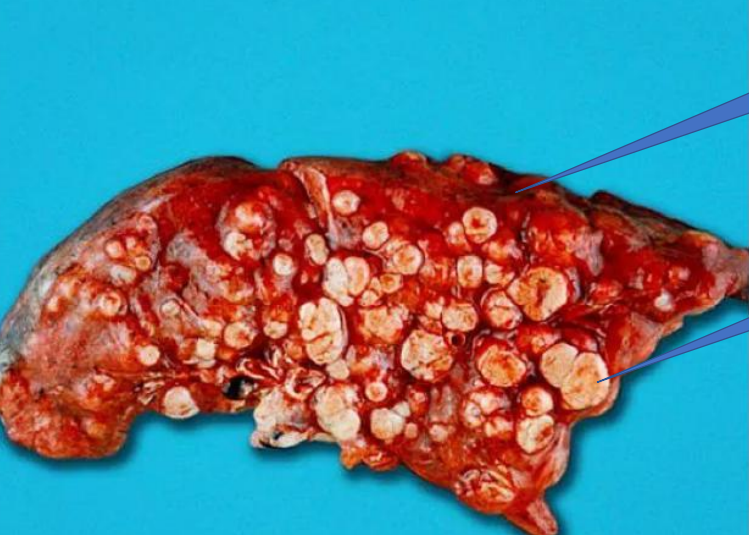
1- Normal Lung
2- Lung Metastasis
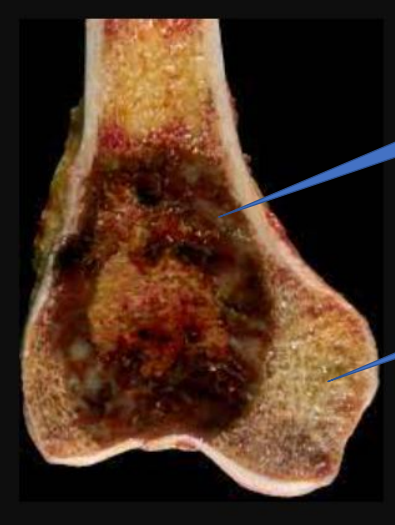
1- Bone Tumor
2- Normal bone
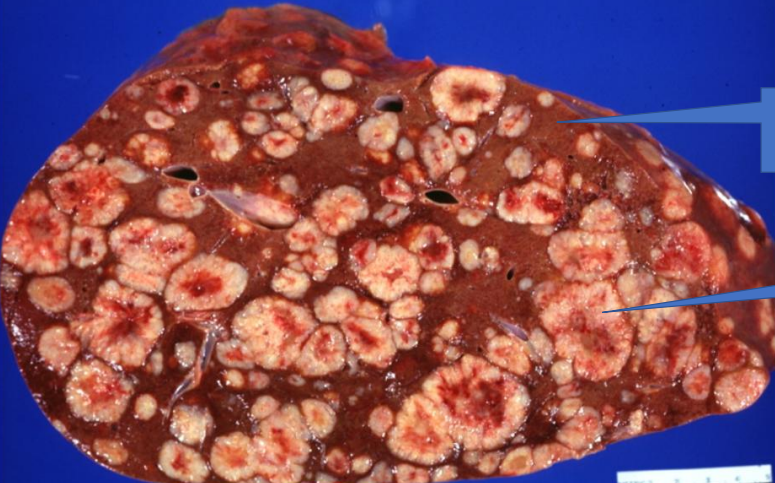
1- Normal Liver
2- Liver Metastasis
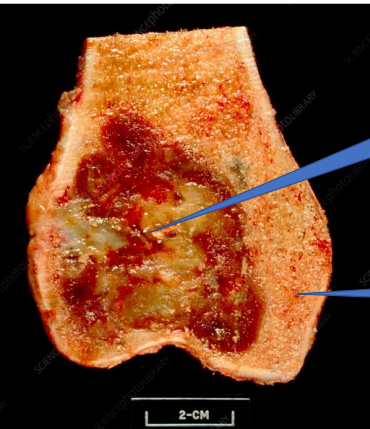
1- Bone Tumor
2- Normal Bone
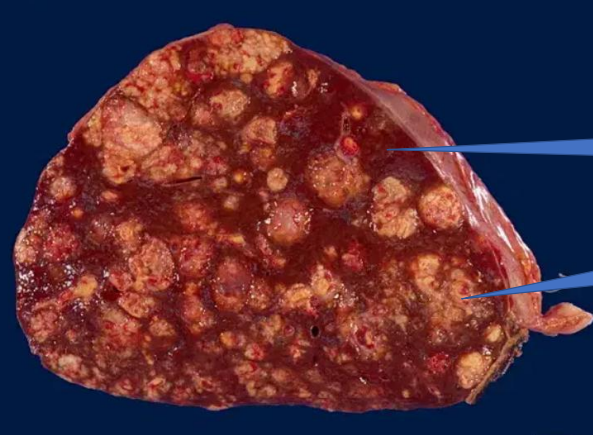
1-normal liver
2- Liver metastases

