Infection and response
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What are comunicable diseases
Spread by contact e.g. flu, cold
What are non-comunicable diseases
don’t spread e..g. type 1 diabeties
What is a pathogen
Any microorganism that can produce disease.
4 types of pathogens
fungi
viruses
bacteria
protist
Bacteria - how it makes you ill, cell and type of cell and examples?
Very small cell, body cell unicellular
They produce toxins that damage your cells & tissues
e.g. salmonella bacteria- food poisoning
virus how it makes you ill, cell and type of cell and examples?
No cell
The host cell bursts releasing all the new viruses causing you to feel ill.
Examples - HIV - infects and destroys cells that normally help defend your body against diseases.
Protist how it makes you ill, cell and type of cell and examples?
eukaryotic cell ( single celled)
lives on or inside other organisms - often transferredd to the organism by a vector
e.g. an insect that carries the protsis maleria - mosquito vector ( carrier)
Fungi how it makes you ill, cell and type of cell and examples?
Single celled
multicellular - hyphae grow & penertrate human skin, produces spores - causing fungus to spread.
e.g. the black spot fungus infects rose plants.
How do bacteria make you ill
They reproduce rapidly inside your body, they produce toxins which damage your cells
How do viruses make you will
This pathogen invades the living host cell which reproduces rapidly once inside. They damage the cell by bursting out of the cell
Transmission of pathogens and diseases
Air born
touching
water
contact with animals
contaminated food
blood and other body fluids
sexual contact
food and water
ways to reduce or prevent spread of diseases
cook food properly, vaccinations, simple hygiene, destroying vectors, isolation of infected individual
Gonorrhoea
Type of pathogen : bacteria
Description : pain when they urinate, Thick yellow or green discharge
How pathogen transferred : sexually transmitted disease e.g. having unprotected sex
How to prevent infection and treatment : originally treated with an antibiotic called penicillin, it has because trickier due to the strains of bacteria and people have become resistant to it. To prevent the spread you can treat it with other antibiotics and should use barrier methods of contraception such as condoms.
HIV
Type of pathogen : Virus
Description : flu like symptoms
How pathogen transferred : sexual contact, exchange of bodily fluids e.g. Blood when sharing needles when taking drugs
How to prevent infection and treatment : HIV can be controlled with antiretroviral drugs. These stop the virus replicating in the body
TMV (Tobacco Mosaic virus )
Type of pathogen : Virus
Description : virus which affects many species of plants e.g. tomatoes
How pathogen transferred : Infected leaves rub against healthy plants, or contaminated tools. They become contaminated with viruses from cigarettes.
How to prevent infection and treatment : you can dig up and destroy infected plants, Wash hands after handling infected plants, Wash tools that have come in contact with infected plants in detergent or bleach.
Salmonella
Type of pathogen : bacteria
Description : food poisoning, Suffer from fever, stomach cramps, vomiting and diarrhoea
How pathogen transferred : by eating food that's been contaminated with Salmonella bacteria.
How to prevent infection and treatment : In the UK most poultry are given a vaccination against Salmonella. This is to control the spread of the disease.
Measles
Type of pathogen : Virus
Description : red skin rashes, Fever (high temperature)
How pathogen transferred : It spreads by droplets from an infected person's sneeze or cough.
How to prevent infection and treatment : They are vaccinated against measles when they're young.
Rose Black spot
Type of pathogen : Fungus
Description : causes purple, black spots to develop on the leaves of rose plants. The leaves can then turn yellow and drop off
How pathogen transferred : Spread through the environment in water or by the wind
How to prevent infection and treatment : Gardeners can treat disease using fungicides and by stripping the plant of its affected leaves.
Maleria
Type of pathogen : protist
Description : causes repeating episodes of fever (can be fatal)
How pathogen transferred : They are carries by mosquitoes. They pick up the malarial protist when they feed on an infected animal. Every time the mosquito feeds on another animal, it infects it by inserting the protist into the animals blood vessels.
