Lecture 20: Yersinia spp.
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are the characteristics of Yersinia spp?
Gram _
Shape?
Ferment Lactose?
Motility?
Unique Features?
Gram -
Non-lactose fermenter
Bipolar Rods
Motile
Except for Yersinia pestis
Psychrophilic
Able to withstand extreme low temperatures
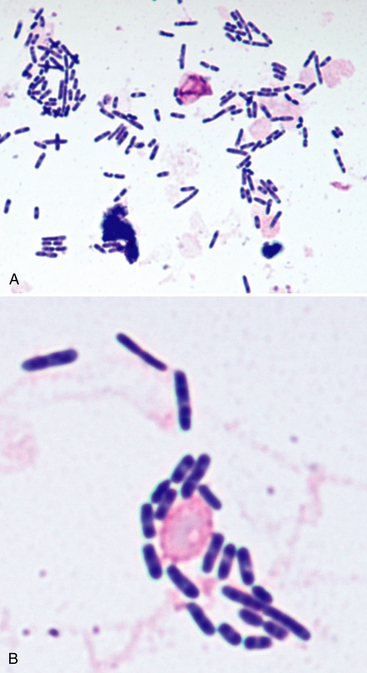
What are the 4 Yersinia species of veterinary importance?
Y. pestis
Y. pseudotuberculosis
Y. enteriocolitica
Y. ruckeri
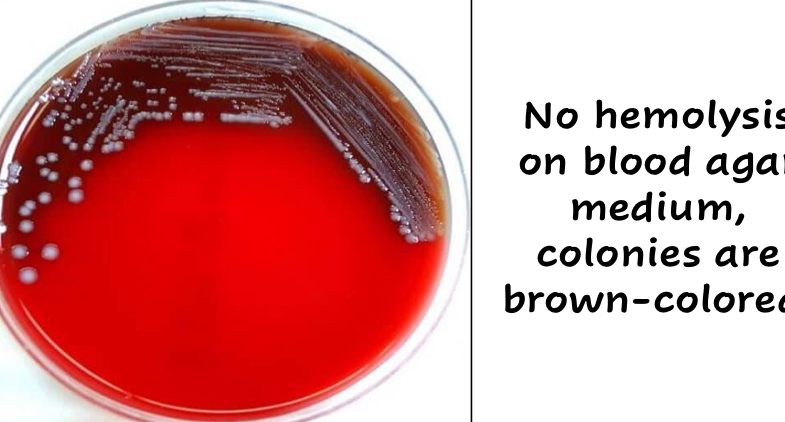
What unique feature does Yersinia spp. have when they grow on BAs?
They produce dark brown colonies due to the absorption of hemin
Yersinia pestis is a primary pathogen that causes what well known disease?
The plague
Yersinia are Psychrophilic, what does this mean?
They can grow in extremely cold temperatures
What is the optimal growth temperature for Yersinia pestis?
27°C
T/F: Yersinia pestis is zoontic
True
What is the reservoir and vector of Yersinia pestis?
Reservoir
Wild rodents
Vector
Rat flea
T/F: There is a human vaccine for Yersinia pestis
False
What plasmids allowed Yersinia pestis to adapt to flea-borne transmission?
Phospholipase-D
Pla protease
Cell surface protease/plasminogen activator
How did Yersinia pestis become a pandemic pathogen?
A single amino acid modification in Pla protease
It caused increased invassiveness/dissemination and transmissability
Yersinia pestis contains 3 virulence plasmids unlike any other Yersinia species, what are they?
Plasmid pMT1
Plasmid pPCP1
Plasmid pYV
Present in all Yersinia spp.
Injects effector proteins called Yops into host cell
Alters the cell functions and Kills PMNs and macrophagfes
Chromosomally encoded virulence factors
High pathogenicity Island (HPI)
Creates biofilm that prevent defgradation via the flea proventriculus
What are the 2 different ways that Yersinia pestis transmits via fleas?