1- Normal Skin
2- Melanoma
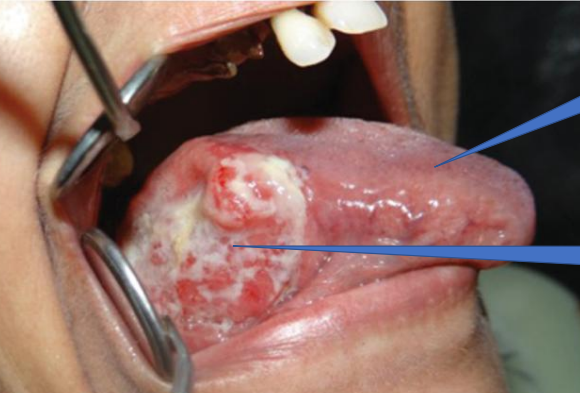
1- Normal Tongue
2- Carcinoma

1- Normal Liver
2- Hepatocellular Carcinoma

1- Tumor
1- Mandible
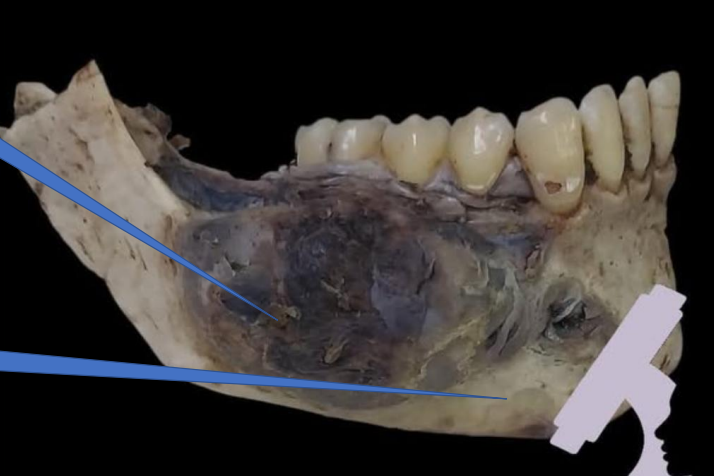
1- Tumor
2- Mandible

1- Blood vessel
2- Vascular invasion
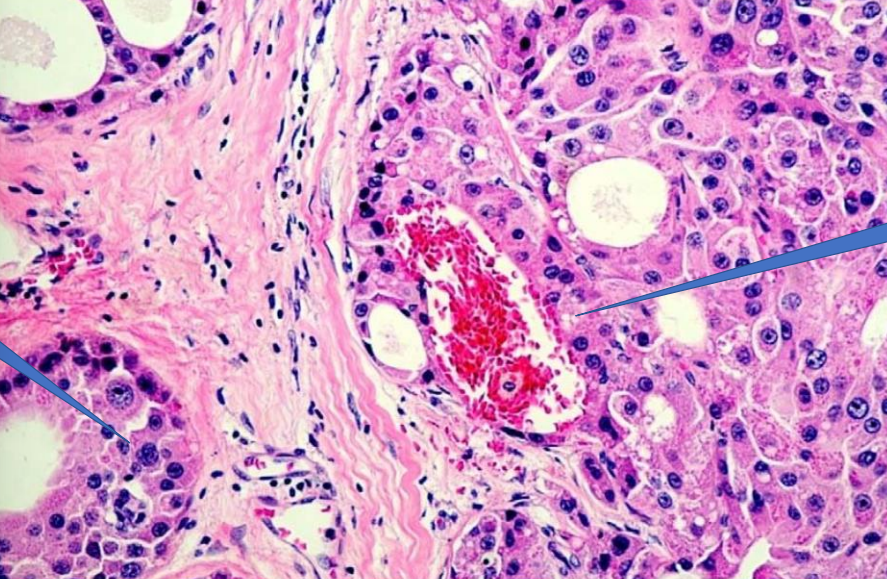
1- Malignant Tumor
2- Vascular invasion
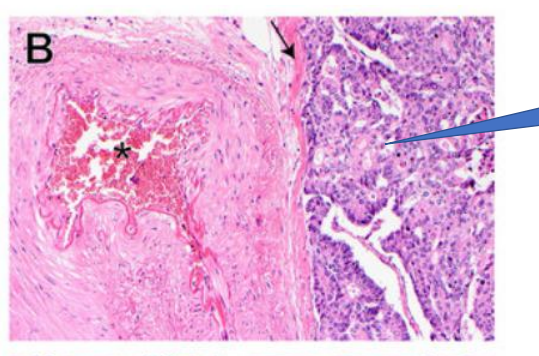
Malignant Tumor

