Unit 2 Human Anatomy
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Long bones
longer than they are wide and serve as a lever
Made up of diaphysis, epiphysis, and epiphyseal plate
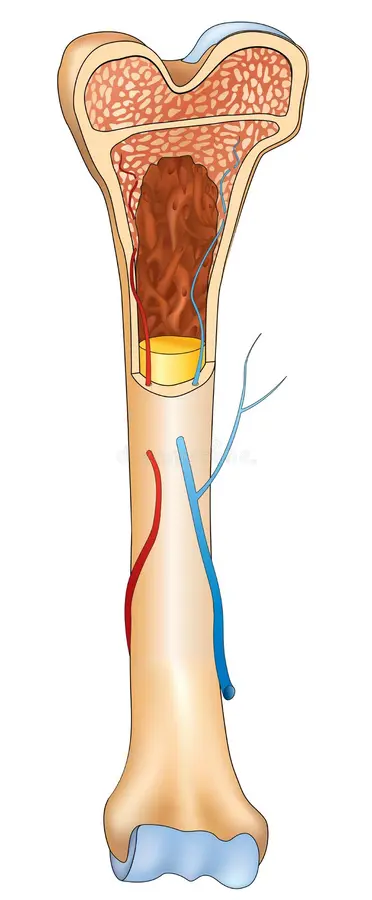
Diaphysis
long shaft of a long bone
hollow cylinder
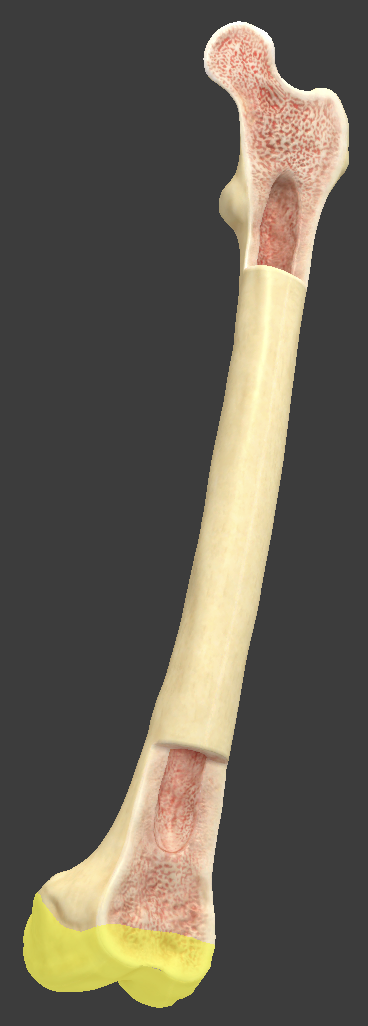
Epiphysis
area on the end of a long bone where a joint occurs
Epiphyseal plate
hyaline cartilage that separates the diaphysis and epiphysis marrow cavities
new cartilage cells born and old cartilage cells are replaced by bone → epiphyseal line appears when new cartilage cells stop proliferating and growth in length of long bone stops
Epiphyseal line (growth plate)
when this appears, growth in length of the long bone is done
dictated by growth hormones
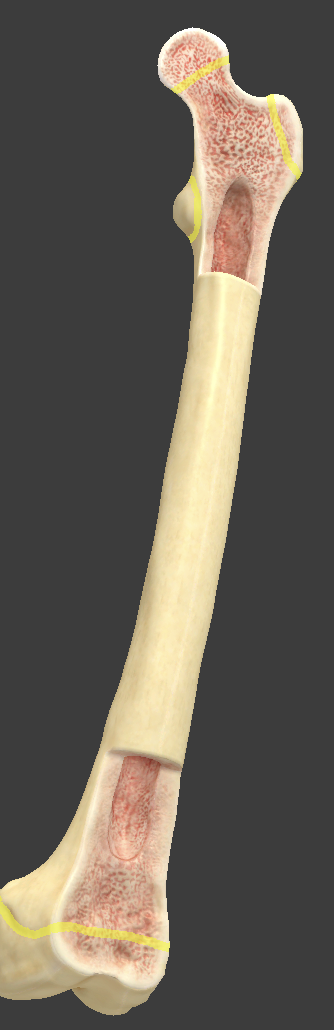
Metaphysis
area between the diaphysis and epiphysis
where the growth plate lives

Yellow bone marrow
hollow cavity in the diaphysis that is occupied with adipose tissue (fat)
can be an energy reserve
no longer produces blood
Red bone marrow
at the epiphysis, and where blood cell production occurs (hemopoiesis)
most commonly harvested from the pelvis for marrow donation
Periosteum
connective tissue covering on the outside of long bones
serves as place for muscle attachment
only place with sensory nerves
Articular cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the articular surface of a bone at a synovial joint