How to prevent infection and treatment : stopping the mosquitoes from breeding. They can breed in standing water, so they can be prevented by removing these water sources.
What is the first line of defence to prevent / stop pathogens entering your body and making you ill?
Eyelashes
nose hair ( silia )and mucus to trap the pathogen.
Tranchea and bronchi - mucus traps pathogen & cilia to waft the nucleus to the back of the throat
Skin - barrier + secretes antimicrobial substances to kill pathogens.
Stomach - contains hydrochloric acid
Breaking the first line of defence
Platelets are able to
release chemicals that cause soluble proteins to form a mesh of fibers across the wound.
they stick together to form clumps that get stuck in the mesh
Red blood cells also get stuck in the mesh, forming a clot. This develops into a scab which protects the wound as it heals.
What are the second line of deffence
Phagocytosis
Antibody production
Antitoxin production
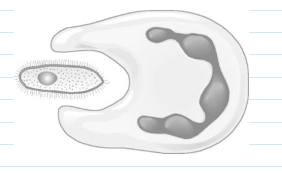
What happens during phagocytosis
The white blood cells consume the pathogen and digest them. They produce antitoxins and produce antibodies. White blood cells can surround, englulf & digest a pathogen.
How does the production of antibodies lead to the destruction of pathogens?
The antibodies lock onto the invading cells so that they can be found and destroyed by other white blood cells.
White blood cells produce y shaped structures called antibodies which bind ( attatch on ) to the antigens on the pathogen and destroy it.
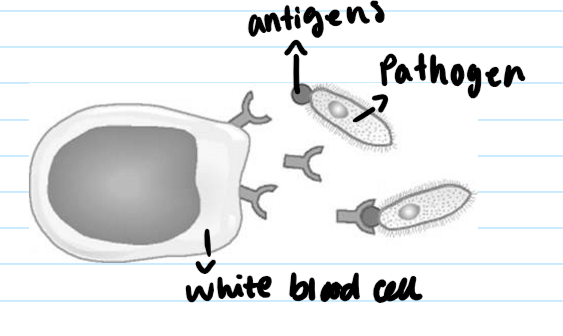
Would a measles virus antibody be effective against HIV?
Antibodies are specific for one type of pathogen. This means an antibody will only bind to a pathogen with a complementary ( matching) shape.
What are toxins and where do they come from?
Antitoxins counteract toxins produced by the invading bacteria. Some pathogens produce harmful chemicals called toxins which can damage cells.
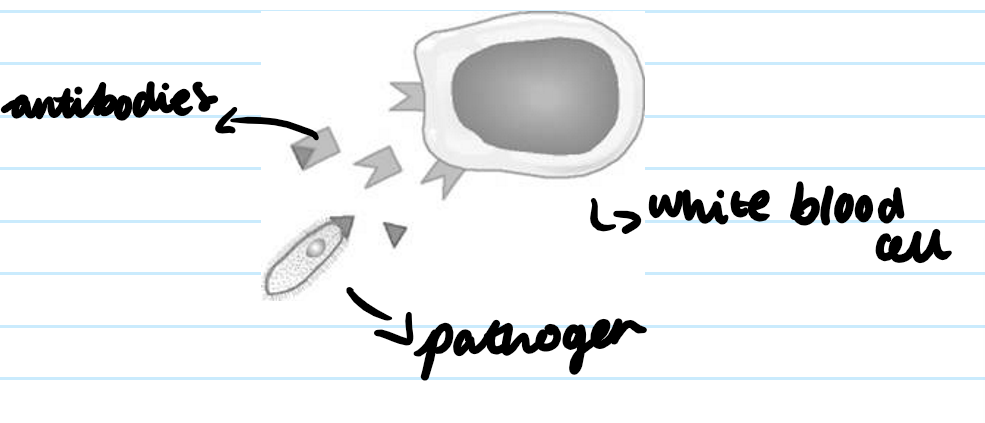
How do toxins stop people from getting ill
White blood cells produce antitoxins which bind to and neutralise the pathogens toxin.
