space
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
galaxy
gases, dust, billions of stars held together by gravity
nebula vs galaxy
nebula is where stars are born vs galaxy is a large collection of stars
shapes of galaxies
spiral, elliptical, irregular
galaxy characteristics
all spinning and contain large numbers of stars
differ in size mass, brightness, colour, speed of spin
more spin means flatter galaxy
globular clusters
stars held together by gravity in spherical shape
open clusters
have less stars than globular clusters
nebula
large cloud of gas and dust
protostar
earliest stage of a star’s life
a star is born
all stars start as nebulas
gravity can pull some of gas and dust in a nebula together
contracting cloud then called a protostar
a star is born when the gas and dust from a nebula become so hot that nuclear fusion starts
when a star has “turned on: it is known as a main sequence star
when a main sequence star begins to run out of hydrogen fuel, it turns into a red giant or red super giant
star birth order
nebula, protostar, main sequence star, red giant/red super giant
death of medium mass star
after becoming a red giant, the outer parts grow bigger and drift into space, forming a cloud of gas called a planetary nebula
bluewhite hot core of sun that is left cools and becomes a white dwarf
white dwarf eventually runs out of fuel and dies as a black dwarf
death of a high mass star
dying red super giant star can suddenly explode
after explosion, some materials from star are left behind
they may form a neutron star
the most massive stars become black holes when they die
after a large mass star explodes, a large amount of mass may remain
the gravity of the mass is s strong that gas is pulled inwards, pulling more gas into a smaller and smaller space
eventually gravity becomes so strong that nothing can escape, not even light
supernova
sudden explosion of dying red super giant star
neutron star
remains of high mass stars
past beliefs to now
for centuries people believed there was only earth and sky
26 centuries ago, anaximander figured out that there’s space on all sides
other ancient greeks concluded that the earth was a sphere, with celestial objects orbiting it
copernicus figured out that the earth orbited the sun
then figured out our solar system was one of a hundred billion in our galaxy
then that our galaxy is one of a hundred billion galaxies
gravitational singularity
one dimensional point which contains a huge mass in an infinitely small space, a point of infinity, laws of physics as we know do not operate at this point
doppler effect
apparent change in the frequency of a wave caused by relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer
the thing that is emitting waves moves
in front, it bunches up, behind the thing, it spreads out
when it’s moving towards a stationary object, these bunched up waves are observed at a high frequency, moving away - waves observed at a low frequency
blue/red shifts
blue shift - star moving towards earth, wavelengths of light have been compressed, spectral lines shifted towards blue end, higher frequency
red shift - star moving away from earth, wavelengths of light become longer, spectral lines shifting towards red end, lower frequency
elemental fingerprints
each element gives off unique spectral signature/fingerprint
can analyze light coming from different objects in space and determine their composition by comparing fingerprints
different elements emit different wavelengths of light
emission spectrum
spectrum consisting of several narrow, bright, bands of light
spectroscopy
technique of splitting light (electromagnetic radiation) into its wavelengths (a spectrum) in the same way as a prism splits light into a colour of rainbows
electromagnetic radiation
energy that is carried or radiated in the form of rays (microwaves, radio waves)
spectrum
band of rainbow colours created when white light passes through the prism
each colour of spectrum represents different wavelength of light
edwin hubble
american astronomer
discovered all galaxies were moving away form each other
galaxies further away from our galaxy (milky way) were moving away from each other faster than galaxies that are closer to ours
galaxies twice as far away were moving twice as fast as closer galaxies
suggested that all galaxies must have had a common point of origin
discovered this through spectroscopy
spectral lines were all shifted towards the red part of the spectrum -indicates that galaxy is moving away from observer on earth
occurs because light’s wavelengths are getting longer