Vascular invasion
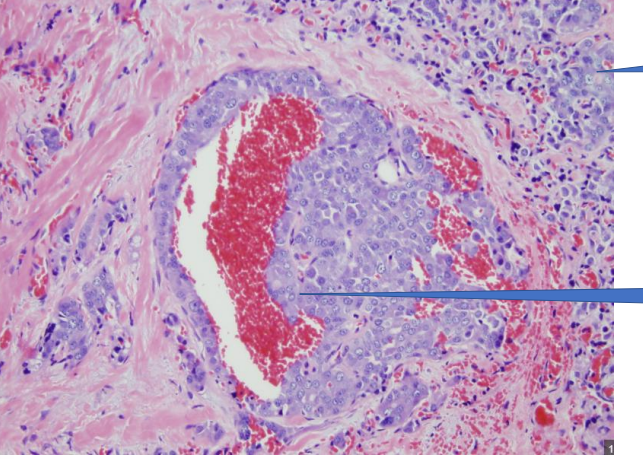
1- Malignant Tumor
2- Vascular invasion

Squamous cell carcinoma
1- Squamous epithelium
2- Ivasion of Tumor to CT
3- Tumor island with keratin pearl
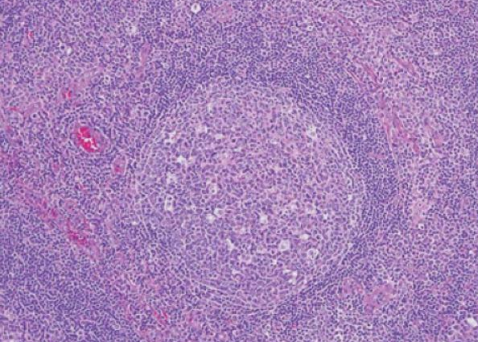
normal lymph node
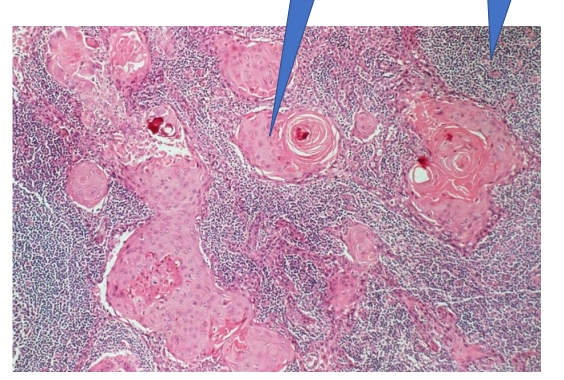
Lymph node w metastases
1- squmous cell carcinoma island
2- normal myphoid tissue
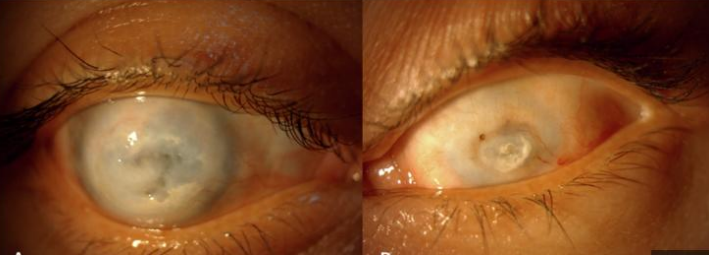
Keratomalacia
—> lack of vitamim A
—> extreme dyness of eyes and clouding of cornea
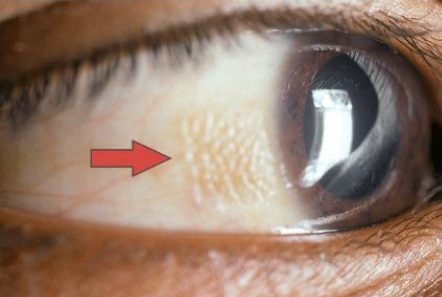
Bitot spots
foamy white grey spots form on the conjunctiva of the eye, the white part
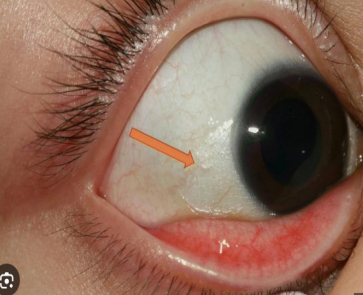
Bitot spots
are foamy white grey spots that form on the conjuctiva of the eye, the white part
Vitamin A deficiency
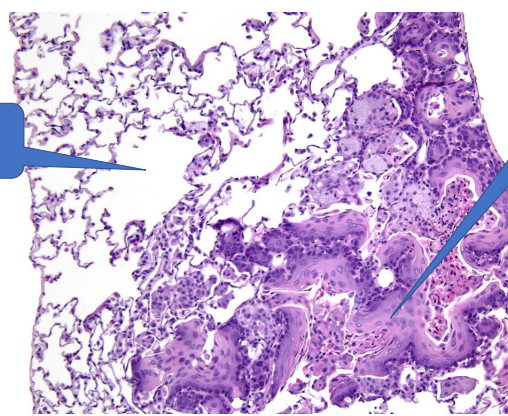