What is a vaccine?
A vaccine is a dead or inactive pathogen.
What does a vaccine do? (4 marks)
Vaccines are injected dead or inactive pathogens to give you the antibodies. These antibodies form into memory cells so that if that pathogen hits you again then it knows how to fight it off.
Why doesn't a vaccine make you feel ill?
Dead or inactive pathogen are not able to reproduce.
What does it mean to be immune?
A person who is immune is resistant to a particular pathogen. This means that if they were exposed to this pathogen again, they would not get the disease. Having antibodies from a previous infection that can help you fight off the disease.
How does this ensure immunity going forward?
Antibodies information is stored (memory cells) and reproduced rapidly if infection occurs again (immunity).
Pros and cons of vaccinations
Pros
Helps control majority of communicable diseases from occuring - herd immuntiy
Can help build a stronger immune system
Stop large outbreaks of diseases from spreading (epidemics)
Cons
Do not always work - sometimes immunity is not gained
Side Effects
Some people are against getting vaccination
Religious issues / beliefs
Bad reaction to the vaccine (very rare)
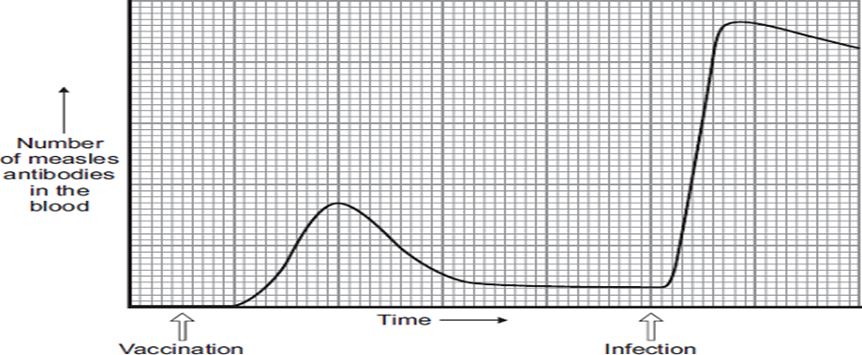
Describe and explain the differences in antibody production after vaccination compared with after infection (4 marks)
