L10 Touch and pain
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
The skin is the largest what ?
sense organ in the body
Area of skin
1.8m^2
Weight of skin
5kg
What are the two types of skin (examples)?
Glabrous skin (palms, soles) and hairy skin (everywhere else).
What two parts of the brain are skin sensation signals processed?
The primary somatosensory cortex and secondary somatosensory cortex.
What body part do signals travel via to reach the brain
spinal cord
Receptors are sensitive to what 4 senses
touch, pain, body sense and temperature
What is a receptive field?
The area of skin that a specific sensory neuron responds to
What are the 4 types of tactile receptors
merkel’s disc, Meissner corpuscle, ruffini organ and Paccinian corpuscle
What does Merkel's disc detect?
Fine details (e.g., reading Braille).
What does Meissner's corpuscle detect?
Flutter (e.g., objects slipping through fingers).
What does the Ruffini organ detect?
Skin stretching and pressure (e.g., picking up objects).
What does Pacinian corpuscle detect?
Vibration, deep-pressure and fine textures (e.g., using tools)
Why are there multiple tactile receptors?
To detect diverse types of sensory information as a single stimulus can activate many different receptor systems
This suggest that the skin sense is a single or group of senses?
group of senses
Which tactile receptors have larger receptive fields
Paccinian corpuscles
What is two-point discrimination?
The smallest distance at which two stimuli are perceived as separate
Two-point discrimination differencing finger tip vs arm
2mm vs 3.5cm
2 explanations for two-point discrimination
number of receptors and amount of cortex in the primary somatosensory cortex
What body area has the highest number of receptors per square cm?
Fingertips, also known as the "fovea" of the skin
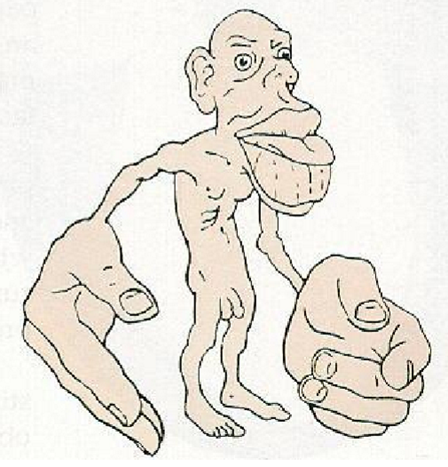
What is the homunculus representation?
Areas with more receptors occupy larger portions of the somatosensory cortex
3 places we are most sensitive
lips, hands and face
Acuity of tactile perception on fingertips can change with what ?
experience
What is active touch?
Actively exploring objects with movement.
What is passive touch?
Perceiving sensations while body is stationary.
2 reasons why is active touch advantageous?
Allows exploration of diagnostic object features and engages kinesthetic senses
2 cues to perceiving texture
spatial cues and temporal cues
What are spatial cues in texture perception?
Bumps and grooves felt through stationary or moving contact
What are temporal cues in texture perception?
signals detected during finger motion
Which receptor aids in texture perception?
Paccinian corpuscles
What is tactile agnosia?
Inability to identify objects through touch despite normal spatial processing (can describe it)
What is tactile extinction?
Difficulty perceiving multiple simultaneous touches without impairing object recognition
What two brain regions are responsible for object identification
primary and secondary somatosensory cortex
What is the superior parietal area responsible for
spatial localisation of an object
3 top-down influences on touch
must update, emotional effect, expectation
What is Aristotle's illusion?
Crossing fingers makes one object feel like two.
What is the cutaneous rabbit effect?
Widely spaced taps perceived as evenly spaced jumps.
Why does tickling oneself feel less ticklish?
Predicting one's actions reduces perceived ticklishness.
What are nociceptors?
Specialized receptors for detecting pain
What are the two types of pain fibres and their respective type of pain?
A delta fibers (fast, sharp pain) and C fibers (slow, dull pain).
Both systems can be activated by ?
the same stimulus
3 modulators on pain
a person’s mental state, absence of stimulation and attention
Control of pain
degree to which painful information reaches the brain
2 ways pain can be reduced by
non-painful tactile inputs (massage, rubbing) or top-down input (expectations etc)
What is phantom limb sensation?
Feeling a missing limb after amputation due to its representation in the brain
What is proprioception
where your body is in space
How does proprioception help body awareness?
Signals from muscles and receptors inform spatial position
What is kinesthesis
movement of the limbs in space