called cosmological red shift - red has longest wave length
main evidence for big bang theory
big bang theory evidence
cosmological red shift
cosmic background radiation is evident
leftover radiation from initial explosive expansion of the universe, echo of big bang
predicted by astronomers
mapping of background radiation (satellite COBE in 1989)
mapping of microwave radiation (by spacecraft WMAP in 2001)
expansion implies that universe was smaller in the past
big bang theory (summary)
universe began with gigantic expansion13.8~ billion years ago
not explosion - they fly outward into empty space that there was prior to the explosion
with the big bang, there was no space for it to expand into
nothing existed before this - no space, no time
out of nothingness came the universe and it started to expand
universe was too hot right after the explosion for subatomic particles to form
subatomic particles present (protons, electrons, quarks, etc) but they were moving so fast due to the heat they didn’t form atoms
as universe cooled, particles slowed down and combined with each other to for hydrogen atoms (380 000 years after the Big Bang)
so hot that first hydrogen atoms gave off radiation that can still be measured today (CMB - cosmic background radiation)
as universe continued to cool down, the hydrogen atoms could condense and form stars
condensation/cooling allowed for all other bodies in the universe to form
big bang + right after
at the moment of the big bang, the entire universe existed as an infinitely small, dense, and hot point - singularity
contained everything we see in universe today
not explosion, but rapid expansion (cosmic inflation)
moments after big bang, period of rapid exponential expansion of the universe
lasted fraction of second - universe expanded faster than speed of light
after this period it began to expand at a more gradual pace at which it’s still moving today
timeline
big bang
inflation
after 380 000 years, electrons cool enough to combine with protons, universe transparent to light
dark ages - clouds of dark hydrogen gas cool and coalesce
first stars - gas clouds collapse, fusion of stars begins
galaxy formation - gravity causes galaxies to form, merge, and drift
dark energy accelerates expansion of universe at slower rate than inflation
dark ages - hot - billions of degrees
dense - crammed together tightly, bursting at seams
fast - infinitely small to size of softball in less than a billion of a second
dark - crammed so tightly light couldn’t get out
plasma - hot soup of charged particles
what did the big bang create
space, time, energy, matter
matter/energy relationship
shortly after big bang, matter and energy were indistinguishable, but less than a second later, they separated into two separate things
prior to einstein, astronomers understood universe according to newton’s laws of motion (1686)
e=mc² shows energy and mass are interchangeable - different forms of same thing, (matter can be converted into energy and vice versa)
mass is concentrated energy and has lots of energy in it
energy was turned into matter after big bang
mass increases with speed
near speed of light, mass is so high it reaches ∞, would require infinite energy to move it, capping how fast object can move
light moves at the speed because photons(quantum particles that make up light) have a mass of 0
how did energy change over time
transferred by forces - push/pull
after big bang, energy split into 4 fundamental forces of nature within a fraction of a second
these laws govern the universe today (gravity, weak nuclear force, strong nuclear force, electromagnetism
gravity
first force to emerge, force of attraction between all matter - pull only, weakest force, infinite distances
strong nuclear force
second force to emerge, holds nucleus together, basically attractive, can repel (mostly pull can push), strongest forces, short distances
electromagnetism
third force to emerge, push (repulsion of like charges) and pull (attraction of opp charges), acts between matter carrying an electrical charge, infinite distances, second most powerful
weak nuclear force
fourth force to emerge, stronger than gravity, extremely small distances, cause tiny particles of matter to change identity, causing radioactive decay, push
matter
anything that has mass and volume
building blocks - what give matter form
electrons/quarks
protons/neutrons
atomic nuclei
plasma
atoms
electrons and quarks
moments after origin of universe, quarks have partial charges - up quarks and down quarks
protons and neutrons
quarks combined into groups of large particles - neutrons
