Mechatronics Devices 3: phototransistors, color sensors
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a sensor and how is it an energy converter?
A sensor detects a physical property (like light or temperature) and converts it into an electrical signal, acting as an energy converter.
What is an optical sensor and what are its two main types?
An optical sensor measures light intensity, usually in the ultraviolet to infrared range. The two main types are quantum sensors and thermal sensors.
What is the operating range of quantum and thermal sensors, and what are examples of quantum sensors?
Quantum sensors operate in the ultraviolet to mid-infrared range, and thermal sensors operate in the mid to far infrared. Examples of quantum sensors include photodiodes, photoresistors (LDRs), and phototransistors.
What is a phototransistor?
A phototransistor is a three-layer semiconductor device with a light-sensitive base region that converts light into current flowing between collector and emitter.
How does the construction and symbol of a phototransistor differ from a regular transistor?
A phototransistor has no base terminal and uses light as input instead of base current. Its symbol resembles a standard transistor with arrows indicating incoming light.
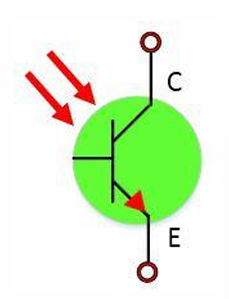
How does a phototransistor work?
When light hits the phototransistor’s base region, it creates electron-hole pairs. These carriers act like a base current in a normal transistor. This "light-induced base current" allows a much larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. The more light that hits the base, the more carriers are generated, and the more current flows — meaning the output current is directly controlled by the light intensity.

What limits the frequency response of phototransistors?
Phototransistors have a low-frequency response due to the large capacitance of the base-collector junction.
What materials and techniques enhance phototransistor sensitivity?
Modern phototransistors use light-sensitive materials like gallium arsenide. A small lens and hole on the collector-base junction surface help focus incoming light for better performance.
How do homo- and hetero-structure phototransistors compare in gain and cost?
Homo-structures have a gain of 50 to a few hundred, while hetero-structures can reach up to 10,000 but are more expensive to produce.
How does the noise level of phototransistors compare to avalanche photodiodes?
Phototransistors have much lower noise levels than avalanche photodiodes.
What is dark current in a phototransistor?
Dark current is the small leakage current that flows even when no light is present, caused by thermally generated carriers in the base-collector junction.
How do photodiodes and phototransistors differ in current gain and sensitivity?
Phototransistors have higher current gain and sensitivity than photodiodes under the same light level.
How can a photodiode be converted into a phototransistor?
By removing the emitter terminal from the photodiode, it can act more like a phototransistor.
How do the response times of photodiodes and phototransistors compare?
Photodiodes respond in nanoseconds, while phototransistors respond in microseconds.
What are the typical bandwidths of homo- and hetero-junction phototransistors?
Homo-structure phototransistors have a bandwidth of about 250 kHz, while hetero-junction types can reach up to 1 GHz.
What are the two main circuit configurations for phototransistors?
Common emitter and common collector.
Why are common base circuits not usually used for phototransistors?
Because the base is typically left floating and not connected in most phototransistor designs.
How does a common emitter phototransistor circuit work?
The collector is connected to supply via a load resistor, and output is taken from the collector. Light generates current in the base, which is amplified by the transistor's current gain.
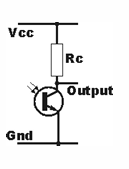
What happens to the output voltage in a common emitter phototransistor circuit when light is detected?
The output voltage moves from a high state to a low state when light is detected.
How does a color sensor detect color?
A color sensor detects the color of a material, typically in the RGB scale, categorizing it as red, blue, or green.
What are the main blocks in a color sensor system?
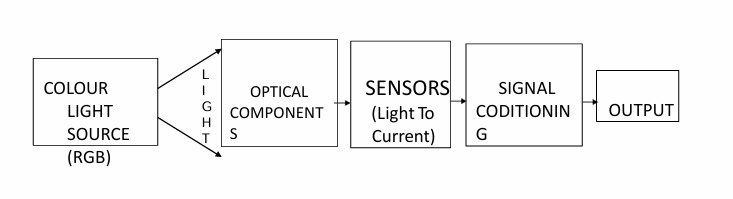
What is the function of optical components in a color sensor system?
Optical components filter and focus light rays onto the optical sensors to ensure accurate color detection.
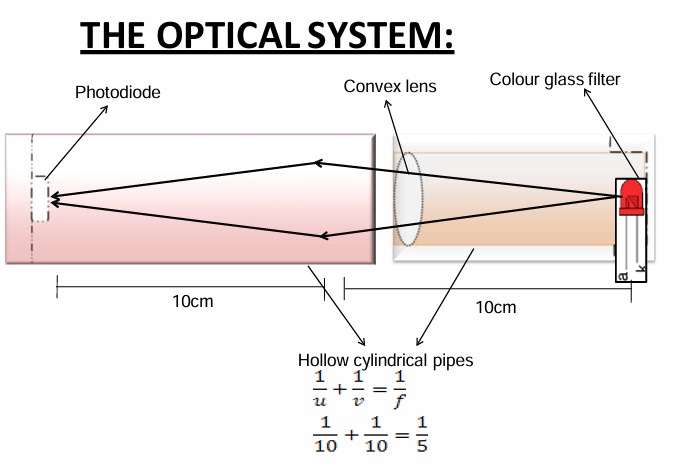
What is the role of the photodiode in the optical system?
The photodiode converts light to current based on the photoelectric effect.
What is the function of the convex lens in the optical system?
Color glass filters allow only a single color wavelength to pass through, acting as absorption filters.
List some applications of color sensors.
Applications include measuring and detecting surface colors in industrial, medical, and security systems, such as light color temperature measurement, RGB LED consistency control, medical diagnosis, health fitness, and industrial process control.