Conditions affecting the Wrist and Fingers
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
______ is damage to the radio-ulnar ligament leads to this deformity where the ulnar styloid moves up and down.
Piano key sign
The distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) is a ________ ____ joint that allows pronation and supination.
uniaxial pivot
The DRUJ is formed by the distal radius, ulna, and the ________ __________ complex.
triangular fibrocartilage
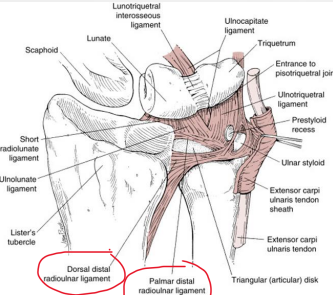
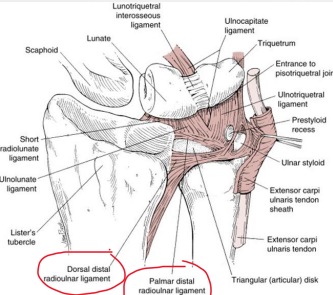
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is located between the medial _____ carpal row and the distal ________.
proximal, ulna
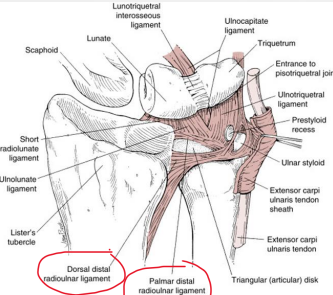
The articular disc of the is made of fibrocartilage and is positioned between the _______ and _______.
lunate, triquetrum
The meniscus homologue is a disc located between the ________ ligament and the ________ tendon sheath.
ulnotriquetral, ECU
Name the 4 structures that are included in the TFCC.
Articular disc, ECU, ulnocarpal, radioulnar ligaments
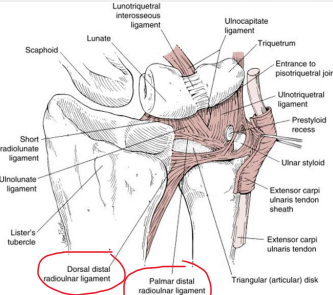
The ulnocarpal ligaments of the TFCC include the ulnolunate and ________ ligaments.
ulnotriquetral
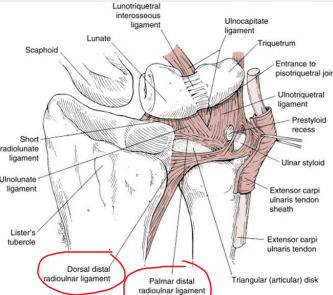
The dorsal and palmar ________ ligaments provide additional stability to the TFCC.
radioulnar
The TFCC helps cover the ___ head by extending the articular surface of the distal ________.
ulna, radius
The TFCC transmits load across the ulnocarpal joint and acts as a cushion against ________ force.
compressive
The TFCC allows forearm ________ by providing a strong but flexible connection between the distal radius and ulna.
rotation
TFCC injuries typically occur due to a fall on a ______ outstretched wrist or chronic ________ loading.
supinated, rotational
Type _ TFCC injuries are ________ and caused by force or laceration.
1, traumatic
Type _ TFCC injuries are ________ and result from repetitive movements.
2, degenerative
_____ wrist pain just distal to the ulna, worsened by pronation/supination and gripping, suggests a ________ tear.
Medial, TFCC
A positive McMurray test for the wrist is indicated by pain when the wrist is in ________ bend.
ulnar
Passive ______ combined with ________ deviation can reproduce TFCC injury pain.
supination, ulnar
Which imaging method is most sensitive and specific for identifying a TFCC tear?
MRI
What type of fracture might a radiograph reveal in a TFCC injury?
Ulnar styloid avulsion
Which imaging technique uses dye to identify TFCC tears but has low specificity?
Triple Injection Arthrography
How long should a wrist be immobilized for conservative TFCC injury treatment?
3-6 weeks
What type of therapy is recommended after immobilization in conservative management?
Physical therapy
What is the first-line medication for TFCC injury management?
NSAIDs
What type of injection can be used for pain relief in TFCC injuries?
Steroid injection
When can ROM exercises start after arthroscopic repair of a Type 1 TFCC injury?
One week
How soon can a patient start light ball contact after arthroscopic TFCC repair?
3 weeks
When can an athlete return to full sports activity after TFCC surgery?
4-6 weeks
True or False: One of the symptoms of a TFCC tear is numbness
False
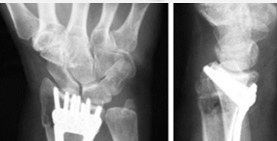
Colles’ fracture is a fracture of the ______ with ____ displacement of the distal fragment.
distal radius, dorsal
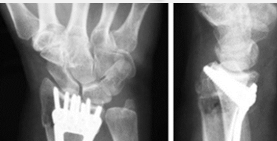
The characteristic deformity seen in Colles’ fracture is called ______ deformity.
dinner fork
A predictor of subsequent fractures in osteoporosis is a fracture of the ______.
distal radius
Non-operative management of Colles’ fracture includes ______ and ___ immobilization.
closed reduction, cast
Colles’ fracture is treated nonoperatively if it is ______ (inside or outside) the joint.