reduces friction and eases joint movement
Compact (cortical) bone
layer located on the outside of bones
made up of osteons
Spongy (cancellous) bone
bone with large spaces
primarily located within the epiphysis
where red bone marrow is
made up of trabeculae
Matrix
made up of organic (collagen) and inorganic (mineral salt) components
Collagen
organic component
makes bones flexible
Mineral salts
inorganic component
calcium and phosphates
provide hardness to bone
Organic > inorganic
bendy bones
rickets/osteomalacia - bones bend with any force
Organic < inorganic
brittle bones
osteogenesis imperfecta
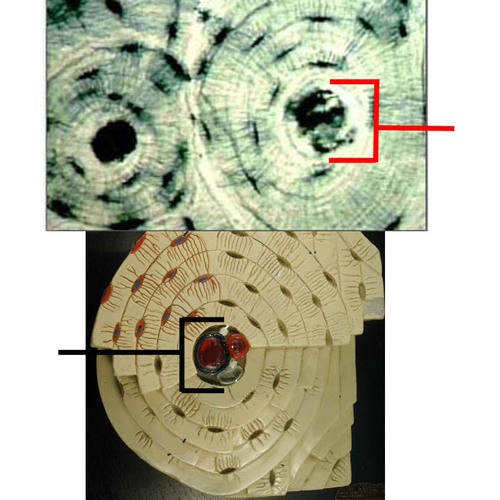
Osteon
basic functional unit of compact bone
made up of a central canal, lamellae, lacunae, and canaliculi
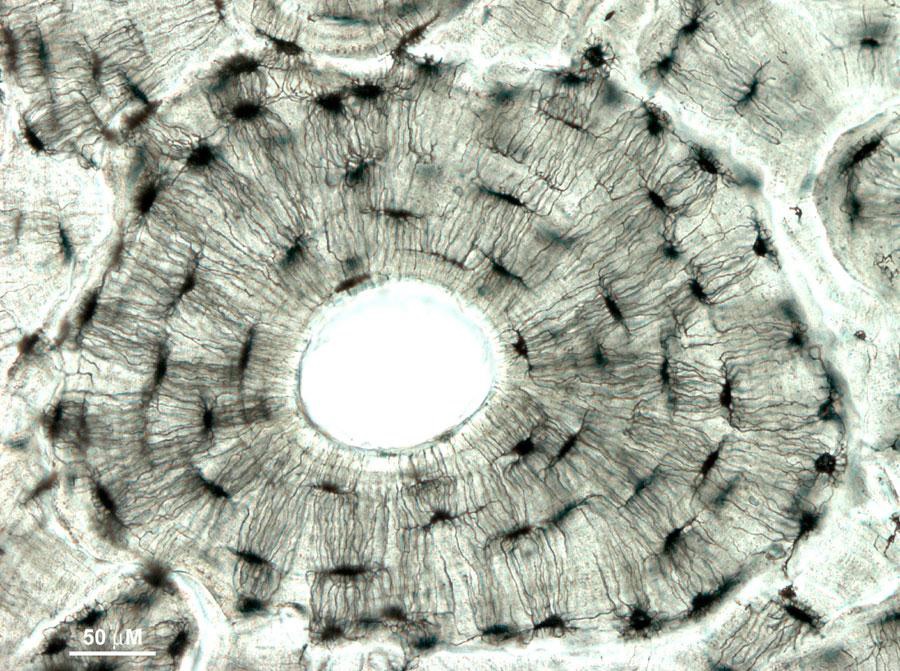
Central canal
contains the neurovasculature (arteries, nerves, and veins)
Lacunae
the canals forming a ring around the central canal where the osteoblasts live
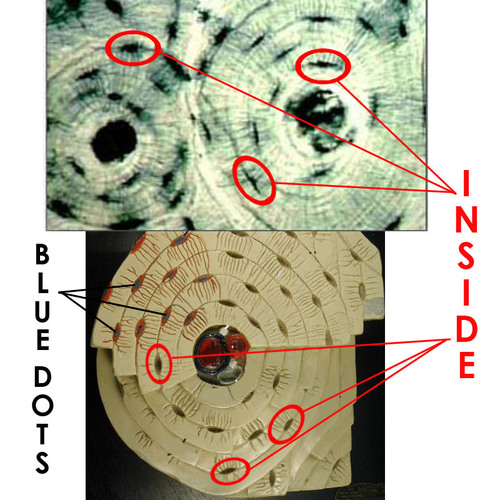
Lamellae
a ring of connective tissue around the central canal made up of lacunae
3 form concentric rings around the central canal
Canaliculi
tunnels between the processes of neighboring osteoblasts
gap junctions
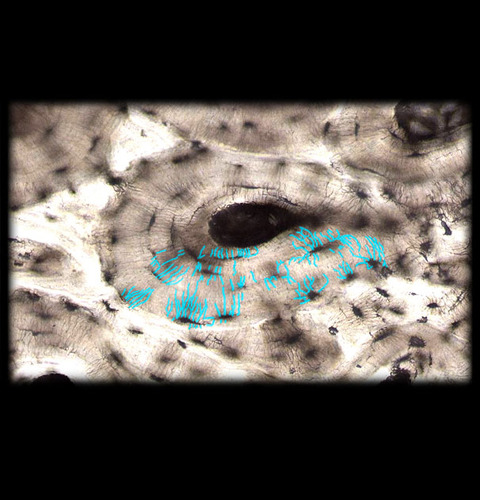
Trabeculae
seemingly random arrangement of spicules (“sticks”) in spongy bone
