Calc 1 Rules and Definitions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Informal Definition of the Limit
limx→af(x)=L if we can force f(x) as close as we like to L by choosing x close enough but not equal to a
Formal Definition of the Limit (Epsilon Delta)
For every ε>0, there exists a δ>0 so that if )<lx-cl<δ, then lf(x)l<ε
Squeeze Theorem
If f(x)<g(x)<h(x) and limx→∞=L=limx→ah(x) then limx→ag(x)=L
Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
If f is continuous on [a,b] and f(a)<N<f(b), there exists some c in (a,b) were f(c)=N
Limit Definition of the Derivative
f’(x)=limh→0[f(x+h)-f(x)]/h
Tangent Line Equation
y-f(a)=f’(a)(x-a)
Mean Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b), there exists a c in (a,b) where f’(c)=[f(b)-f(a)]/[b-a]
Rolle’s Theorem
If f is continuous on [a,b], differentialble on (a,b), and f(a)=f(b), then there is a c in (a,b) where f’(c)=0
Fermat Theorem
If f has a local max/min at c, then c is a critical number of f
Extreme Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a,b], then f attains an absolute max and absolute min on [a,b]
First Derivative Test
If c is a critcal number of f and
f’ changes sign from + to - at c, then f has a local max at c
f’ changes sign from - to + at c, then f’ has a local min at c
Concavity Definition
f is concave up on an intercal if the graph of f lies above all of its tangent lines on the interval
Second Derivative Test
If f’(c=0 and
f”(c)>0, then f has a local min at c
f”(c)<0, then f has a local max at c
Newton’s Method
Xn+1=Xn-[f(Xn)]/[f’(Xn)]
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC) Part 1
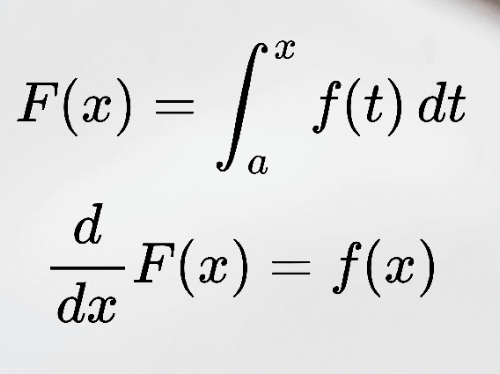
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC) Part 2
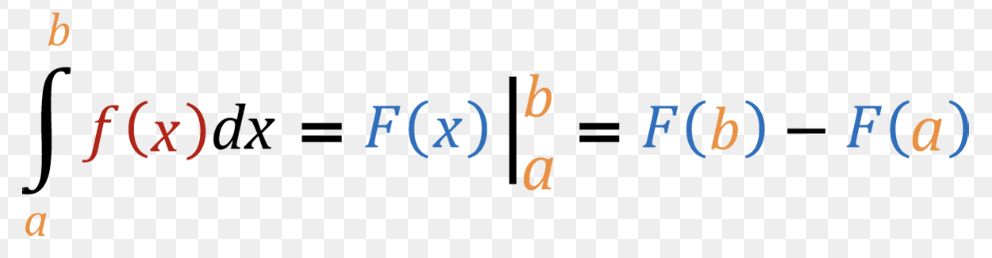
Net Change Theorem
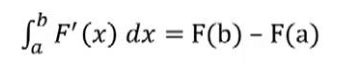
Reimann Sums