1- normal alveoli
2- Squamous metaplasia
Normal alveoli epithelium replaced by squamous epithelim which cant help gas exchange
Vitamin A deficiency
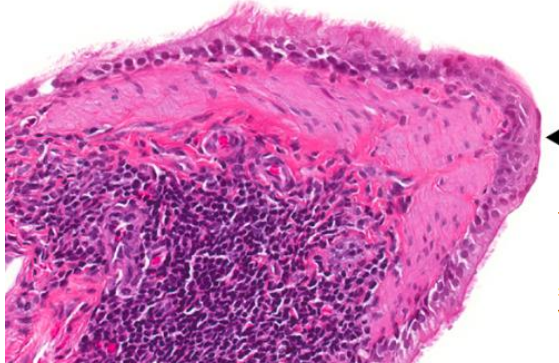
1- squamous metaplasia
pseudostratified ciliated columnar —> squamous
loss of infection:
1- Loss of cilia: Without cilia, the epithelium can no longer sweep mucus and trapped microbes out of the airway.
2- Impaired mucociliary clearance: Goblet cell function is disrupted, so mucus isn’t produced or moved properly. Mucus and debris accumulate, allowing pathogens to multiply and cause infection.
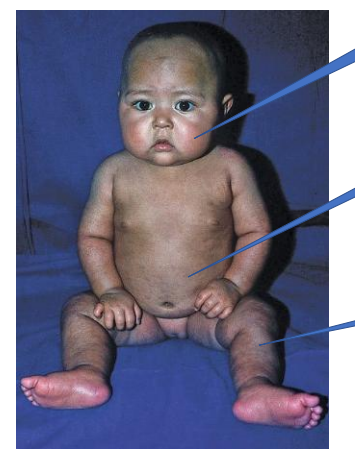
Protein Deficiency - Kwashiorkor
1- odema of the face
2- odema of the stomach
3- No muscle wasting
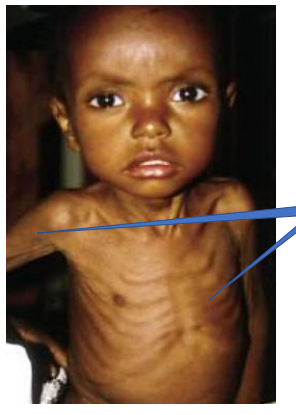
Calories Deficiency - Maramus
1- Muscle wasting
2- Prominent ribs

