PEDS
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AVN, developmental dysplasia, nursemaid elbow, Osgood-Schlatter disease, SCFE, Scoliosis, Salter-Harris
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
AVN (Legg-Calve-Perthes disease)
Idiopathic decreased blood supply to the proximal femoral epiphysis usually seen in boys (5X) 4-8 years old
Fam hx, low birth weight, abnormal birth presentation, secondhand smoke exposure, maybe abnormal clotting factors
Risk factors for Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
AP pelvis and frog leg xrays, MRI (most sensitive)
7 y/o male presents to the clinic for hip pain that radiates to the knee. The mother states, “He use to just limp, it’s gotten so much worse.” She smokes. On physical exam you note the loss of abduction and IR in the hip, and a trendelenburg gait. What diagnostics do you want?
Observation, NWB activity management, PT, Petrie casting and bracing with legs outstretched, Pain management with tylenol/NSAIDs, CALL ortho
7 y/o male presents to the clinic for hip pain that radiates to the knee. The mother states, “He use to just limp, it’s gotten so much worse.” She smokes. On physical exam you note the loss of abduction and IR in the hip, and a trendelenburg gait. Xrays reveal a CRESCENT SIGN. MRI reveals cystic changes and femoral bone edema. What is your initial treatment?
osteotomy
7 y/o male presents to the clinic for hip pain that radiates to the knee. The mother states, “He use to just limp, it’s gotten so much worse.” She smokes. On physical exam you note the loss of abduction and IR in the hip, and a trendelenburg gait. Xrays reveal a CRESCENT SIGN. MRI reveals cystic changes and femoral bone edema. What is your operative management - for like a late stage presentation?
under 6 y/o, maintained spherical femoral head shape
What are some good signs when treating AVN in Peds?
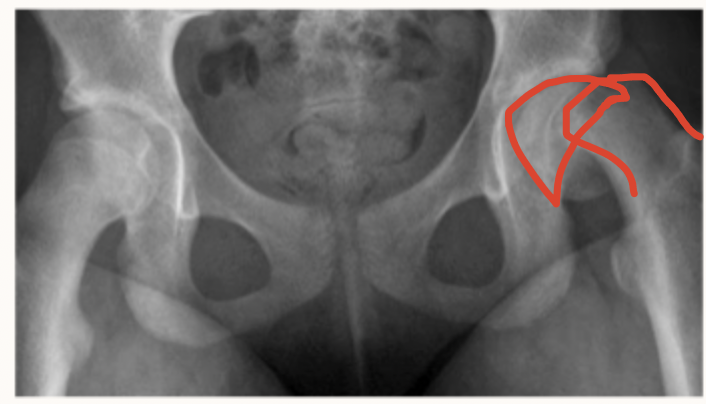
Developmental Dysplasia of Hip (DDH)
Abnormal development of the acetabulum resulting in dysplasia, subluxation, and dislocation of hips due to mechanical instability - most common ortho disorder in newborns?
Female, hip dislocation at birth, family hx, oligohydraminos, breech birth, firstborn child, tight swaddling, improper use of baby carriers
Risk factors of DDH
Newborn screening, 2 weeks of life
When should you screen for DDH (barlow→ ortolani, limb discrepancy)?
dislocation of the hip by adduction and depression of flexed femur
Describe the barlow’s sign
Reduction of a Barlow’s based dislocation by elevation and abduction of flexed femur
Describe the Ortolani sign
Ortolani negative
If a hip is dislocated but NOT reducible - its giving…
U/S (1st one at 6 weeks)
Imaging for DDH from birth to 6 months
AP pelvis
Imaging for DDH for 6 months+
Pavlik harness (abduction splinting/bracing) for those under 6 months (ortolani positive)
Non-operative management for DDH
femoral nerve palsy, Avascular necrosis, Pavlik harness disease (iatrogenic)
Complications of a Pavlik harness
closed reduction with spica casting
For patients with DDH over 6 months or who have failed Pavlik → what is the game plan?
Open reduction and spica casting
For patients with DDH over 18 months or who have failed closed reduction → what is the game plan?
open reduction and osteotomy
For patients with DDH over 2 years→ what is the game plan?
Nursemaid elbow
Sudden, longitudinal traction through the forearm with elbow extended and forearm pronated AKA a pulled elbow
annular ligament slips and gets caught between the radial head
Patho for nursemaids elbow - most common in 1-4 y/os
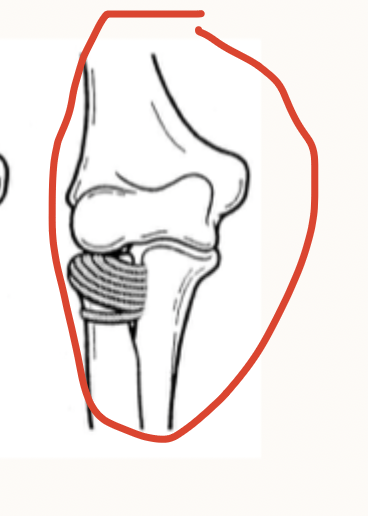
any motion that pulls the child’s arm while pronated
Causes for a nursemaid’s elbow
Closed reduction (supination or hyperpronation), give him nasal versed beforehand, NO immobilization
3 y/o male presents to the ER for elbow pain. Father states that they were wrestling when he felt a click in the boys elbow followed by immediate tears. On physical exam you note the boy is using his uninjured arm to support the other one and the elbow is flexed and pronated. He screams when you try to supinate the arm. What’s your treatment plan?