Extra-articular
Nonoperative treatment is indicated if ______ shortening is less than ______ mm.
radial, 5
A dorsal angulation of less than ______ degrees qualifies for nonoperative treatment.
5
Nonoperative treatment is possible if the angulation is within ______ degrees of the contralateral distal radius.
20
Joint type of Radiocarpal joint (Wrist joint)
Condyloid joint
Smith’s fracture is sometimes called ______ Colles’ fracture.
Reverse
Smith’s fracture involves a complete fracture of the distal radius with ______ displacement of the distal fragment.
Palmar
The usual mechanism of injury for Smith’s fracture is a fall on the ______ of a flexed hand.
back
Madelung’s deformity is caused by instability of the ______ articulation.
Distal radioulnar
Movement affected with Madelung’s deformity?
Supination
The growth disturbance in Madelung’s deformity results in progressive ______ and ______ tilting of the distal radius.
Volar, ulnar
Madelung’s deformity is more common in ______ (gender).
Females
The most noticeable sign of Madelung’s deformity is a ______ prominence of the ______ end of the ulna.
Dorsal, lower
Barton’s fracture is an ______ fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the _______ joint.
Intra-articular, radiocarpal
Barton’s fracture is caused by direct violent injury or sudden _____ of the distal _____ on a fixed wrist.
pronation, forearm
The more common type of Barton’s fracture involves the ______ rim of the ______.
Volar, distal radius
Conservative treatment for Barton’s fracture includes ______ _______ with the wrist in ______, ______, and ______.
closed reduction, full supination, mid extension, ulnar deviation
The scaphoid is palpated just distal to the ______ in the anatomic snuffbox.
Radial styloid
The ______ is the most commonly fractured carpal bone.
Scaphoid
Avascular necrosis of the scaphoid is called ______ disease.
Preiser’s
The ______ is the most commonly dislocated carpal bone.
Lunate
The ______ articulation is the most common area for carpal instability.
Scapholunate
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the lunate is called ______ disease.
Kienbock’s
In radiographic findings, osteonecrosis appears ______ initially but later shows flattening and abnormal density.
Negative
The ______ retinaculum prevents tendons from ______ when they turn a corner at the wrist.
extensor, Bowstringing
The extensor retinaculum also extends to the ulnar styloid, ______, and ______.
Triquetrum, pisiform
There are ______ dorsal compartments in the extensor retinaculum.
6
The lateral boundary of the anatomic snuffbox consists of the tendons of ______ and ______.
Abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis
The medial boundary of the anatomic snuffbox is formed by the tendon of ______.
Extensor pollicis longus
The floor of the anatomic snuffbox consists of the ______ and ______ bones.
Scaphoid, trapezium
De Quervain’s is a ______ inflammation of the ___ dorsal compartment.
Stenosing tenosynovitis, 1st
The tendons affected in De Quervain’s include ______ and ______.
Abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis
Postpartum women are prone to De Quervain’s due to ______ ligaments during pregnancy.
Laxed
Pain in De Quervain’s is located on the ______ side of the wrist.
Lateral
In De Quervain’s, pain can radiate into the ______ or up into the forearm.
Thumb
The special test for De Quervain’s is ______ test.
Finkelstein’s
A positive Finkelstein’s test occurs when pain is felt over the ______ process of the _____.
Styloid, radius
Ice therapy is used for ______ cases, while heat is used for ______ cases.
Acute, chronic
The carpal tunnel contains the ________ and ________ flexor tendons.
Median nerve, 9
Name the 10 structures that pass deep in the flexor retinaculum.
Flexor digitorum superficialis, profundus, flexor pollicis longus, median nerve
The roof of the carpal tunnel is formed by the ________.
flexor retinaculum
The ulnar border of the carpal tunnel is the ________.
hook of hamate
The radial border of the carpal tunnel is the ________.
trapezium
The floor of the carpal tunnel consists of the ________ ligaments and the palmar ligament complex.
radiocarpal
The median nerve originates from the ________ cord of the brachial plexus.
median lateral
The ________ nerve is superficial to the flexor retinaculum and provides sensory innervation to the central palm.
anterior cutaneous
The median nerve enters the hand through the ________.
carpal tunnel
The median nerve divides into a ________ branch and a _____ branch.
motor, sensory
The motor branch of the median nerve passes ________ to the flexor retinaculum.
posterior
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the ________ nerve.
median
A common traumatic cause of carpal tunnel syndrome is ________ fracture.
Colles
Numbness and tingling in carpal tunnel syndrome commonly affect the ____, ________, and _____ fingers.
thumb, index, middle
Canal of Guyon syndrome is caused by impingement of the ________ nerve.
ulnar
Weakening of the hand grip in Canal of Guyon syndrome is due to paralysis of the ________ muscles.
intrinsic
A positive Froment’s test indicates weakness of the ________ muscle.
adductor pollicis
In Wartenberg’s sign, the ________ digit is observed in an over-adducted position.
fifth
Sensory involvement in Canal of Guyon syndrome affects the medial palm and ________ half of the fourth digit.
ulnar
Absence of extrinsic muscle weakness points to a lesion at ________.
Guyon’s canal
______ ____is performed by tapping at the site of suspected nerve compression.
Tinel’s sign