arrangement determined by forces placed on the bone
Endochondral ossification
produces most bones
development of bone from a cartilage template
hyaline cartilage template becomes invaded by a blood supply
primary and secondary ossification centers form
blood carries osteoblasts and lays down matrix
Intramembranous ossification
produces the flat bones of the skull, part of the mandible, and the clavicle
develops within a fibrous sheet
mesoderm becomes mesenchyme, which is invaded by osteoblasts that lay down osteoid tissue
compact bone on the outside and spongy on the inside
Bone remodeling
involves absorption of old bone and deposition of new bone
reshapes bone in response to use and disuse and repairs microfractures
Fracture
caused when forces are greater than resistance
Fracture repair
hematoma formation
soft callus formation
hard callus formation
bone remodeling
Reduction
realignment of bones
open - placing screws, braces, or metal plates through surgery
closed - manually easing bones back into alignment
Osteopenia
when bone mass decreases from too few forces on the bone
ex. bed rest
Hyperostosis
bone mass increases (too thick)
Osteoblasts > osteoclasts
tearing down bone faster than it can be laid down
osteoporosis
Skull bones
made up of a layer of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone
attached at joints called sutures
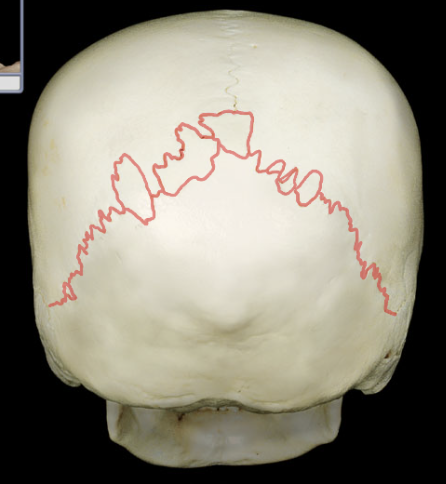
