CONSEQUENCES OF TOOTH LOSS WHEN MANAGING OLDER PATIENTS
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
has the life expectancy of males and females increased or decreased since the 1900s
increased
what factor significantly influences life expectancy
socio-economic status
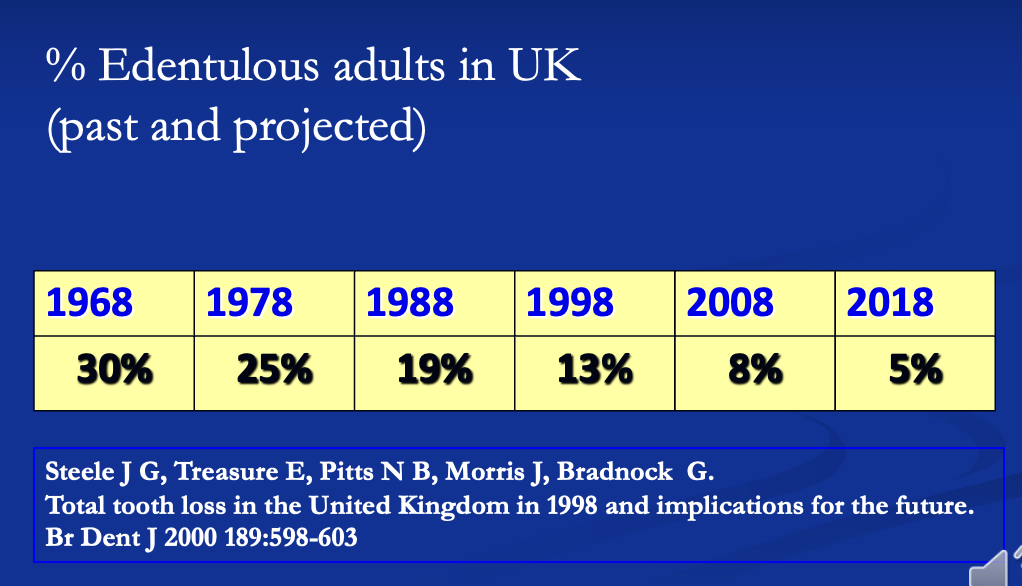
table showing % of edentulous adults in the UK
problems relating to treatment and patient management often ________ with the age of the patient
problems relating to treatment and patient management often increase with the age of the patient
why may older people neglect oral health
elderly may be reluctant to seek treatment until absolutely necessary
medical health issues may take priority so dental health is ignored
what issues may there be physically providing treatment to the older population
do we visit them in their own house?
do we provide an ambulance/ taxi to bring them to the surgery for treatment?
do we rely on their own capability of travelling?
do we rely on their ability to get family or close ones to bring them in?
outline domiciliary dentistry provision
easy for the patient but more difficult for clinician
taking all equipment necessary including light is difficult
not feasible for complex procedures
chaperone needed
why may the dental surgery environment be difficult for the older patient to manage
busy environment
bright lights
noise
postural problems
long procedures
may lead to:
confusion
lack of compliance
how can the dental experience be made easier for the elderly
seating: keep upright or slowly alter position
noise: low tones, reduce noise and speed
confusion: reduce speed, less instruction, check medical history
timing of appt.: medication, convenience
how can you help older patients adapt to denture changes
make small changes to existing dentures
copy features of existing dentures after making alterations
what problems can affect treatment during complete denture construction (2)
age
consequences of tooth loss
which stages in denture construction can be affected by patient age
rapport with patient
getting a clear medical history
understanding the patient’s problems
deciding on appropriate treatment
deciding on where best to treat the patient
ability to adapt to denture wearing
which stages in denture construction can be affected by consequences of tooth loss
impression taking
jaw registration
retention and stability of the denture
ability to wear the denture
outline the relationship between tooth loss, alveolar resorption and denture retention
after tooth loss, the remaining alveolar bone forms the alveolar ridge
this gives support to a denture and forms the denture bearing area
following tooth loss, the alveolar bone resorbs rapidly at first but decreases with time
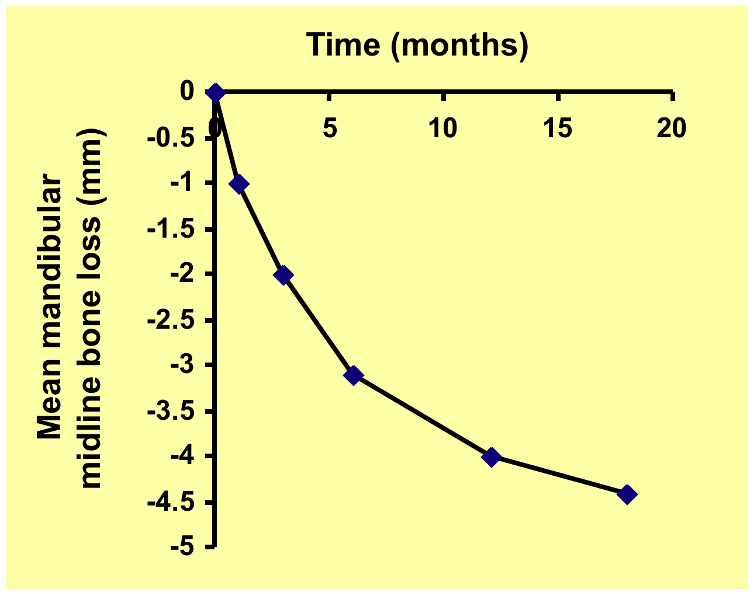
graph showing mandibular midline bone loss against time following extraction
what is the relationship between the maxilla and mandible in terms of bone resorption
there is approximately x4 more resorption in the mandible than the maxilla
