comp ah
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
ARM assembly language supports two types of comments.
false
If the processor requests data that is available in the cache, it is returned quickly. How do we call it?
cache hit
Store 0x87664422 into memory using little-endian fashion
0 = 22, 1 = 44, 2 = 66, 3 = 87
Store 0x87664422 into memory using big-endian fashion
0 = 87.1 = 66, 2 = 44. 3 = 22
Commonly used operands are stored in registers. True/False?
True
This status flag shows 1 when instruction causes an overflow
V
This status flag shows 1 when instruction causes an Negative
N
This status flag shows 1 when instruction causes an Zero
Z
This status flag shows 1 when instruction causes an Carry
C
BIC r0, r1, r2 performs
it computes r1 AND NOT r2, and stores the result into r0
Specific arrangement of registers, memories, ALUs, and other building blocks to form a microprocessor is _
Microarchitecture
The memory address is the base register value. An offset is added or subtracted from the base register value and the result is written back to the base register. What type of indexing is this?
Postindex
The memory address is formed in the same way as for offset addressing. The memory address is also written back to the base register. In other words, the base register value is incremented or decremented by the offset value. The exclamation point signifies
Preindex
For this addressing method, indexing is not used. An offset value is added to or subtracted from the value in the base register to form the memory address.
Offset
What is the third level of memory hierarchy?
Hard drive
What is the second level of memory hierarchy?
main memory (physical memory)
What addressing mode is used for indexing?
displacement
The instruction sets of different architectures are more likely different dialects than different languages. True/False?
true
This addressing mode requires only one memory reference and no special calculation. About what type of the addressing mode do we talk?
direct
The condition flags are stored in the LSB of the CPSR
false. it stored in MSB of CPSR
You are given the code in a high-level language: a = mem[3]. Write this code in the ARM assembly language. Assume that the variable a is stored in register r0.
mov r1, #0 LDR r0, [r1, #12]
Inputs for the operation are called
operands
It is used to translate a code written in a high-level language into a machine code
compiler
If the processor requests the data from main memory, how do we call it?
cache miss
Operation is determined by a binary code, known as
operation code or opcode
ARM architecture represents each instruction as
32-bit word
digital systems that read and execute machine language instructions
Microprocessors
• Humans consider reading machine language to be tedious, so we prefer to represent the instructions in a symbolic format called
assembly language.
Almost all architectures define basic instructions such as add, subtract, and branch that operate on memory or registers.
true
Each assembly language instruction specifies both the operation to perform and operands on which to operate.
true
ARM assembly language supports only single-line comments.
true
The ARM architecture has 16 registers called
register set or register file
In the ARM architecture, data stored in memory must be moved to a register before it can be processed.
true
ARM and most other architectures use ___________ to skip over sections of code or repeat code.
branch instructions
Branches can be unconditional or conditional. Branches are also called jumps in some architectures.
true
Memory system performance metrics
miss rate, hit rate, AMAT(average memory access time)
In this type of shift operation, the data are treated as a signed integer and the sign bit is not shifted.
Arithmetic shift right
What is the type of addressing mode given by the algorithm Operand = A?
immediate
What is the type of addressing mode given by the algorithm EA = A?
direct
What is the type of addressing mode given by the algorithm EA =(A)?
indirect
What is the type of addressing mode given by the algorithm EA =(R)?
register indirect
What is the type of addressing mode given by the algorithm EA = R ?
register
What is the type of addressing mode given by the algorithm EA = A + (R) ?
displacement
load register instruction, (LDR)
to read a data word from MEMORY into a REGISTER
store register instruction, (STR)
to write a data word from a REGISTER into MEMORY.
No left rotation instruction
true
one that may be referenced by means of the machine language that the processor executes.
user-visible register
Advantages: 1) No memory reference to obtain the operand 2) Size of the number is restricted to the size of the address field.
Immediate addressing
It requires only one memory reference and no special calculation. It provides only a limited address space.