Sutures
joints that appear as seams on the surface of the skull
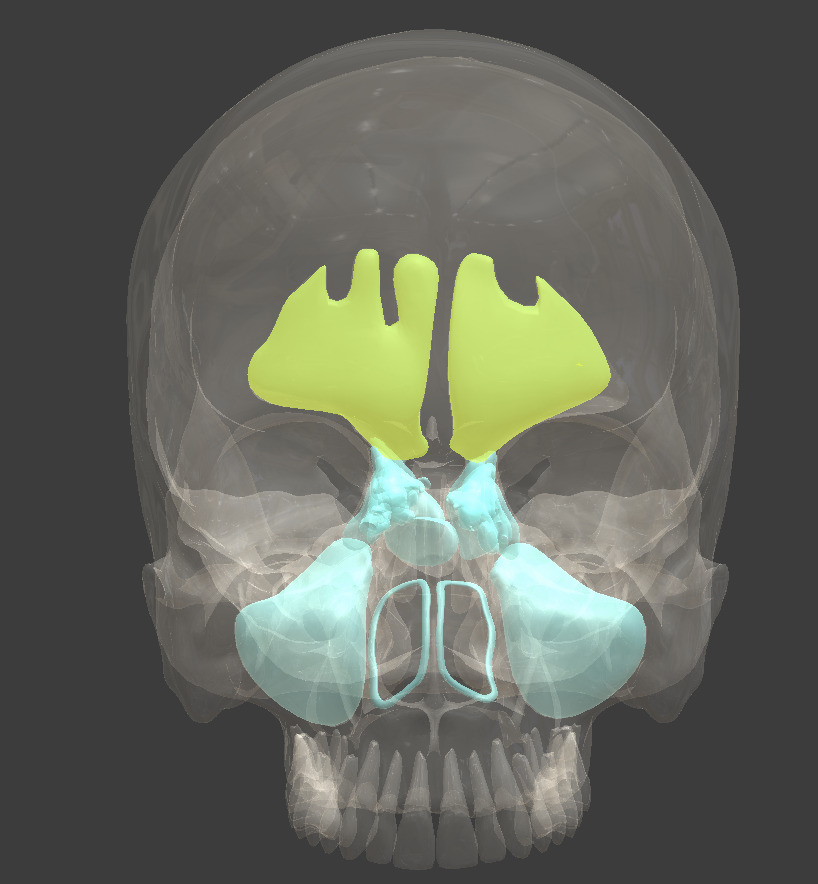
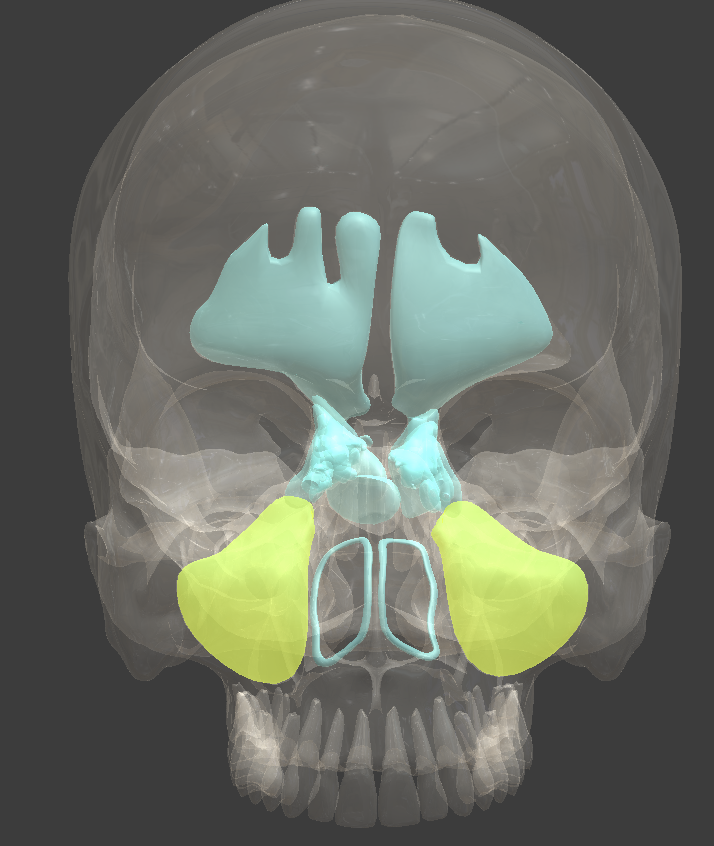
Paranasal sinuses
spaces in four of the skull bones that surround the nasal cavity
resonate sound
Frontal sinus
an air-filled space in the bone of the forehead
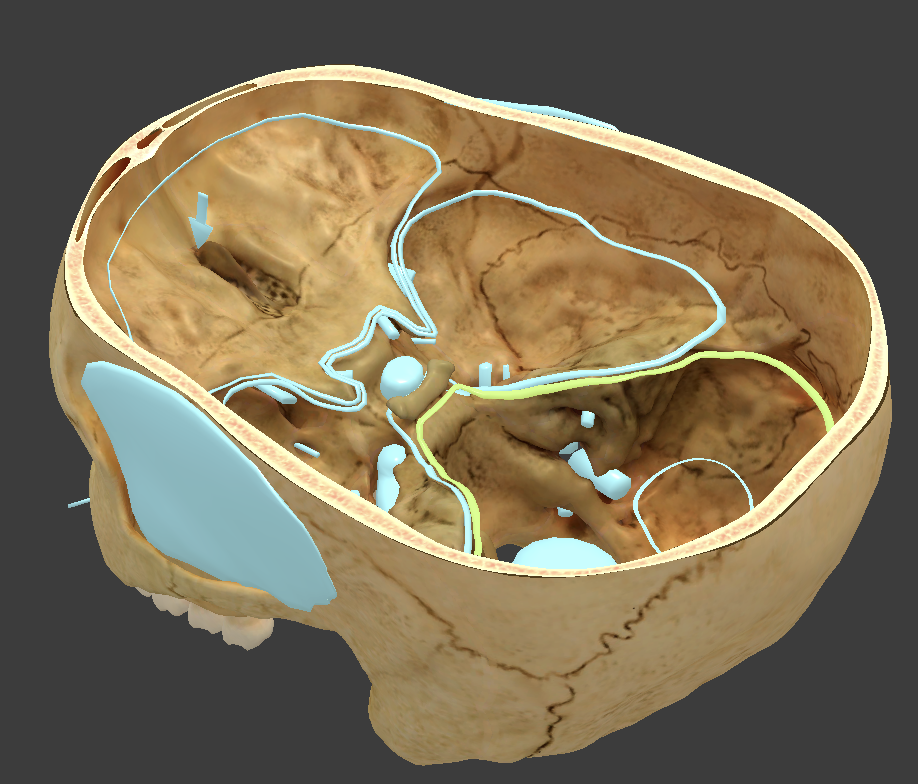
Anterior cranial fossa
where frontal lobe is located
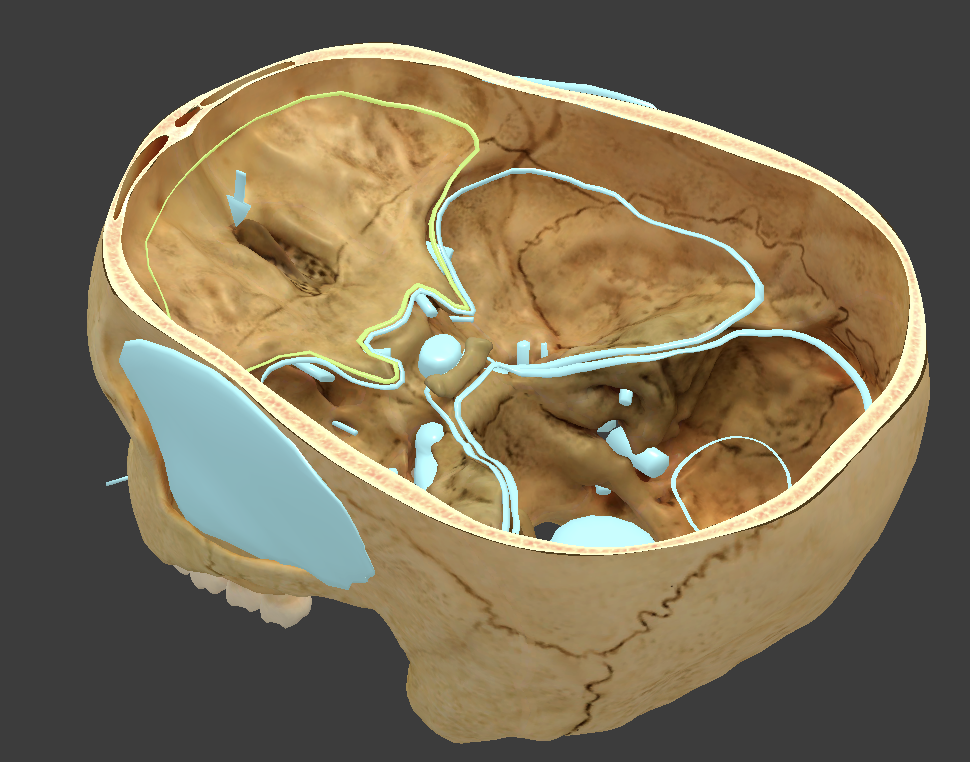
Middle cranial fossa
where temporal lobe is located
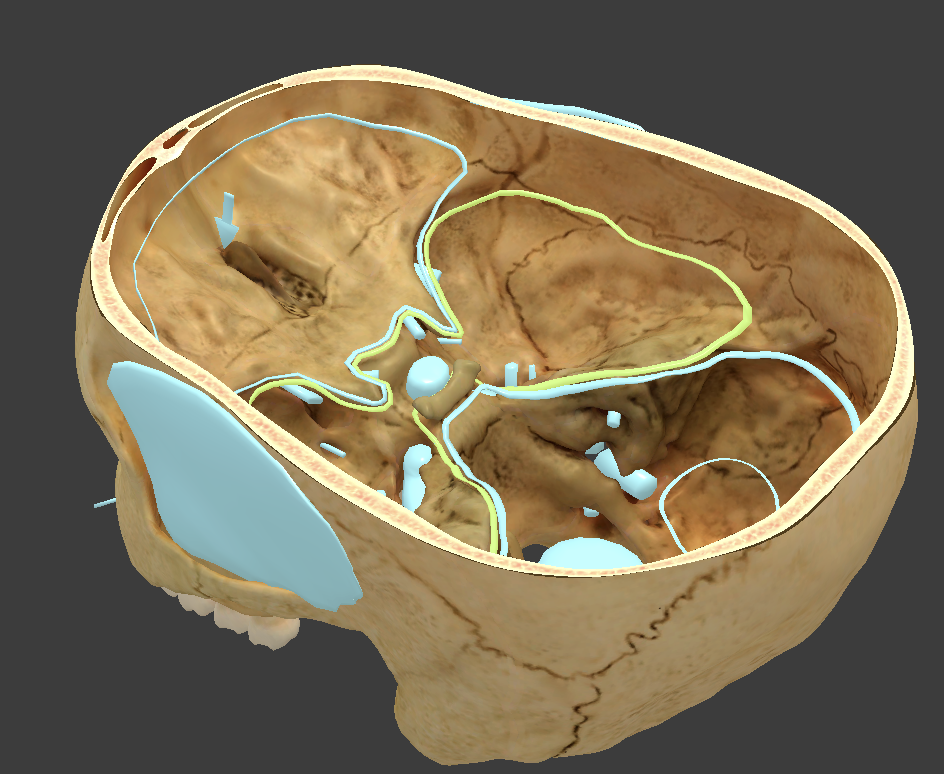
Posterior cranial fossa
where cerebellum is located
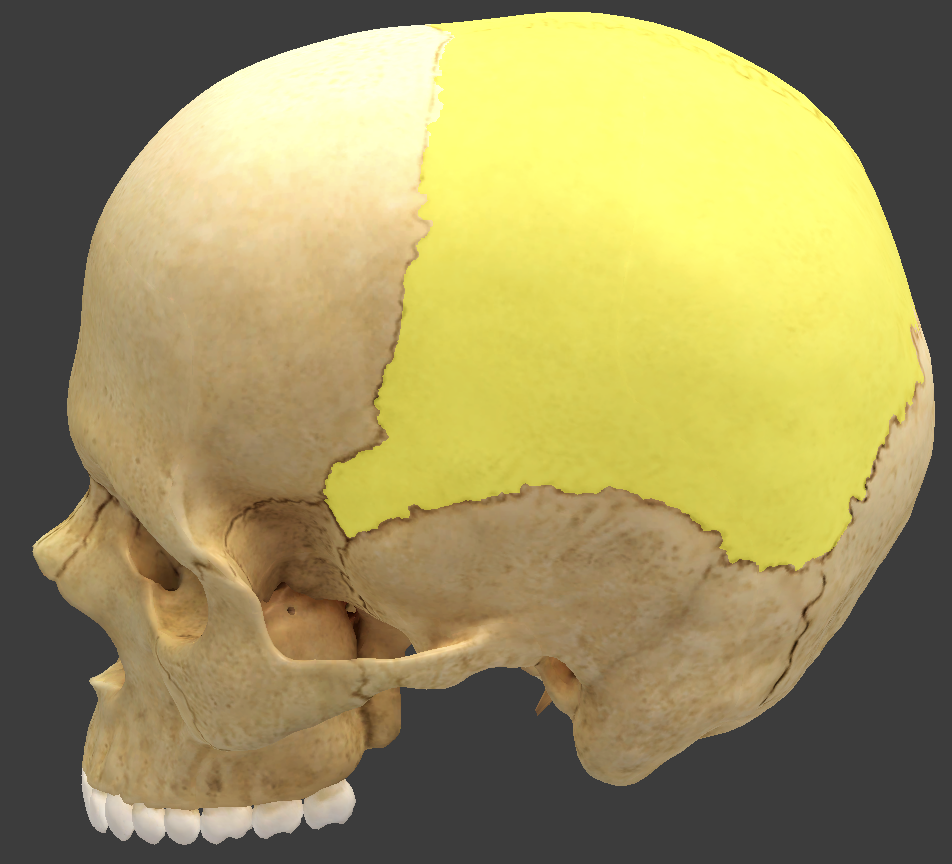
Parietal bones
form most of the cranial roof and part of its walls
bordered by four sutures
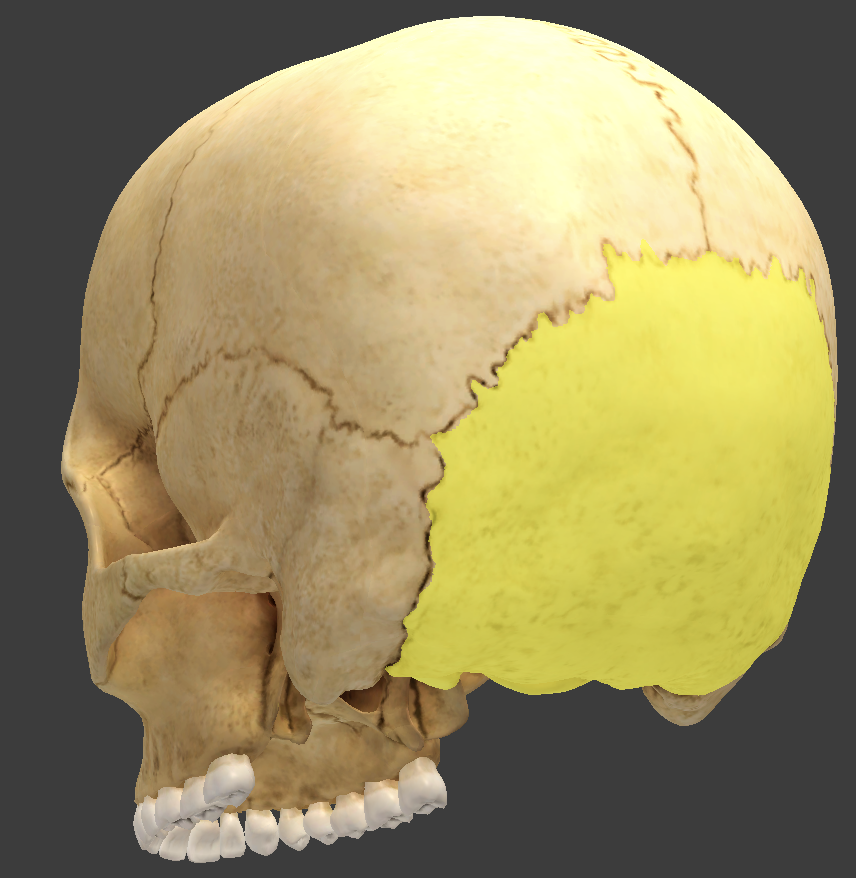
Occipital bone
located in the rear of the skull
Occipital condyle
articulate with the first bone of the spine
small knob where the skulls rests on the vertebral column
allows you to nod your head
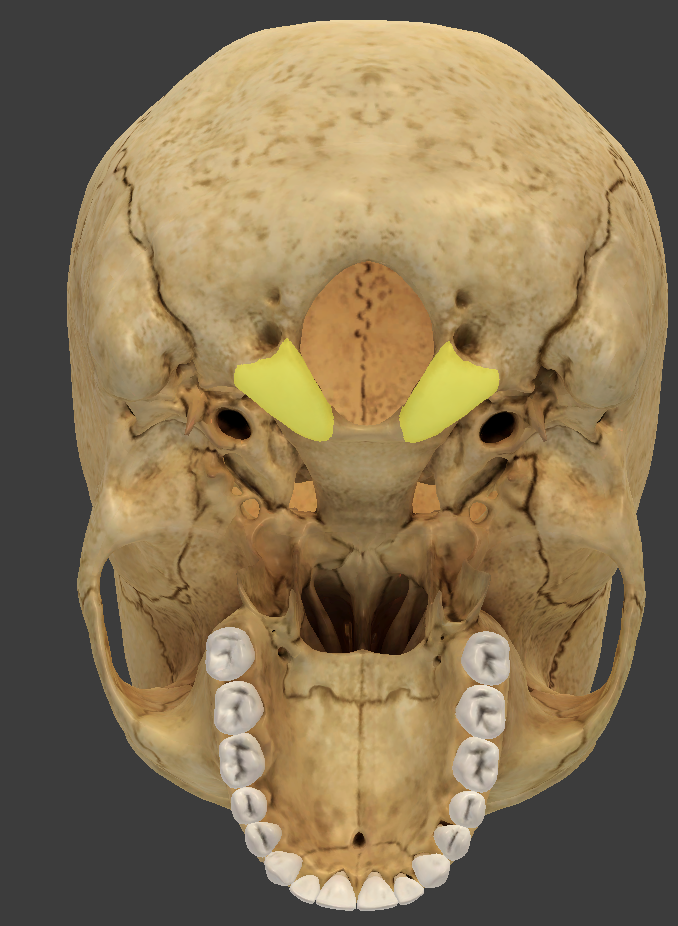
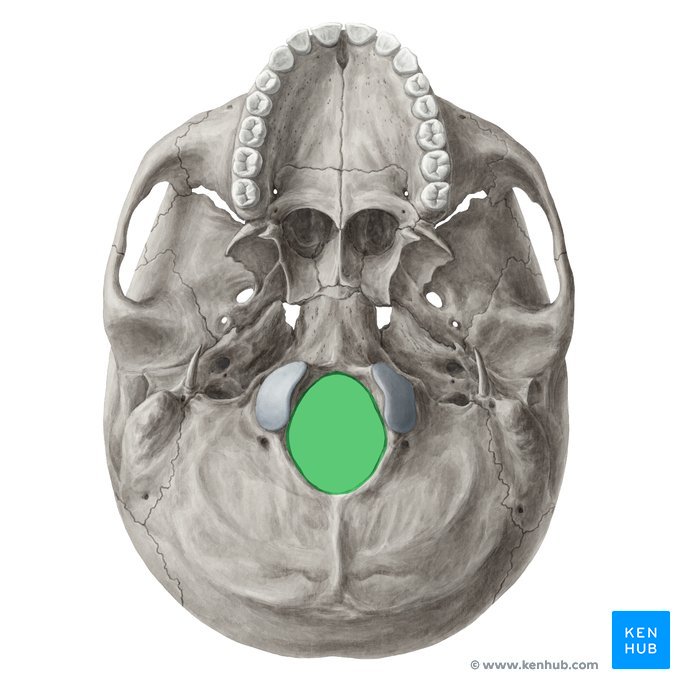
Foreman magnum
located in the occipital bone
allows passage of the spinal cord and vertebral arteries into the cranial cavity
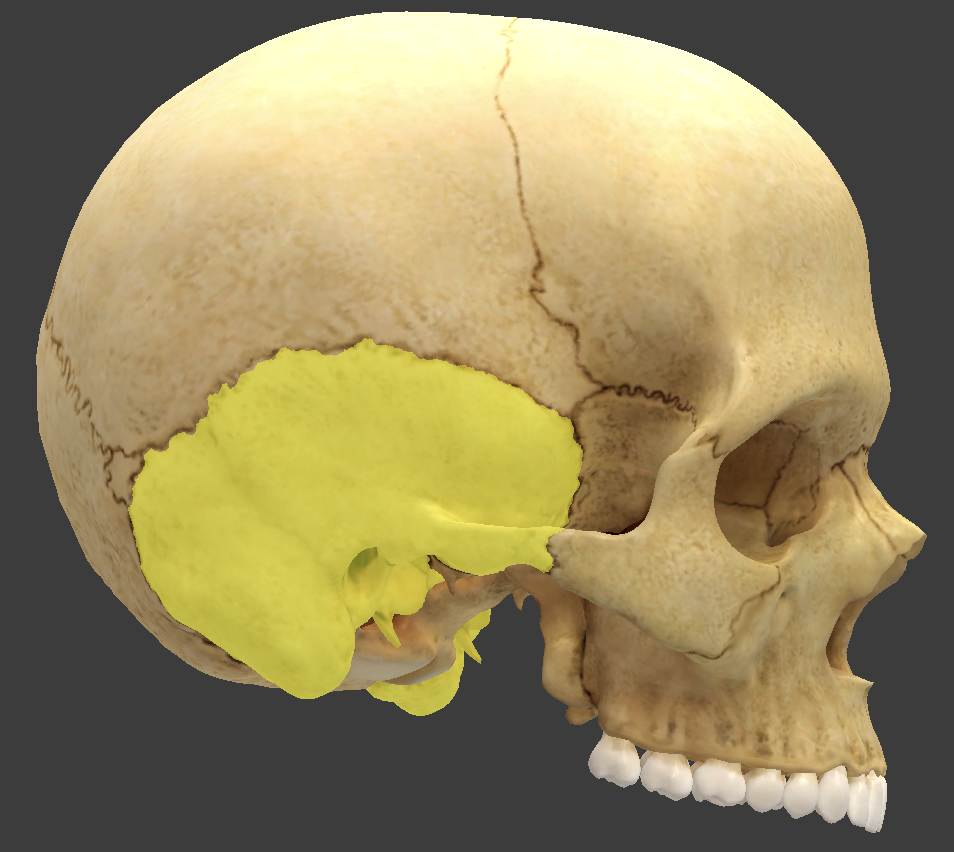
Temporal bone
forms the lower wall and part of the floor of the cranial cavity
Mandibular fossa
condyle where the mandible sits to form the temporomandibular joint
