Muscles
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Striated
striped appearance. This striped appearance is due to these muscles' light and dark bands
Voluntary
Can be consciously controlled
Sarcomere
the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber
Muscle Fiber
consists of densely packed, alternating thin and thick filaments within the sarcoplasm; gives skeletal muscle its striated appearance
Cross-Bridge
Where myosin will bind to actin
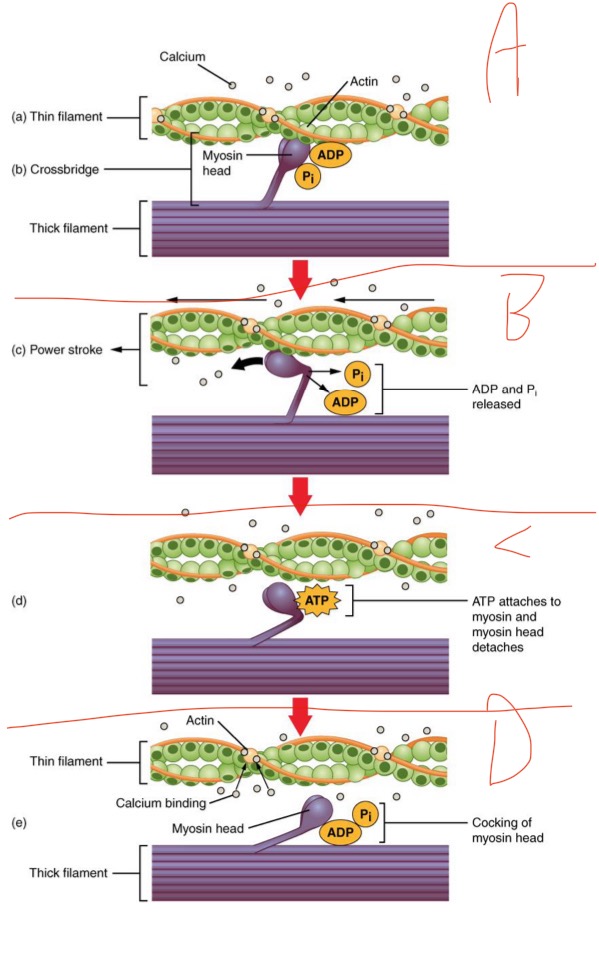
What is happening in A?
Ca released from SR —> exposes the myosin binding sites —→ myosin binds to actin
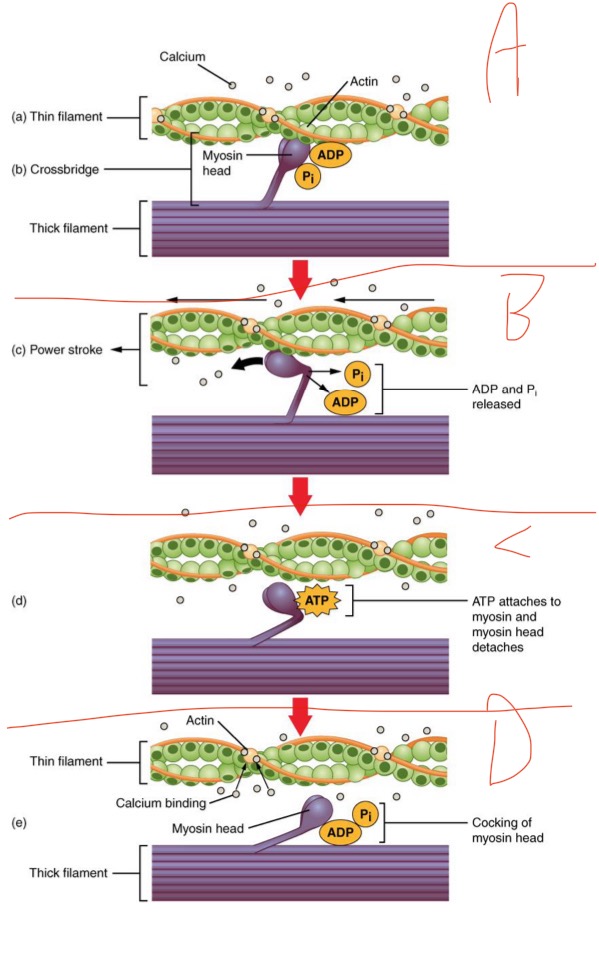
What is happening in B?
Myosin head flexes + pulls thin filament (powerstroke) —> ADP released
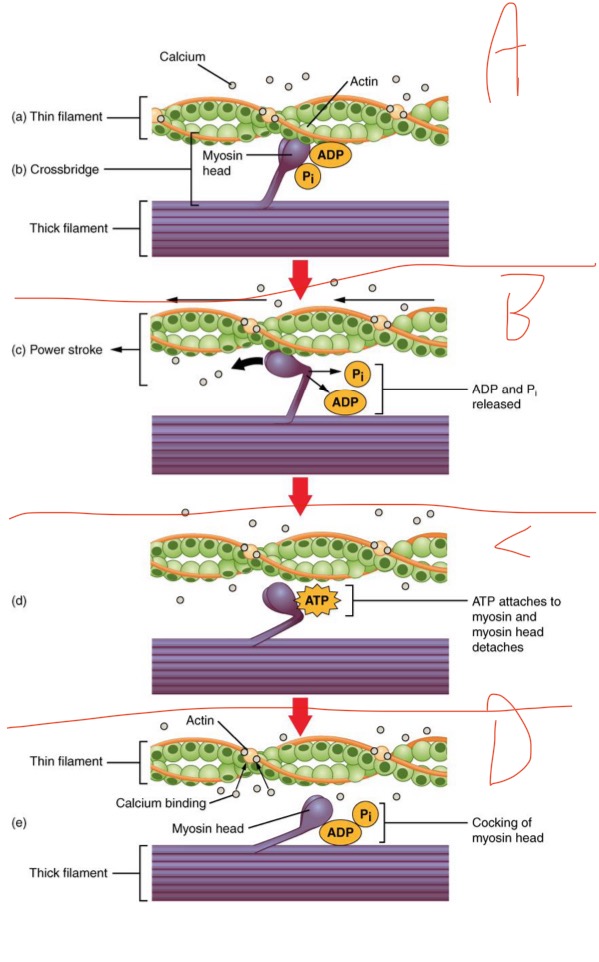
What is happening in C?
ATP binds to myosin head —> detaches
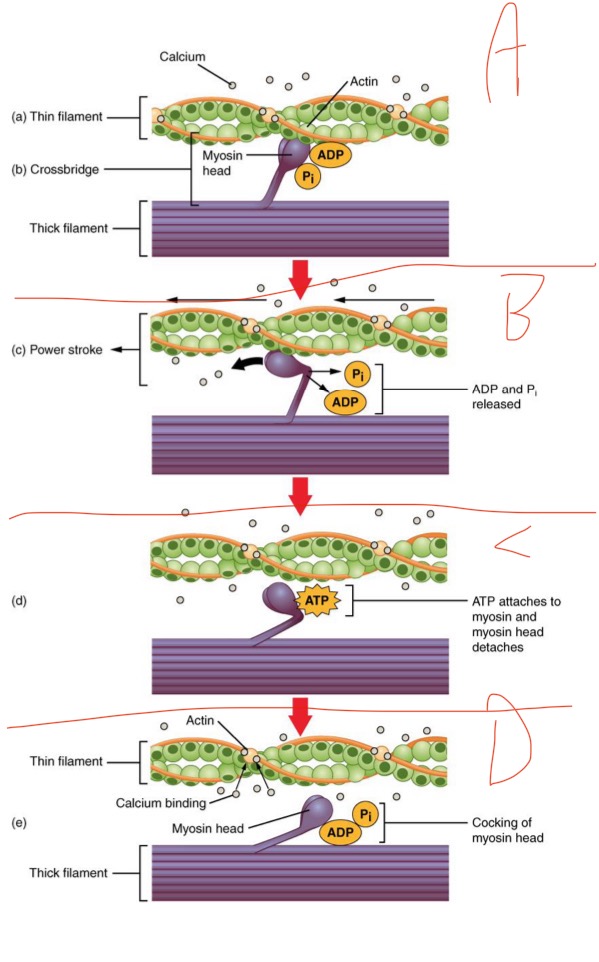
What is happening in D?