After vaccination a small, gradual increase of antibodies are produced
To destroy/kill the dead or weakened version of the pathogen in the vaccine.
After infection a rapid, large quantity of antibodies are produced
As information (antigen) was stored (memory cells created), which allowed white blood cells to produce the correct antibodies rapidly
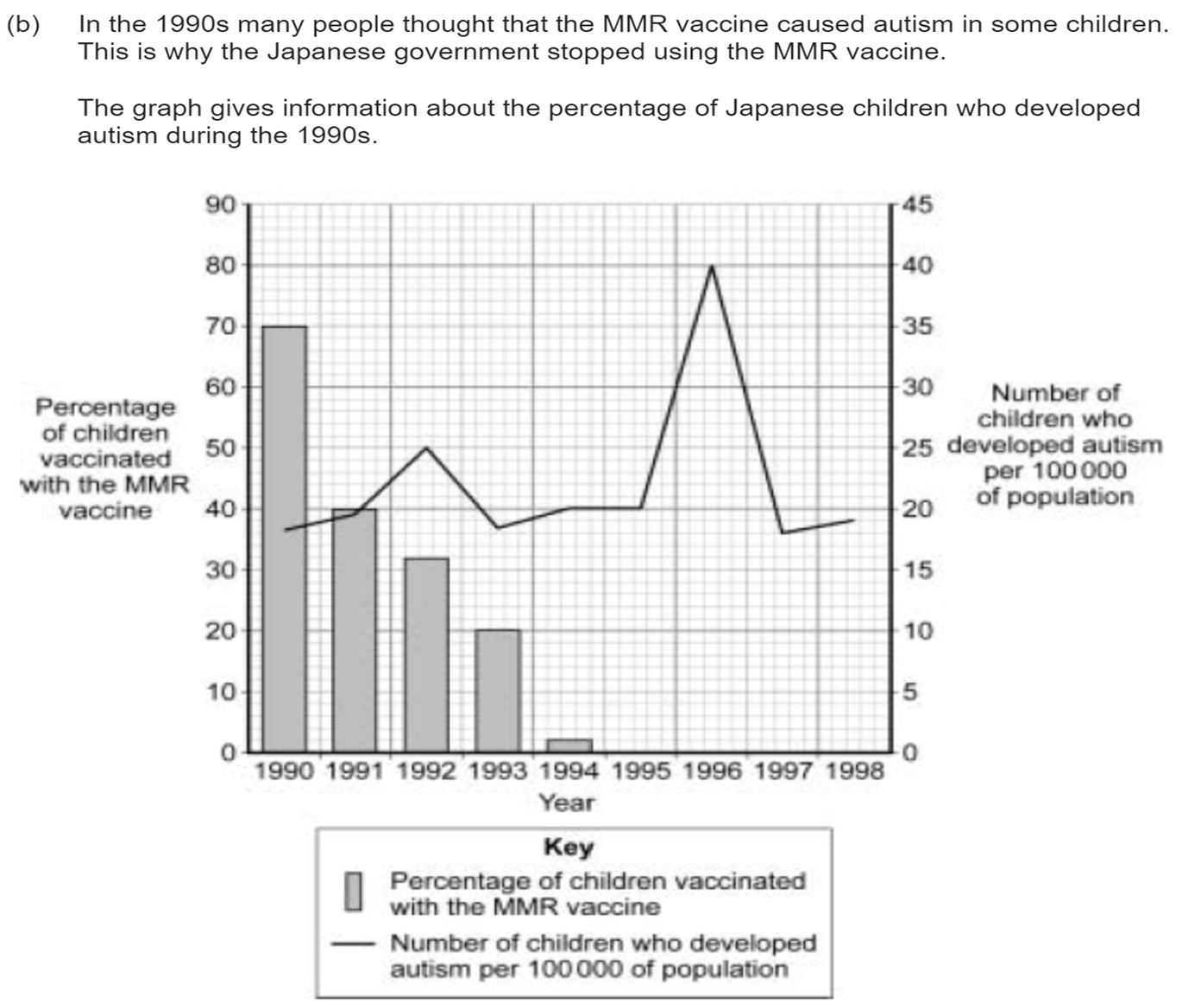
The data in the graph support the view that there is no link between MMR vaccination and autism. Explain why (4 marks)
The number of children who developed autism per 100000 of population increases the most from late 1994 till the middle of 1996. The number of children with autism then decreases until 1997. When the number of children with autism increases the most no child has had the vaccine. This increase and decrease is clearly shown to have not been causes by the vaccine but by other causes.
The highest percentage of children vaccinated had the lowest number of children who developed autism. The number of children developing autism peaked after MMR vaccination had ceased so there is no correlation.
What is a drug?
A drug is any substance that is taken into the body that changes or affects chemical reactions in the body.
Where are drugs from?
