SOCPSY W10: Aggression
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Aggression
Behaviour intended to injure another
Characteristics of aggression
It is a behaviour (not upset feelings)
It is intentional (not accidental harm)
It is aimed at hurting (not due to assertiveness or playfulness)
Assertiveness
Behaviour intended to express dominance or confidence (eg. returning an undercooked dish in a restaurant)
4 Types of aggression:
Indirect aggression
Direct aggression
Emotional aggression
Instrumental aggression
Indirect aggression
Hurting someone without obvious face-to-face conflict
Eg. Spreading negative rumours about your classmate behind their back
Direct aggression
Hurting someone to “his or her face”
Eg. Insulting/name-calling your classmates in class
Emotional aggression
Hurting someone stemming from angry feelings
Eg. in a race, you intentionally trip your opponent because you overheard them speaking badly of you, which made you angry
Instrumental aggression
Hurting someone to accomplish another (non-aggressive) goal
Eg. in a race, you you intentionally trip your opponent because you really want to win
Gender differences in aggression displaying
No clear sex difference in reported anger, but women are more prone to:
Experience jealousy in r/s
Use physical aggression against partners eg. slapping
Use more indirect aggression
Men’s aggression more associated with physical harm
eg. men commit vast majority of homicides (increasing over the years)
4 Goals of aggressive behaviour: (CGGP)
Coping with feelings of annoyance
Gaining material and social rewards
Gaining or maintaining social status
Protecting oneself or others
Coping with feeling of annoyance (no definition)
Frustration-aggression hypothesis (original theory)
Frustration (and only frustration) from any blocking of goal-directed behaviour ALWAYS leads to aggression (of all forms)
Revised theory:
Any unpleasant stimulation (eg. frustration, pain, heat) tends to lead to negative feelings which lead to emotional aggression
Excitation transfer theory
Any form of emotional arousal (negative, positive, and even neutral) can increase aggressive responses
Eg. students become more aggressive after watching nonviolent erotic films or riding bikes
What contributes to arousal and irritability?
The intensity of the emotions rather than the type (anger is physiologically similar to other emotional states)
Type A behaviour pattern
Group of personality characteristics consisting of time urgency, competitiveness, and chronic irritability
4 things type A people are associated with:
More success in business
Conflict with subordinates
More aggressive driving
Higher risk of coronary disease
4 types of unpleasant experiences/situations
Pain
Heat
Poverty
Unemployment
Pain
(study)
3 things increase in temperatures are associated with:
More aggressive horn-honking
Increases in assaults, murders and urban riots
Major league pitchers throwing more balls at batters
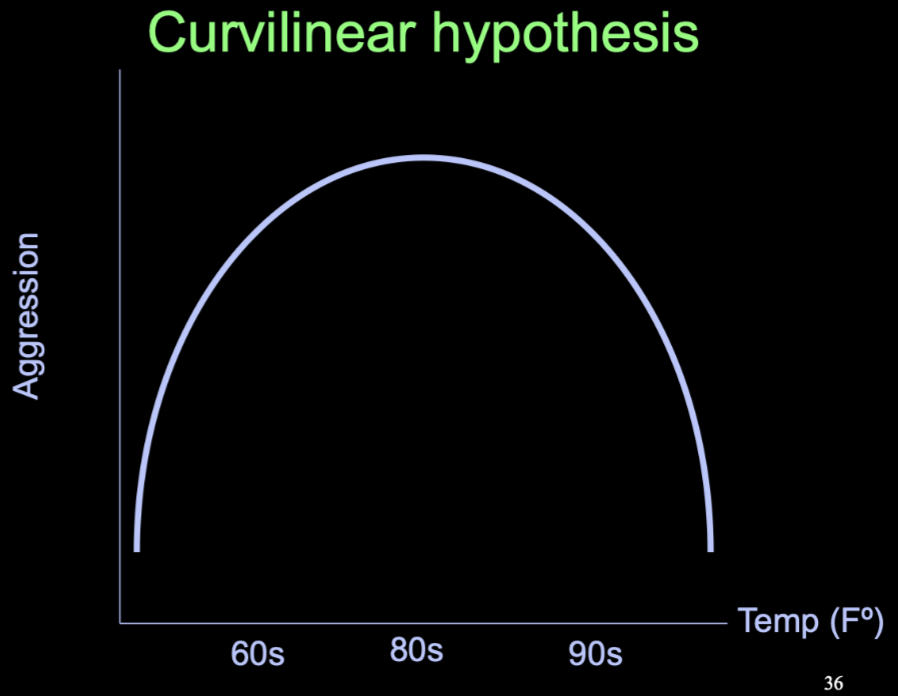
Graphical explanation
Curvilinear hypothesis of heat and aggression
Relative deprivation
The unpleasant feeling in which one has less than others in the group they compare themselves to
We usually compare ourselves to
People of similar levels (eg. peers)
Real life example of aggression and economic downfall
Lynching events in South America increased when cotton prices dropped (negatively related)
R/S between unemployment and aggression
Catalano et al. interview: the odds of violence (been in a fight, used weapons etc) are 6x higher among respondents who had lost their jobs in the past year, even for those with no history of violent behaviour
Weapons effect
Tendency for weapons eg. guns to enhance aggressive thoughts, feelings and actions
(study)
Gaining material and social rewards
Material rewards can motivate aggressive and unethical actions