Myosin head releases (recovery stroke) (repeats until activation stops or muscle runs out of energy) —> after Ca gets pumped back into SR
Motor Unit
one motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
Neuromuscular (myoneural) Junction
Site where motor neuron stimulates the muscle fiber
Sliding-Filament Theory
thin and thick filaments sliding against one another, folding in
Motor End Plate
The specialized area on sacrolemma where motor neurons stimulate muscle cells
Cardiac Muscle
striated, branched, cardiocytes, 1 nucleus per cell, involuntary, in heart
Skeletal Muscle
striated, multi-nucleated, cells=fibrous muscle fibers, voluntary, attached to bones + skin
Smooth Muscle
non-striated, involuntary, fusiform myocytes, one nucleus per cell, skin+ eyes+glands +inherent contractivity
Fast Glycolytic Fibers
white, fast twitch, easily fatigued, fast contracting, doesn’t need O2 (excitable, contractile, stretchable, and elastic)
Slow Oxidative Fibers
red, slow twitch, fatigue resistant, slow contracting, needs O2 (excitable, contractile, stretchable, and elastic)
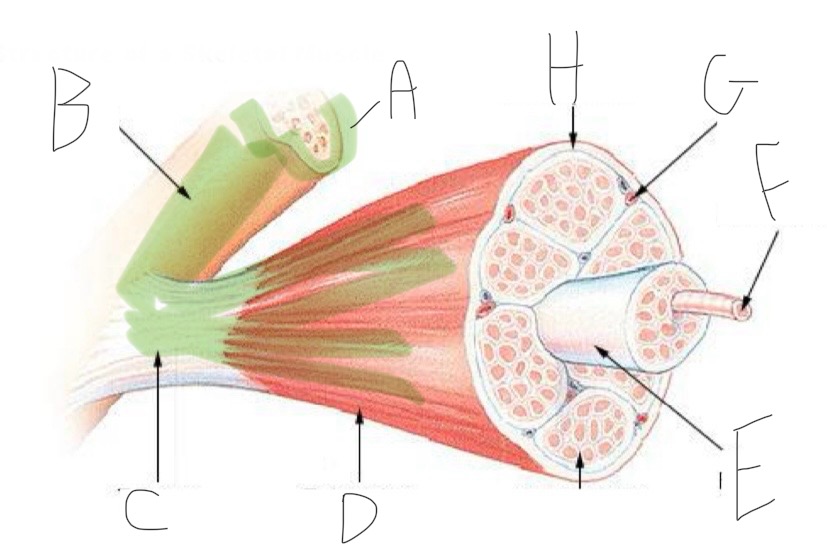
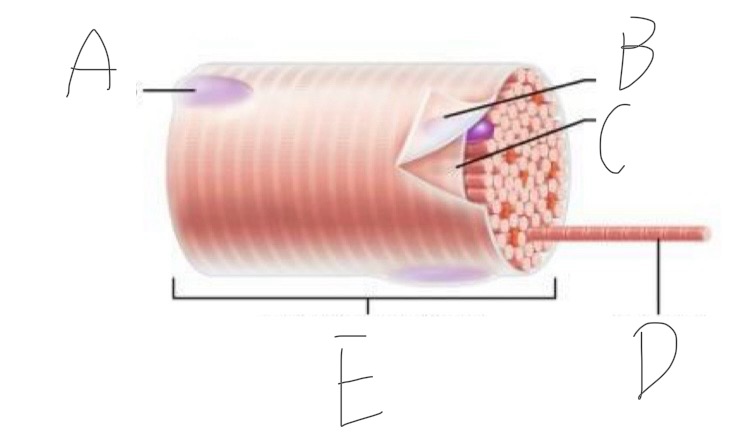
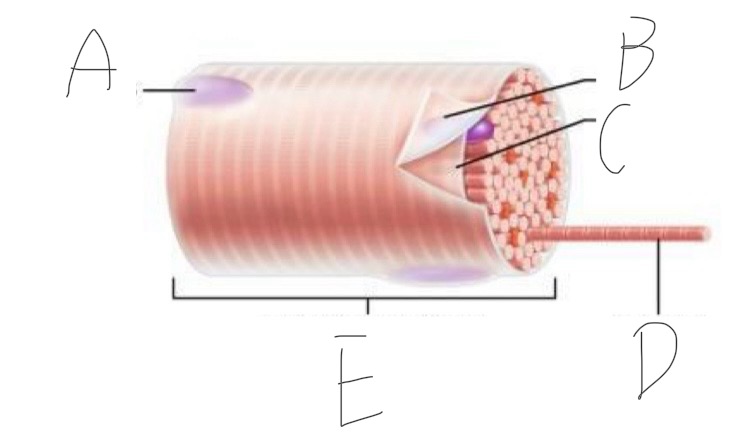
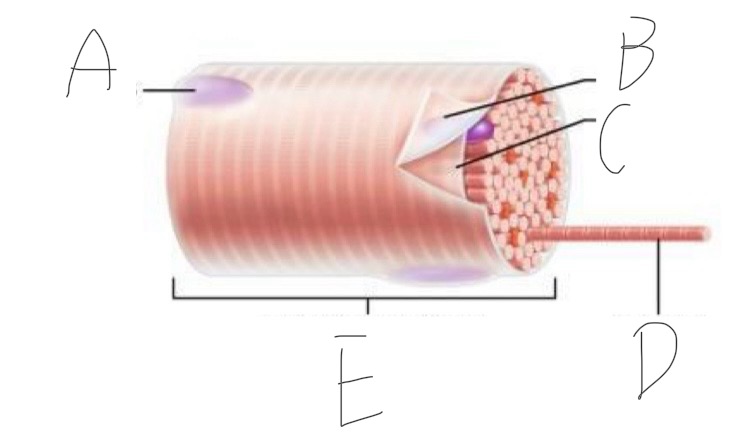
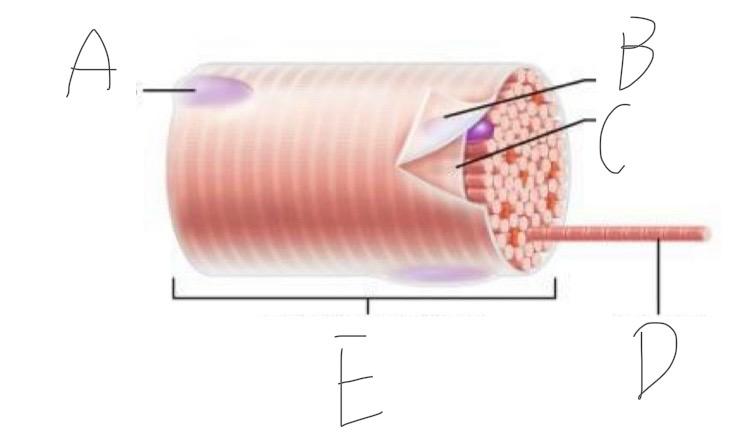
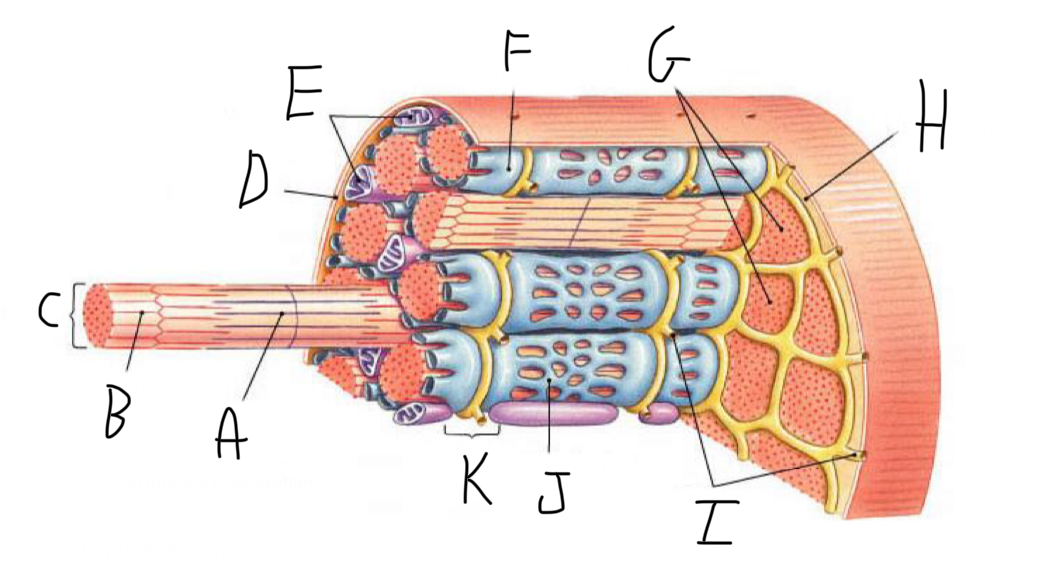
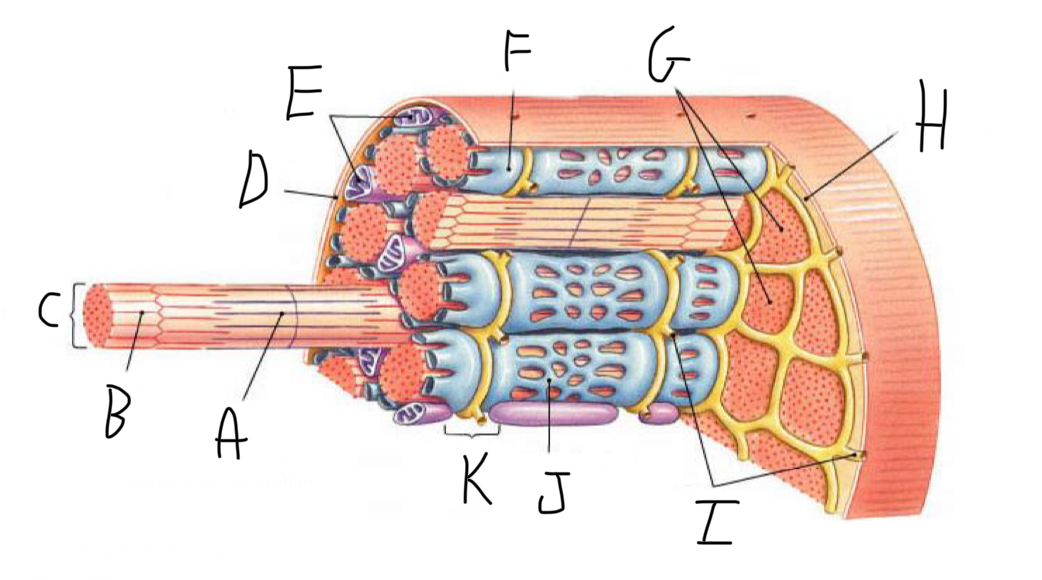
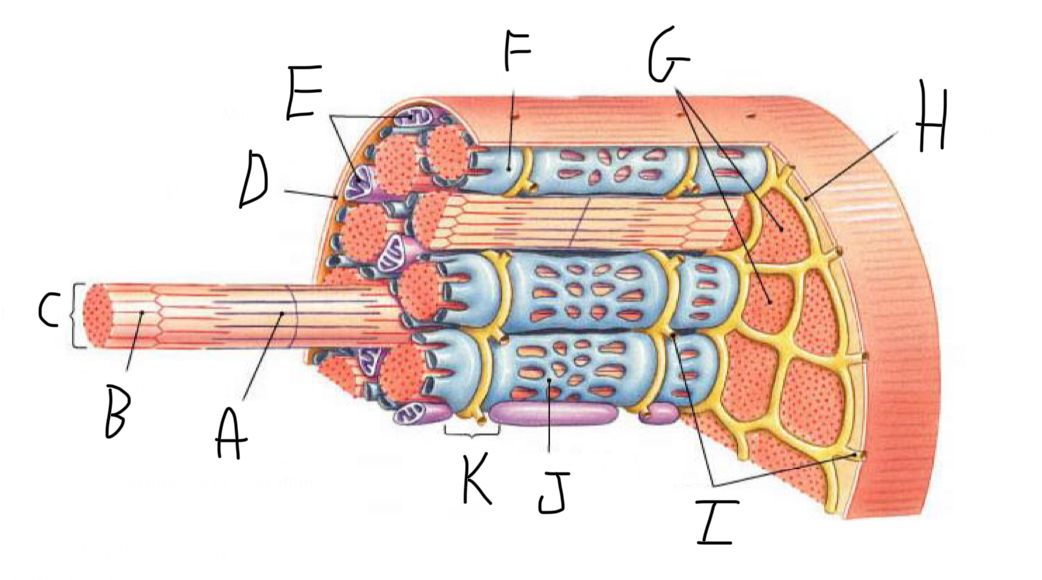
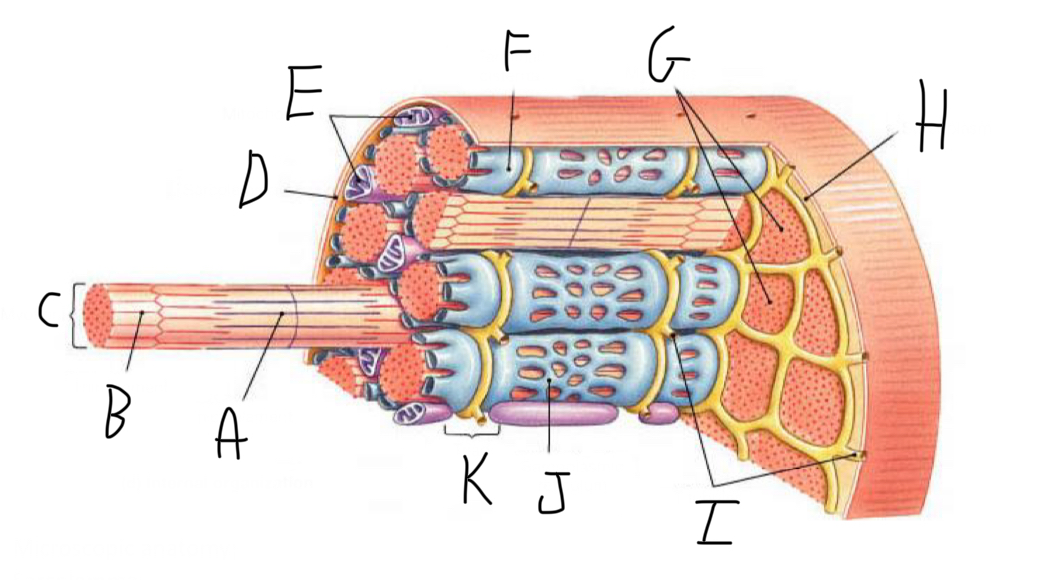
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is A?
Periosteum
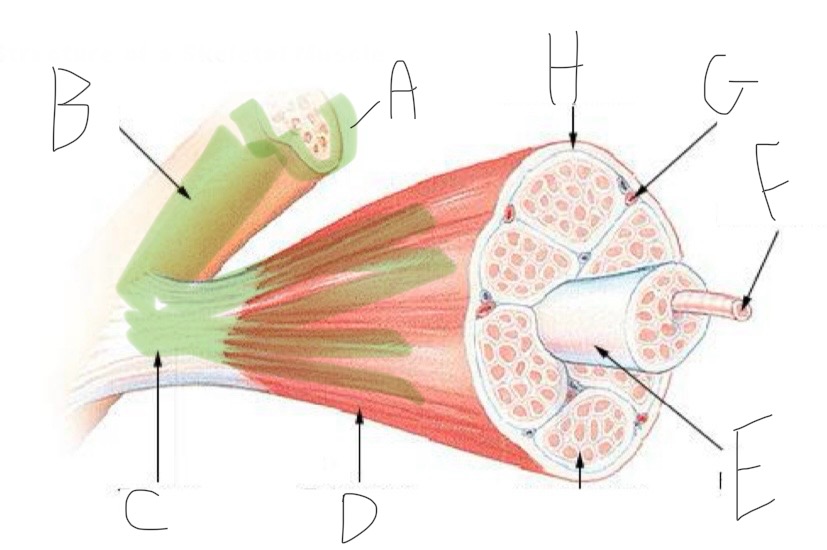
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is B?
Bone
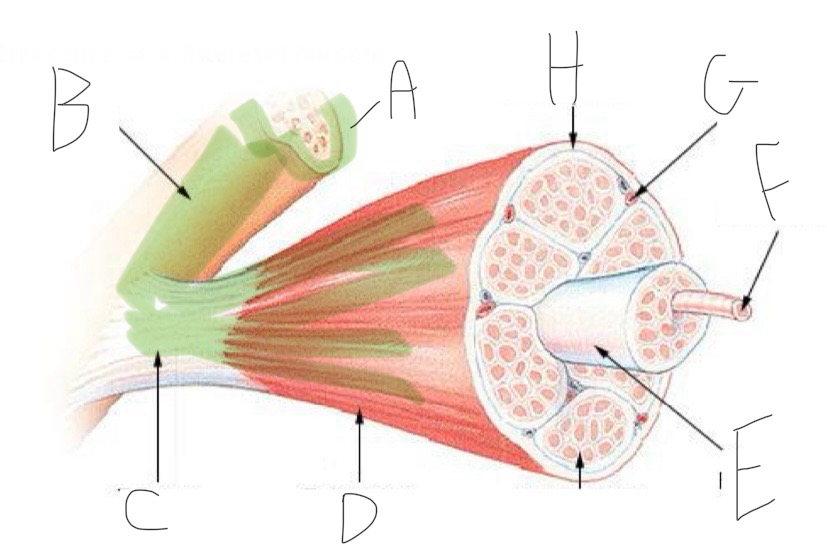
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is C?
Tendon
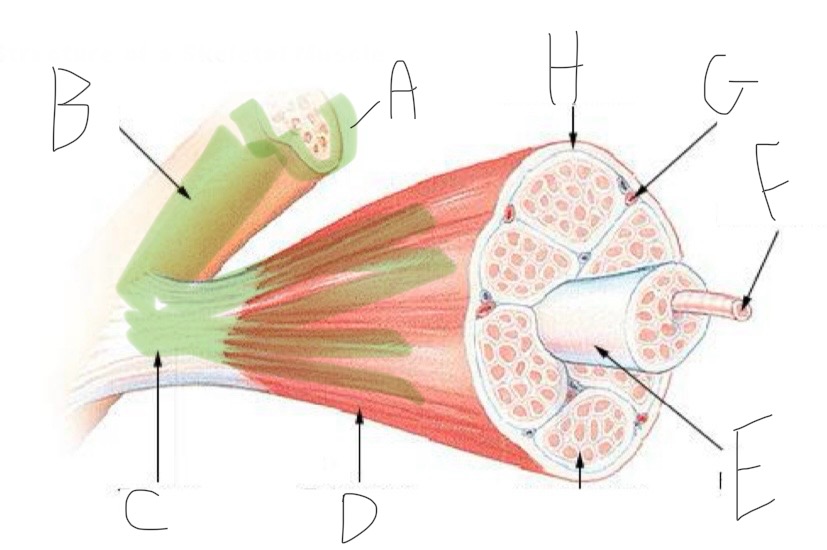
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is D?
Fascia
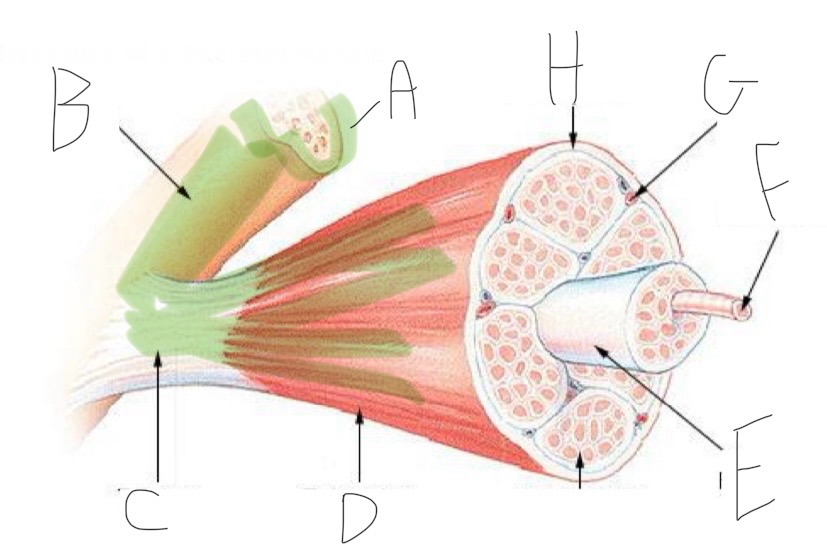
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is E?