Mechanical transmission
Biological transmission
Y. pestis replicates in the flea digestive tract
Dependent on the fleas ability to form a biofilm in the proventriculus (High Pathogenicity Island (HPI))
What are the different ways that humans can be infected with Y. pestis? Which is the main way?
Bitten by an infected rodent
Bitten by an infected flea
Human-Human aerosol transmission
What are the 3 forms of the plague? Briefly describe each
Bubonic
Infection of the L.Ns
Most common, least fatal
Septicemic
Infection of the blood
Can cause massive septicemia, endotoxin shock, DIC
Pneumonic
Infections of the lungs
Most severe form
100% mortality if untreated
T/F: Y. pestis is an eliminated disease
False, it is a re-emerging infectious disease
T/F: Y. pestis is endemic in some areas of the U.S
True
What is the general life cycle of Y. pestis in the US today?
Wild rodents exist as reservoirs
Fleas transmit Y. pestis among wild rodents
Humans/cats are at risk from
Flea bites
Rodent contact
Aerosols
Humans are mainly infected by cats
T/F: Dogs are immune to Y. pestis
False, they are more resistant but can still be infected
What 2 wild animals were decimated by the arrival of the Sylvatic Plague in NA?
Prairie dogs
Black-footed ferrets (predator of Prairie dogs)
Black-footed ferrets almost went extinct
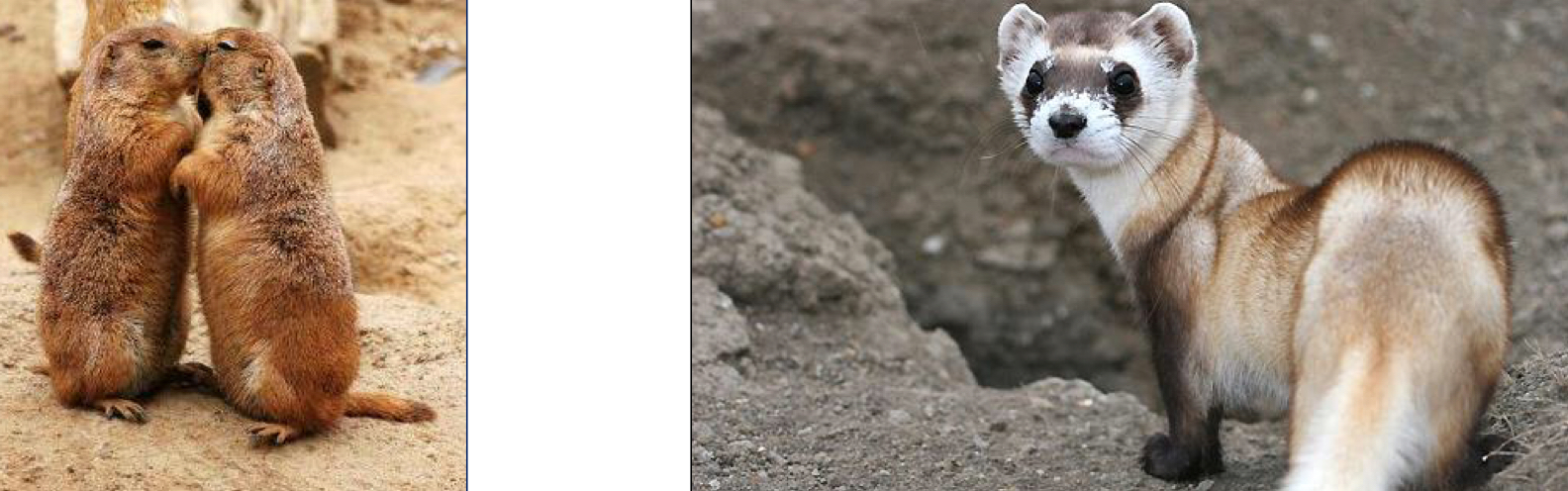

How did we attempt to save the black-footed ferret from Y. pestis?
Dropping vaccine-laced penut butter pellete via drones to be eaten by prairie dogs
What are signs of Feline Plague?