Rickets
Vitamin D / Calcium deficiency
1- Bowing of legs
2- Knock Knees
3- Knock Knees
4- Bowing of legs
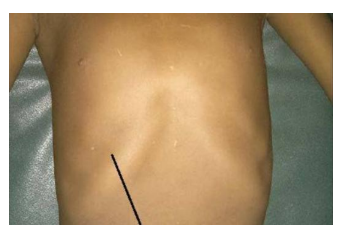
Rickets
vitamin D deficiency
1- Harrison Sulcus / Harrison groove
an indentation of the chest roughly along the 6th rib
unusally bilateral but can occus as unilateral
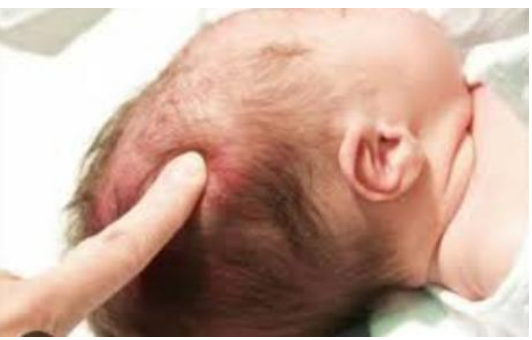
Rickets (Vitamin D deficiency)
Craniotabes: Softening in certain area of the skull
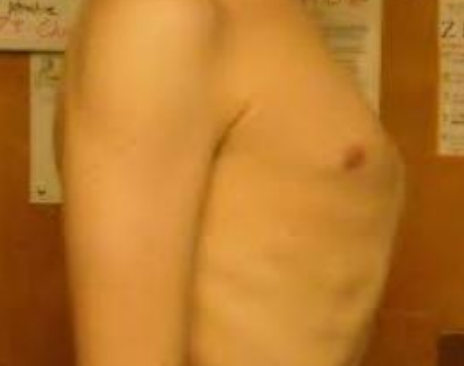
Rickets
Pigeon chest: As the soft ribs are pulled inward, the breastbone (sternum) is pushed forward, causing it to stick out and creating the characteristic "pigeon chest" appearance.
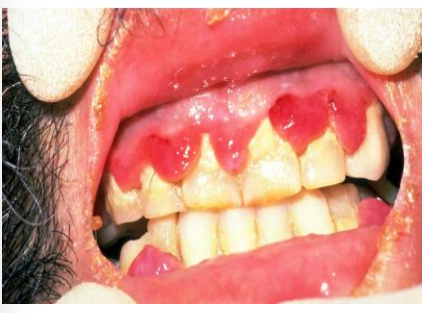
Scurvy (vitamin C deficiency)
Scrobutic gingivitis
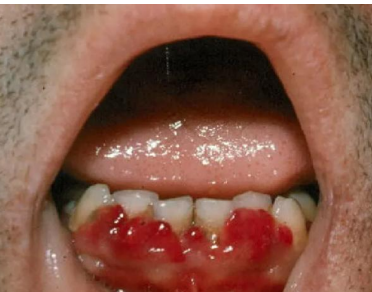
Scurvy (vitamin C deficiency)
Scrobutic gingivitis
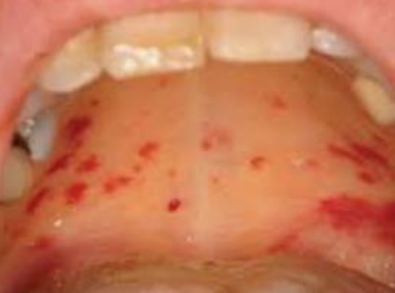
Scurvey (vitamin K deficiency)
Ecchymosis
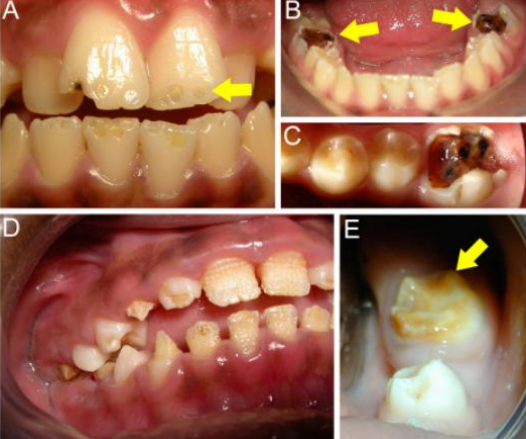
Vitamin A and D deficiency
Enamel hypoplasia