Fascicle bound by perimysium
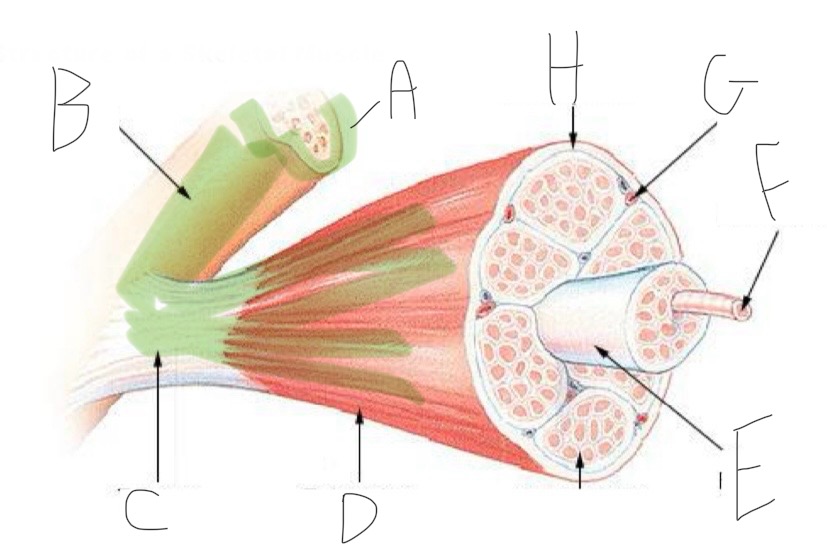
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is F?
Muscle cell/fiber
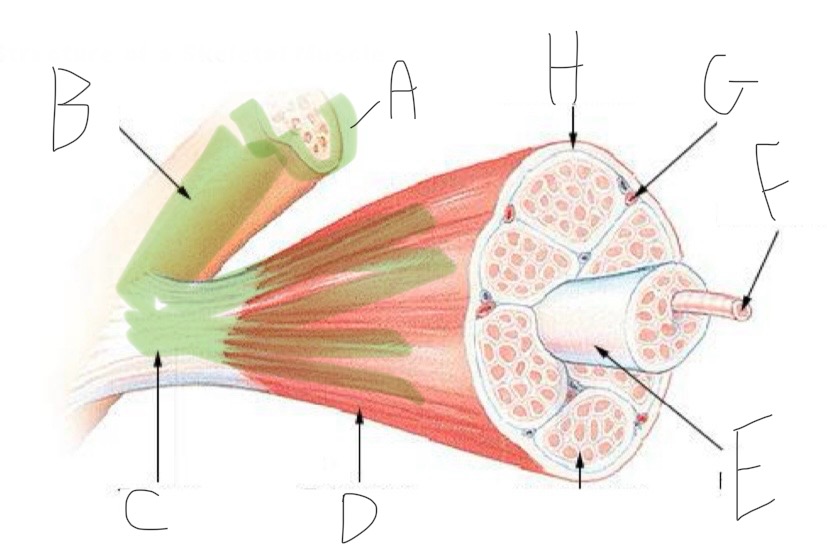
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is G?
Blood vessels + nerves
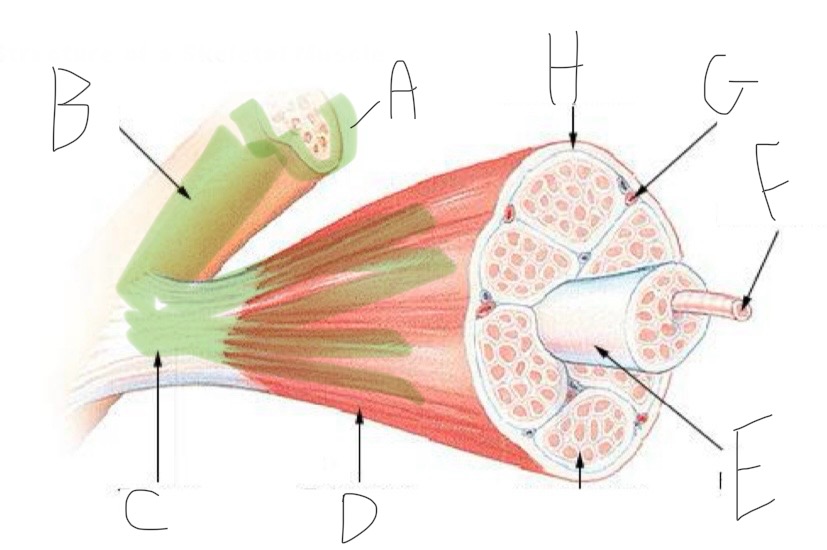
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is H?
Epimysium (surrounds muscle)
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is A?
nucleus
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is B?
Endomysium - surrounds individual muscle cells
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is C?
Sarcolemma (cell membrane of muscle cell)
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is D?
Myofibrils (cytoskeleton w/ contractile elements)
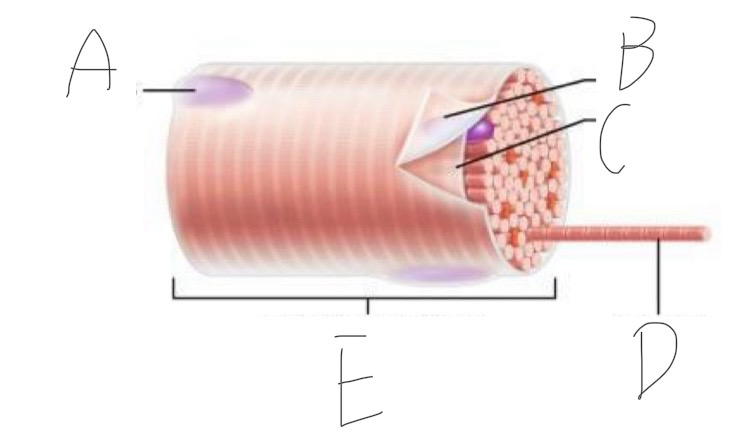
Skeletal Muscle Structure: What is E?
Part of a muscle cell (muscle fiber)
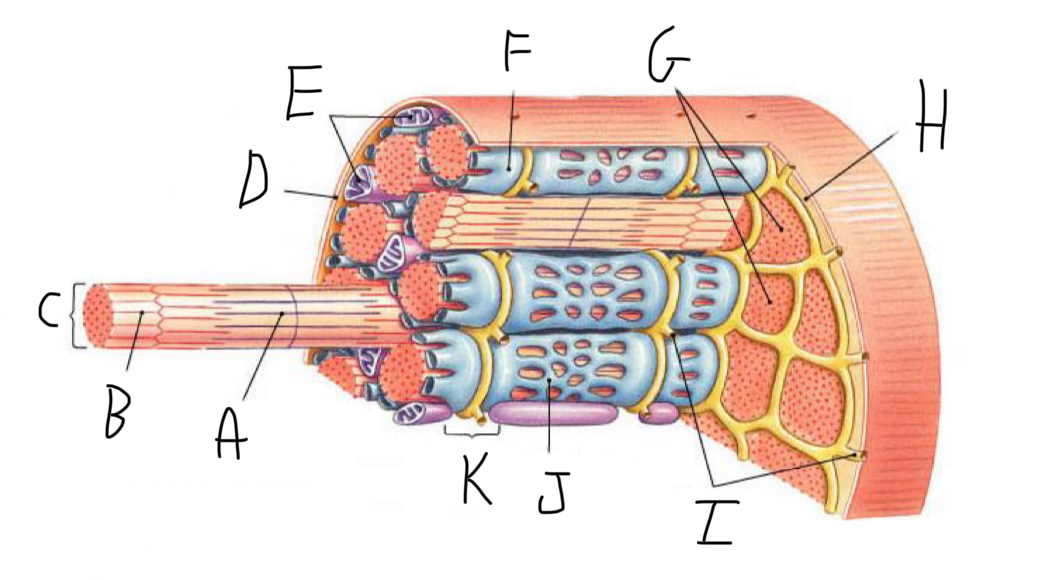
Closer look: What is A?
Thick Filament
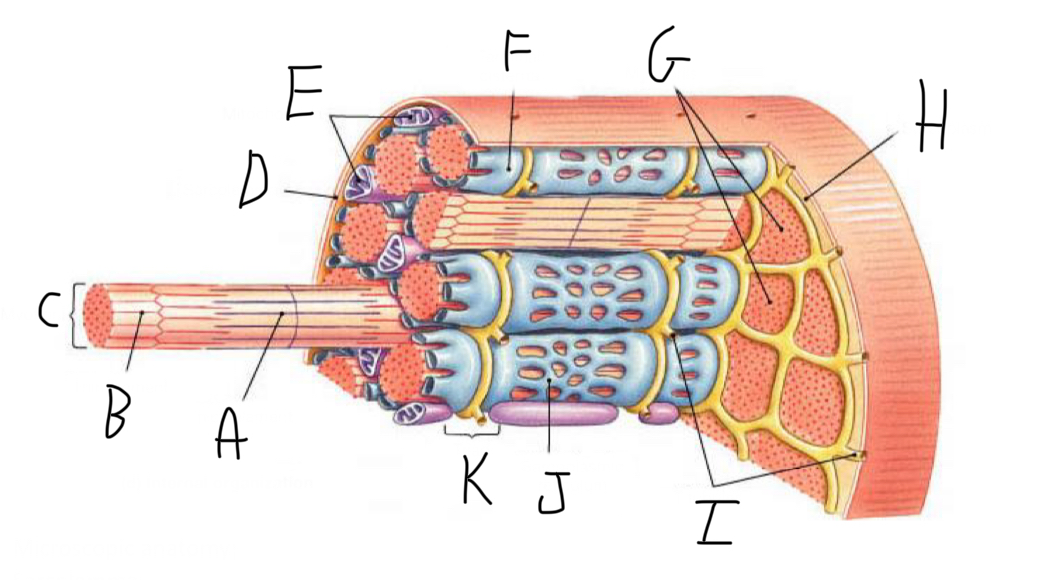
Closer look: What is B?