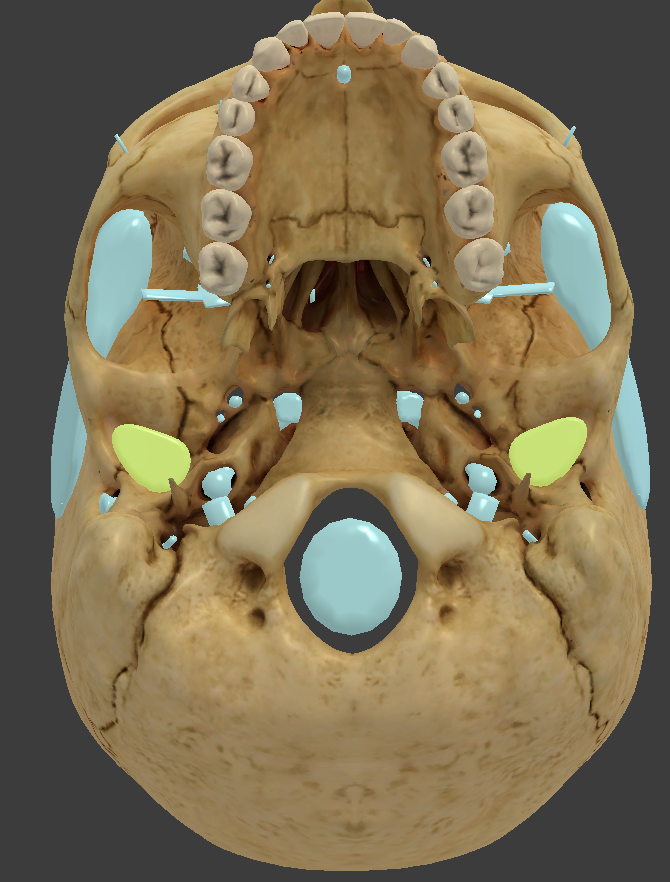
External acoustic meatus
a canal in the temporal bone that conveys sound waves to the eardrum
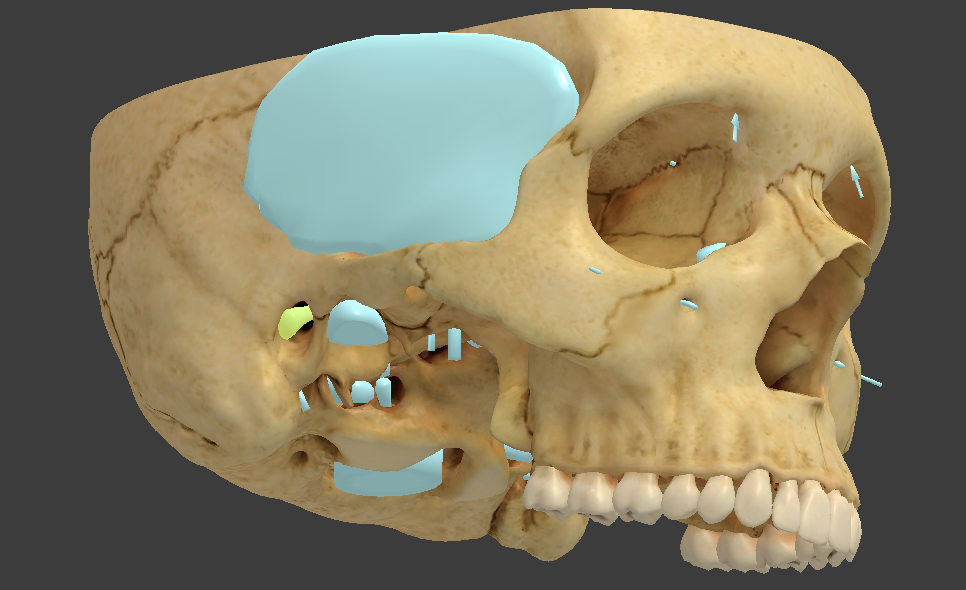
Mastoid process
lump behind the ear
filled with small air sinuses
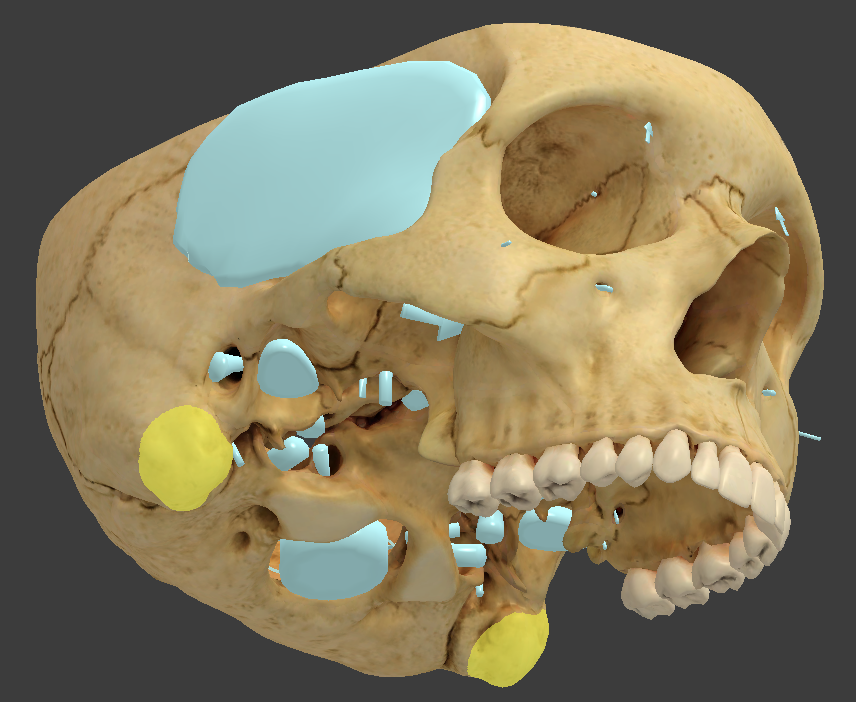
Petrous
portion of the temporal bone where the inner ear is found
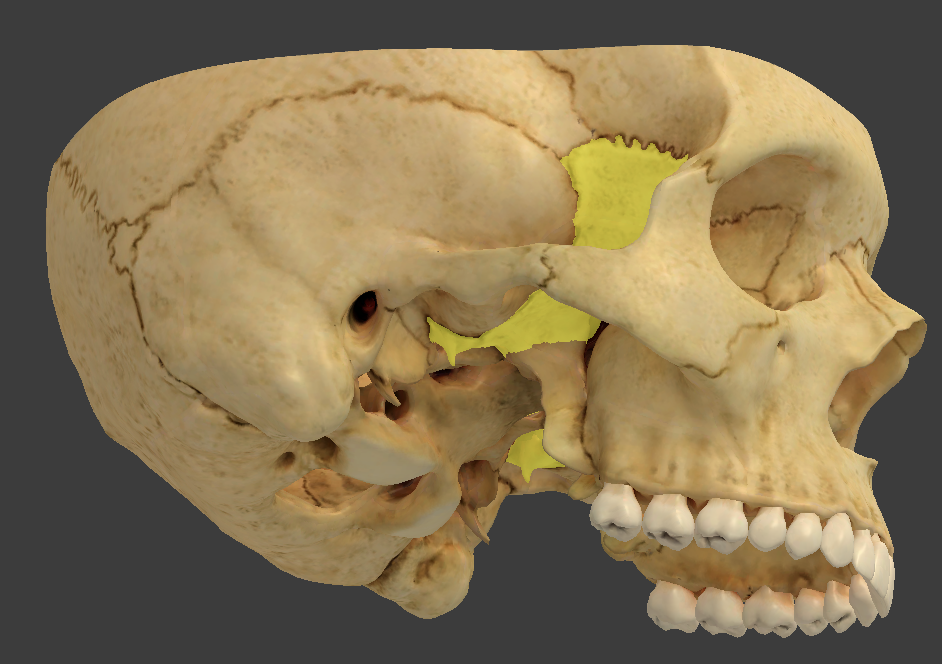
Sphenoid bone
contacts every other cranial bone
made up of a median body and greater and lesser wings
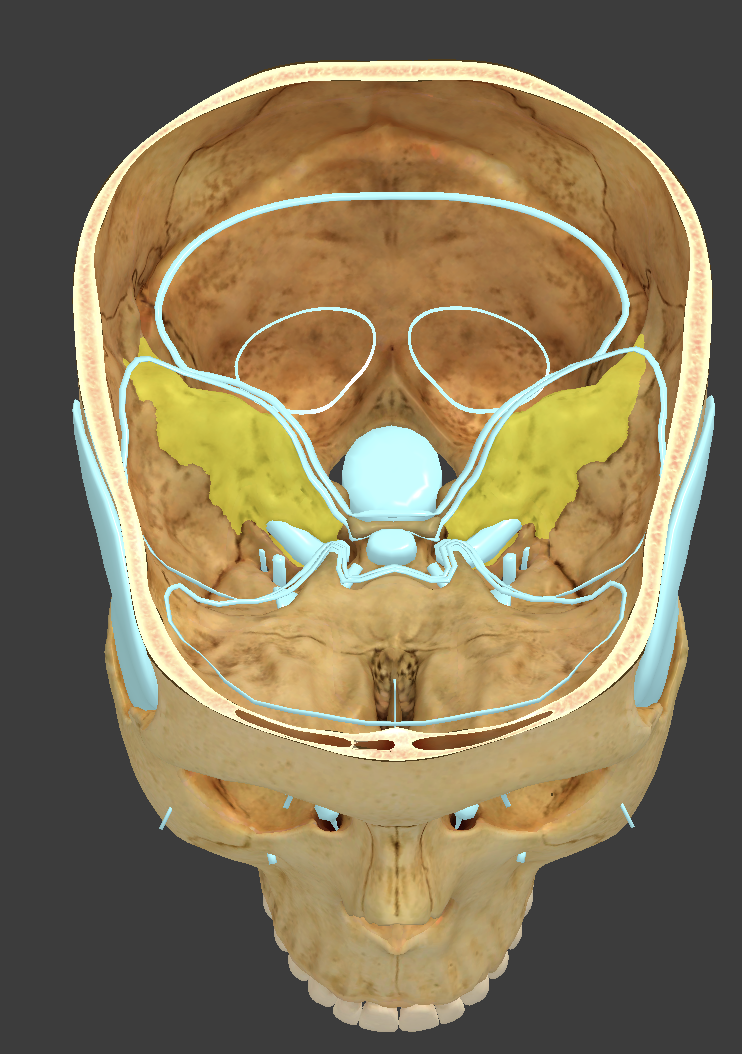
Sella turcica
saddlelike surface feature in the median body of the sphenoid bone
Sphenoidal sinuses
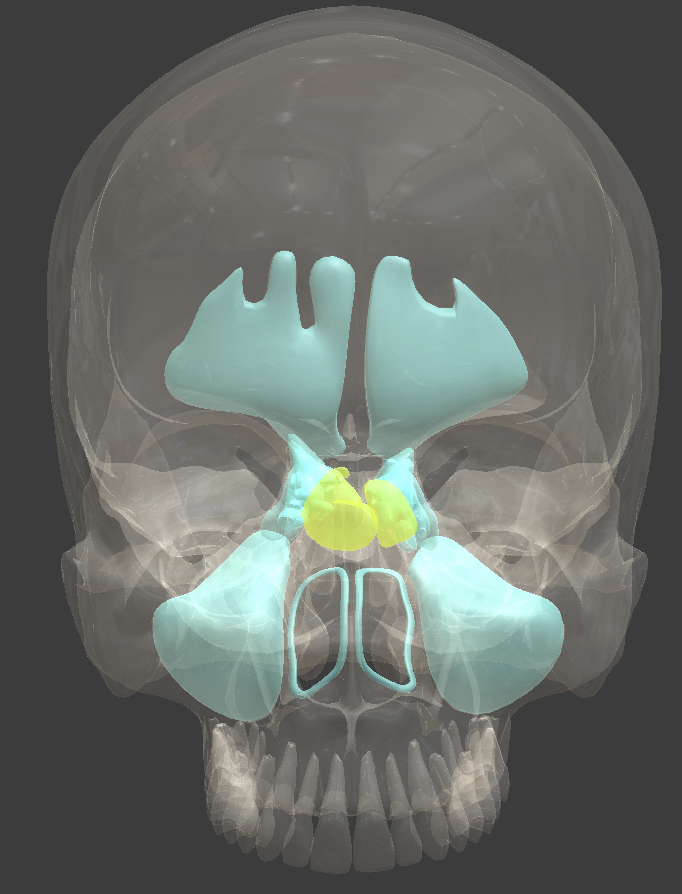
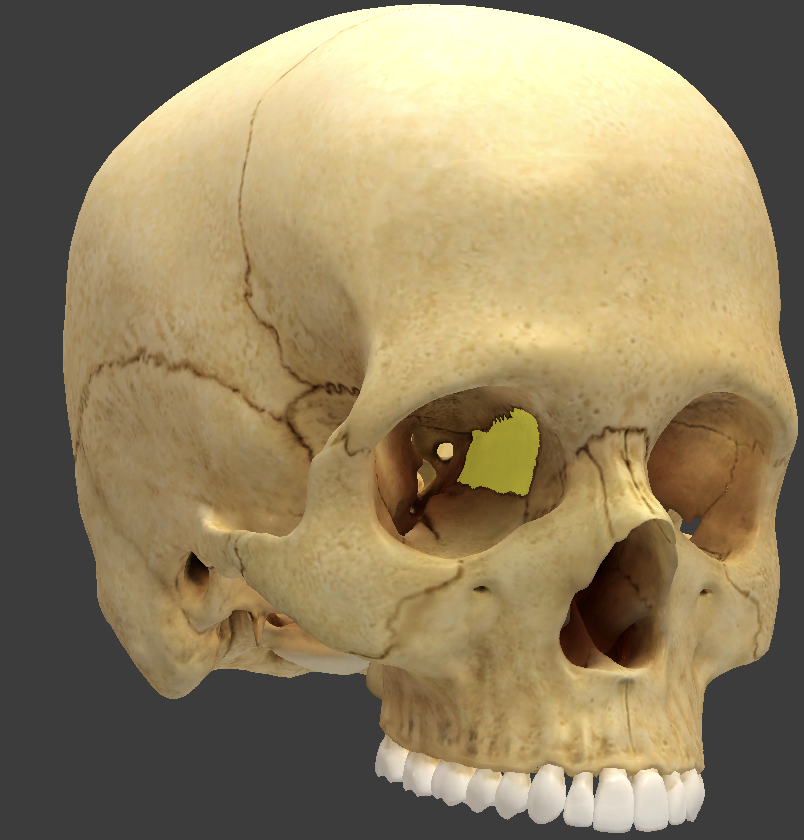
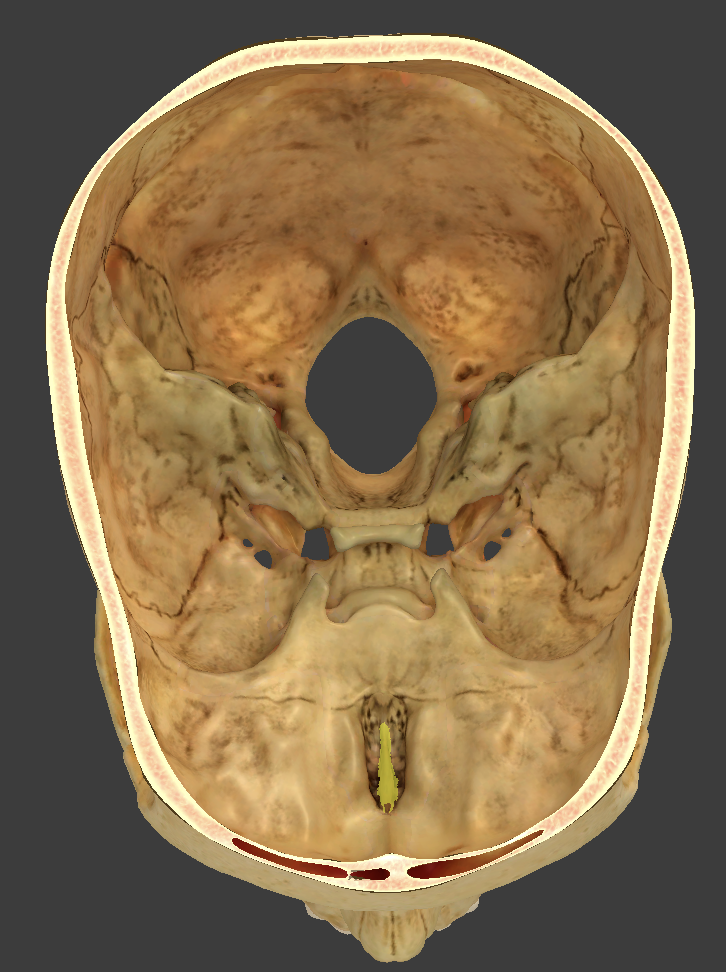
Ethmoid bone
anterior cranial bone located between the eyes
Horizontal cribriform plate
full of pin holes that lead to the roof of the nasal cavity
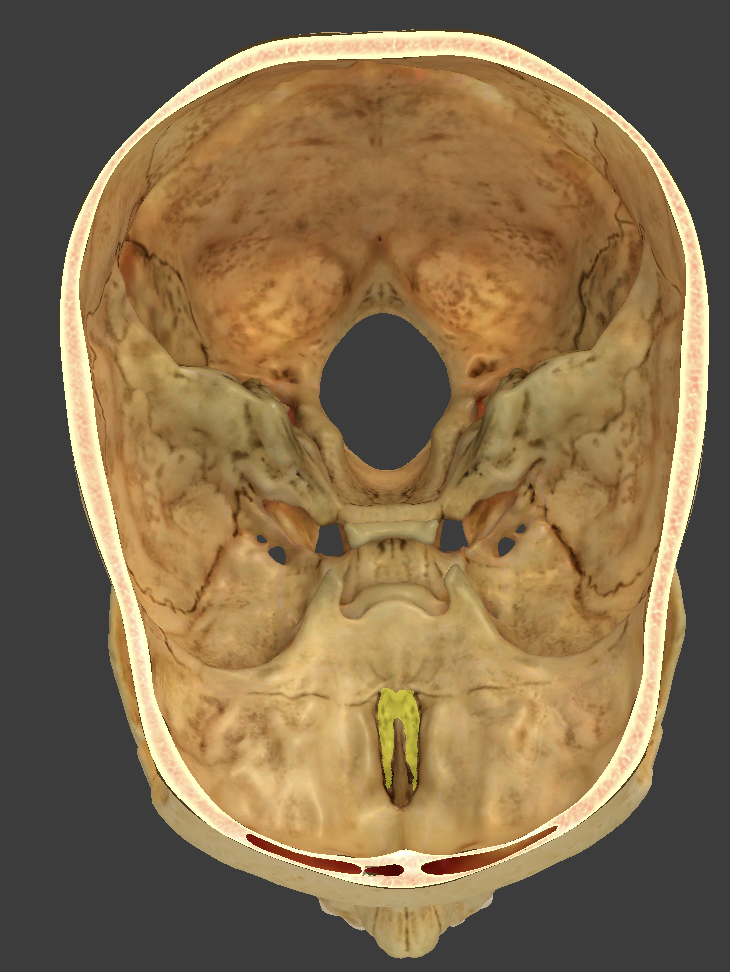
Crista galli
median crest located on the cribriform plate
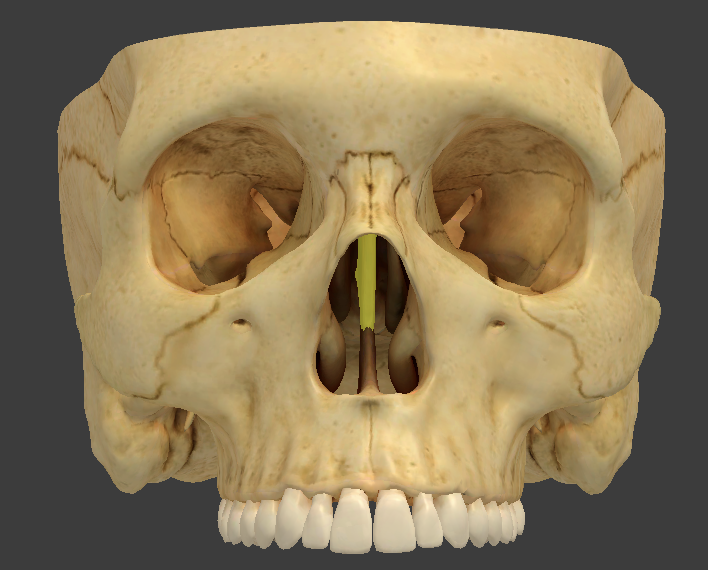
Vertical perpendicular plate
thin median plate that forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum
Mandible
supports the lower teeth and provides attachment for muscles of mastication and facial expression
Mandibular fossa
condyle where the mandible sits to form the TMJ
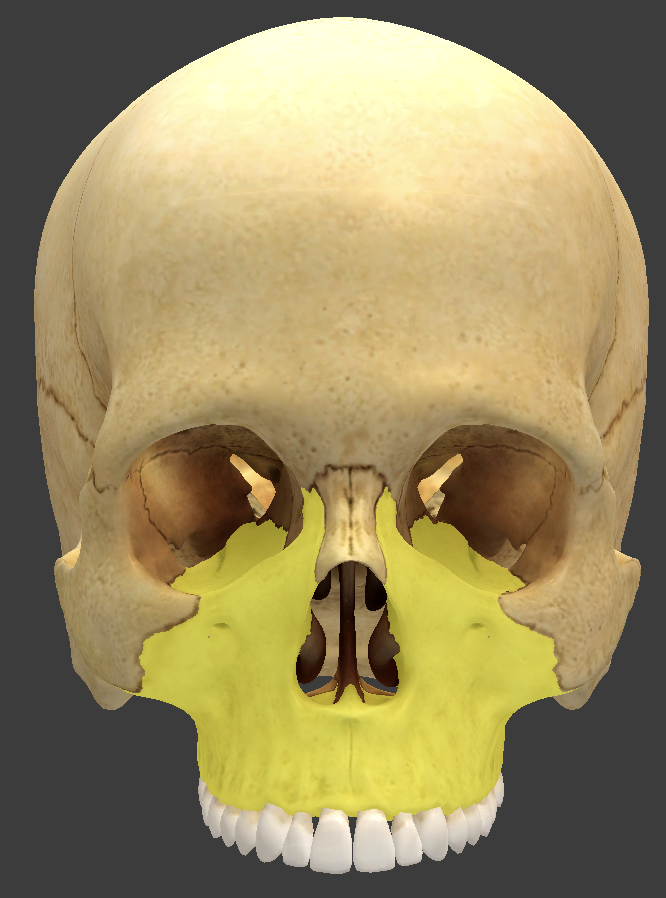
Maxilla