Vitamin A and D deficiency
Enamel hypoplasia

Hypocalcemic tetany
Trousseasu sign
carpopedal spasm: An involuntary contraction of the muscles in the hand and wrist
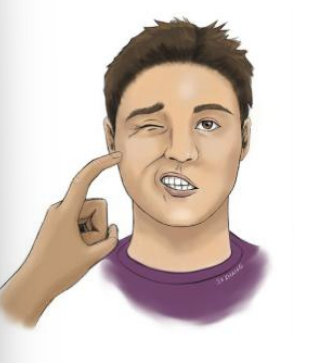
hypocalcemic tetany
chvostek sign
twitching of the facial muscle in response to a light tap on the facial nerve, located just in front of the ear
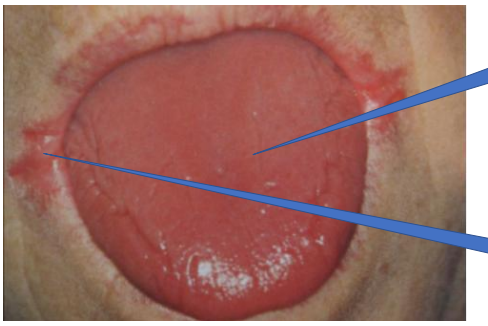
Angular chellitis
glossitis
vitamin b1 b2 deficiency
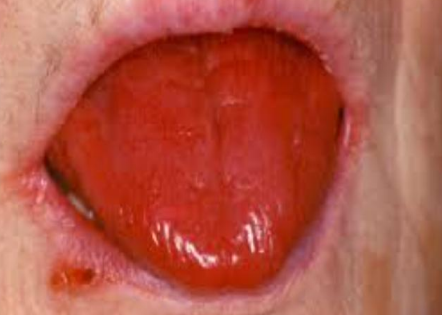
B9 / b12 deficiency
beefy red tongue

Pallor
iron deficiency anemia

Pallor
iron deficiency anemia
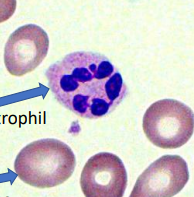
Megaloblastic anemia
hypersegmented neutrophil
macrocytes
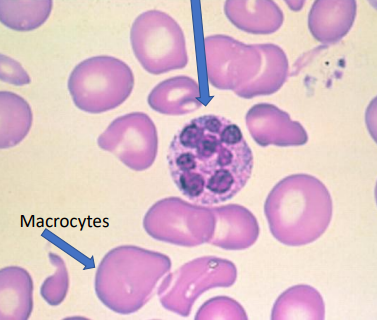
megaloblastic anemia
Hypersegmented neutrophil
macrocytes
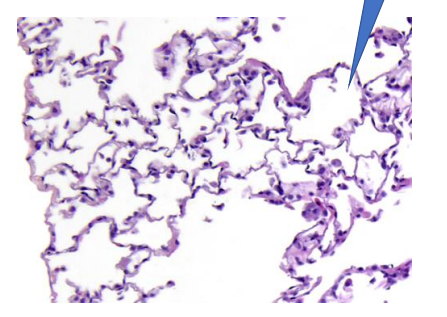
Normal lung
—> alveoli
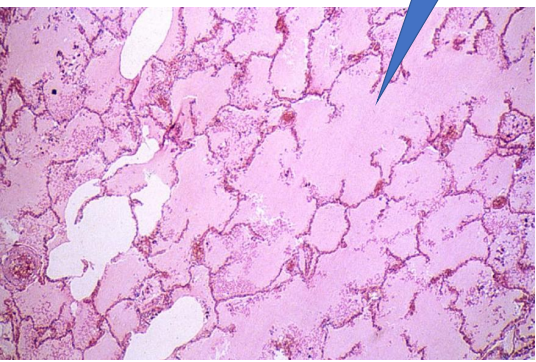
Pulmonary oedema
—> alveolar spaces filled with hematogenous eosinophili susbtace = edematoeuos fluid
1- oedematous fluid

