Module 1: General Principles of Positioning
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
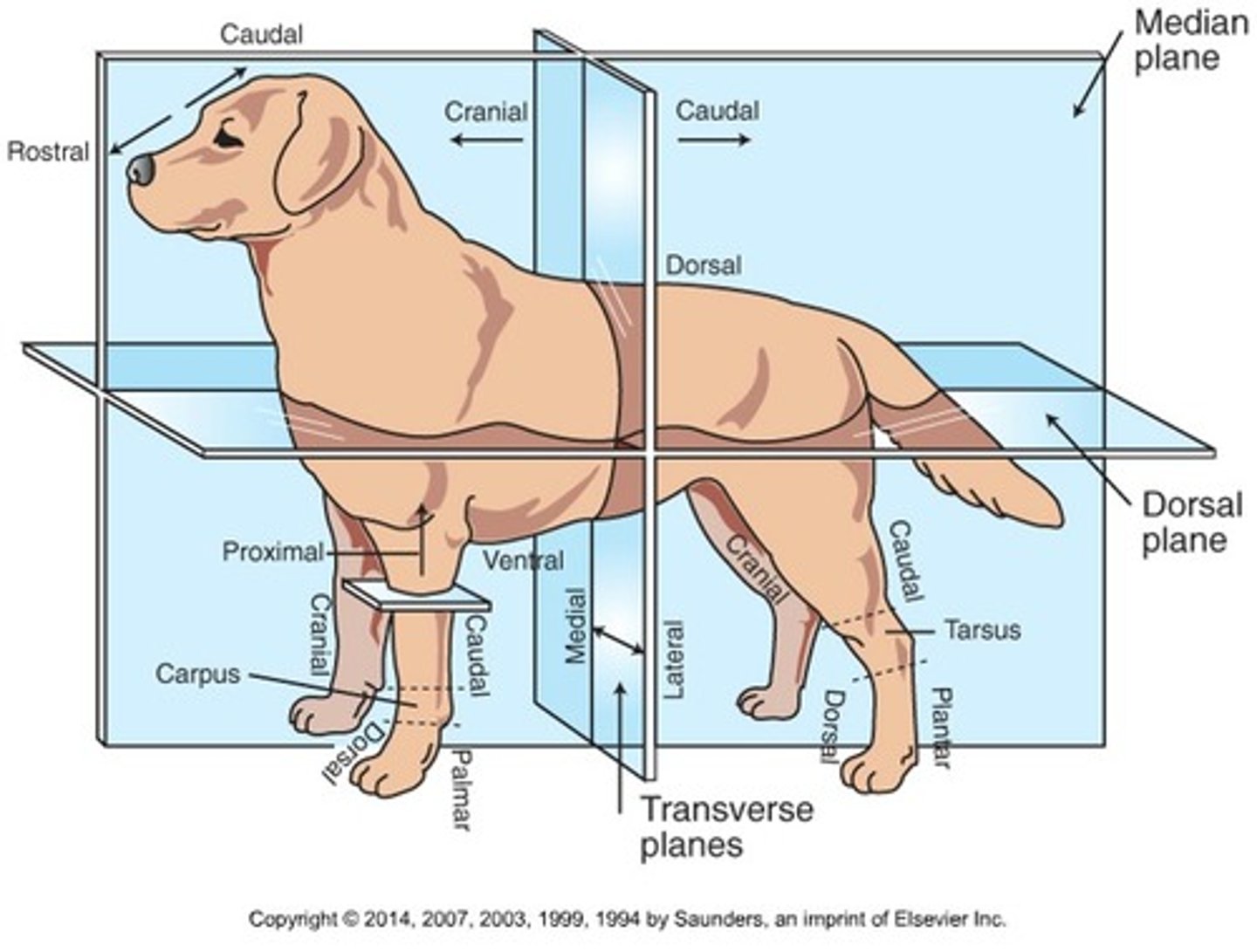
Cranial (Trunk)
Toward the head
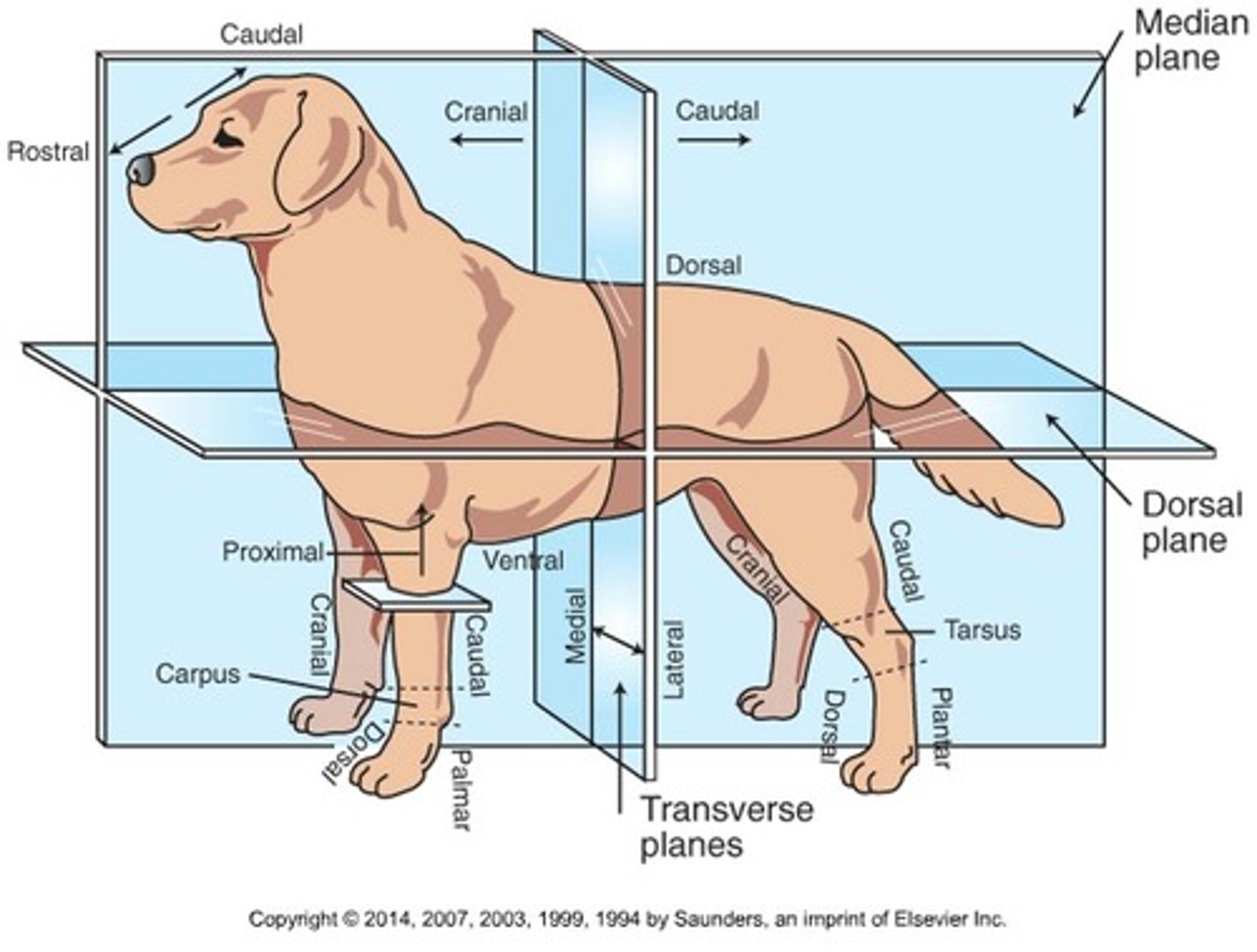
Caudal (Trunk)
Toward the tail
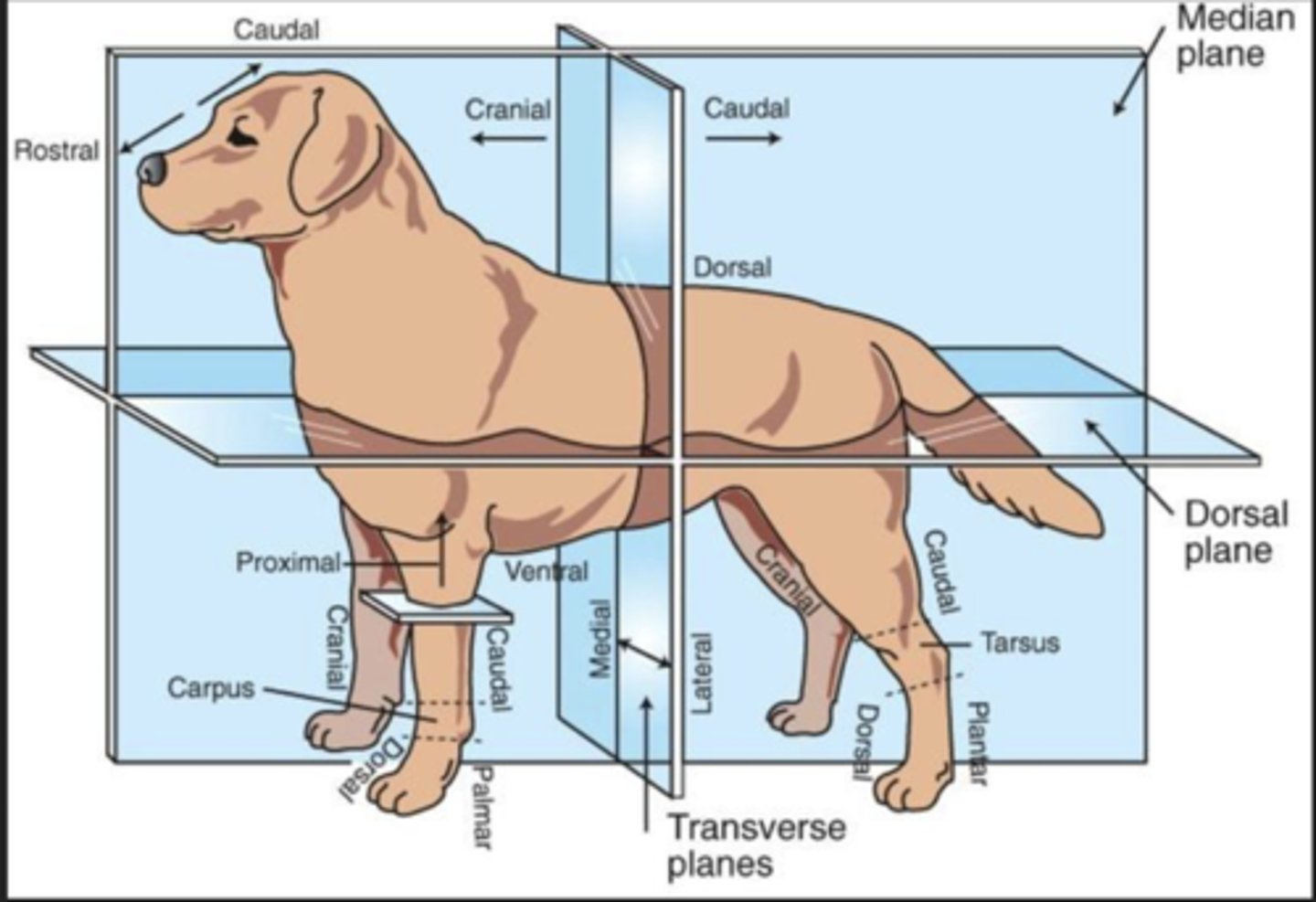
Rostral
Toward the nose (only when referring to the head)
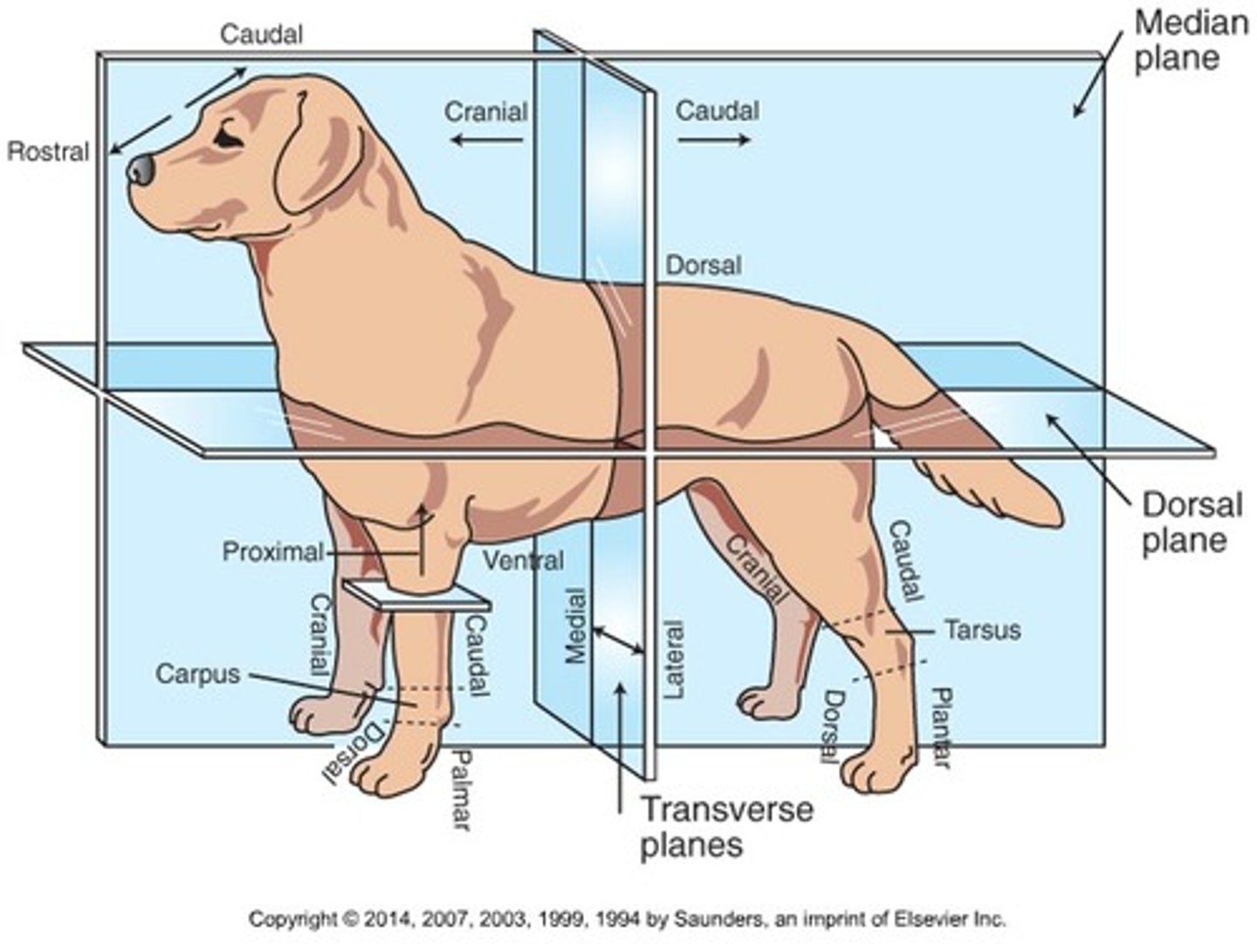
Dorsal (Trunk)
Toward the back or top of the body
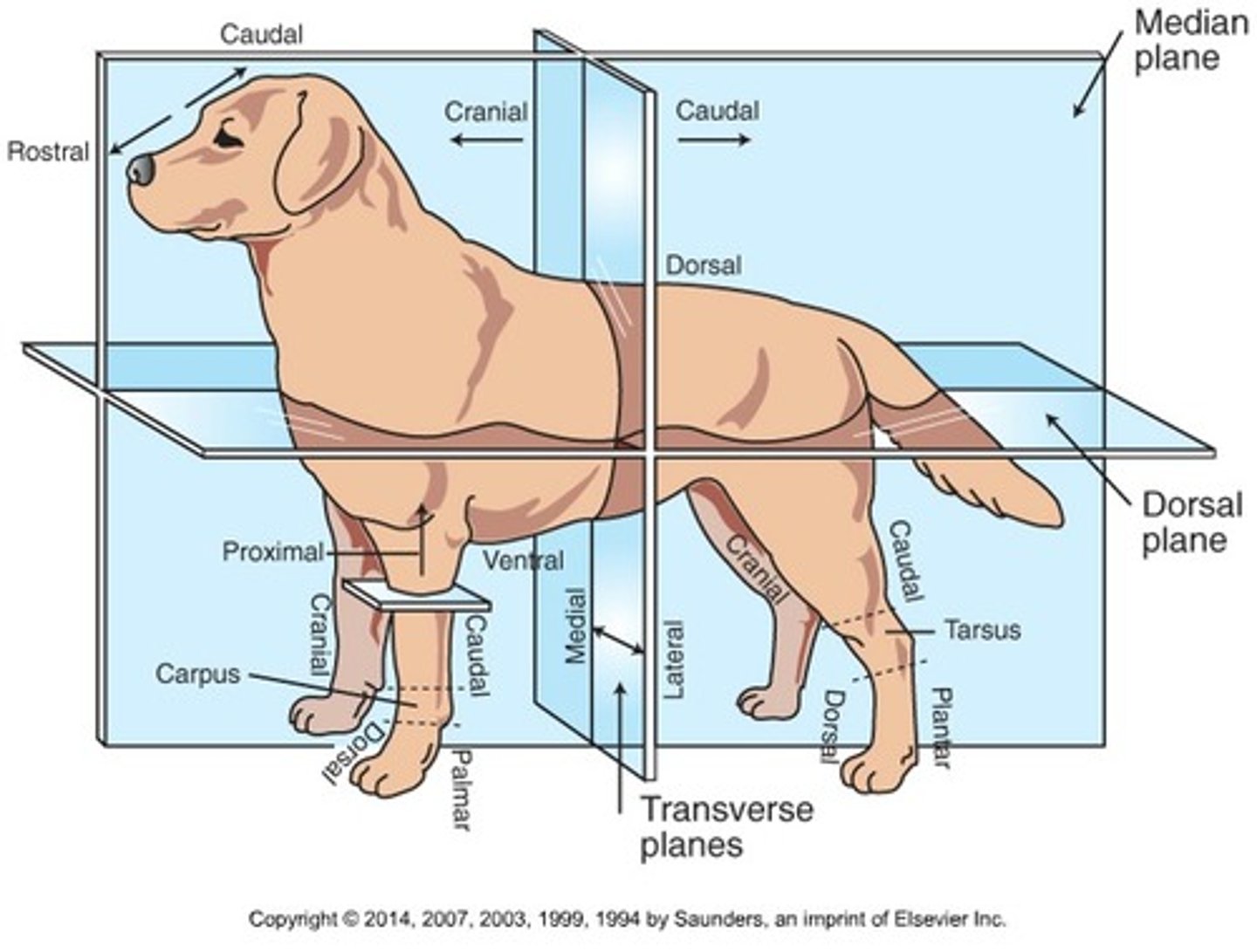
Ventral (Trunk)