Thin Filament
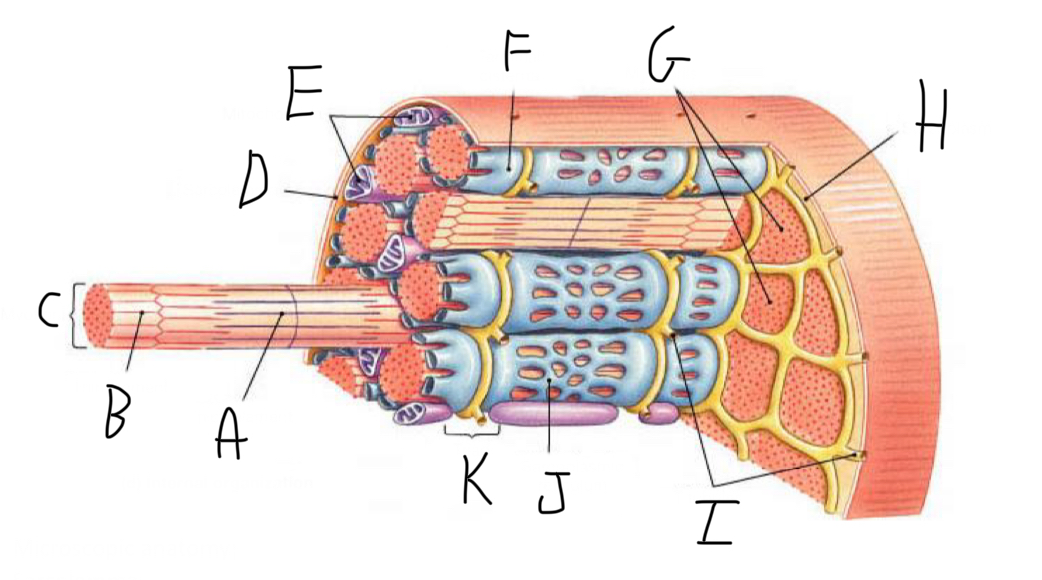
Closer look: What is C?
Myofibril (part of cytoskeleton + contractile)
Closer look: What is D?
Sarcolemma (cell membrane + forms t-tubules)
Closer look: What is E?
Mitochondria
Closer look: What is F?
Terminal Cisterna (In sarcoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER of muscle cell) - stores Calcium)
Closer look: What is G?
Myofibrils (part of cytoskeleton + contractile)
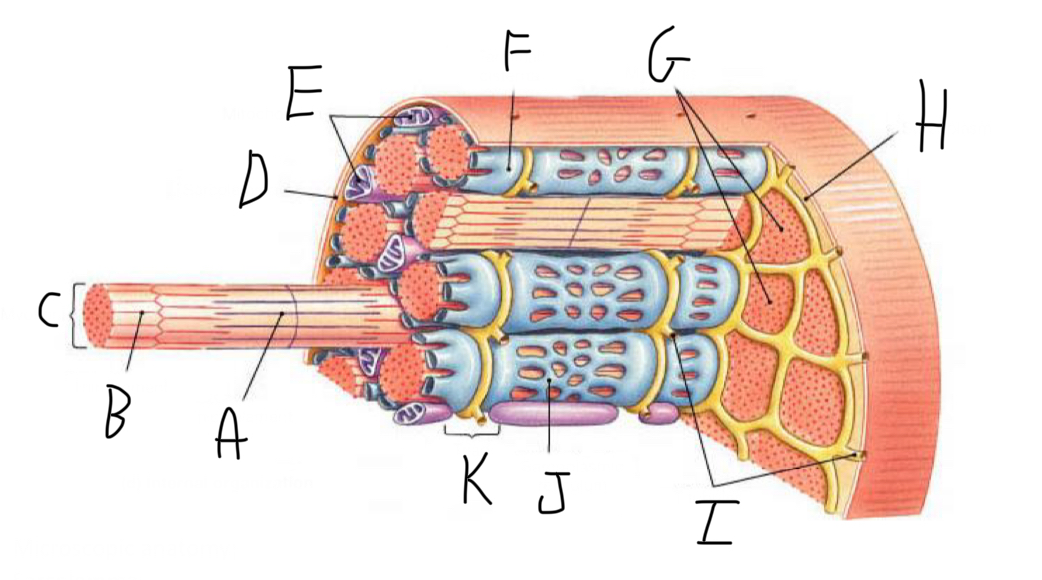
Closer look: What is H?
Sarcoplasm (cytoplasm of striated muscle)
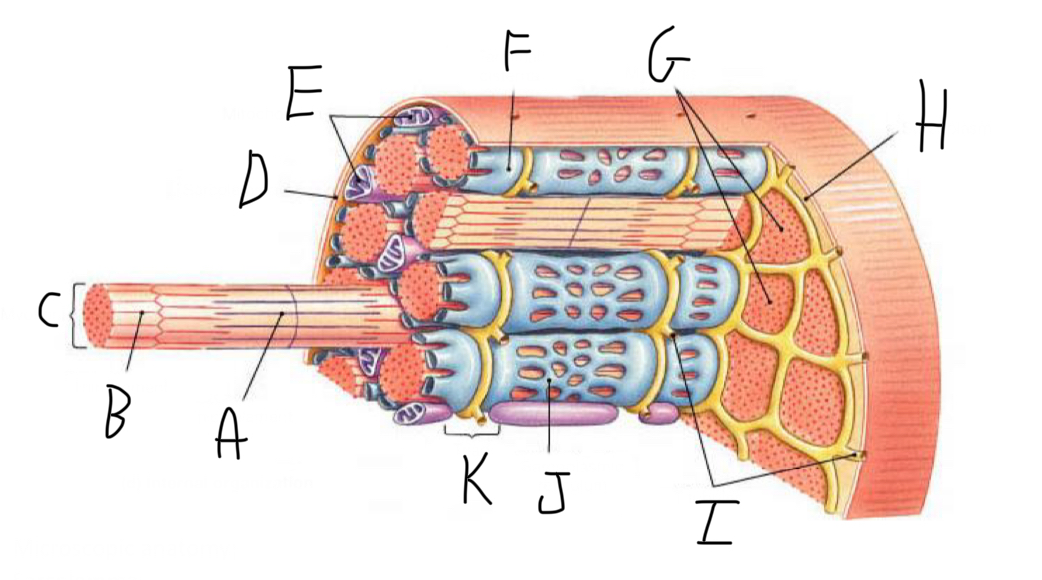
Closer look: What is I?
T-Tubules - transmit electrical signals (action potentials) from the cell surface to the interior, ensuring rapid and coordinated muscle contraction. + release calcium ions
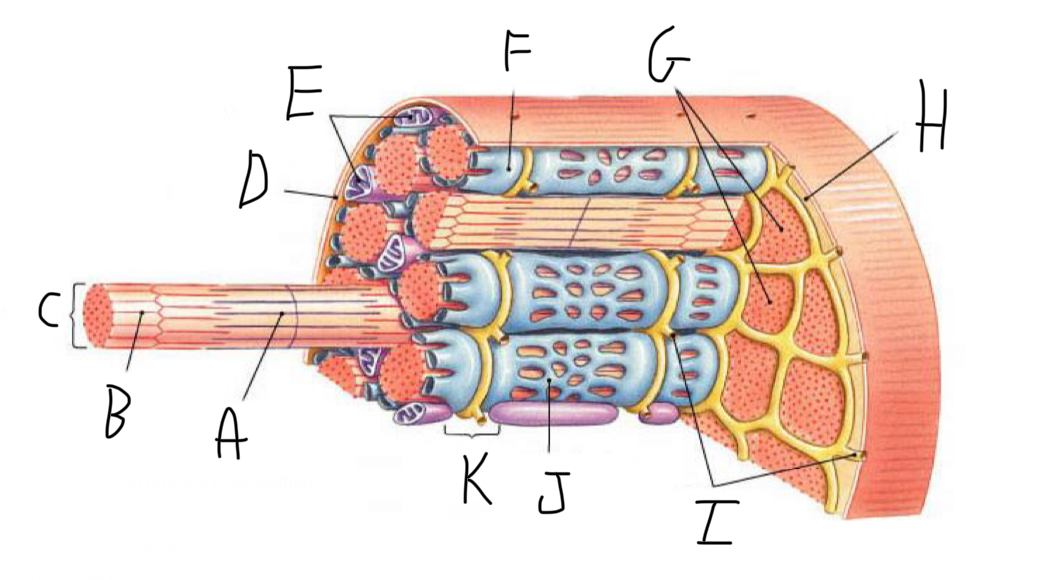
Closer look: What is J?