Direct addressing
The disadvantage is that instruction execution requires two memory references to fetch the operand: one to get its address and a second to get its value.
Indirect addressing
Advantages: 1) Only a small address field is needed in the instruction 2) No time-consuming memory references are required Disadvantage: the address space is very limited
Register addressing
Register indirect addressing uses one less memory reference than indirect addressing.
Register indirect addressing
Common uses of displacement addressing
Relative addressing, Base-register addressing, Indexing
You are given: r1 = 0100 0110 1010 0001 1111 0001 1011 0111, r2 = 1111 1111 1111 1111 0000 0000 0000 0000. What is the result of BIC r6, r1, r2?
0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 0001 1011 0111
Shifting a value left by N is equivalent to multiplying it by 2^N (logic shifting)
true
Arithmetically shifting a value right by N is equivalent to dividing it by 2^N
true
ARM includes two types of branches:
Simple branch (B) , Branch and link (BL)
the average time a processor must wait for memory per load or store instruction.
Average memory access time (AMAT)
The relationship between the address of data in main memory and the location of that data in the cache is called ______
mapping
What is Nibble?
4 binary digits in symbols(1010=A…,1111=F)
Reasons to use hexadecimal notation:
1)compact
2)used in most computers
3)extremely easy
ALU
Digital logic devices that can store binary digits and perform Boolean logic operations

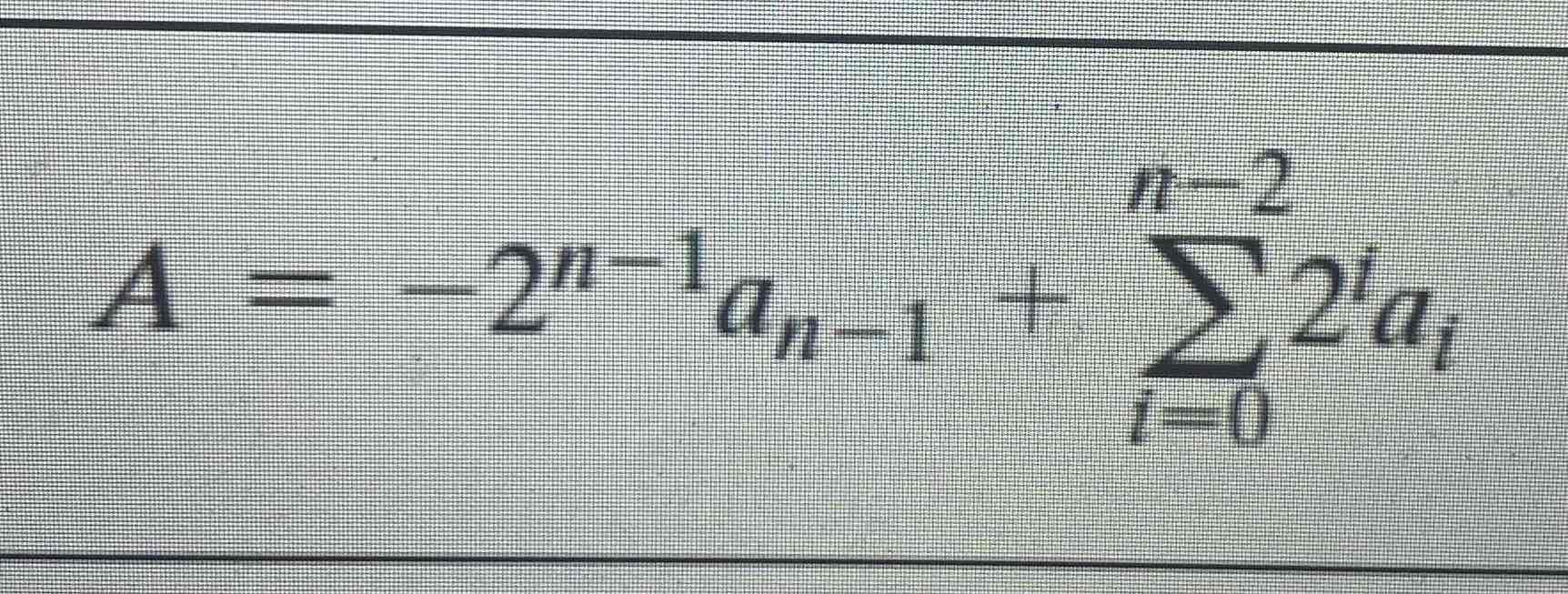
Range extension
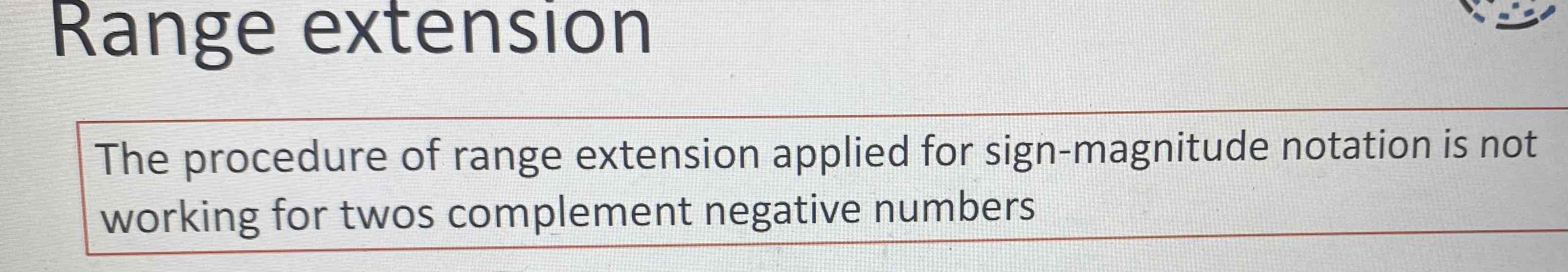
Range extension
1) for (+) numbers:move to leftmost position and fill with zeros