Toward the sternum and belly or bottom of belly
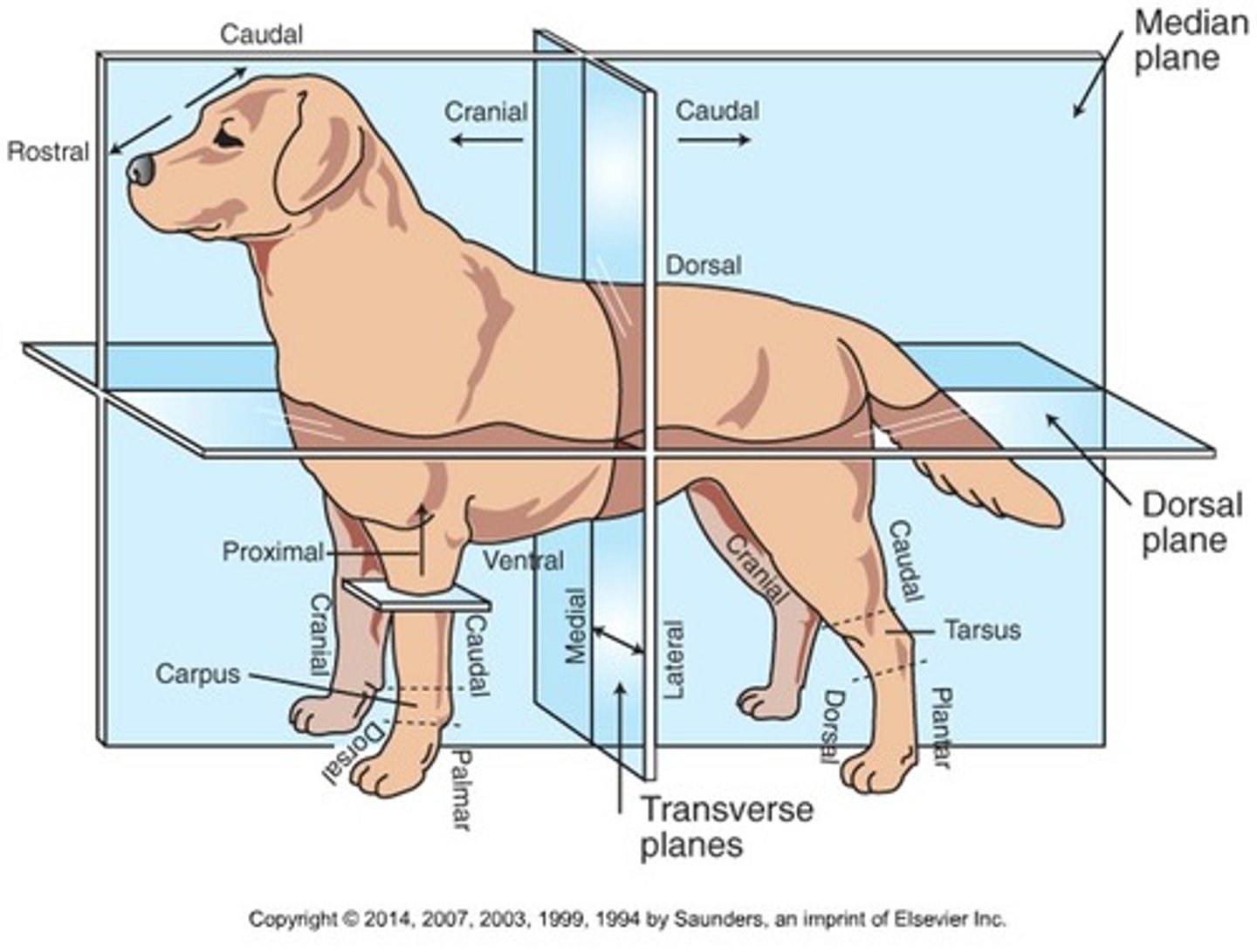
Cranial (Extremities)
Front surface of the limbs above the carpus (Forelimb) or tarsus (Hindlimb)
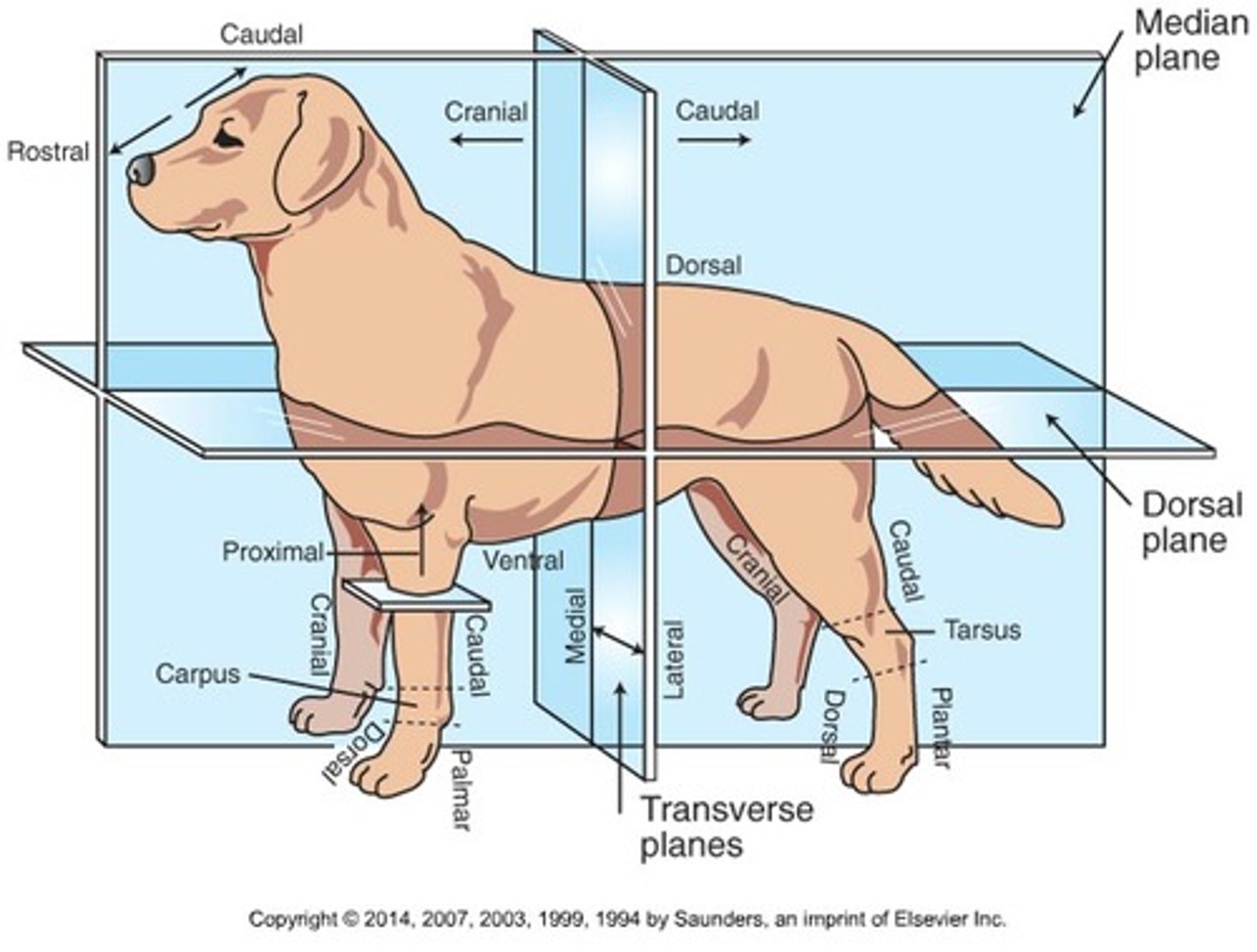
Caudal (Extremities)
Back surface of the limbs above the carpus (forelimb) or tarsus (hindlimb)
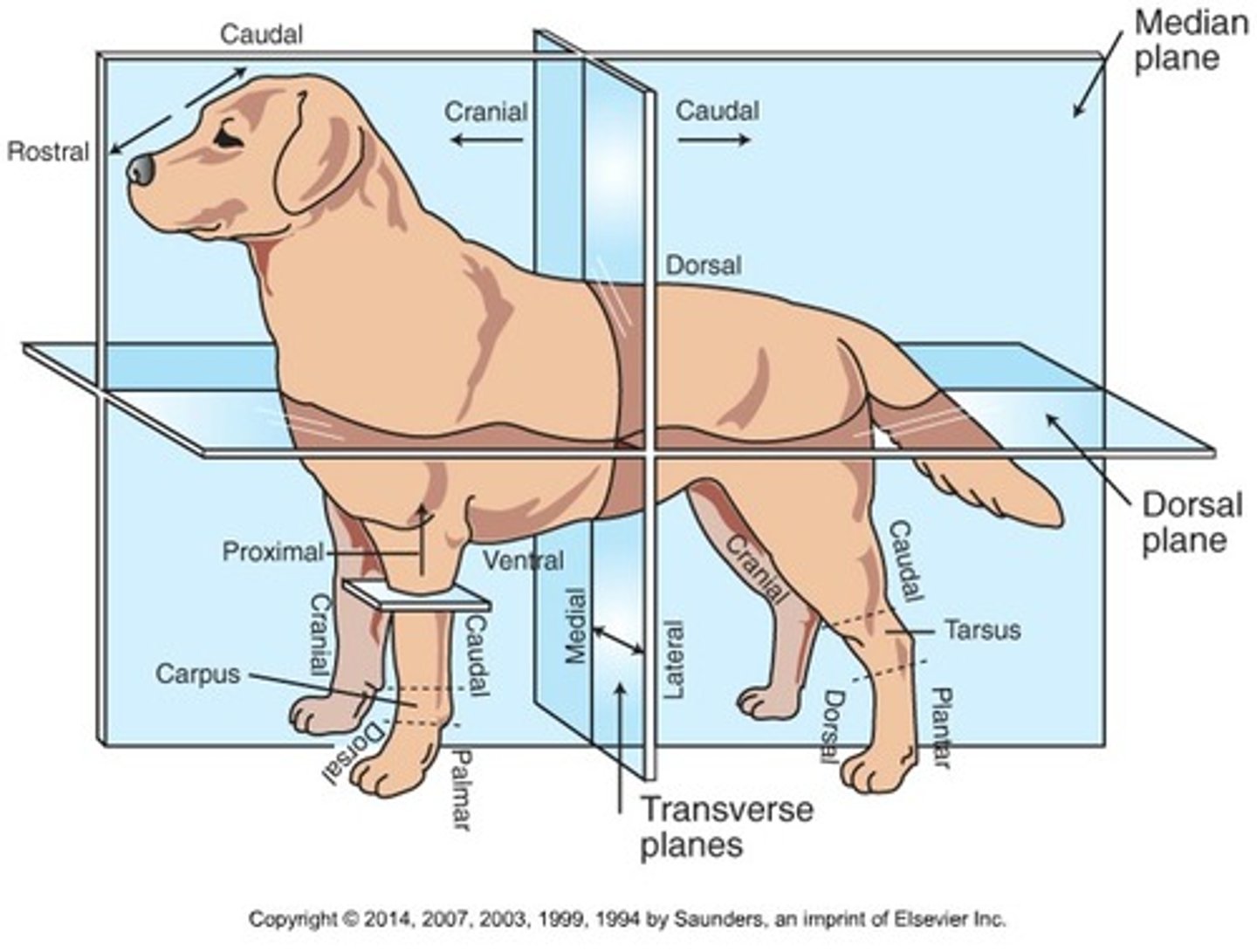
Dorsal (extremities)
Front surface of the limbs from the level of the carpus (forelimb) or tarsus (hindlimb) through the foot
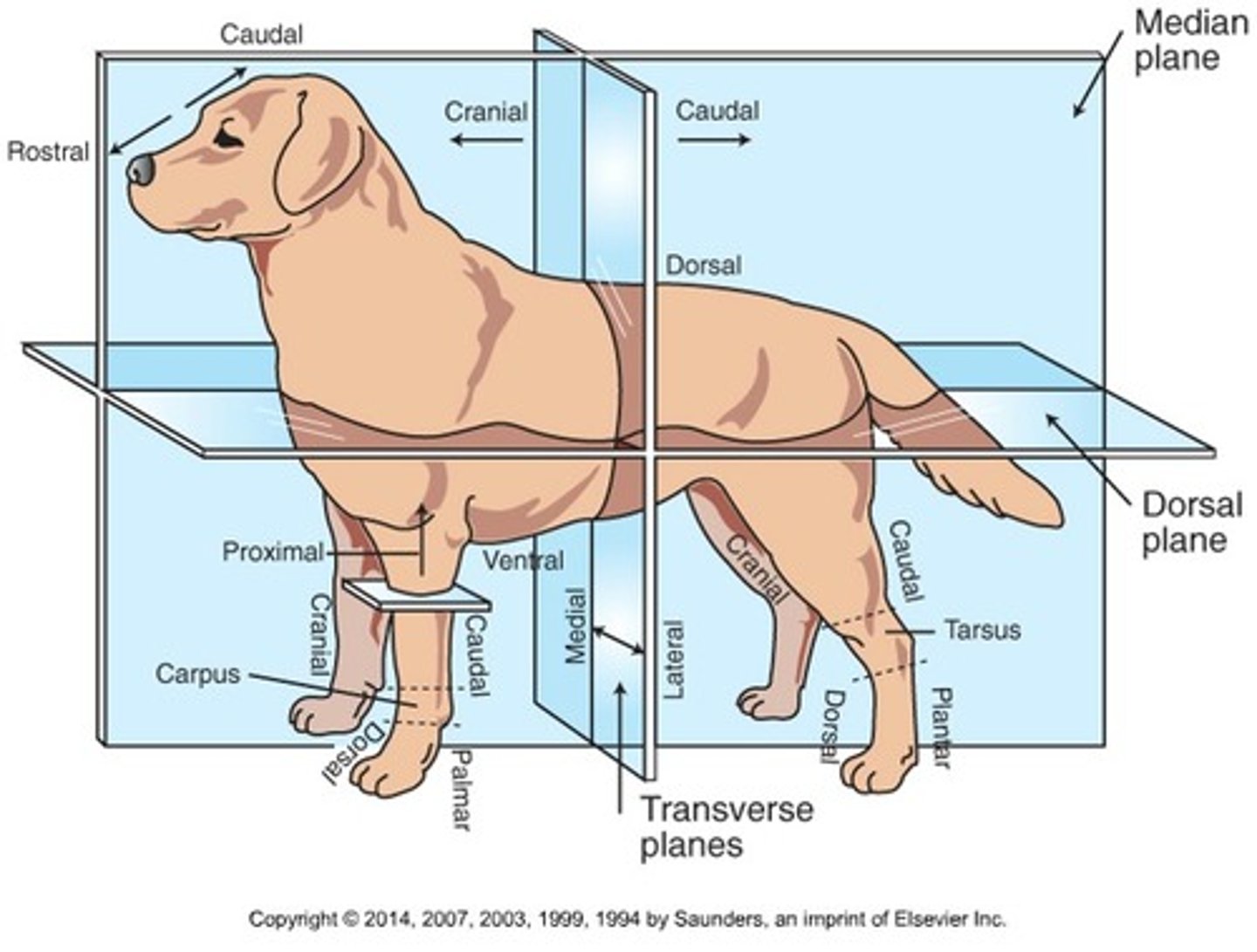