Plants. – asprin (painkiller) is found in willow and digitalis (a heart drug) is found in foxgloves
Mould – Alexander Flemming found that mould could prevent bacterial growth
Syntheic – Produced by large pharmaceutical companies (most made this way
Why is it difficult to develop drugs to kill viruses without damaging the body tissue? (3 marks)
Painkillers - They just kill the pain. They help you feel better it doesn't kill the pathogen. Your immune system
Antibiotics - You can't use antibiotics to kill viruses because you would end up killing your own cells becuase a virus is inside your cells. Antibiotics are used to kill bacteria
Function and examples of PainKillers
Function: Relieve symptoms
Doesn't kill the pathogen - therefore doesn't solve the problem - the white blood cells fight the pathogen
Examples: Paracetamol & aspirin
Function and examples of Antibiotics
Function: Kill or prevent growth of bacteria ONLY. Will not harm your cells
Examples: Amoxicillin, penicillin
What is antibiotic resistance
1. A mutation occurs during bacterial reproduction
2. Allowing some bacteria to survive when an antibiotic is taken.
3. The new mutated gene in the bacteria is resistant to the antibiotic
4. This resistant gene is passed onto offspring via asexual reproduction/ mitosis and population of resistant strain increases
How to prevent antibiotic resistance
Do not overprescribe antibiotics
Do not prescribe for non serious / mild infections
Finish your full course of antibiotics when ill because even if you feel better there is a high chance that the bacteria is still inside you and no completely destroyed. The bacteria is still mutating and developing resistance if you take them a few days later when you feel ill you will find that the bacteria has become immune and no longer will destroy the bacteria.
Eukaryote, prokaryote, protist, fungi have nucleus mitochondria cell wall and are they uni or multicellular?
Eukaryote | Prokaryote | Protist | Fungi | |
Nucleus | yes | no | yes | yes |
Mitochondria | yes | no | yes | yes |
Cell wall | yes/no ( some have cell wall others don’t) | yes | no | yes |
UniCellular or multicellular | multi | uni | uni | multi |
What was thalidomide used to treat?
It was intended as a sleeping pill but it was also found to relieve morning sickness in pregnant women.
When was thalidomide developed?
1950s
What was the problem with this drug?
It has not been tested on pregnant women, it could pass through the placenta causing abnormal limb development in babies. 10,000 babies were affecting and half of them died. Babies were born without arms or legs.
What happened after this?
The drug was banned and more rigorous testing procedures were introduced. It now treats leprosy (bacterial infection).
What do we test drugs for
Toxicity : How harmful the drug is
Dosage : How much of the drug works best
Efficacy : How well the drug works.
Order of drug testing?
Pre-clinical: Drugs are tested in cells/tissues and using computers to try to test for efficacy and toxicity.
Pre-clinical Drugs are tested in two animal species to check that they are not toxic and to find the best dosage
Clinical: Drugs are tested on a few healthy volunteers at low doses to ensure they are safe and to check for side effects.
Clinical Drugs are tested on patients with the disease to test for dosage, efficacy and side effects.
Drugs are tested on large numbers of patients for a long period. A Double-blind trial - Half are given the new drug, half receive a placebo.
After peer review drugs receive a license so doctors can prescribe them to patients and it is monitored.
Why are some people given a placebo during a drug trial?
A placebo is a fake drug. A medicine or procedure prescribed for the psychological benefits to the patient rather than for any physiological effect.
A substance that has no therapeutic effect, used as a control in testing new drugs.
What is a pathogen
microorganism that can produce a disease
What is an antigen
substance that causes an immune response
What is an antibody
produceed by white blood cells, attatches to the antigens to destroy them
Types of white blood cells
Phagocytes - engulf and digest pathogens in a process called phagocytosis
B Lymphocytes - Produce antibodies to help destroy all types of pathogens.
How could we stimulate an organism to produce antibodies without making them ill?
A vaccine to provide immunisation ( injecting a dead or inactive pathogen) OR injecting the specific antigen.
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are produced from a single clone of white blood cells (lymphocytes)
The antibodies are specific to one binding site on one protein antigen and so are able to target a specific chemical or specific cells in the body
How to make monoclonal antibodies
Inject mice with antigen targeted to stimulate lymphocyte cells.
Correct B lymphocytes are extracted from mice, that produce a particluar antibody
A tumour cell is then fused with the b lymphocytes to form a hybridomas
The hybridomas is then cloned many times and used to produce the correct antibodies.
