MYCVIR LEC CNS-RABIES VIRUS
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Rabies Virus
A bullet-shaped, enveloped virus with linear, (-) sense ssRNA and a helical nucleocapsid
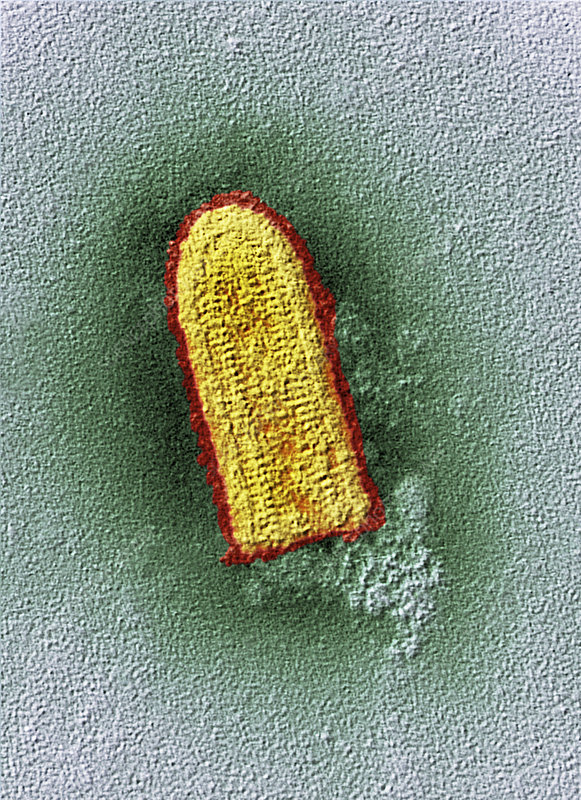
Rabies
Most lethal of all infectious dse
Furious rabies
Dumb rabies
2 forms of rabies
Furious rabies
RABIES
Limbic/nervous system
Headache, fever, irritability, restlessness, anxiety and muscle pain, salivation and vomiting
Dumb rabies
RABIES
Neocortex
Depression and paralysis followed by coma
Death results from respiratory arrest
Difficult to diagnose clinically
Hydrophobia
This phase of furious rabies continues until patient lapses into coma
3-8 weeks to 1 year
Incubation period of Rabies
Bite of rabid animal
Superficial abrasion of skin
Human to human via saliva
3 MOT for Rabies (BSH)
Bite of rabid animal
Most common way of transmitting rabies
Direct immunofluorescence assay
Fastest assay for rabies
Impression smears
What smear uses:
Various areas of brain
Biopsy of skin
Cornea
Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test (RFFIT)
in vitro cell culture neutralization test
measures rabies neutralizing antibody
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Most sensitive out of all the serological tests for rabies
CSF
spx in serological test for rabies
positive only in infected but not in vaccinized individuals
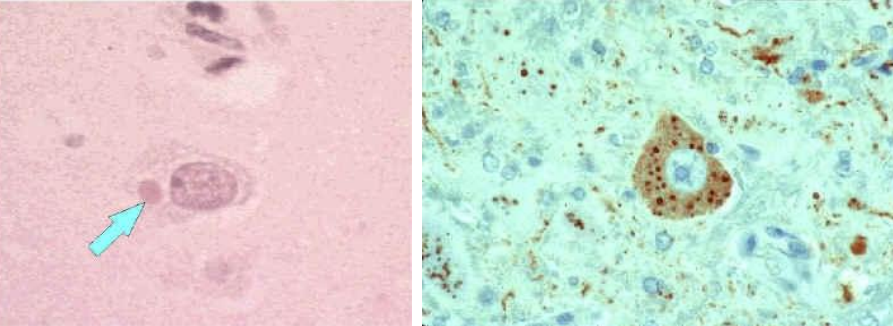
Negri bodies
Histologic exam of Rabies shows _________ bodies