Palmar
The back surface of the forelimb from the level of the carpus through the foot
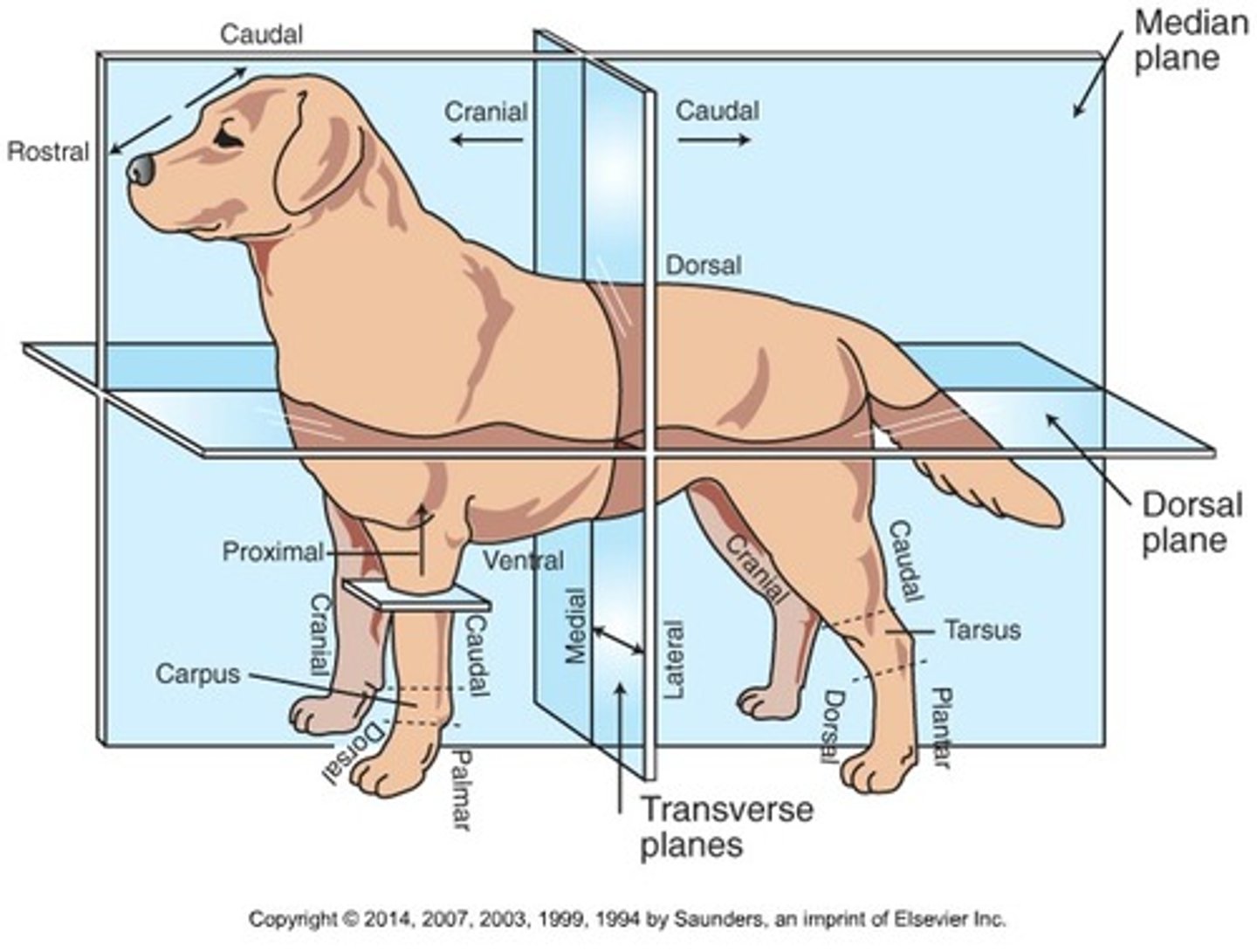
Plantar
The back surface of the hindlimb from the level of the tarsus through the foot
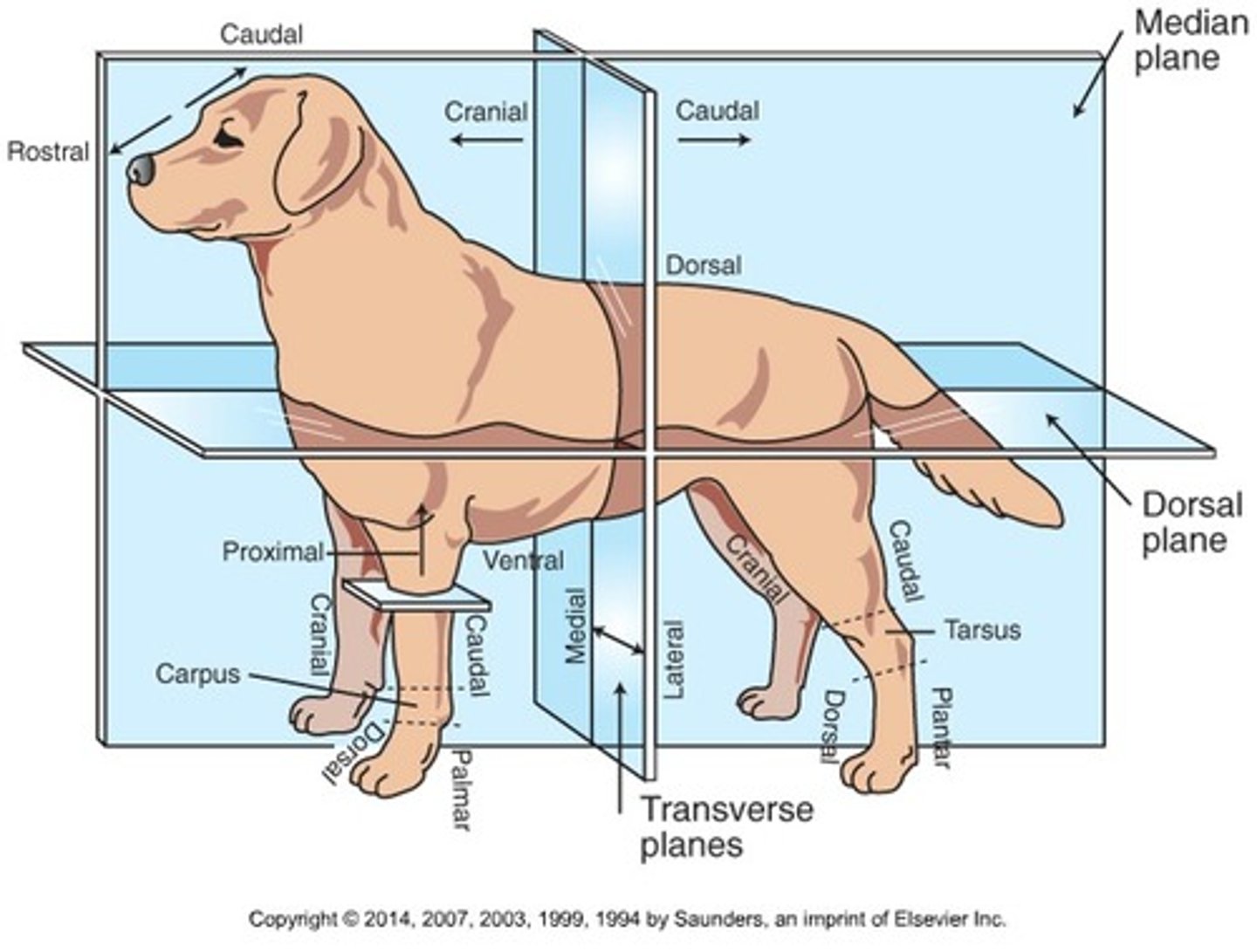
Proximal
Toward the body (only when referring to limbs)
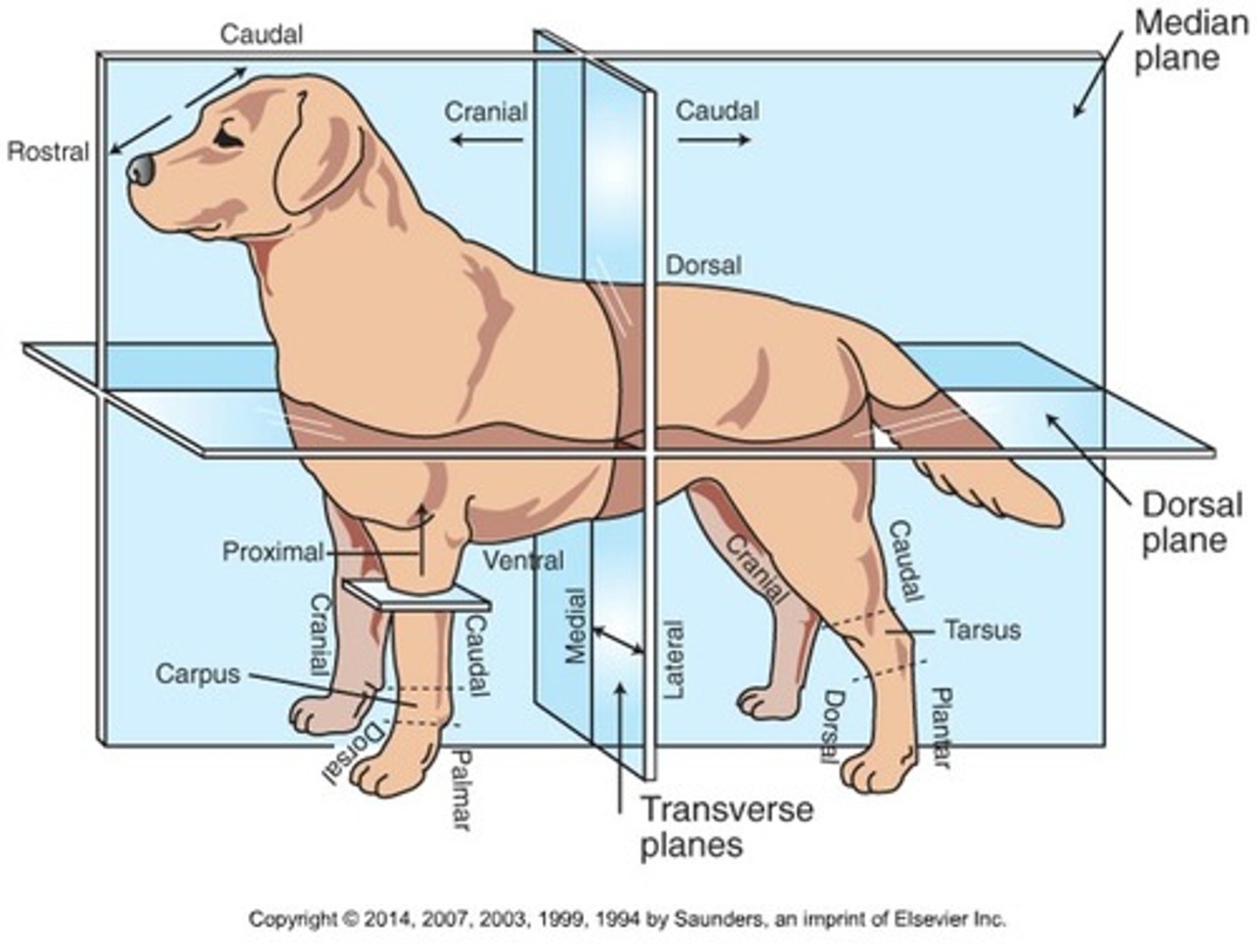
Distal
Away from the body (only when discussing limbs)
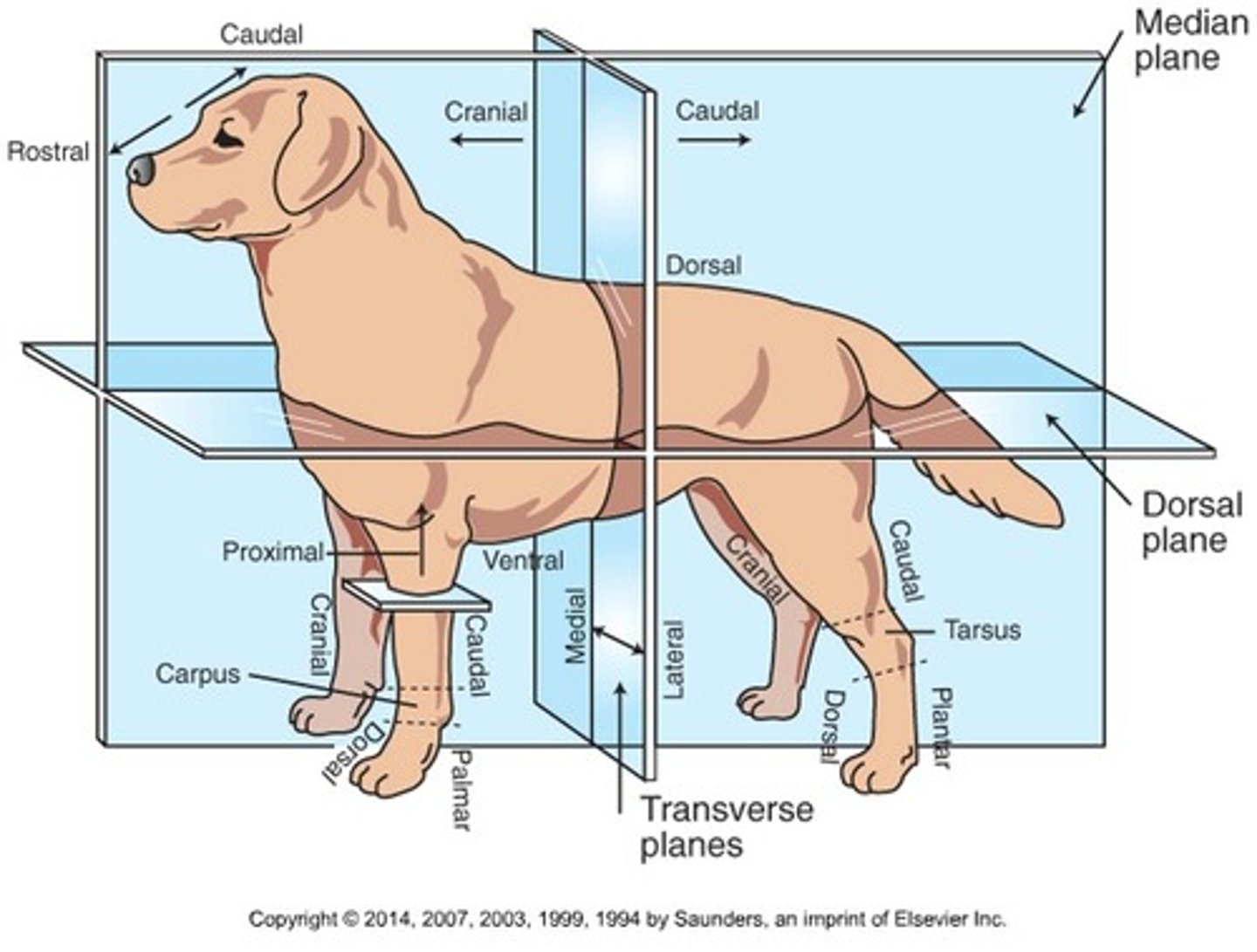
Medial
Toward the midline of the body