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (smooth ER of muscle cell)
What is muscle contraction?
the shortening of sacromeres
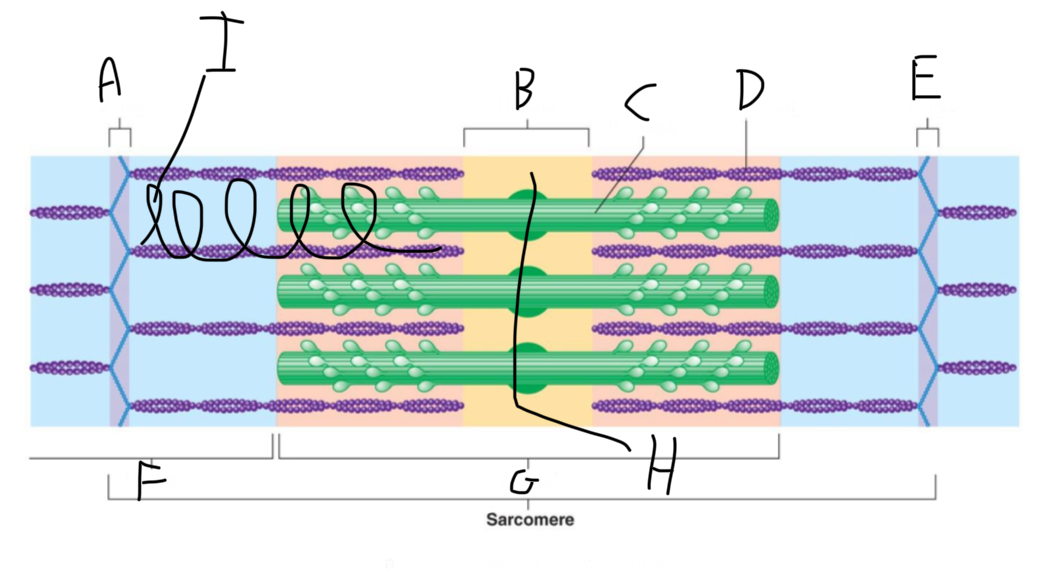
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter A?
Z Disc (anchors thin filaments)
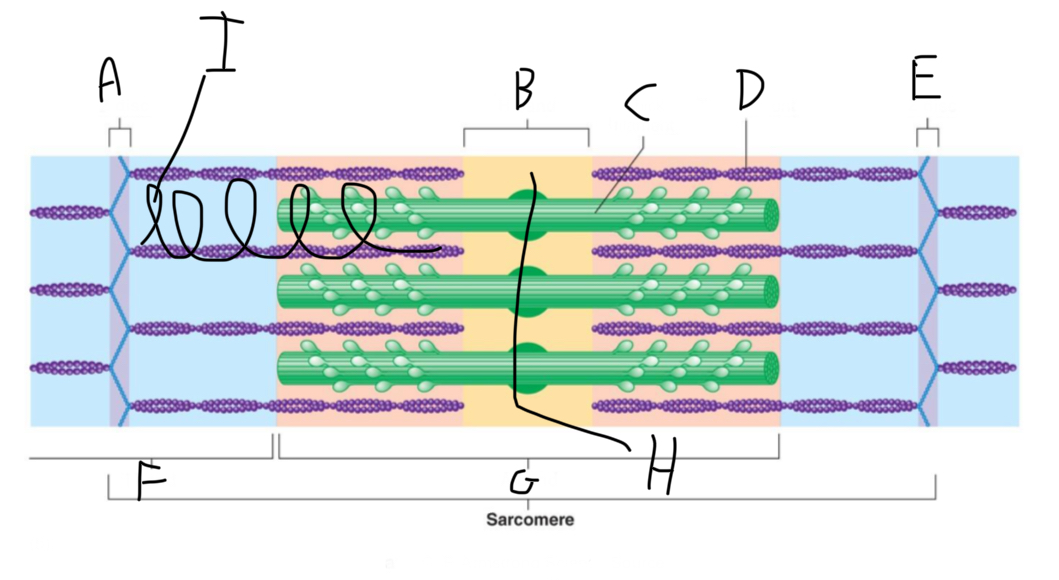
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter B?
H band
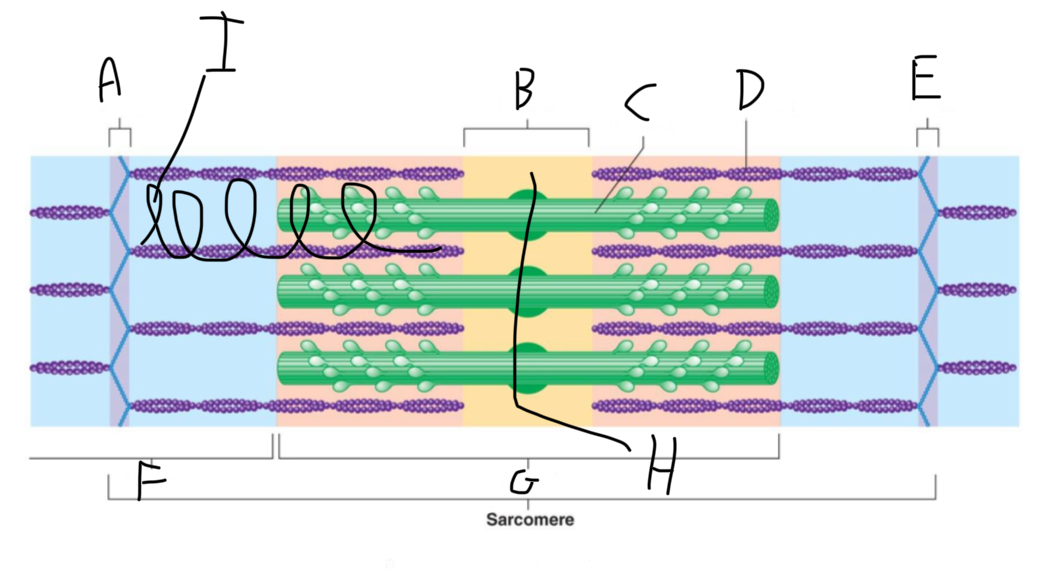
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter C?
Thick Filament
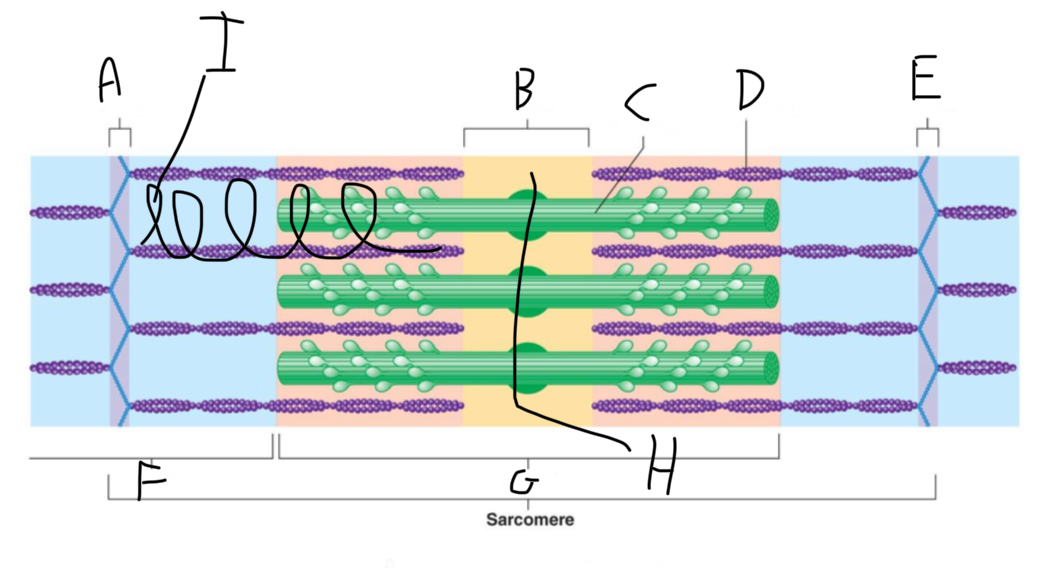
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter D?
Thin Filament
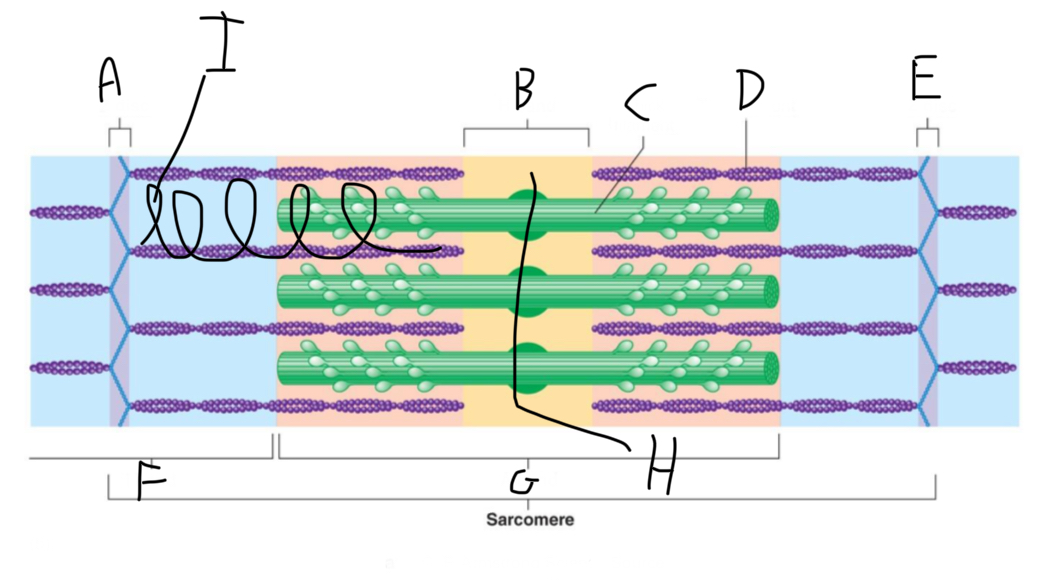
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter E?