Pulmonary odema
—> alveolar spaces filled with hematogenous esinophilic substance = edematous fluid
1- oedematous fluid
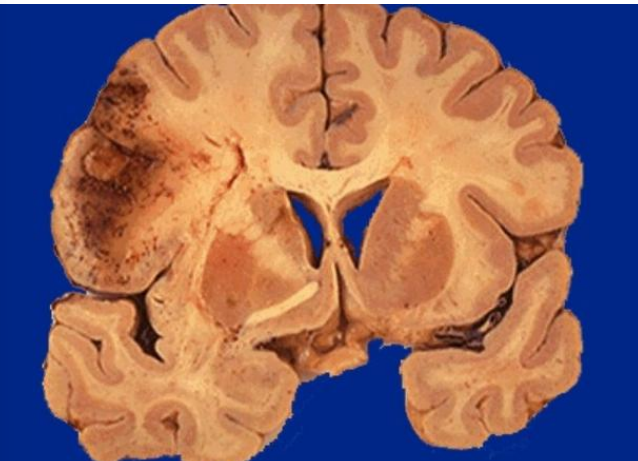
Cerebral infract (early stages)
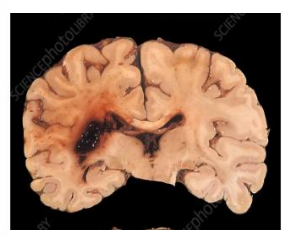
Cerebral infract

cerebral infract
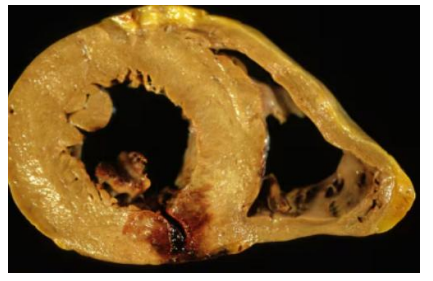
myocardial infract (early stages)
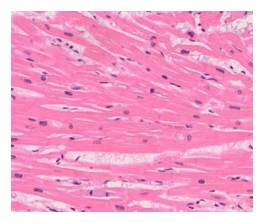
normal heart muscle
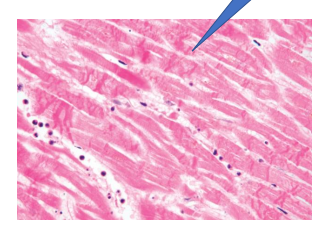
Mycardial infract
1- ischemic necrosis

Myocardial infract early stages
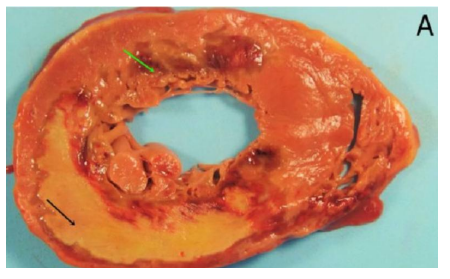
Myocardial infract
green = early infract
black = late collagenized infract
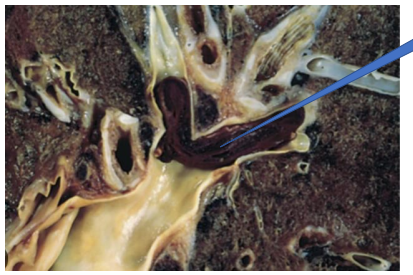
Thrombosis
1- thrombus inside blood vessel