Eg. winning the Olympic medal motivated figure skater Tonya Harding to involve in carrying out an attack against Nancy Kerrigan (both favourites for 1994 Olympic medal in figure-skating)
Social learning theory of aggression
Theory that aggressive behaviour is learnt (through TV, parents’ behaviour etc)
Eg. Andrew Golden and his gun buddy carried out a school shooting with bullets & guns taken from their kin
2 types of people who finds rewards in violence
Psychopaths who are:
Impulsive
Irresponsible
Lowly empathetic
Insensitive to punishment
Alcohol intoxicated people
May turn off normal empathetic feelings
Eg. men who beat wives drank 13x as much as nonviolent patrons of the same pub
Violent media
Watching violence magnifies violent inclinations
Evidence of violent TV-watching and violence
Children who watch a lot of violent TV become more violent towards their peers
Movie watching and aggression
(study)
Evidence of violent video gaming and aggression
VVG is associated with history of property destruction and hitting other students
Gender variances in VVG and aggression
(study)
Gaining or maintaining social status (no definition)
Differential parental investment
The theory that the sex with higher obligatory parental investment (typically females in many animal species - carrying foetus & nursing young) becomes more selective in choosing mates, while the other sex (typically males) becomes more competitive and aggressive with e/o to pursuit more valuable mating opportunities
Gender proportion in same-sex homicides
Men commit 90% to near 100% of same-sex homicides across countries like Canada, Miami & Denmark
The effect of testosterone on aggression and social dominance
Higher levels of testosterone leads to higher aggression and social dominance
Evidence for that
Dabbs & colleague found high testosterone levels in
Aggressive boys
Men & women with criminal records
Violent criminals
Military veterans who went AWOL or got into trouble after service
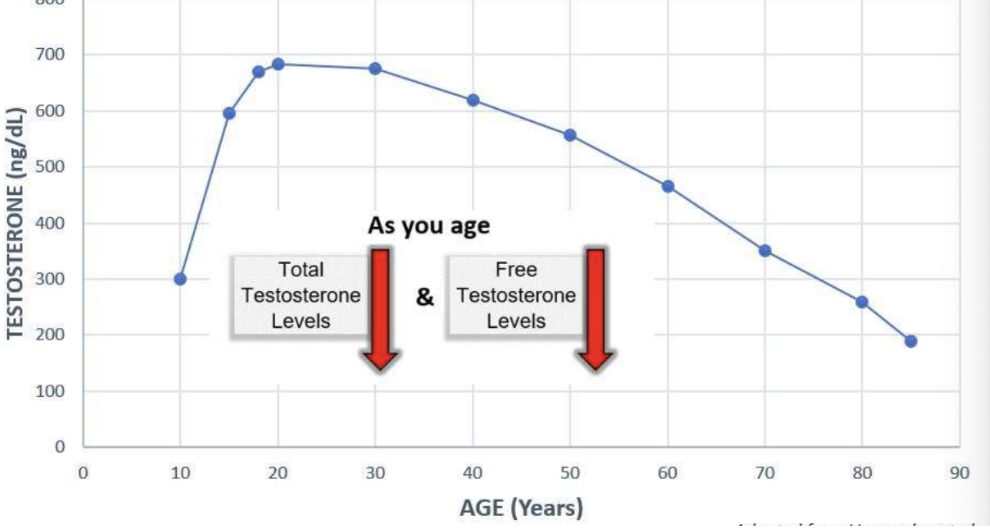
R/S between testosterone and age
Total and free testosterone levels declines with age (dips after 20-30y/o)
R/S between testosterone and marital status
Testosterone levels decreases from unmarried men > married with no children > married with children; fathers
R/S of gender deaths (male-to-female ratio) with age through external & internal mortality
External: during ages 25-34, over 5 times as many males as females die due to external causes like homicides & accidents
Internal: much lower, and relatively similar & stable deaths for both genders due to internal causes like diseases
Why do more young men suffer from external mortality?
Young men engage in more high-risk behaviours compared to young women
Sex change operations
Women —> men (got testosterone injections): became more aggressive and sexual
Men —> women (got testosterone suppressants): became less aggressive and sexual
R/S between SES, testosterone and delinquency
(study)
Examples of altercations linked to insults:
Aggressive behaviour In the lab
Teenager’s description of events that made them most angry
College students’ homicidal fantasies
Urban gang fights
A substantial portion of male homicides
Culture of honour
Set of societal norms where people (particularly men) should be ready to defend their honour; pride with violent retaliation if necessary
Cultural differences in related aggression
Southerners are more aggressive than northerners
The south has more honour-related homicides
Southern students respond more aggressively to an insult in a lab setting
Protecting oneself or others (no definition)
What is rated the most justified aggression in Spain, Finland and Poland?
‘Self-defence’ and ‘protecting others’
Exception to apparent self-defence weapons eg. guns
Guns more often used to kill friends, acquaintances, or self
owning guns triples chance of being killed
risk of teen suicide is 4-10x higher in homes with guns