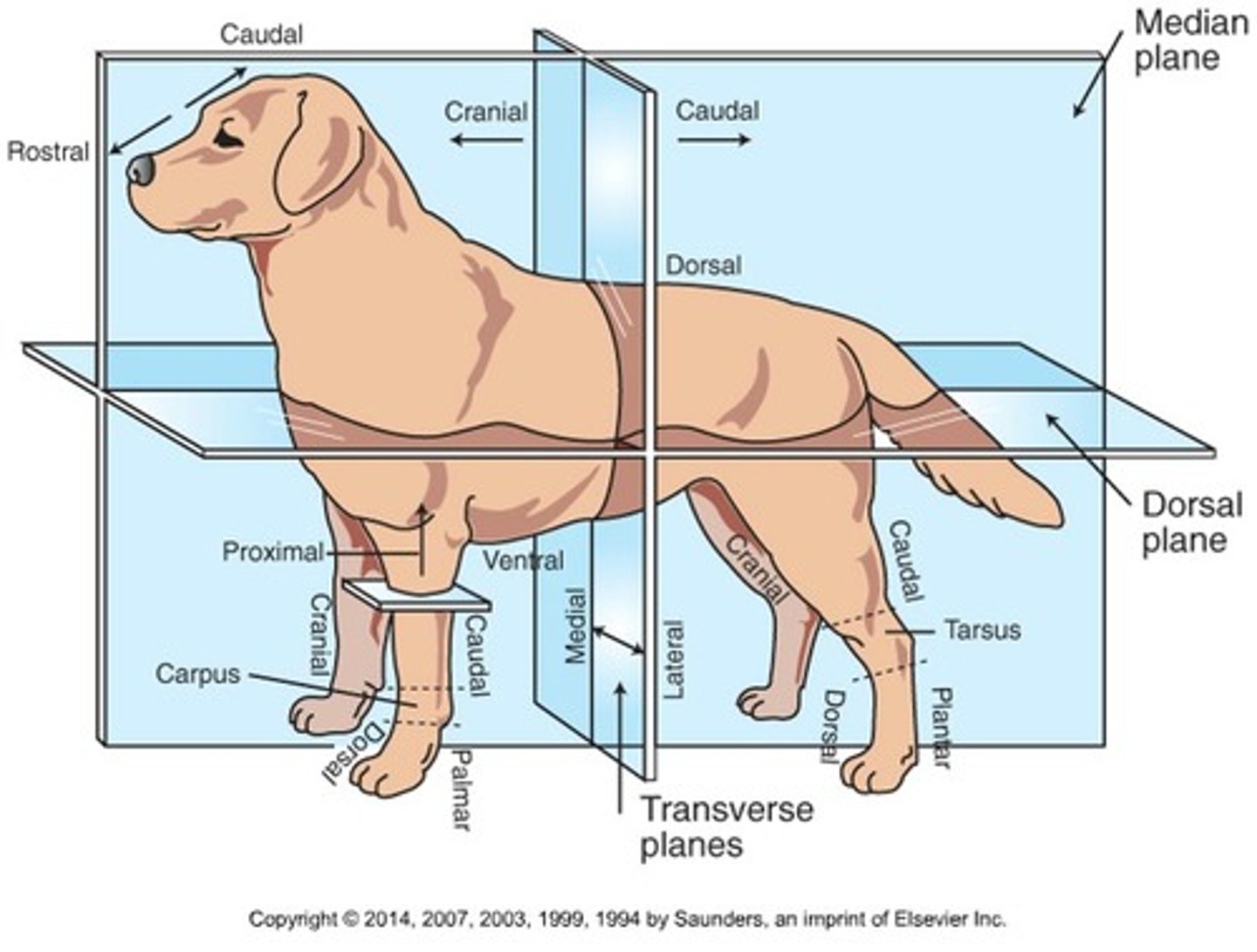
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
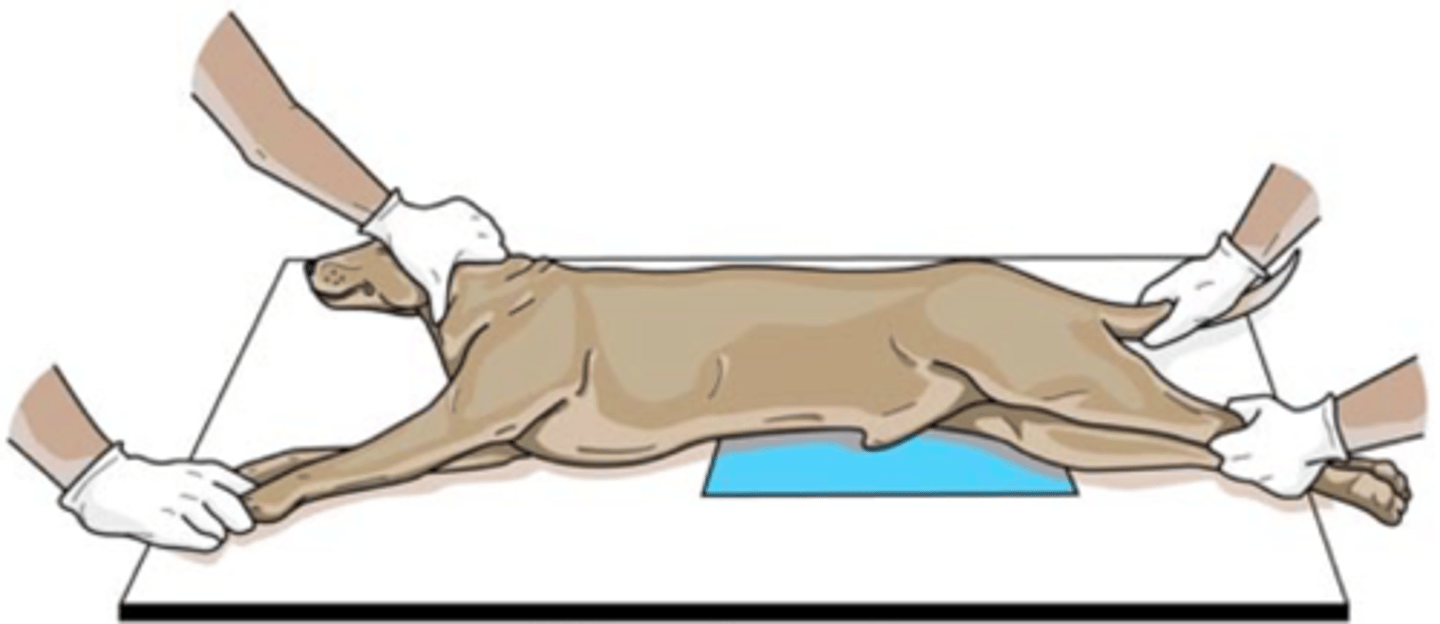
Dorsal recumbency
Patient lying on back

Sternal recumbency
Patient laying on sternum
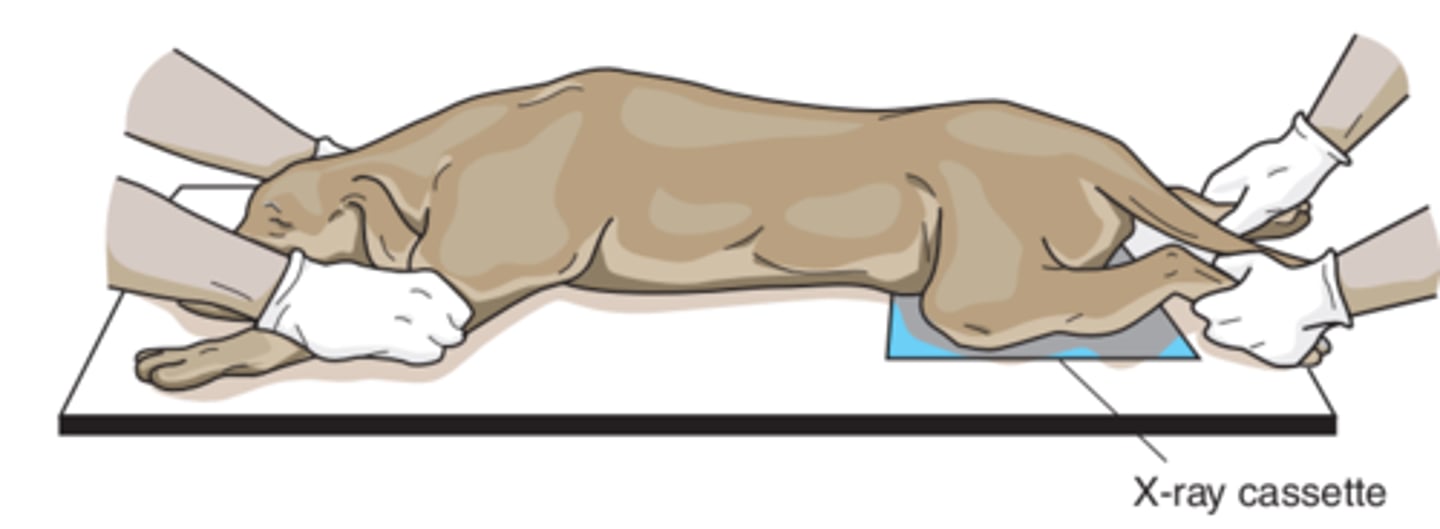
Lateral recumbency
Patient laying on side (right/left refers to side that is touching the table)
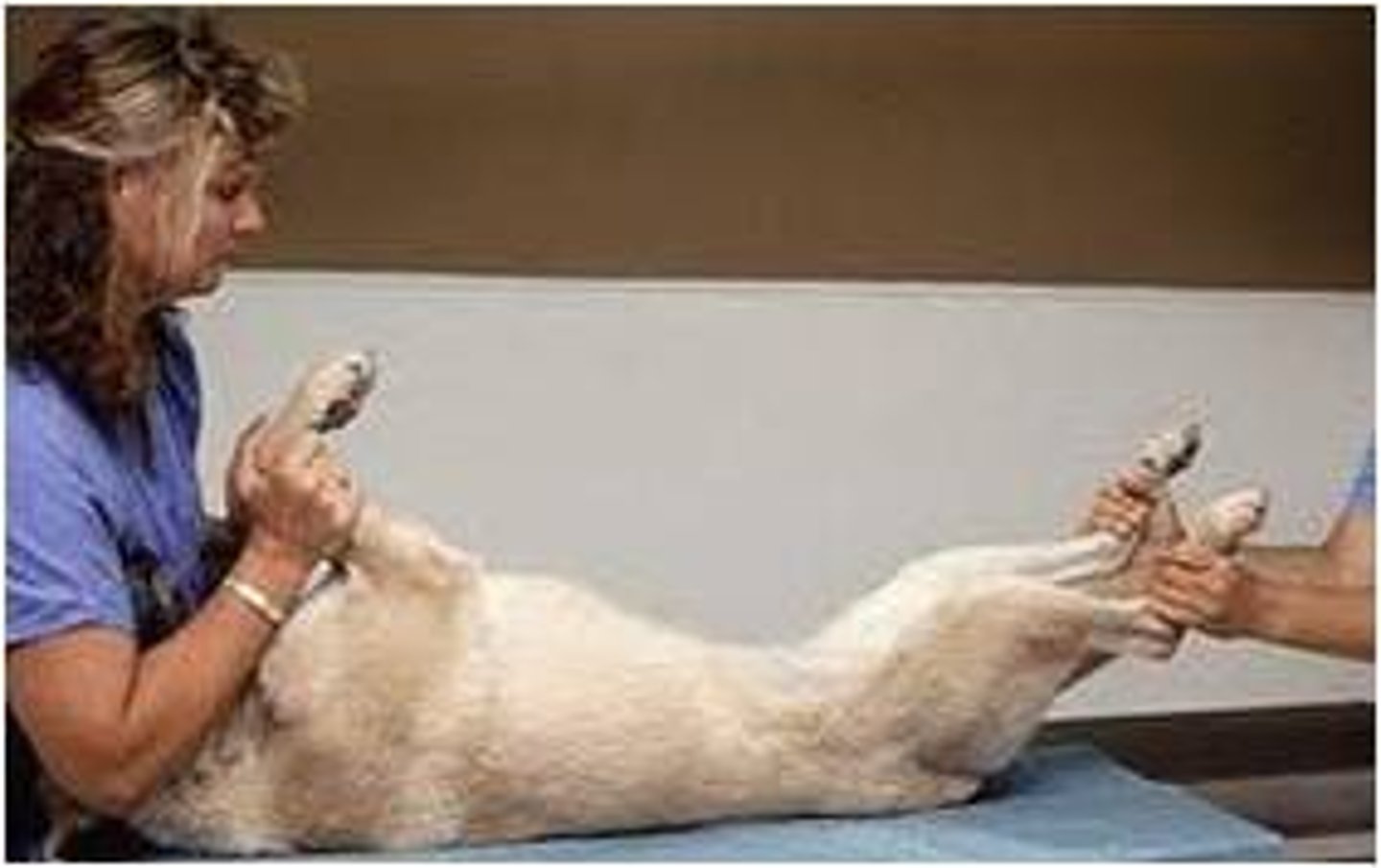
Ventrodorsal (VD)
Patient is in dorsal recumbency
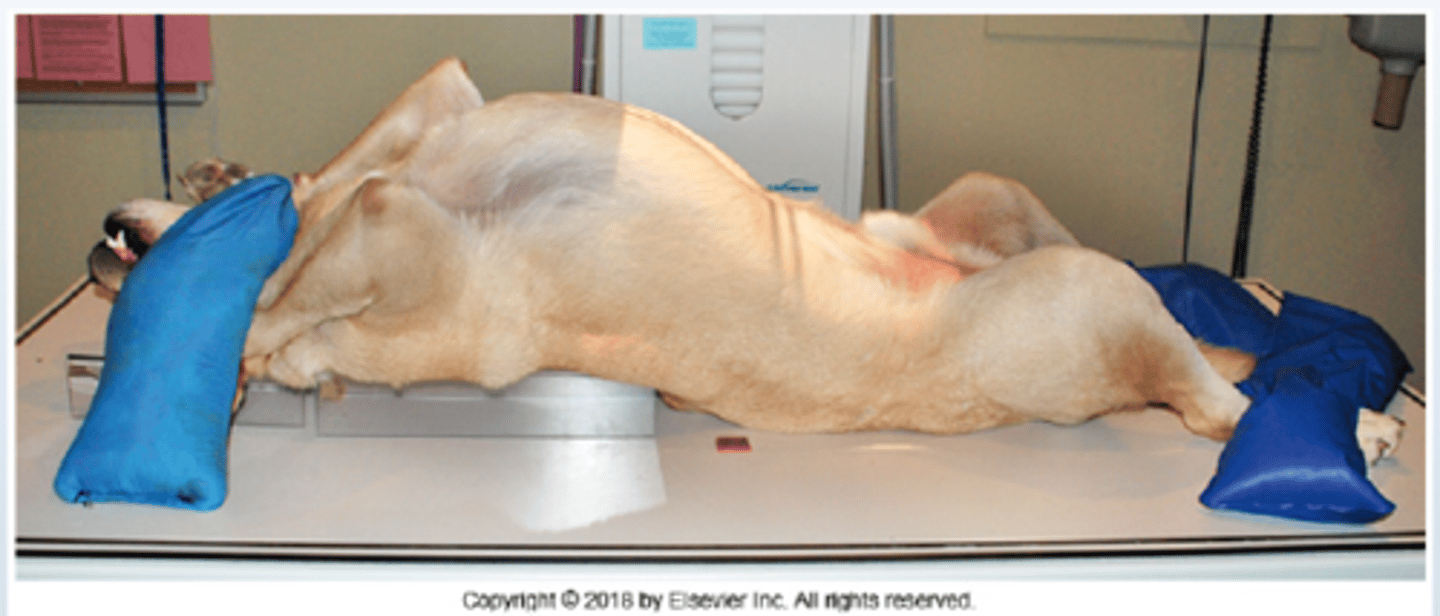