2 up quarks and 1 down quark created proton, opposite created neutron
atomic nuclei
protons and neutrons then bound together - by strong nuclear force
plasma
for next 380 000 years, universe consisted of mostly uniform plasma of charged particles - positive atomic nuclei, negatively charged electrons
atoms
universe cooled enough to form first atoms
electromagnetic force caused positively charged electrons to become attracted to negatively charged electrons
electrons began to swirl around nuclei and first neutral atoms came into existence
first atom was hydrogen, second was helium
light atoms were first, hydrogen and helium first and second most abundant
73% of mass of visible universe is hydrogen, 25 is helium, everything else was created after big bang within stars and represents 2%
solar system basic info
sun is centre, heliocentric
solar system full of planets, moons, asteroids, and comets
all revolve around the sun at the centre
when a star forms from a nebula, gravity pulls most of the material into the new star, some may also clump together to form objects in a solar system
ormed 4.5+ billion years ago
planet
celestial body that orbits one or more stars, may spin on axis as it orbits the sun
planet requirements
celestial body must orbit one or more stars, be large enough that its own gravity holds it in a spherical shape, and be the only body occupying the orbital path
planet order
sun, mercury, venus, earth, mars, jupiter, saturn, uranus, neptune
inner rocky planets and outer, gaseous/jovian planets
after the sun formed, material closest to the sun developed into inner/terrestrial planets
small, solid cores, rocky crusts
mercury, venus, earth, mars
material further from the sun developed into the outer/Jovian planets
large gaseous bands, cold temperatures
jupiter, saturn, uranus, neptune
astronomical units
how distance between planets in the solar system is measured
1 au - sun to earth
mars - 1.5 au, jupiter - 5.27 au, neptune - 30.06 au
rotation
motion of earth as it spins on its axis from west to east
spins on axis at 1670km/hr (one full rotation takes almost a day)
revolution
motion of earth as it orbits usn
orbits sun at 30km/sec - one full revolution takes almost a year
sun
contains more than 99% of mass in solar system
composed of mainly hydrogen gas
nuclear reactions in the sun’s core causes hydrogen to form helium
energy is radiated to earth, keeping it warm enough to support life
solar wind
sometimes gases from sun erupt outwards like bursting soap bubble
resulting solar wind is full of high energy particles that would kill any life on earth they struck
our magnetic field deflects this solar wind
see the deflection when we see the northern lights
asteroid
small leftover remains from the formation of the solar system
1000s of asteroids orbit in asteroid belt between mars and jupiter
comet
composed of ice, rock, and gas (dirty snowballs)
leaves trail of gas and dust when in contact with sunlight
rocky travelers - following orbits far outside planets in the oort cloud
other solar system bodies
bodies smaller than planets in our solar system
moons found around all planets except mercury and venus
oort cloud
at farthest reach of the sun’s gravitational pull, almost 25% of way to next nearest star, proxima centauri
trans-neptunian o bjects
beyond neptune
compoesd of fragments of material left over from formation of the solar system
these objects orbit the sun in a larger area known as the kuiper belt
pluto is a dwarf planet
plutoid
dwarf planets past neptune
dwarf planets
orbit sun, have enough gravity to pull itself into spherical shape
pluto
demoted at the 26th general assembly of international astronomical union in prague (2006)
only argument for keeping it was “tradition” - no scientific justification for calling pluto a planet
pluto in kuiper belt, where nearly all are chunks of ice and rock like pluto, we just discovered pluto first
pluto isn’t even biggest , eries - 25% bigger by mass than pluto
haumea, makemake, ceres
up to 100 big things in kuiper belt
downgrade because so many big planets - planet would stop being useful as a term
new criteria : orbit sun, have enough gravity to pull itself into spherical shape, clear everything out of mass
only 0.07 times mass of everything in orbit vs earth is 1.7mil times
kuiper belt
asteroid belt past neptune, has trillions of things in it
geocentric model of celestial motion
earth considered centre of universe, everything revolved (moon, mercury, venus, sun, mars, jupiter, saturn) earth, based on ptolemy (greek astronomer)’s work
our understanding
