Psych/Soc 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
anxiety disorder
excessive fears and/or anxiety for future real and hypothetical threats and no clear present threats
2
New cards
phobia
a specific fear
3
New cards
panic disorder
suffered at least one panic attack and worried about more of them
4
New cards
Social anxiety disorder
fear/anxiety around social sitatuions
5
New cards
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
excessive anxiety or worry without cause
6
New cards
Depression
sad, empty, irritable feeling or worthlessness
7
New cards
major depressive disorder
suffered more than one major depressive episodes
8
New cards
bipolar disorder
cyclic mood episodes between poles of depression and mania
9
New cards
Bipolar 1 disorder
intense mania huge upswings followed by big crash
10
New cards
Bipolar II Disorder
manic phases less extreme more depression driven
11
New cards
Schizophrenia
A mental disorder characterized by abnormal thinking, hallucinations, delusions, and difficulty in distinguishing between reality and fantasy. It often includes social withdrawal and impaired cognitive function.
12
New cards
PTSD
Exposure to a traumatic event resulting in intensive fear or horror
13
New cards
Personality Disorder
personality traits that deviate from the norm and inflexible behaviours with high comorbidity
14
New cards
Cluster A
(weird behaviours) milder versions of schizophrenia
Paranoid PD, Schizoid PD, Schizotypal PD
Paranoid PD, Schizoid PD, Schizotypal PD
15
New cards
Cluster B
(Wild) over the top or unstable
Antisocial PD, Borderline PD, Histrionic PD, Narcissistic PD
Antisocial PD, Borderline PD, Histrionic PD, Narcissistic PD
16
New cards
Cluster C
(worry), anxiety or OCD related
17
New cards
Paranoid PD
Manifest paranoid tendencies and mistrusts and misinterprets others and their motives
18
New cards
Schizoid PD
a loner with little interest or involvement in close relationships and doens’t care about interactions with others
19
New cards
Schizotypal PD
manifests odd behaviour and distorted thinking
20
New cards
Antisocial PD
sociopathy with no regard for right or wrong or others rights, aggressions against people and animals, breaking the rules
21
New cards
Borderline PD
terrified of abandonment by others, inability in impulse control, mood, and image of self and others
22
New cards
Histrionic PD
Wants to be the centre or attention, seeks attention
23
New cards
Narcissistic PD
inflated sense of self and lack of empathy
24
New cards
Avoidant PD
very shy, fear of rejection and feels inferior
25
New cards
Dependent PD
over dependence on people to meet needs and needs to be taken care of by others and very submissive
26
New cards
Obsessive Compulsive PD
rigid concern with order and perfectionism and won’t comply with authority unless things are done his way
27
New cards
OCD
obsessions of uncontrollable thoughts or impulses that cause anxiety or compulsions of repetitive mental and physical behaviours in order to reduce threat
28
New cards
Somatic Symptom Disorder
distress by persistent physical symptoms and concerns which can mimic a disease but aren’t real, always think are sick, lots of distress and disrupt daily life
29
New cards
Illness Anxiety Disorder
mainly psychological, have an unrealistic fear that they have a serious medical condition or fear that they're at high risk of becoming ill.
30
New cards
Conversion Disorder
physical and sensory problems, such as paralysis, numbness, blindness, deafness or seizures, with no underlying neurologic pathology
31
New cards
Factitious Disorder
fabricated an illness but gone to falsify evidence or symptoms of illness
32
New cards
Dissociative Disorder
disruptions to awareness, memory, and identity are extreme and frequent triggered by severe stress
33
New cards
Dissociative Identity Disorder
alternates between 2 or more distinct identities which only one interacts with other people
34
New cards
Dissociative Amnesia
at least one episode of forgetting some important personal info and creating gaps in memory related to severe stress of trauma
35
New cards
Depersonalization Disorder
recurring or persistent feeling of being cut off or detached from body, out of body experience
36
New cards
Derealization Disorder
feels that people and objects in external world are not real, detached from from surrounding
37
New cards