Dorsoventral (DV)
Patient is in sternal recumbency
Craniocaudal (CrCd)
From the front of the limb to the back of the limb
Caudocranial (CdCr)
From the back of the limb to the front of the limb
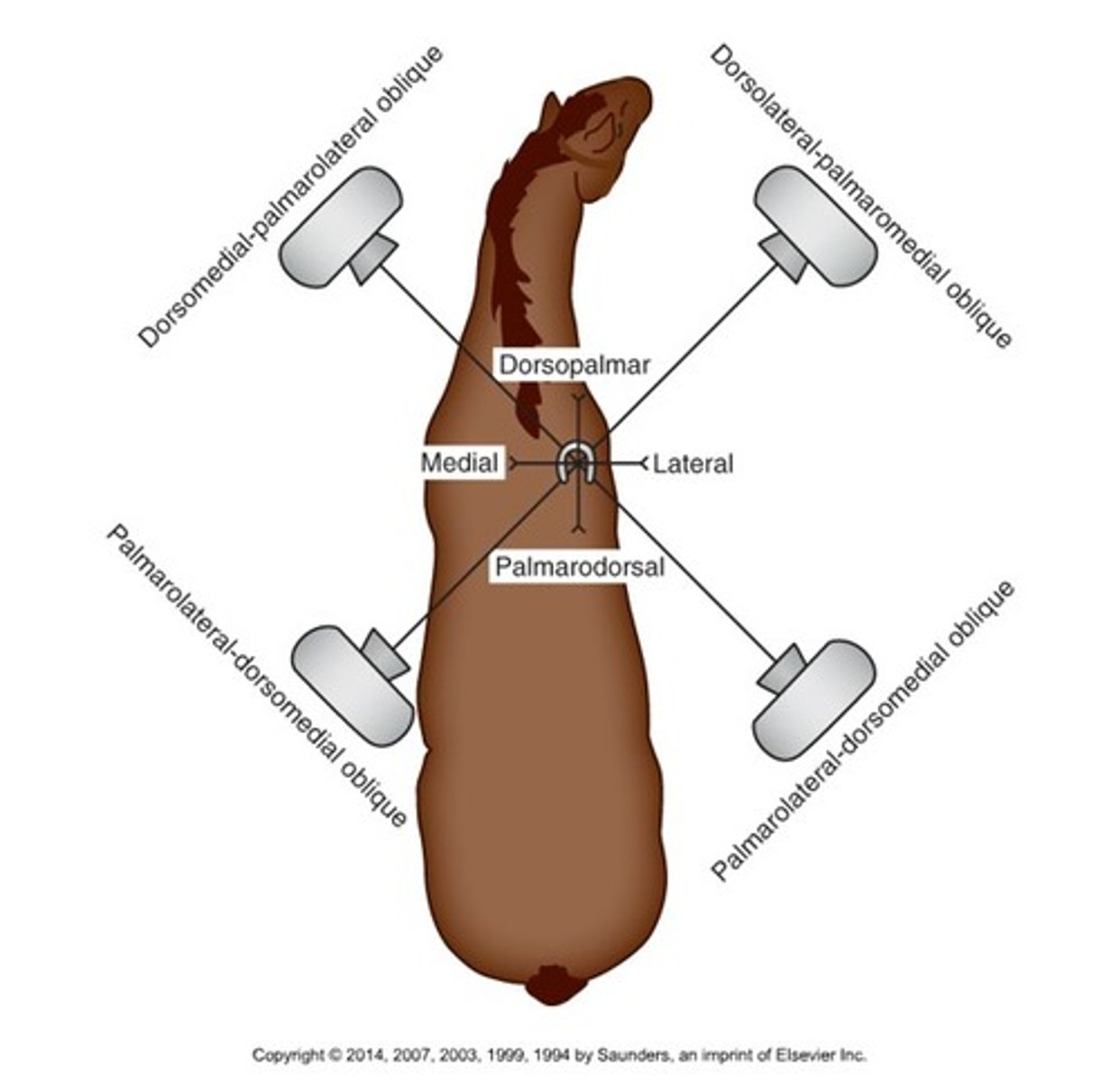
Dorsomedial-palmarolateral oblique (DMLPO)
Beam enters on the dorsally on the medial side and exits at the palmar aspect on the lateral side
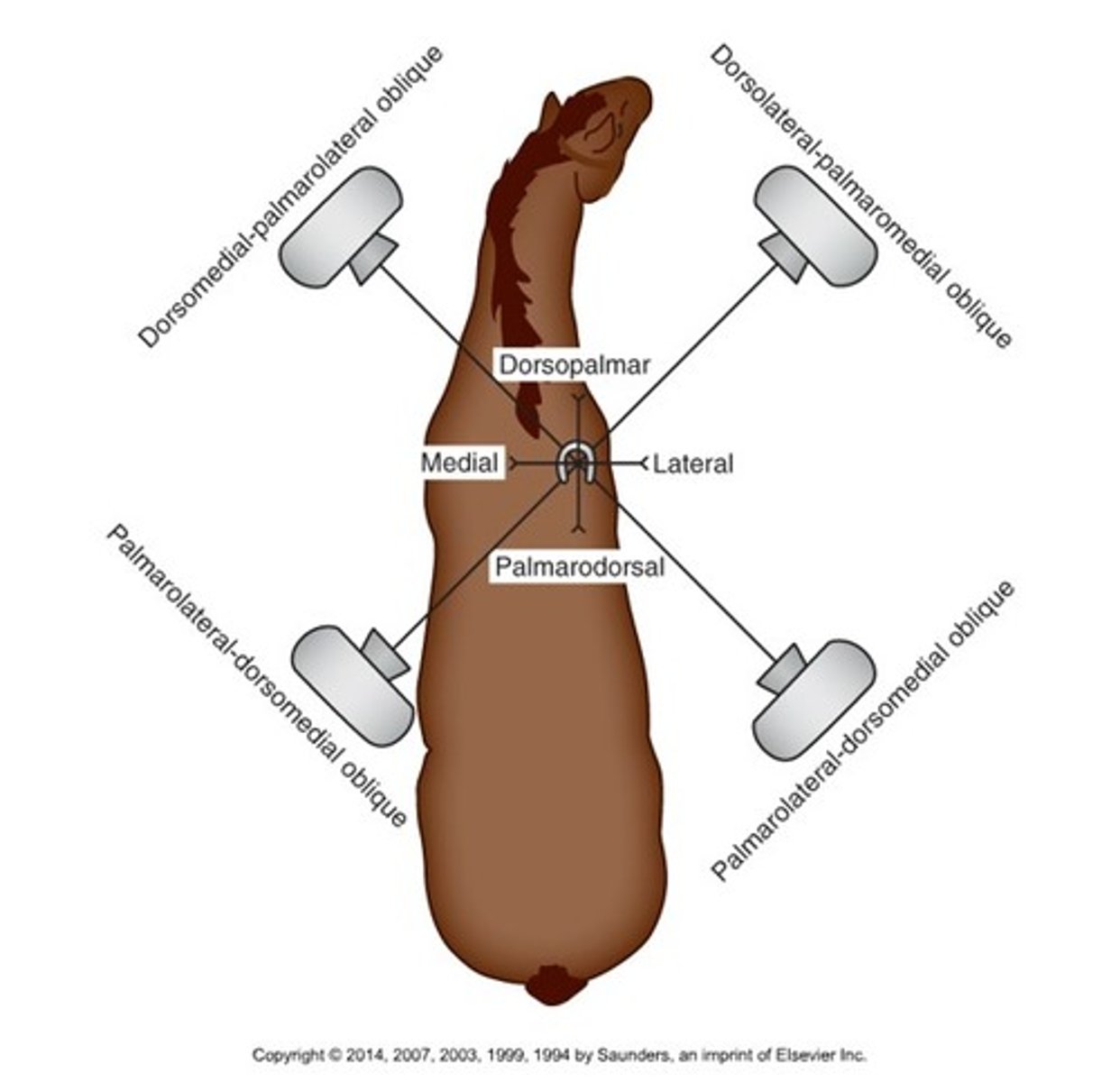
Dorsolateral-palmaromedial oblique (DLPMO)
Beam enters dorsally on lateral side, exits at palmar aspect on medial side