Z disc (anchors thin filaments)
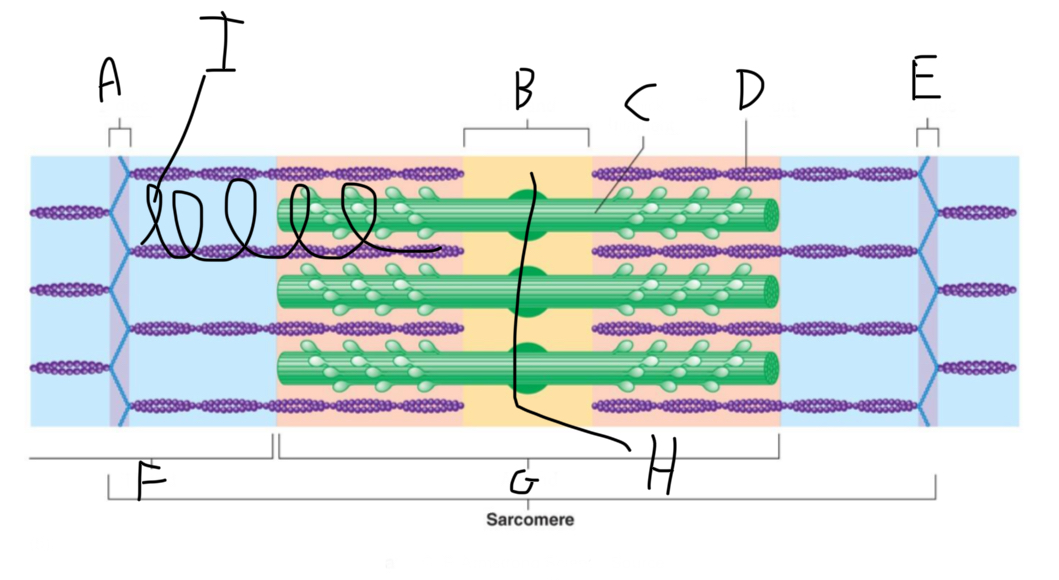
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter F?
I band (shortens and disappears)
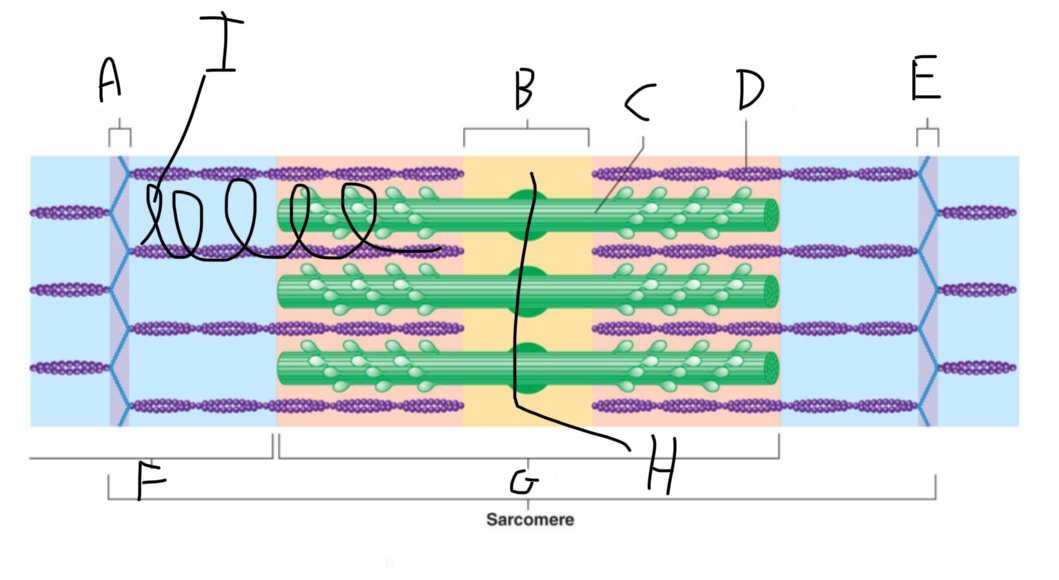
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter G?
A band - Constant
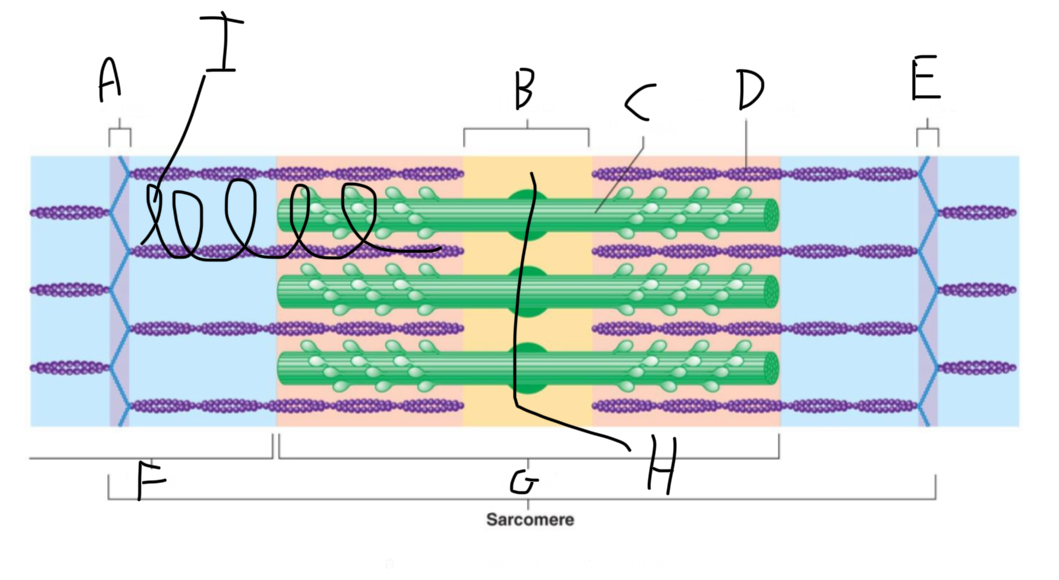
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter H?
Mid-line (centers + attaches to thick filaments)
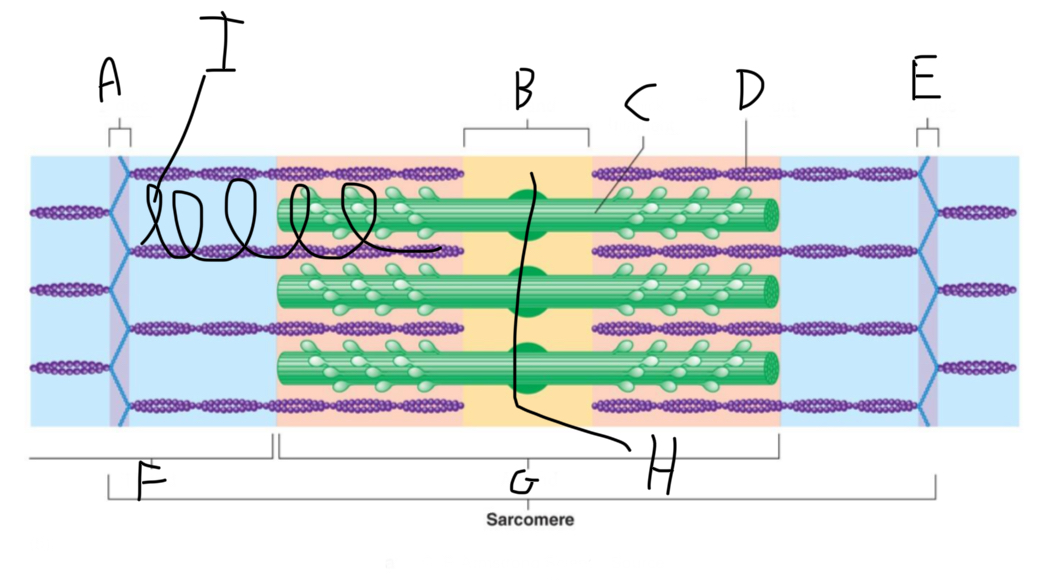
Sarcomere Structure: What is letter I?
Elastic filament
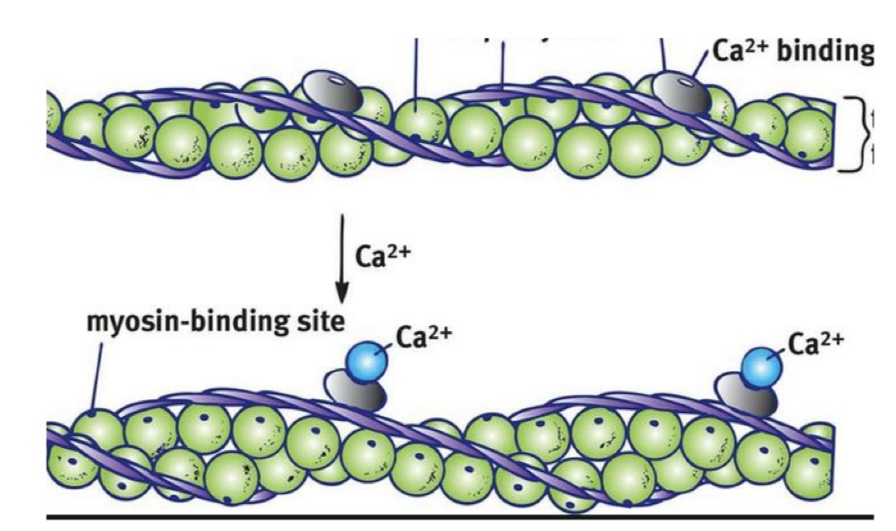
Thin Filament: What are the green balls?