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
manifest early in development, hard to treat, characterized by intellectual development and communication disorders
38
New cards
ADHD
Motor restlessness, difficulty paying attention, distractibility, impulsive
39
New cards
Autism
complex can be minor or extreme, impaired social interaction, repetitive movements, inability to play with kids
40
New cards
Neurocognitive disorder
cognitive decline from previous level in learning, memory, language, motor and social skills
41
New cards
Alzheimers Disease
destruction and death of nerve cells causing memory failure, personality change, and problem carrying out normal activity has two abnormal structures amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles
42
New cards
Amyloid Plaques
clumps of proteins fragments that build up outside of cell
43
New cards
Neurofibrillary tangles
clumps of altered proteins inside cell
44
New cards
Parkinson’s disease
due to low dopamine levels, dopaminergic neurone in substantial nigra of the basal ganglia die off harder to control movements, build of of lewy bodies in neurons
45
New cards
Sleep-wake disorder
disturbance in quality, timing or amount of sleep
46
New cards
insomnia
cant fall asleep
47
New cards
Narcolepsy
periodic, overwhelming sleepiness during day
48
New cards
sleep apnea
intermittent stoppage of breathing which results in repeated awakening
49
New cards
Dyssomnias
abnormality in amount, quality, or timing of sleep
50
New cards
Somnambulism
sleep walking, happens during stage 3, grown out of for children n
51
New cards
night terrors
screaming while in deep sleep happen in stage 3 (nightmares happen in REM)P
52
New cards
Parasomnias
abnormal behaviours that happen during sleep
53
New cards
Hallucinogens
LSD, Weed, distorts perception
54
New cards
Stimulants
Caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, increase availability and action of neurotransmitters
55
New cards
Depressants
Alcohol, barbiturates, opiates, depress the CNS
56
New cards
Dependence
develops when a person needs to use it in order to function normally
57
New cards
Tolerance
happens when a person must use more of a drug to achieve the desired effect
58
New cards
Withdrawal
symptoms that occur when a person formed a dependance to a drug and then doens’t get it or enough of it
59
New cards
Addiction
compulsive drug use despite its harmful consequences and cant stop
60
New cards
Consciousness
awareness that we have of our selves, internal states, and environment, needed to do complex tasks but less so for easier tasks
61
New cards
Recticular Activating System
alertness and arousal in brain
62
New cards
Alpha
8-12 Hz and associated with relaxed normal consciousness
63
New cards
Beta
12\.5-30 Hz more alert consciousness
64
New cards
Theta
3-7 Hz meditative states and stage 1 sleep
65
New cards
Delta
0\.5-3 Hz occurs during slow wave sleep
66
New cards
Circadian Rhythm
control the increase and decrease in our alertness in predictable ways over 24 hrs
67
New cards
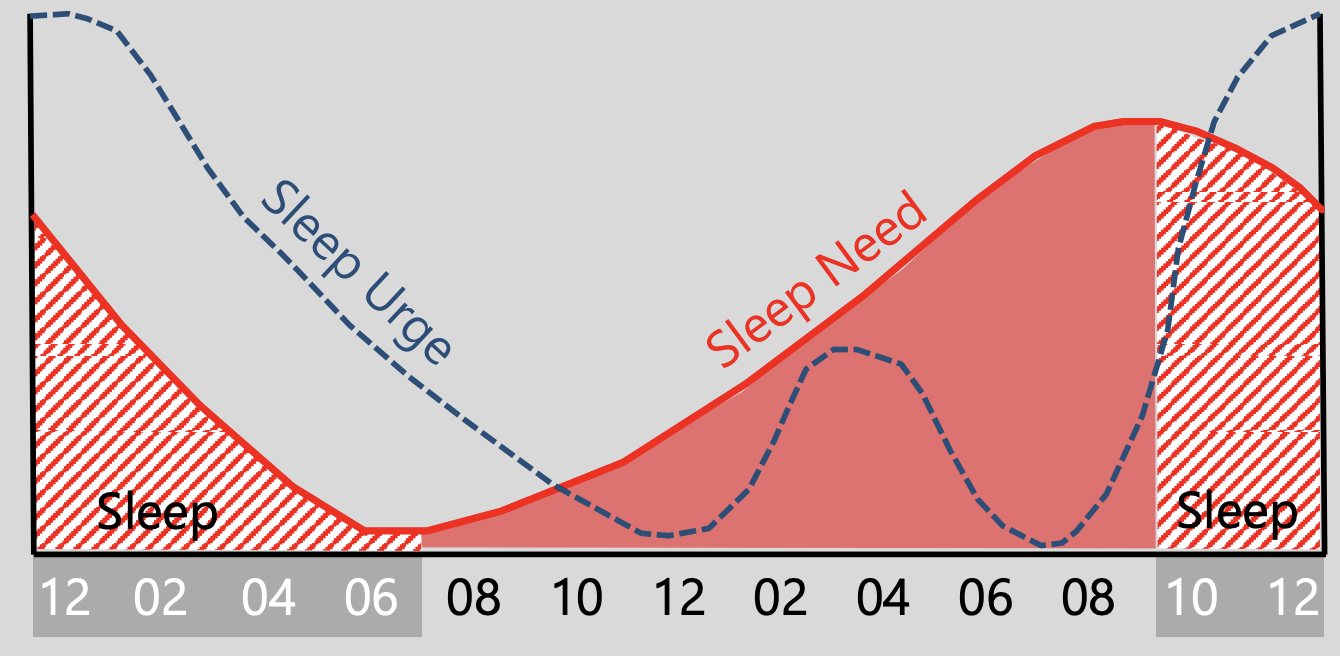
During sleep our sleep urge goes down
during awake our sleep need goes up but in mid afternoon sleep urge goes up for a nap but goes down again
during awake our sleep need goes up but in mid afternoon sleep urge goes up for a nap but goes down again
68
New cards
3 physiological indicators of mammalian circadian rhythm
Melatonin release by pineal gland, body temp, and serum cortisol levels
69
New cards
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
in the hypothalamus regulates sleep, melatonin production in pineal gland, body temp
70
New cards
hypnosis
state of consciousness in which attention is more focused and peripheral is reduced and highly suggestible and easily convinced
71
New cards
Meditation
a person induces a mode of consciousness for a purpose
lower frequency alpha and theta waves, improved health, concentration
lower frequency alpha and theta waves, improved health, concentration
72
New cards
NREM1
Light sleep non rem sleep
73
New cards
NREM2
increased relaxation, decrease temp/HR/respiration
74
New cards
NREM3
heart and digestion slow, growth hormone secreted deepest sleep stage 4 has physical repair
75
New cards
REM
when dreams happen Sle
76
New cards
Sleep spindle
high oscillations in EEG, happens in Stage 2
77
New cards
K-Complex
happens in stage 2 and is a big spike