2) for (-) numbers:move to leftmost position and fill with ones
Overflow Rule:
If two numbers are added, both(+) or (-), then overflow occurs if and only if the result has the opposite sign
Commutative Law
A•B = B•A
A+B = B+A
Distributive Law
A•(B+C) = (A•B) + (A•C)
A+(B•C) = (A+B) • (A+C)
Identify Elements
1•A=A
0+A=A
Inverse Elements
A•~A=0
A+~A=1
0•A=?
1+A=?
0•A=0
1+A=1
Associative Law
A•(B•C)=(A•B)•C
A+(B+C)=(A+B)+C
DeMorgan’s Theorem
(A*B)’=A’+B’
(A+B)’=A’•B’
List the ways of defining a combination logic circuit :
Truth table, graphical symbols, Boolean functions
Program counter contains?
Address of the next instruction
Positional number system
Each number represented by string, has weight r^i (r=radix, base of the system )
Combinational logic circuit
Interconnected set of gates (output=input)
Sequential circuits
output=input+history of input
Multiplexer
Multiple input= single output
Decoders
Only one output asserted at any time
Demultiplexer
Inverse multiplexer, single input =several output
Flip-flop
Bistable device, 1-bit memory, 2 output =Q and Q’
Parallel register
1-bit memory written simultaneously
Serial register
And/or information serially 2^n-1
Memory arrays
used to store large amounts of data.
The row is specified by an…
Address.
The value read or written is called
Data
Each row of data is called as
word
The depth of an array is the number of rows. The width of an array is the number of columns. The size of an array is given as depth x width.
true
Memory arrays are built as an array of ________, each of which stores 1 bit of data.
bit cells
All memories have one or more ports. In _________case, each port gives read and/or write access to one memory address.
singleported memory