Databases (Flat File & Relational) and SQL
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is a database?
A structured collection of data that stores data in tables.
What is a table?
A collection of records with a similar structure.
What are fields? What do they store?
Fields are the columns and are used to store a specific piece of information
What are records? What do they store?
Records are the rows of the table, a record uses the fields to store details about a specific item.
What does each field in a record have?
A specific data type assigned to it.
What does each table in a database have? What is this?
A primary key. It is a field that can uniquely identify any record in the table. There can only be one primary key field per database table.
What are some key benefits of electronic databases:
Easier to add, delete, modify and update data
Data can be backed up & copied easier
Multiple users, from multiple locations can access the same database at the same time
What are the 2 main types of database:
Flat file database
Relational database
Flat file database
A database that stores all the data in one table.
Flat file pros & cons:
👍Simple to set up
👍Easy to understand
👎Causes data redundancy - inefficient storage
👎Uses more memory or storage than it needs to
👎Takes longer to search for data
👎Harder to maintain
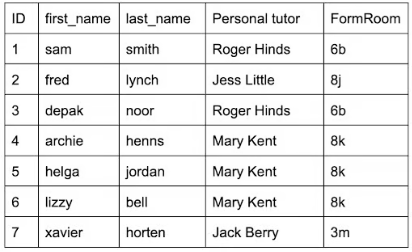
Relational databases
They are made up of multiple tables that are often linked together using primary keys and foreign keys.
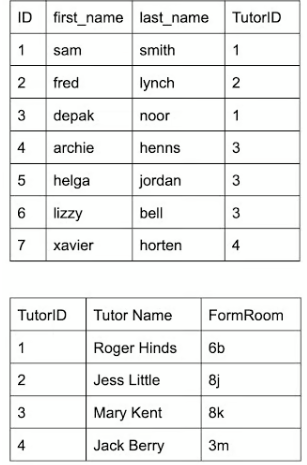
Foreign key
A field that references the primary key of another table - creating a link between the two tables.
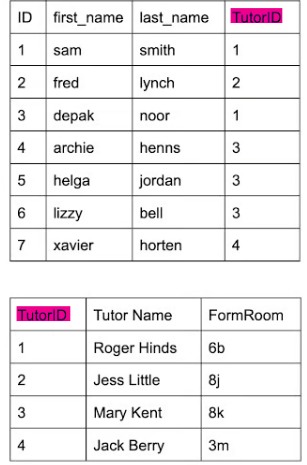
Relational databases advantages:
Data is only stored in one place and then referenced - inputting, updating or deleting data only has to be done in one place - preventing inconsistencies
Only storing the same piece of data once will also save storage space
Are more secure - some tables can be made confidential so only some users can see certain data
Data redundancy definition:
Storing the same data more than once in a database in multiple locations. It will lead to data inconsistency.
Problems with data redundancy:
Wasted storage space
More difficult database update
Will lead to data inconsistency
Retrieval of data is slow & inefficient
Data inconsistency definition:
When the same data exists in different formats in multiple tables. Can cause unreliable & meaningless info.
What is SQL?
Structure Query Language is a programming language used to interact with a database.
What does the use of SQL allow a user to do?
Select data (flat file & relational)
Order data
Insert data
Update data
Delete records
What does the ‘SELECT’ command do?
Retrieves data from a database table.
What does the ‘FROM’ command do?
Specifies the tables to retrieve data from.
What does the ‘WHERE’ command do?
Filters the data that will be displayed based on a specified condition
What does the ‘AND’ command do?
Combines multiple conditions in a WHERE clause.
What does the ‘OR’ command do?
Retrieves data when at least on of the conditions is true.
What is a wildcard command and what does the command do?
* is a wildcard command used to select all fields in a table.
What does the ‘ORDER BY’ command do?
It is used to organise/sort the data into ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order when it is retrieved.
What must all SQL code end with?
a semicolon ‘;’.
How to write a SELECT query:
Use the SELECT keyword followed by the names of the fields you want to retrieve and display. Then, use the FROM keyword followed by the name of the table/tables you want to search. You can also use the WHERE keyword to specify the conditions that a record must satisfy to be returned.