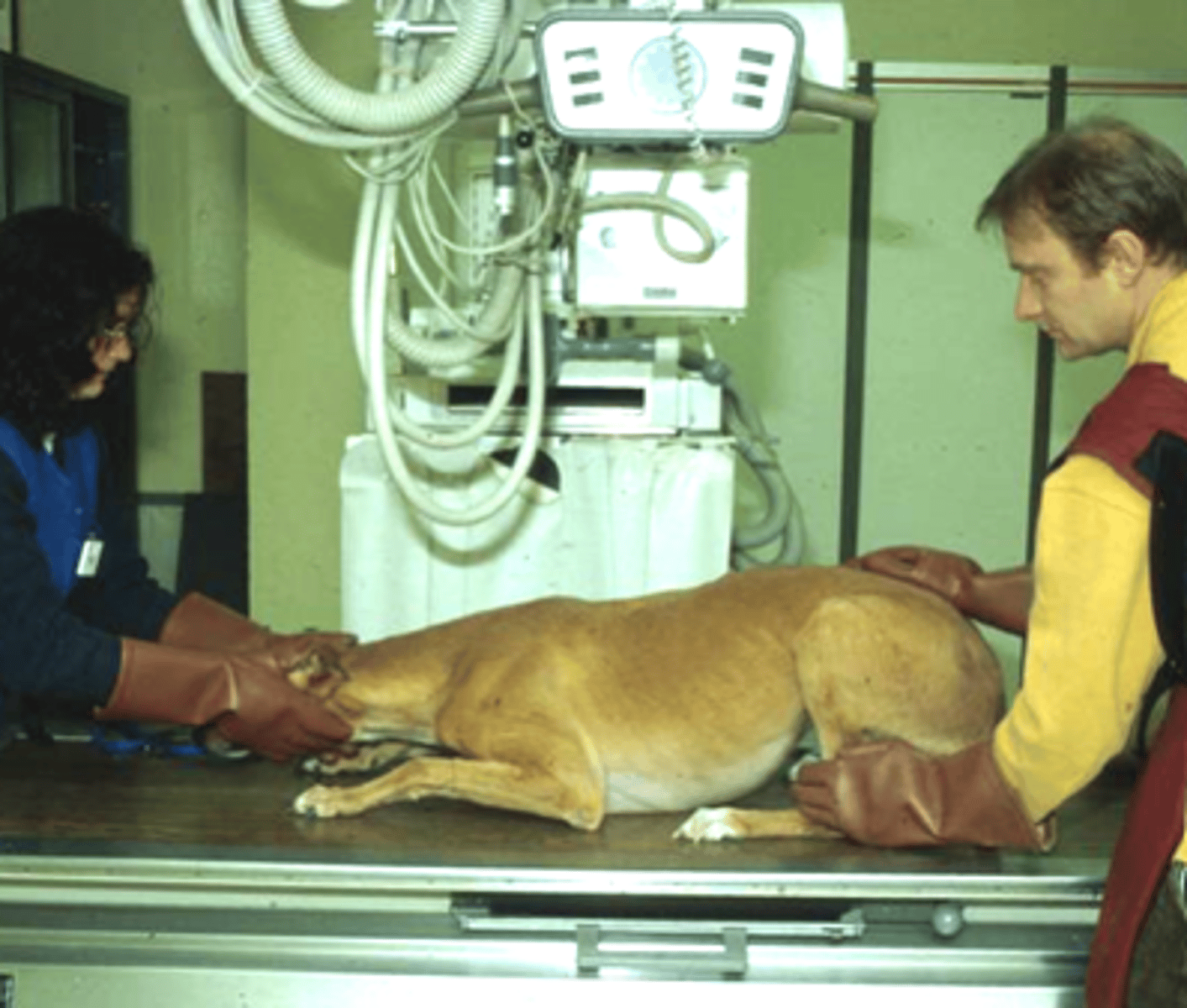
Patient positioning considerations
- Welfare of the patient
- Restraint and immobilization of the patient
- Minimal trauma to the area of interest
- Minimize exposure to the patient and VT
How do we make radiographs as stress free as possible for the patient?
- Minimize anxiety
- Minimize loud/startling noises
- Minimize restraint time
How do we appropriately measure the anatomy of interest?
- Use a caliper to measure the anatomic area