G-Actin with myosin binding sites that expose themselves when excited
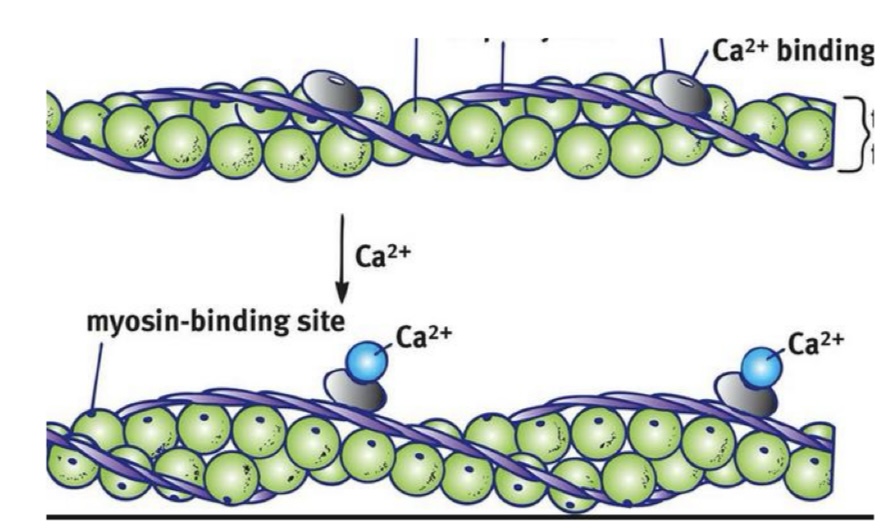
Thin Filament: What is F-Actin?
resembles 2 strands of G-Actin
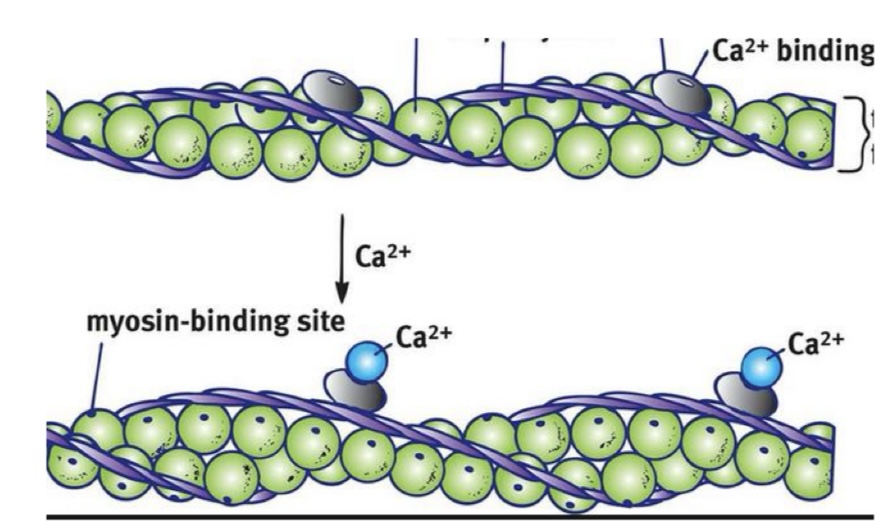
Thin Filament: What are the silver plates?
Troponin with calcium binding sites —> exposes myosin binding sites
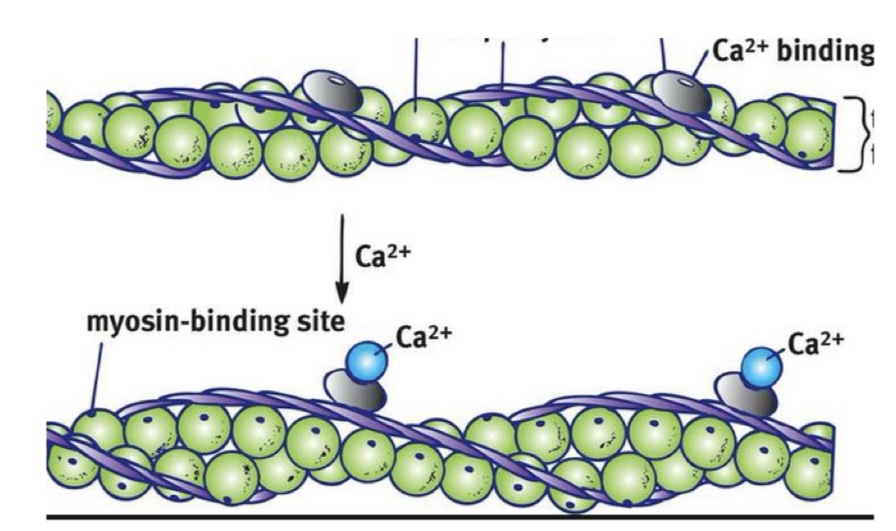
Thin Filament: What are the purple ropes?
Tropomyosin
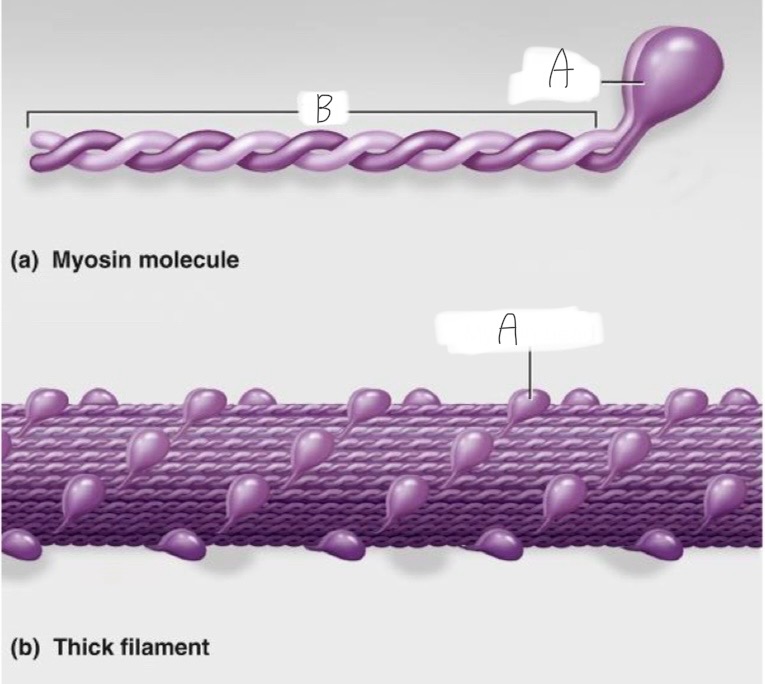
Think Filament: What is A?
Head - actin and ATP binding site
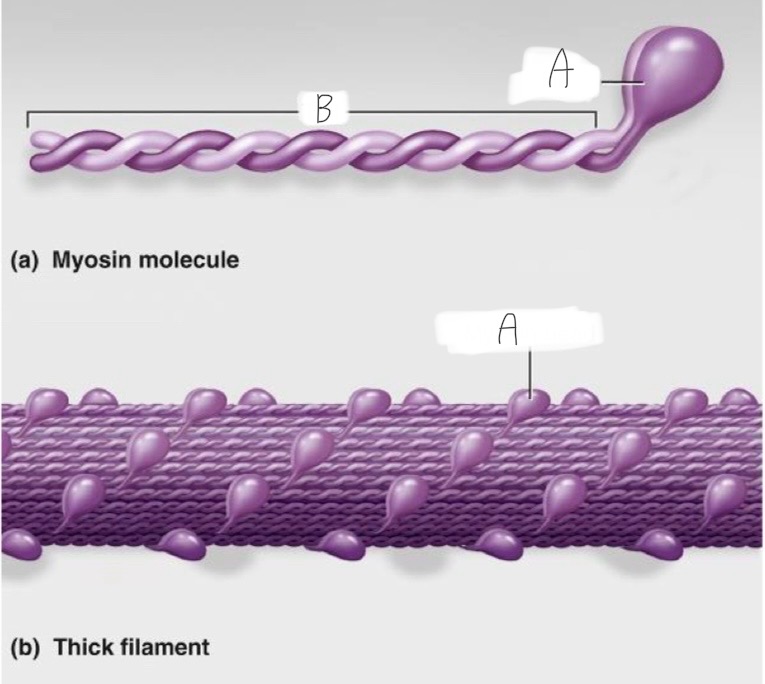
Thick Filament: What is B?
The tail
Why is skeletal muscle striated?
The arrangement of thick and thin fillaments
ATP
Universal energy carrier
ADP
Free energy
ATP in muscle contraction
ATP first binds to myosin, moving it to a high-energy state. The ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) by the enzyme ATPase. The energy released during ATP hydrolysis changes the angle of the myosin head into a “cocked” position. Rigamortis is because the depletion of ATP production
Stimulus
chemical or physical change in the environment that triggers some sort of the behavioral change in a living organism
Motor Unit Recruitment
Number of motor units activated —> determines strength of contraction
Fatigue
a physiological state characterized by a decline in muscle force and endurance
Muscle Twitch
Single contraction in response to a single stimulus
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter released at the skeletal muscle neuromuscular junction
How skeletal muscles relax
Calcium pumped back into SR, sites covered
Oxygen binding protein in muscle cells
myoglobin