Thrombosis
1- blood vessel
2- thrombus inside blood vessel
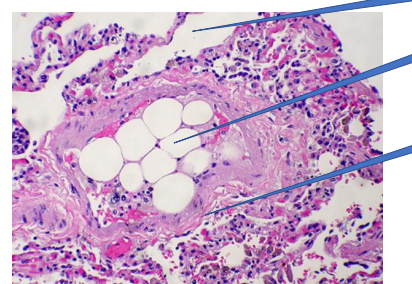
Pulmonary fat embolism
1- normal alveoli
2- fat emboli
3- vessel wall
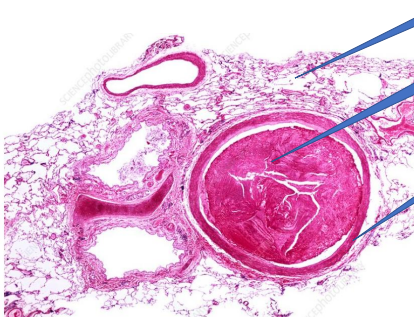
Pulmonary throbuboemboli
1- normal alveoli
2- thrombus emboli
3- vessel wall
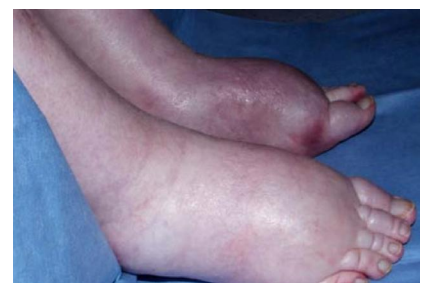
pedal odema
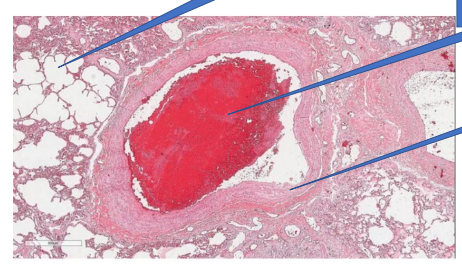
Pulmonary throboemboli
1- normal alveoli
2- thrombus emboli
3- vessel wall
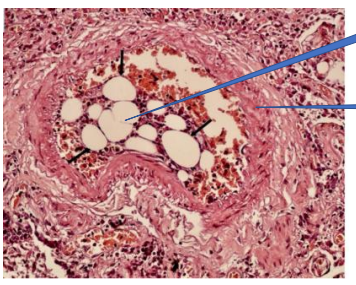
1- fat emboli
2- vessel wall
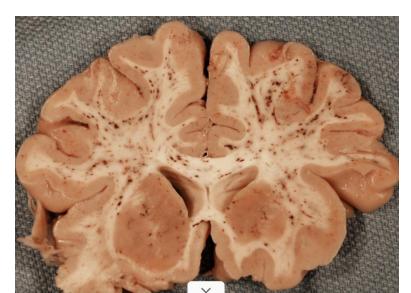
cerebral infract
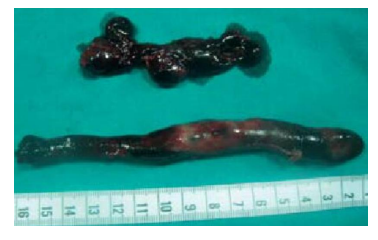
thrombus
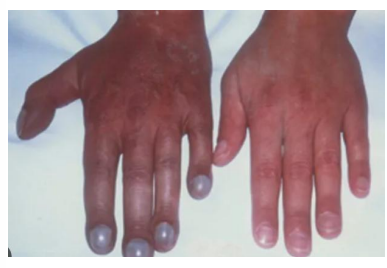
cynosis
increased amount of deoxygenated blood due to obstruction of veins

Hyperemia
increased oxygented blood flow due to dialation of arteries or arteriols

Pulmonary congestion
1- dialted and congested blood vessel
2- alveoli

Lymph node congestion
1- congested and dialated blood vessels

1- purpura
2- petechiae
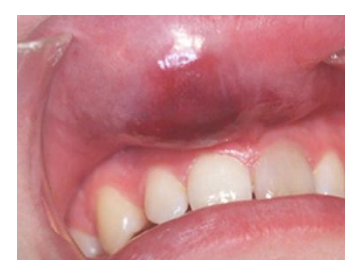
oral hematoma * swelling 1 day duration due to truma
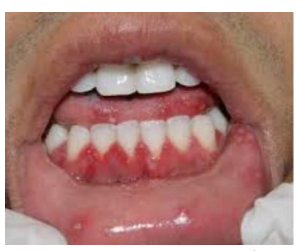
Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis
primary infection of herpes simplex virus 1
affect children
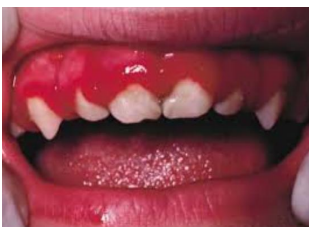
acute herpetic stomatitis
primary infection of herpes simplex virus 1
affect children

Herpes libialis
secondary infection of herpes simplex virus 1
mostly in adults