Osgood-Schlatter Disease (tibial tubercle apophysitis)
Irritation and inflammation of the apophysis due to microtrauma that is common in boys 12-15 y/o ESPECIALLY ATHLETES
RICE, NSAIDs, activity modification, PT that include quadriceps stretching and strengthening, cast immobilization (IF SEVERE), return to sports when there’s no pain
14 y/o male presents to the clinic for knee pain that is worse with kneeling and resisted knee extension. He points to the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia when you ask him where the pain is. The tubercle is tender and enlarged. Xrays show irregularity and fragmentation of the tibial tubercle. What is your treatment plan?
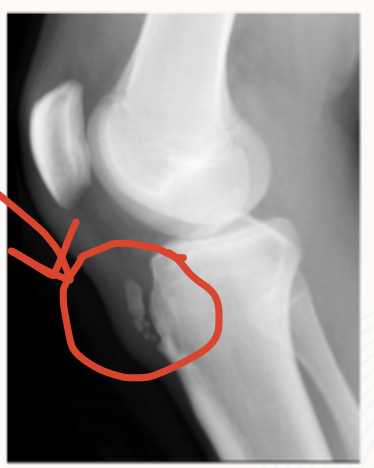
Slipping capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
The most common disorder of adolescent hips that is caused by the slippage of the proximal femoral physis relative to epiphysis (more common on the left)
AP hip and frog leg lateral, MRI if neg
14 y/o obese male presents to the clinic for hip pain that has been going on for the last few months. He states that the pain radiates to the knee. On physical exam you note that the patient prefers to sit with the left hip in external rotation, as well as abnormal leg length, limping gait, and an externally rotated foot. What imaging you want?
Under 10 y/o, pre-puberty, short stature, weight below 50th percentile
Red flags for SCFE that mean we need a TSH, FT4, BUN, creat
Percutaneous fixation, Contralateral hip prophylactically IF initial slip under 10, obese, or endocrine disorders
14 y/o obese male presents to the clinic for hip pain that has been going on for the last few months. He states that the pain radiates to the knee. On physical exam you note that the patient prefers to sit with the left hip in external rotation, as well as abnormal leg length, limping gait, and an externally rotated foot. What is your treatment plan?
Scoliosis (juvenile idiopathic scoliosis)
A lateral curvature (over 10%, right thoracic) of the spine most common in females that presents at 4-10 y/o
genetics, connective tissue abnormalities, growth imbalances during development
Possible risk factors for scoliosis.
Pain, neuro deficits, rapid progression, abnormal reflexes
Red flags of scoliosis
uneven shoulders or hips, truncal shift, limb discrepancy
Signs of scoliosis
Adam’s forward bend, Scoliometer measurement, Leg length eval, neurologic exam
Physical exam for Scoliosis
Xrays (🏆 - to diagnose measure Cobb angle), MRI (for kids under 10, angle over 20, left curve, pain or neuro signs)
Imaging for Scoliosis
Serial imaging every 6-12 months
For scoliosis patients with a cobb angle under 20
bracing 16-23 hrs/day (prevents progression)
For scoliosis patients with a cobb angle 20-50
Posterior spinal fusion
For scoliosis patients with a cobb angle over 50, with progressive deformity, respiratory concerns or issues
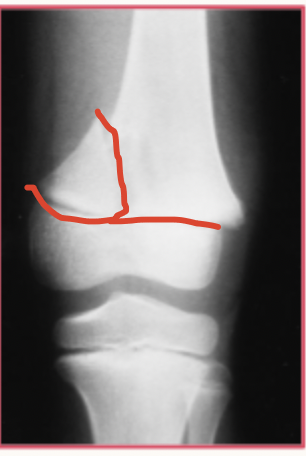
Salter-Harris Fracture
A pediatric fracture involving the physis that is most common among active children - especially the upper extremity
Type I
What type of salter harris is characterized by separation through the physis (straight across)
Type II (most common)
What type of salter harris is characterized by a fracture through the portion of the physis that extends through the metaphysis (ABOVE)
Type III
What type of salter harris is characterized by a fracture through a portion of the physis that extends through the epiphysis (lower)
Type IV
What type of salter harris is characterized by a fracture between the metaphysis, physis, and epiphysis (through everything)
Type V
What type of salter harris is characterized by a crush injury of to the physis (cRush)
closed reduction, casting, splinting; refer to ortho within 7-10 days
6 y/o girl presents to the ED for leg pain following a fall down the stairs at school. On physical exam you note knee swelling which is tender to palpation. She is unable to bear weight of the leg due to pain. What is your treatment plan?
ORIF
Gameplan for Type III and IV Salter Harris
closed reduction, casting, splinting
Gameplan for Type I and II Salter Harris
Emergent ortho consult due to delayed diagnosis
Gameplan for Type V Salter Harris