form the upper jaw and meet at the intermaxillary suture
Maxillary sinus
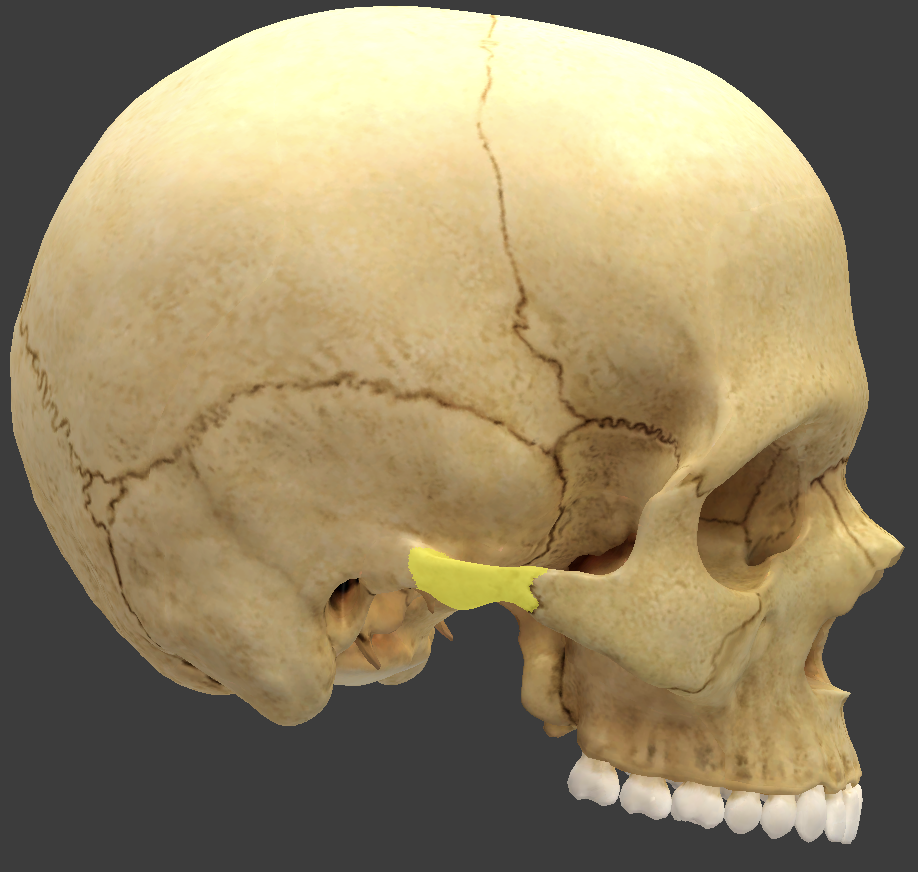
Zygomatic bones
form the angles of the cheeks, inferolateral to the eyes, and part of the lateral wall of each orbit
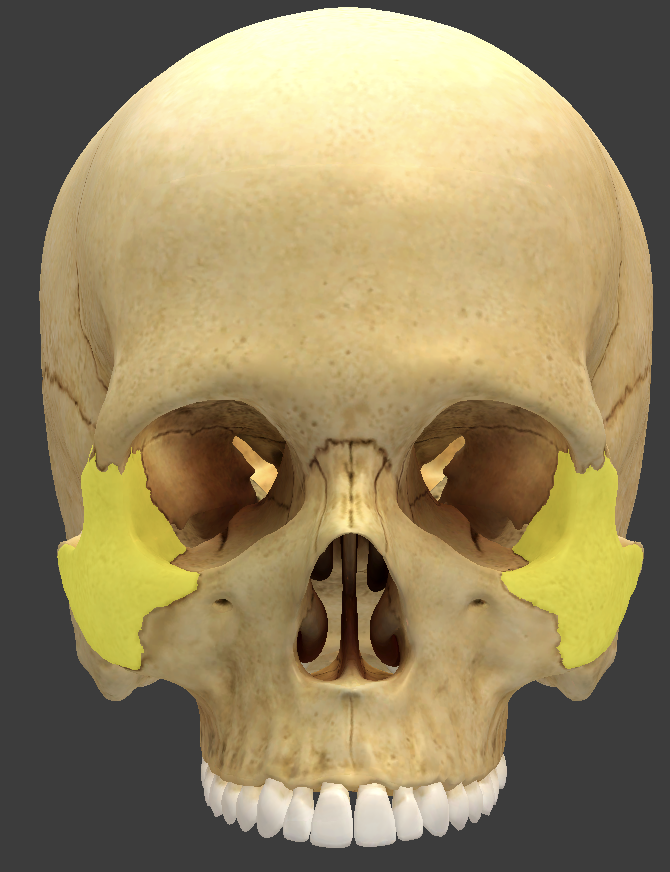
Zygomatic process
extends anteriorly to form part of the zygomatic arch
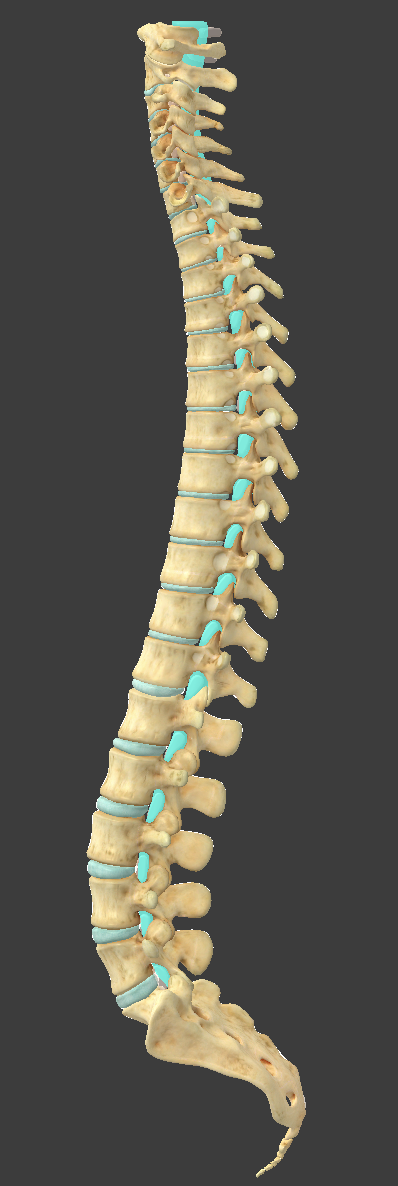
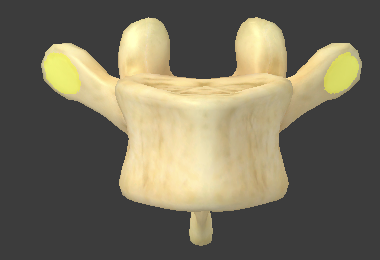
Vertebral column
made up of 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 1 sacrum, and 1 coccyx
Intervertebral disc
a cushion between adjacent vertebrae
two parts: annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus
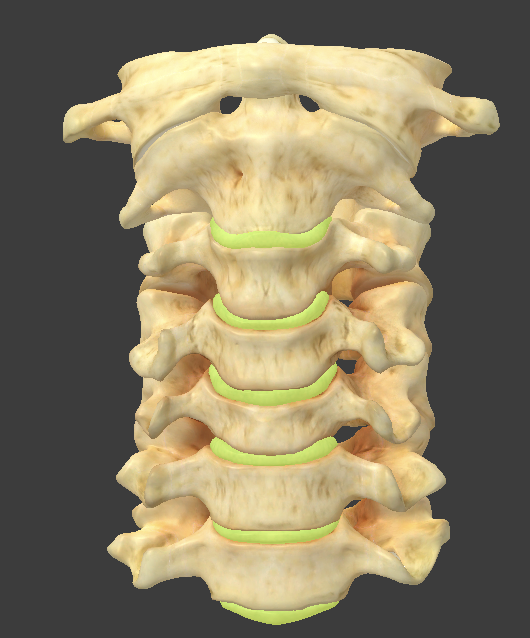
Nucleus pulposus
inner part of the intervertebral disc
Annulus fibrosis
outer part of the intervertebral disc made up of concentric rings of fibrous cartilage
Scoliosis
lateral curvature of the spin
Hyperkyphosis
hunchback
Hyperlordosis
swayback
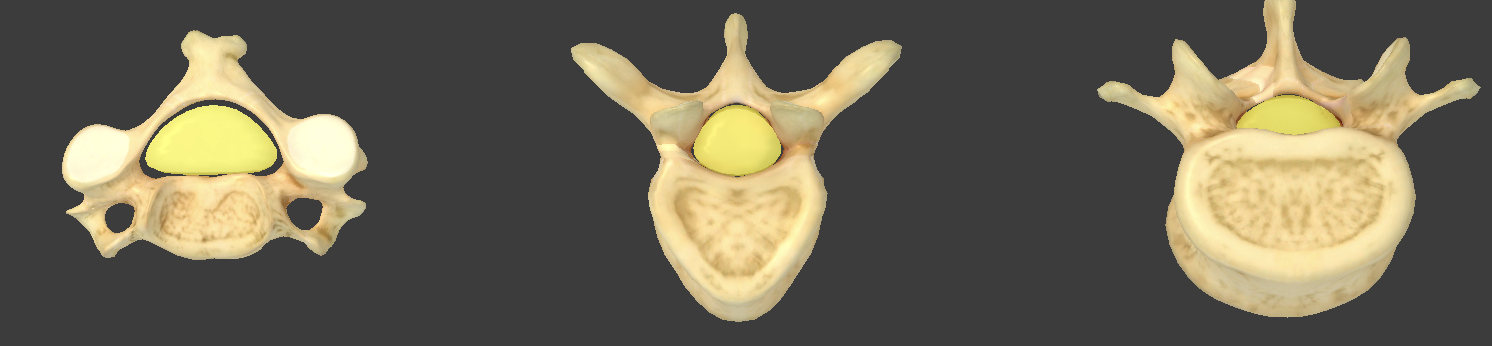
Vertebra body
weight-bearing portion
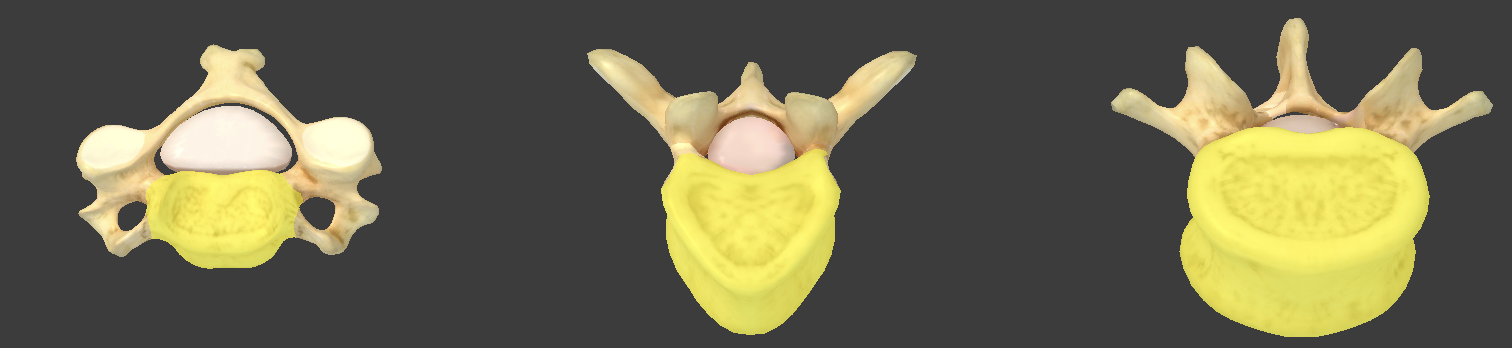
Lamina and pedicles
portion that protects the spinal cord
Vertebral arch
composed of the pedicles and lamina that enclose the vertebral foramen
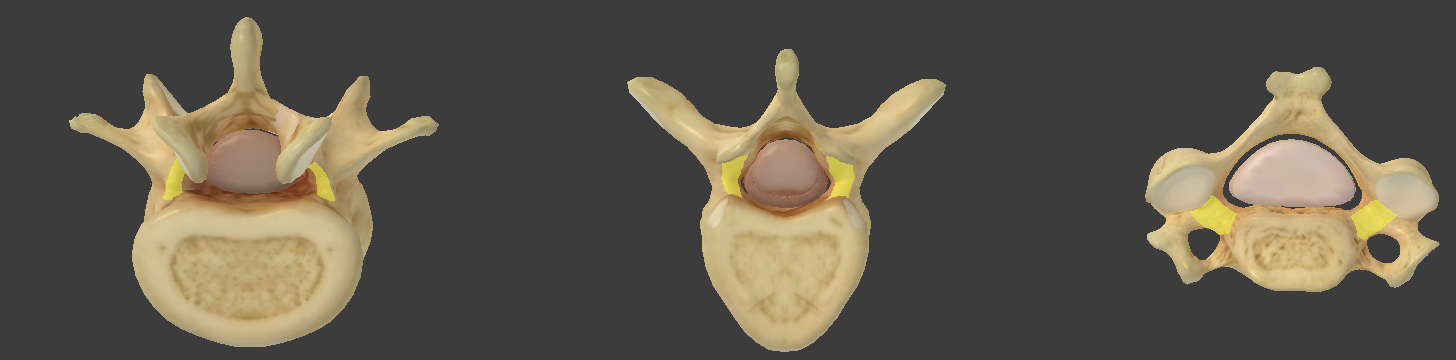
Intervertebral foramen
between the superior and inferior pedicles
spinal nerves leave the spinal cord through this
Vertebral foramen
vertebral arch and body enclose this