Write a query that will select all the fields from the Customers table:
SELECT*FROM Customers
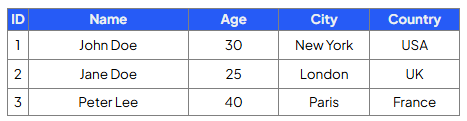
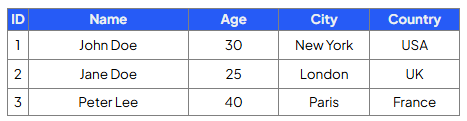
Write a query that will select the ID, name & age of customers who are older than 25:
SELECT ID, name, Age
FROM Customers
WHERE Age > 25;
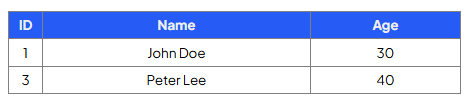
Write a query that will select the name and country of customers who are from the USA:
SELECT Name, Country
FROM Customers
WHERE Country = ‘USA’;

Write a command that orders the records into descending/ascending order:
ORDER BY field DESC
or ORDER BY field ASC
How to add records to a table?
Use the key words INSERT INTO followed by the name of the table & the fields you want to add the records to. Then the the keyword VALUES followed by data you want to add.
e.g.
INSERT INTO users (name, age)
VALUES ('John Doe',25);
(inserts a new user with the name 'John Doe' and age 25)
How to edit data in a database?
Use UPDATE, SET and WHERE. UPDATE followed by the table you want to update, SET followed by the fields you want to change and the values you want to change them to, then use WHERE to specify the condition that determines which records will be updated.
e.g.
UPDATE users
SET name = 'Bob', age = 56
WHERE ID = 4;
(updates name and age details for user ID = 4)
How to remove data from a table:
Use DELETE, FROM and WHERE. DELETE FROM followed by the table you want to delete a record from, then WHERE followed by the condition that determines which records are deleted.
e.g.
DELETE FROM users
WHERE age < 18;
(deletes all users younger than 18 from the 'users' table)
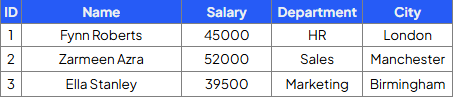
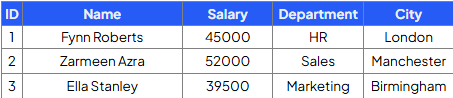
Write a query that will insert a new employee into the Employees table with the ‘Name’, ‘Salary’, ‘Department’ and ‘City’ fields:
INSERT INTO Employees(Name, Salary, Department, City)
VALUES (‘George Rope’, 47250, ‘Sales’, ‘Leeds’)';
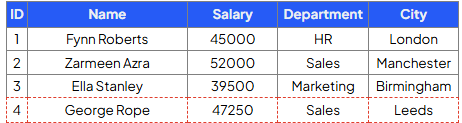
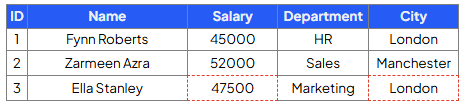
Write a query that will update employee ID 3 to a salary of 47500 and city to London:
UPDATE Employees
SET Salary = 47500, City = ‘London’
WHERE ID = 3';
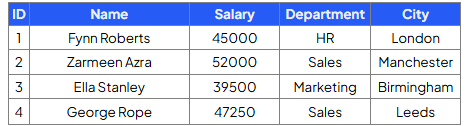
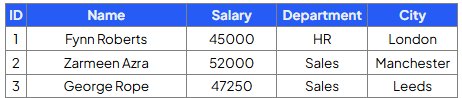
Write a query that will delete all records from the Employees table whose department is ‘Marketing’
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE Department = ‘Marketing’;
How to retrieve data from a Relational database:
SELECT table1.field, table2.field
FROM table1, table 2
WHERE table1.primarykey = table2.foreignkey (table1’s primary key)
AND condition;
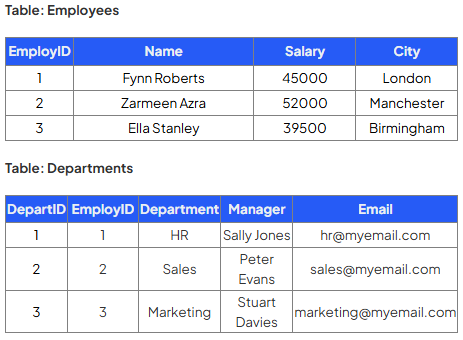
Write a query that selects the name, manager and email address of employees in the ‘Sales’ department:
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.Manager, Departments.Email
FROM Employees, Departments
WHERE Employees.EmployID = Departments.EmployID
AND Department = ‘Sales’;