The monoclonal antibodies are then separated, purifiled and ready to use.
How can you use monoclonal antibodies?
Pregnancy test
Explain how the pregnancy test strip works to show a positive result.
As urine passes through the reaction zone. If the HCG hormone is present it binds to the mobile HCG antibody in the reaction zone. If present, the HCG hormone moves up the test and binds to the immobilised HCG antibodies in the result window. The other antibodies which do not attach to HCG bind to antibodies in the control window. Blue dye appears in both the control and the results zone to show positive result.
Explain how a pregnancy kits use monoclonal antibodies (3 marks)
Urine passes though reaction zone which is the 1st window. Then the HCG hormone binds to the HCG (monoclonal) antibody. The HCG hormone binds to the HCG antibodies in the results zone which is the 2nd window. This causes the colour to change in both windows.
What do cancer cell have on them?
They have antigens on their cell membrane that aren't found on normal body cells. This is called tumour markers.
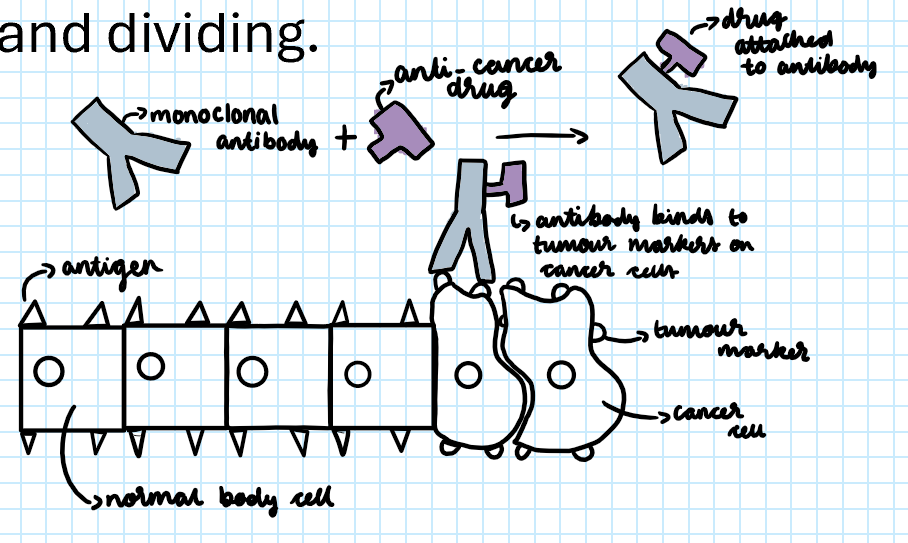
How can monoclonal antibodies be used to deliver anti-cancer drugs?
Anti-cancer drug can be attached to these monoclonal antibodies. This could be a radioactive substance, a toxic drug or a chemical which stops cancer cells growing and dividing.
Advantages and disadvantages of monoclonal antibodies
Advantages
only bind to specific cells that need treatment
healthy cells are not affected
used to treat a wide range of conditions
Disadvantages
Not widely used or not 100% accurate
Attatching monoclonal antibodies to drug is difficult
Some side effects created when using mice cells in hydridomas.
Where is Staphylococcus aureus usually found in humans?
Surface of our skin or in the lining of our nose.
Staphylococcus aureus is usually harmless but what does it cause if it enters the body?
They cause infections such as boils, abscesses or impetigo.
Who is vulnerable from MRSA?
Elderly and young children or people who have a weak immune system.
How can MRSA enter the body?
Through a break in the skin.
How might you tell if a wound is infected with MRSA?
boils, abscesses or impetigo.
What do hospitals do to prevent the spread of MRSA?
Rigorous cleaning. Disinfection of all surfaced, hand wash at every bed and ward entrance.
What do you think the public could do to prevent the spread of MRSA?
Wash hands, reduce contact with people who are unwell.