High fever
Vomiting
Tachycardia
DIC
Submandibular lymphadenopathy with a draining abscess

Why is it Important to diagnose Feline plague?
It is zoonotic and cats have very close contact to humans (cat bites can spread it to humans)
Yersinia pseudotuberculosi and Yersinia enterocolitica have what Virulence plasmid?
Plasmid pYV
Type III secretion system
Yersinia enterocolitica
Important/unique features
Primary reservoir
Unique Features
Foodborne pathogen
Psychrophilic (can grow at 4°C)
Survives in fridge for extended periods of time
Pigs are the primary reservoirs
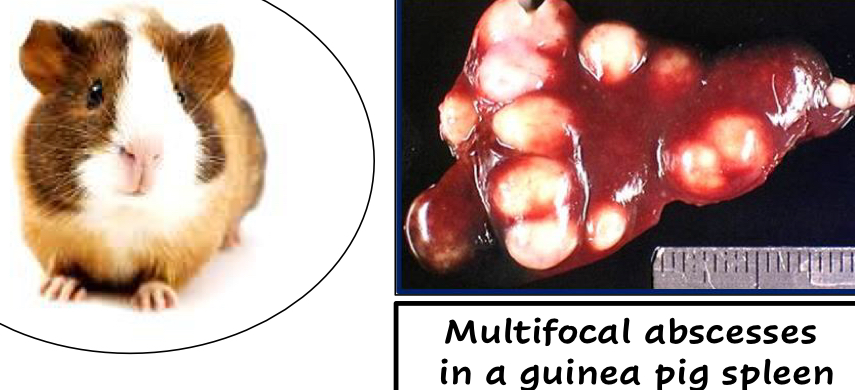
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
Species it infect?
Gross lesions?
Primarily a Rodent and Deer pathogen
Also infects cattle, humans, birds
Micro-abscesses, abscesses, septicemia
Which Yersinia spp. is an Important food-borne pathogen?
Yersinia enterocolitica
Which Yersinia spp. causes “Yersiniosis” in deer?
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
Important disease in commercial farmed deer
What are the C.S of Yersiniosis in deer?
Severe hemorrhagic gastroenteritis
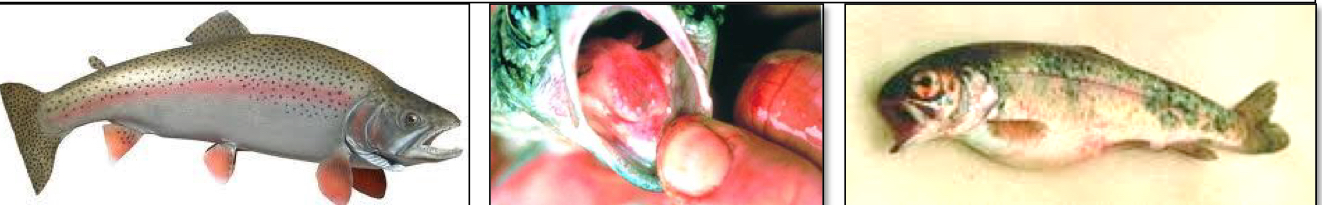
Yersinia ruckeri causes disease in what species? C.S?
Fish (Rainbow trout and Atlantic salmon)
Subcutaneous hemorrhaging of the mouth, fins, and eyes
Yersinia pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. enterocolitica are all invasive enteric pathogens transmitted by fleas. T or F?
False, Y. pestis is only flea transmission
Yersinia pestis sylvatic plague is classified by the WHO as a re-emerging infectious agent that is present only in North America. T or F?
False, it’d found a lot of places
Rodents and their fleas are important reservoirs of sylvatic plague in North America. T or F?
True
A veterinarian is only at risk of Yersinia pestis infection if bitten when handling a cat with undiagnosed plague. T or F?
False
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is a rodent pathogen that can also infect other animals and humans. T or F?
True
Pigs are the primary reservoirs for Yersinia enterocolitica. T or F?
True