VCE Biology U3 AoS1
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Role of Nucleic Acids and Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Nucleic Acid
A class of biomacromolecules that includes DNA and RNA. Store and pass on genetic information.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid. The molecule that carries the genetic information for the development and function of an organism.
RNA (+ three types)
Ribonucleic acid. Single stranded. Intermediate step when converting DNA into proteins. messengerRNA - carries a copy of genetic code from DNA in the nucleus to ribosomes. ribosomalRNA - make up 60% of ribosome structure. transferRNA - carries amino acid from the cell cytoplasm to the ribosome and pairs with the complementary code in the mRNA.
Purines
Double ring structure. Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidine
Single ring structure. Thymine, cytosine and uracil.
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein
Proteome
The collection of all proteins produced by an organism.
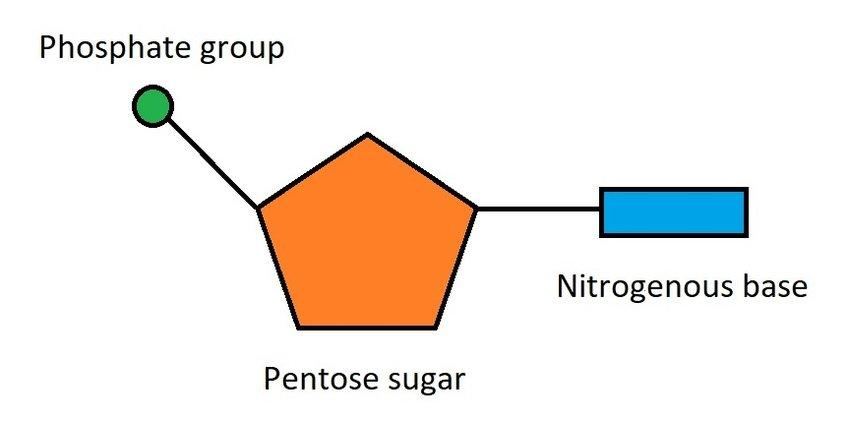
Nucleotide (definition + draw one)
The monomers that make up nucleic acids. Consists of a sugar molecule attached to a phosphate group and nitrogen-containing base.
Proteins
Biomacromolecules made of polypeptides (long chains of amino acids) essential for the structure, function and regulation of cells and tissue.
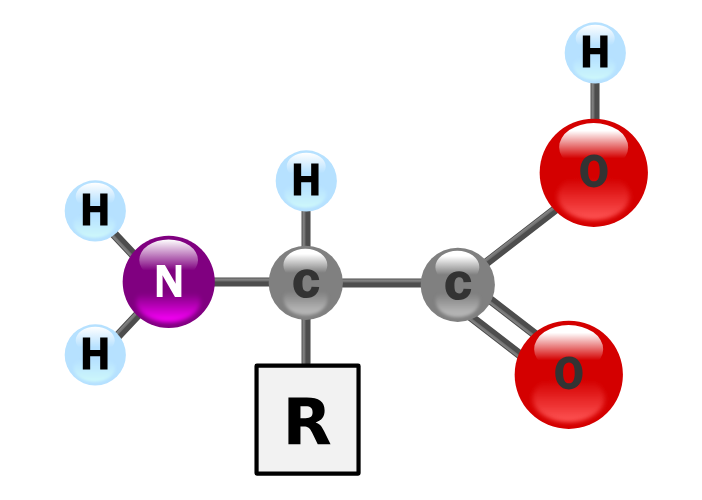
Amino acid
Biomacromolecules which are the monomer of protein.
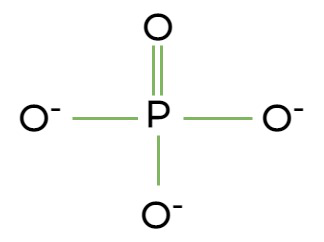
Phosphate
An inorganic compound. PO43-
Pentose sugar
A monosaccharide (simple sugar) with 5 carbon atoms. eg: deoxy/ribose
Ribose
A pentose sugar. Forms the backbone of RNA and ATP.
Deoxyribose
A pentose sugar with one less oxygen than ribose. Backbone of DNA.
Nitrogenous base
An organic molecule containing nitrogen, forming a key part of a nucleotide.
Phosphodiester bond
The strong covalent bond between the 5’ phosphate group of a nucleotide and the 3’ hydroxy group of another.
Polymer
A macromolecule made from many monomers linked together by chemical bonds.
Monomer
A small simple molecule that acts as a building block of a polymer by chemically bonding to other monomers.
Polymerisation
The process of monomers chemically bonding together to form polymers
Peptide bond
The strong covalent bond linking two amino acids. Formed via condensation reaction.
Dipeptide
A molecule formed when two amino acids join together via a peptide bond.
Amino acid residue
An individual amino acid unit within a polypeptide (minus the H and OH due to condensation reaction)
Polypeptide
A long chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The fundamental structure for proteins.
Primary structure of a protein
A chain of amino acids
Secondary structure of a protein
Folding of the polypeptide due to H bonds. Three types of folding: alpha-helices, beta-pleated sheets, random coil.
Tertiary structure of a protein
3D folding pattern due to side chain interactions. Minimal level to be a functional protein.
Quaternary structure of a protein
Protein consisting of multiple polypeptides
Proteome
Collection of all proteins produced by an individual.