humans aware of relationships between earth, sun, moon for 1000s of years, but only recently begun to better understand the true nature of the relationships
ancient civilizations used the seasons, months, positions of stars and other astronomical information in many parts of their lives
used to believe geocentric
polish astronomer copernicus was first to suggest heliocentric model
created contreversy → galileo, italian physicist and astronomer was put on trial for suggesting earth was not centre of universe
with time, heliocentric model was accepted
with kepler (german mathematician and astronomer)s work, accurate predictions of planets’ orbits became possible, further strengthening the validity of this model
moon’s formation - giant impact theory
orgin of moon believed to have resulted during earth’s early formation
planetary body the size of mars slammed into a young earth
impact is thought to have been so large, parts of both planets broke off and scattered into space
impact sped up earth’s rotation and tilted orbital plane 23 deg
earth reformed as large molten body
fragments ended up orbiting earth and eventually built up to form the moon
moon surface
no atmosphere on moon to protect from bombardment from debris from space
results in moon’s surface being covered by many large circular craters, ancient lava flows, high mountains
moon phases
moon produces no light -
moonlight is sun’s light reflected from the moon’s surface
moonlight takes one second to travel to earth
sunlight takes eight minutes
as moon is orbiting earth, sun lights it from different angles
these different angles are called phases
moon takes 29.5 days to revolve earth
rotates at the same rate it revolves, so we always see the same side of the moon
new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full, waning crescent, last quarter, waning gibbous,
full moon phase
when the Sun is lighting up the entire portion of the Moon visible from Earth
new moon phase
when the Sun is lighting up the side of the Moon not visible from Earthwhen the sunlit portion of the Moon increases in size from night to night and it is said to be waning when the sunlit part of the Moon is decreasing
waxing
when the sunlit portion of the Moon increases in size from night to night
waning
when the sunlit part of the Moon is decreasing
lunar gravity
as moon orbits earth, lunar gravity attracts the water in the ocean causing high and low tides
lunar gravity causes tides
effect of centrifugal force on ocean, result of earth orbiting around centre of grav between it and universe
earth’s rotation + tilt
day and night caused by earths spin on its axis from west to east
takes 23hrs 56 minutes, 4sec
axis is tilted 23.5° from flat plane of earths orbit
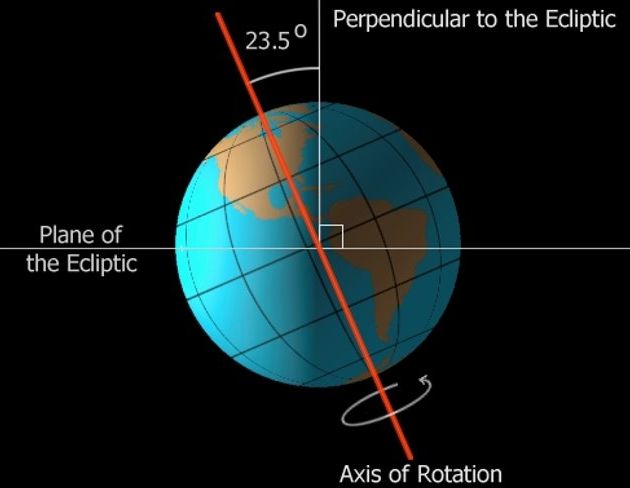
axis tilt means suns light strikes earth at different angles during earths annual orbit around the sun (seasons)
tilt towards the sun in northern hemisphere - summer in northern hemisphere
tilt away from Sun in northern hemisphere - winter in northern hemisphere
equator - imaginary line around middle of earth, hit by suns rays directly all year
June 21 - longest day of year (20-22 - summer solstice)
Dec 21 - shortest day of the year (20-22 - winter solstice
sept 22-23 - autumnal equinox
march 20-21 - vernal equinox
in far northern latitudes, axis tilt is extreme so Sun does not set below horizon in summer; does not rise in winter
eclipse
total or partial overshadowing of one celestial body by another
lunar eclipse
when earth lies directly between moon and sun during a full moon phase and earths shadow is cast on the moon, causing moon to be briefly blacked out, may become red like smog/sunset illuimated with light scattered by earths atmosphere
solar eclipse
when moon is between sun and earth and moon blocks the suns light and the shadow of the moon falls across portions of the earth
(Moons orbit tilts about 5° from the plane of earths orbit so solar eclipses don’t occur once a month)
during a solar eclipse, people living where the umbra touches earth witness a total solar eclipse
people living where the penumbra occurs witness a partial eclipse
constellations
distinctive patterns in night sky formed by groups of stars
Polaris - North Star, tells direction
meteoroids
pieces of rock, broken off from asteroids or planets; floating through space
meteors
meteoroids that burn up as they pass through earths atmosphere
meteorites
meteoroids that are too large to entirely burn up in earths atmosphere and so reach earths surface
asteroids
rocks that are orbiting sun
480 miles to less than a mile in diameter