- Measurement over the part's thickest area
What are the minimum required number of views when taking radiographs?
Two views of each anatomic area at right angles to eachother
When putting 2 views on 1 image receptor, what do you need to ensure?
The body parts being radiographed are both pointing in the same direction
What are the 3 benefits of collimation?
- Improves image quality
- Improves detail
- Reduces scatter radiation
Positioning guidelines
- Measurement over thickest part being imaged
- Cathode Ray Tube centered directly over area of interest
- Position area of interest closest to image receptor
- Include all anatomy of interest for each body region
- L or R markers in each image
Patient Preparation
- Remove any debris
- Fur should be dry
- Collars, harness, leashes removed
- Bandages/splints/casts removed if possible
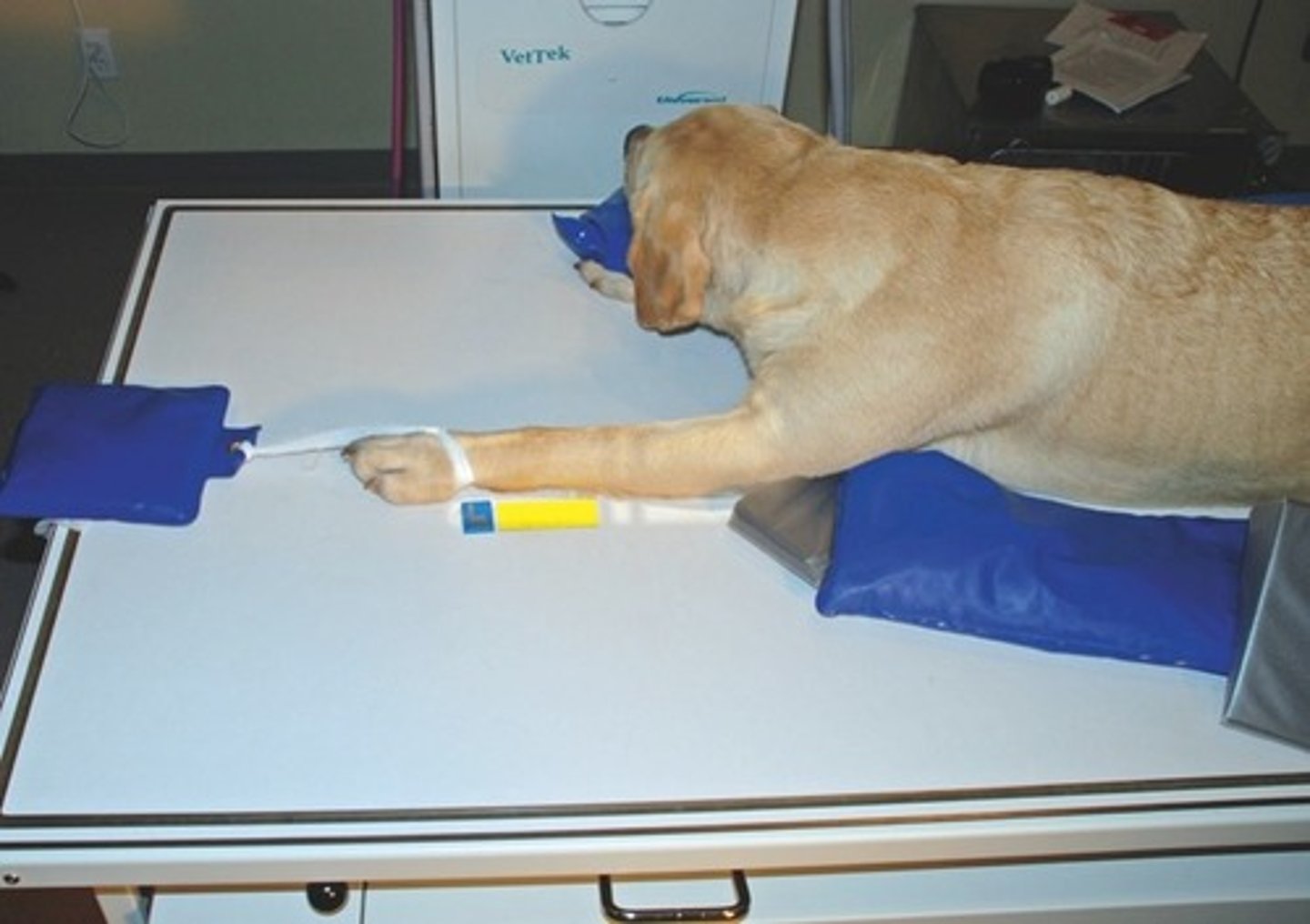
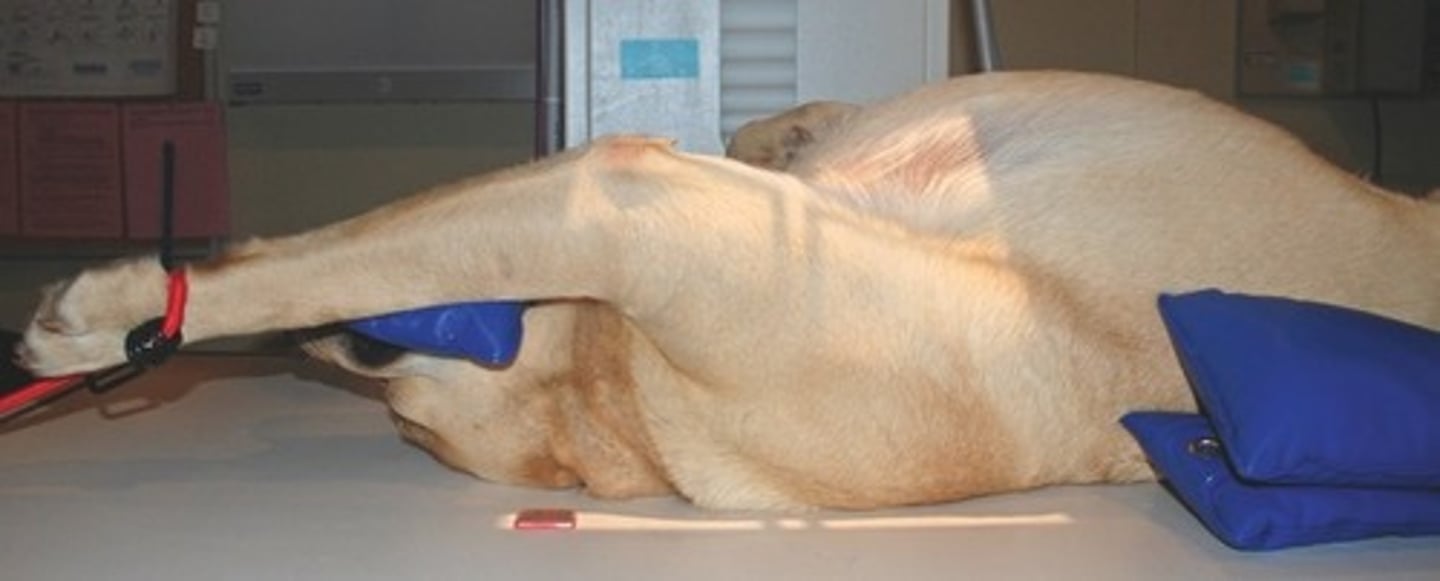
Positioning Aids
- Sandbags
- Sponges
- Tape
- Compression bands
- Plexiglass