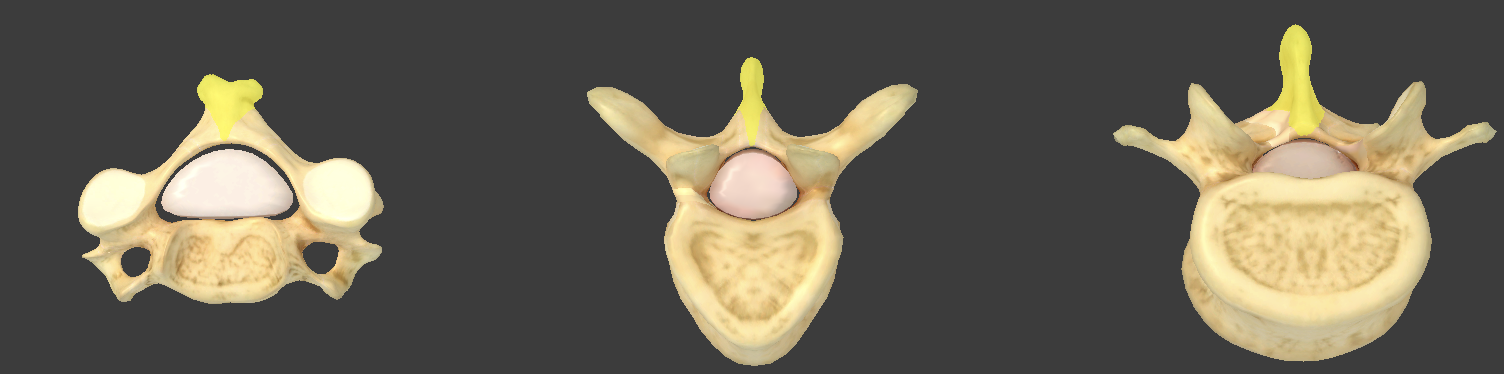
Spinous process
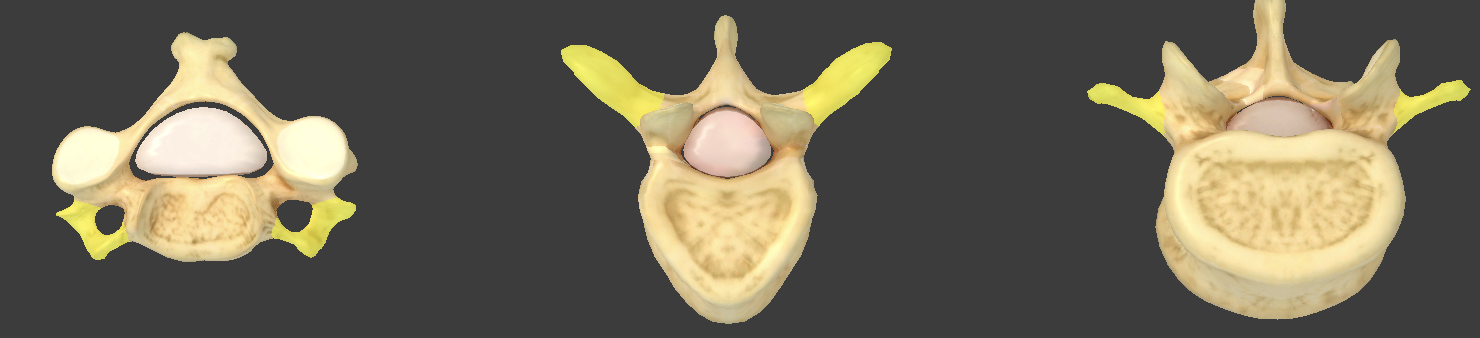
Transverse process
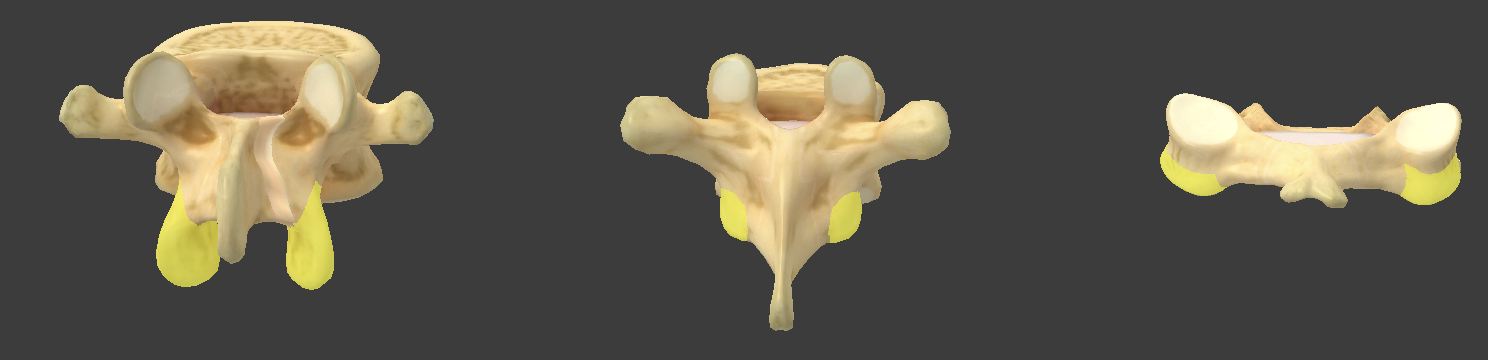
Superior articular processes
project upward from one vertebra
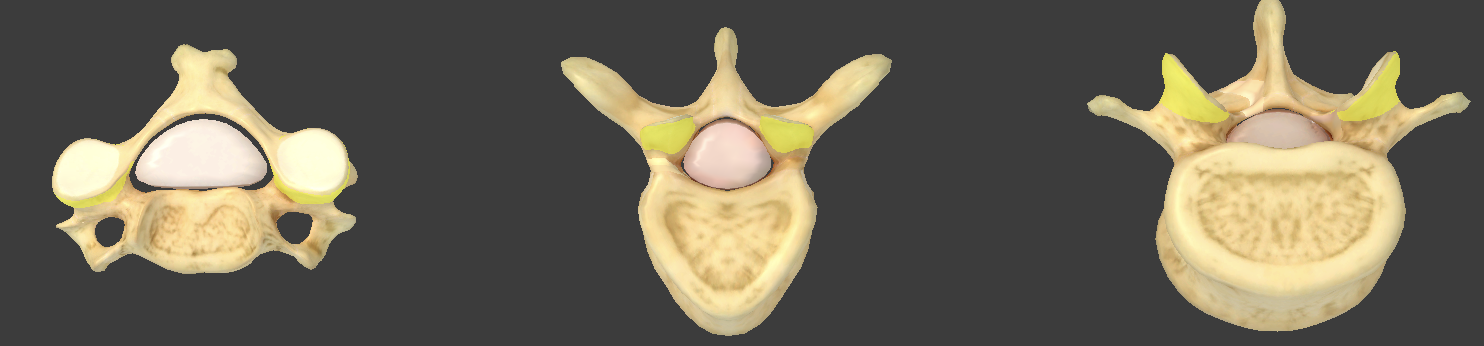
Inferior articular processes
project downward from one vertebra
Superior/inferior vertebral notches
Cervical vertebrae
small and oval-shaped
hole (foramen) in the transverse process for the artery ascending the neck
fork-shaped spinous process
Thoracic vertebrae
large and heart-shaped
long transverse processes that have articular facets for the ribs
long spinous process that points inferiorly
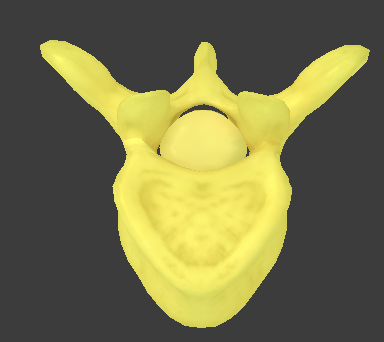
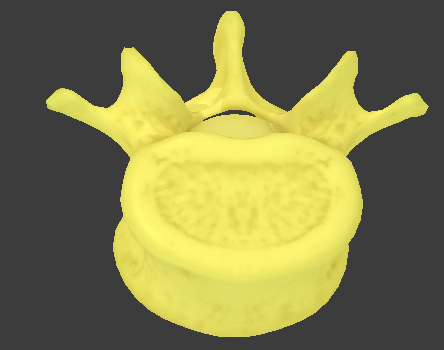
Lumbar vertebrae
largest and kidney-shaped
short transverse processes with no facets or foramina
thick spinous processes that point posteriorly
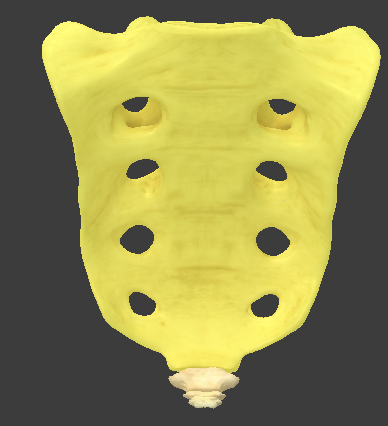
Sacrum
five fused vertebrae
no intervertebral foramen
spinal nerves come out through the anterior and posterior sacral foramina
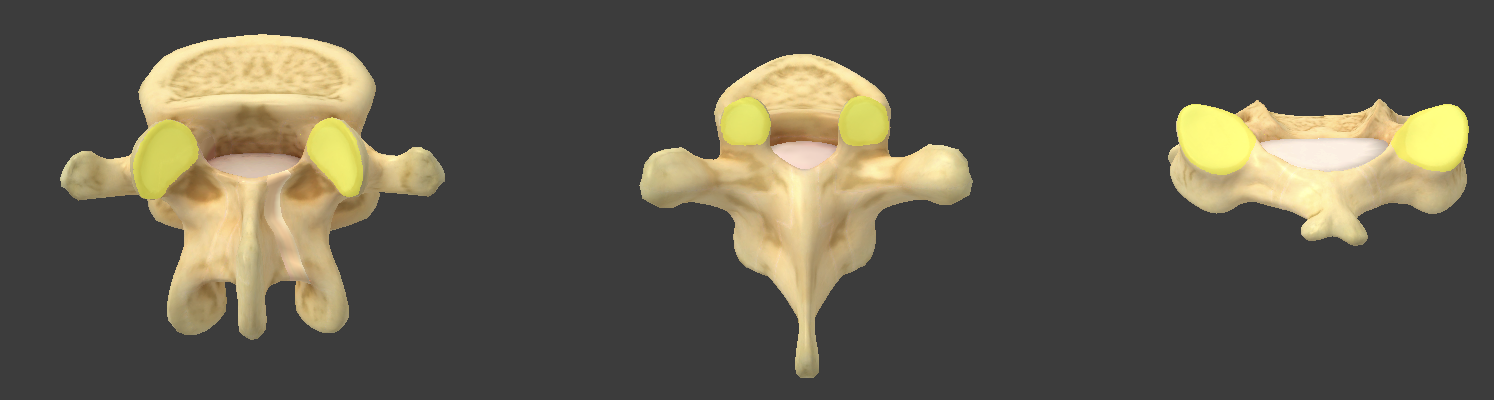
Superior articular facet
articulates with the inferior articular facet and L5
Coccyx
5 fused coccygeal vertebrae, which form the end of the spine
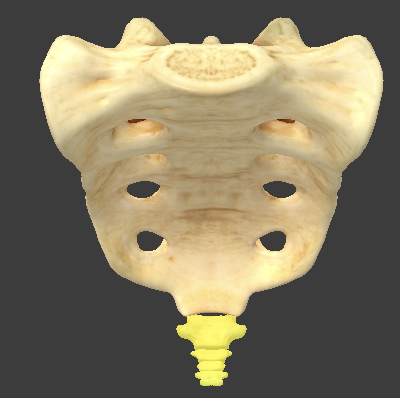
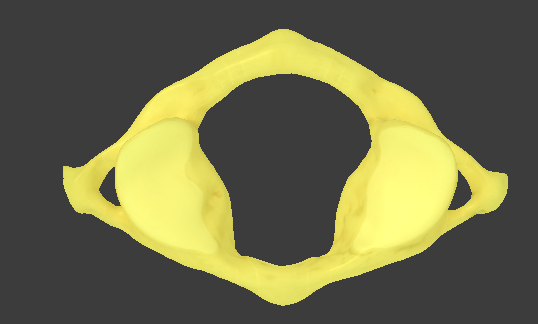
Atlas
C1
superior articular facet that articulates with the occipital condyle