How would you test to see which antibiotics you would give to a patient who has a bacterial infection?
Grow a culture from a sample of blood, urine of body fluid from the patient.
Explain how natural selection could have produced these strains of penicillin resistant bacteria.
Natural selection is when a mutation occurs during bacterial reproduction this allows some bacteria to survive when an antibiotic is taken. The new mutated gene in the bacteria is resistant to the antibiotic and reproduces. This resistant gene is passed onto offspring's via asexual reproduction. This would have saved penicillin and there would be less of a strain and less bacteria would be resistant to it.
What are minerals and vitamins needed for?
They help produce chlorophyll for photosynthesis. They are essential for enzyme function, growth and development
Plants need carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, where do these elements come from?
The carbon comes from the atmosphere surrounding us. The hydrogen and oxygen come from the water which can come from the rain. Oxygen also comes from respiration made in photosynthesis.
Plants also need a range of mineral ions, where do these come from and how does the plant take them up?
Mineral ions come from the soil. Plants take them up through their roots by active transport and diffusion.
Nitrate ions are used to make something necessary for growth, what is it?
Plants use nitrate ions to convert sugars into proteins.
Nitrate ions are used to make amino aids, which are essential for building proteins, necessary for plant growth.
Magnesium ions are used to make something necessary for photosynthesis, what is it?
Magnesium ions are used to make chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis.
Deficiency diseases
Nitrates
Magnesium
Why is nitrates needed, deficiency symptoms
Needed: Protein synthesis for healthy growtn
Deficiency symptoms: Stunted growth, pale leaves
Why is magnesium needed, deficiency symptoms
Chlorophyll construction for photosynthesis.
Deficiency : chlorosis - pale or yellow leaves
Why do farmers spread manures
manures provide essential plant nutrients to the soil to enhance soil fertility and ensure strong Vegetative growth.
How to investigate the effects of minetals
Label 3 petri dishes with your initials, minerals, no nitrate and no magnesium.
Make 2 cotton wool pads quite damp with solution containing all minerals and put them in your petri dish marked minerals.
Sprinkle some cress seeds evenly across the cotton wool.
Repeat experiment but replace water with:
Nitrate deficient solution
Magnesium deficient solution
What are Alphids
Aphids are insects that have a mouth to penetrate the phloem vessel to feed off the plants sugar rich phloem sap
This prevents the plant from using the products of photosynthesis for respiration, growth etc.
They also act as vector, carrying viruses, bacteria and fungal diseases from one plant to another
Name three ways that you could identify the pathogen which is causing a plant disease.
Use a gardening manual or website
Take samples to a lab for testing
Use a testing kit containing monoclonal antibodies.
Physical barriers in plants to prevent pathogens
Bark made from lignin acts as a barrier
Tough waxy cuticle acts as a pathogen barrier
Cellule builds cell walls to strengthen the plant cell
leaf fall - diseased leaves fall from tree to prevent spread
Guard cell close stomata to prevent evtry of pathogens
Chemical barriers in plants
poison is produced to kill attacking organism
produce antibacterial chemicals
mint and hazel produced from plants act as antiseptic
oil released to prevent aphids attaching
Mechanical barriers
Leaves which droop or curl when touched
Thorns and hairs deter animals
Mimicry - some plants mimic unhealthy plants to avoid being eaten or mimic insects.
Explain how different types of organism defend themselves against microorganisms. (6 marks)
Start with humans, humans produce white blood cells which help engulf pathogens through phagocytosis.
In humans nose hairs and mucus prevents you from inhaling bacteria. The hair keeps out dust and microbes.
Our skin releases chemicals which gives you antimicrobial properties preventing bacteria getting through the skin.
Plants have bark made from lignin which acts as a barrier from microorganisms.
Plants use their guard cells to close the stomata to prevent the pathogens from entering the plant.
Plants have a tough waxy cuticle acts as a barrier prevents pathogens from entering .