atlantooccipital joint
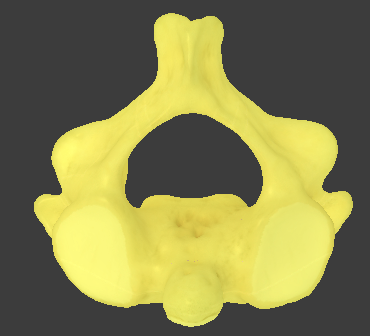
Axis
C2
Inferior articular facet of the atlas articulates with the superior articular facet of the axis at the atlantoaxial joint
responsible for head rotation
Bifid spinous processes
spinous process is forked
only found in cervical vertebrae
Thoracic (rib) cage
composed of 12 pairs of ribs and the sternum
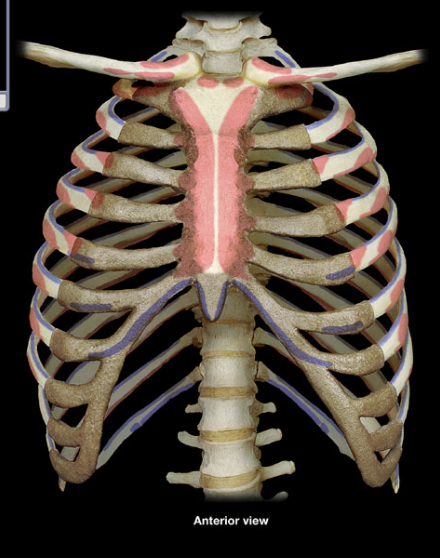
Sternum
made up of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process
Manubrium
broad superior portion of the sternum
suprasternal notch and sternal angle
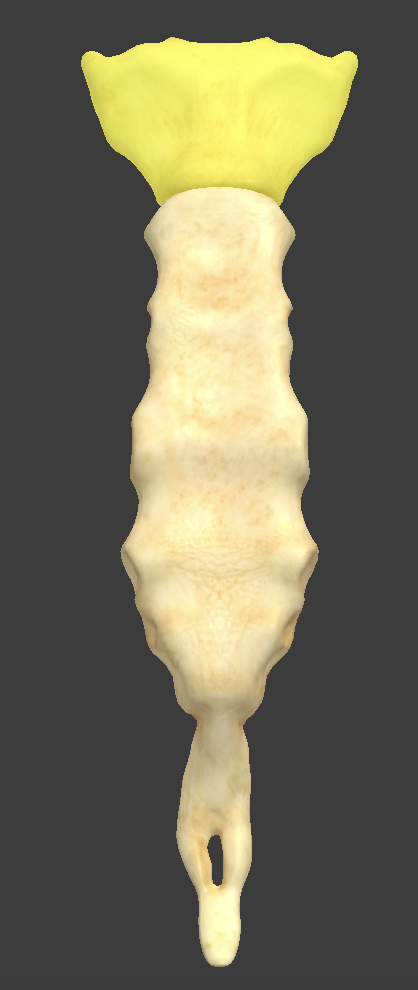
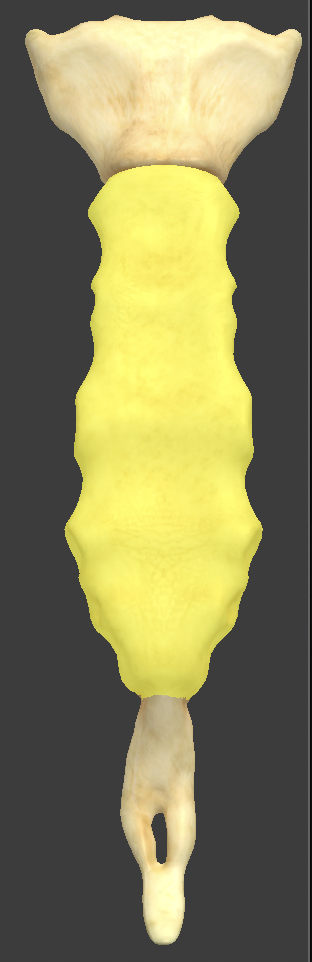
Body
longest part of the sternum
articulates with the manubrium at the sternal angle
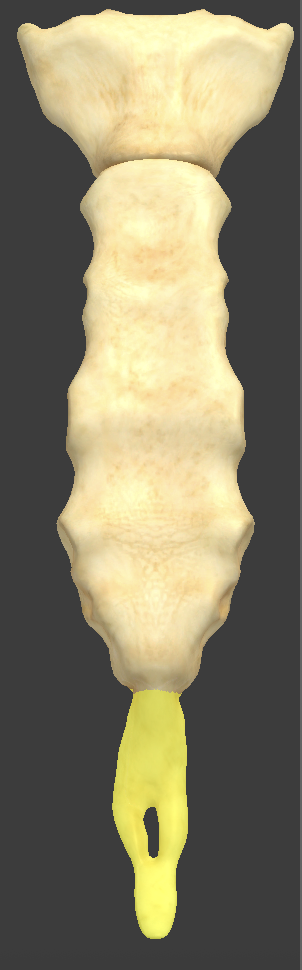
Xiphoid process
smaller, inferior end of the sternum
True ribs
ribs 1—7 which each have their own costal cartilage
False ribs
ribs 7—10 where the costal cartilage runs together
Floating ribs
ribs 11 and 12 which don’t have costal cartilage
Costal cartilage
hyaline cartilage that attaches each rib to the sternum
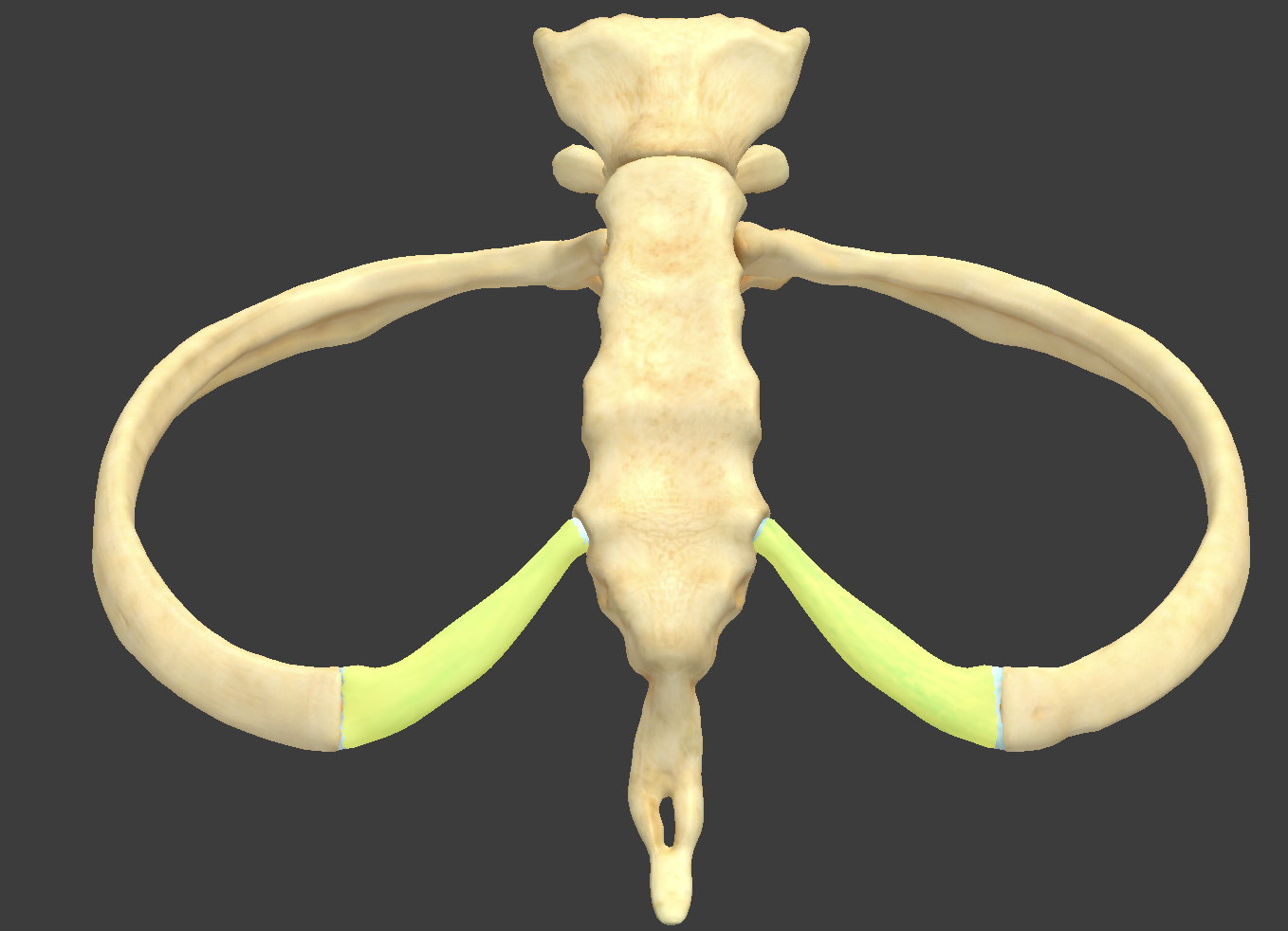
Intercostal space
space between the ribs
filled with intercostal muscles
Costal facet
unique to thoracic vertebrae to connect with the head of a rib
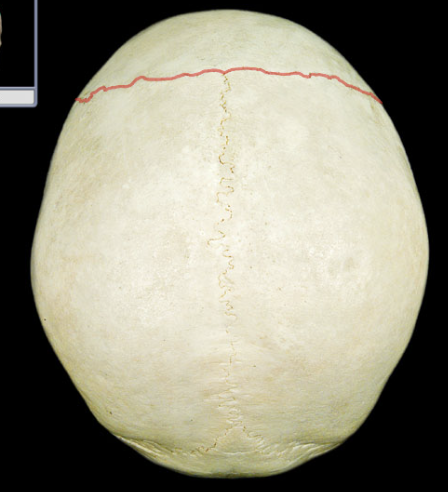
Coronal suture
Lambdoid suture