around an individual tooth, where is resorption greater
where the cortical plate is thinner
in the maxilla what does the loss of the teeth lead to in terms of the cortical plate
in the maxilla the loss of the teeth leads to:
greater loss of the thinner buccal cortical plate
with gradual reduction in the width and length of the residual ridge
in the anterior region of the mandible, in which direction does the residual ridge move and why
anterior region of mandible
the buccal plate is slightly thinner so the residual ridge apparently moves slightly lingually
in the premolar region of the mandible, in which direction does the residual ridge move and why
premolar region of mandible
the buccal and lingual plates are of equal thickness and the residual ridge maintains its position
in the molar region of the mandible, in which direction does the residual ridge move and why
molar region of mandible
the buccal plate is reinforced by the external oblique ridge, resorption of the thinner lingual plate occurs
there is apparent movement of the residual ridge buccally
to what degrees can alveolar resorption occur
too little resorption
irregular resorption
excessive resorption
normal resorption
outline the clinical effects of too little resorption
leads to bulky alveolar ridges with little space in which to place dentures
inevitable consequences are either frequent denture fracture or excessive face height
excessive FH can compromise functions like speaking and eating as well as appearance
outline the clinical effects of irregular resorption
bone may be sharp and the soft tissues may get traumatised under the denture
this leads to ulcers and discomfort
surgical reduction of the ‘knife-edge’ may be needed
outline the clinical effects of excessive resorption
the normal relationship of the posterior teeth may be changed
with the increase in width of the mandible posteriorly, a ‘posterior crossbite’ is produced
outline the clinical effects on the maxilla due to excessive resorption
maxilla
anteriorly, where buccal resorption of the maxilla predominates, an edge-to-edge incisor relationship or prominent mandible may occur
outline the clinical effects on the mandible due to excessive resorption
mandible
atrophy of the alveolus causes the mental foramen to become superficial
the mylohyoid ridge on the lingual aspect of the mandble becomes sharp and prominent
both may cause pain during denture wear
outline the clinical effects of normal resorption
a few months after extraction, the dentures start to feel loose
dentures need relining or replacing to improve retention
what are useful clinical techniques to help prosthetic treatment
check record
windowed trays
neutral zone impression technique
retained roots
polycarbonate
soft liners
how can windowed trays improve prosthetic treatment
used for anterior flabby ridges
with the primary impression done and in the mouth, the ‘window’ is filled with a fluid impression material such as silicone, plaster
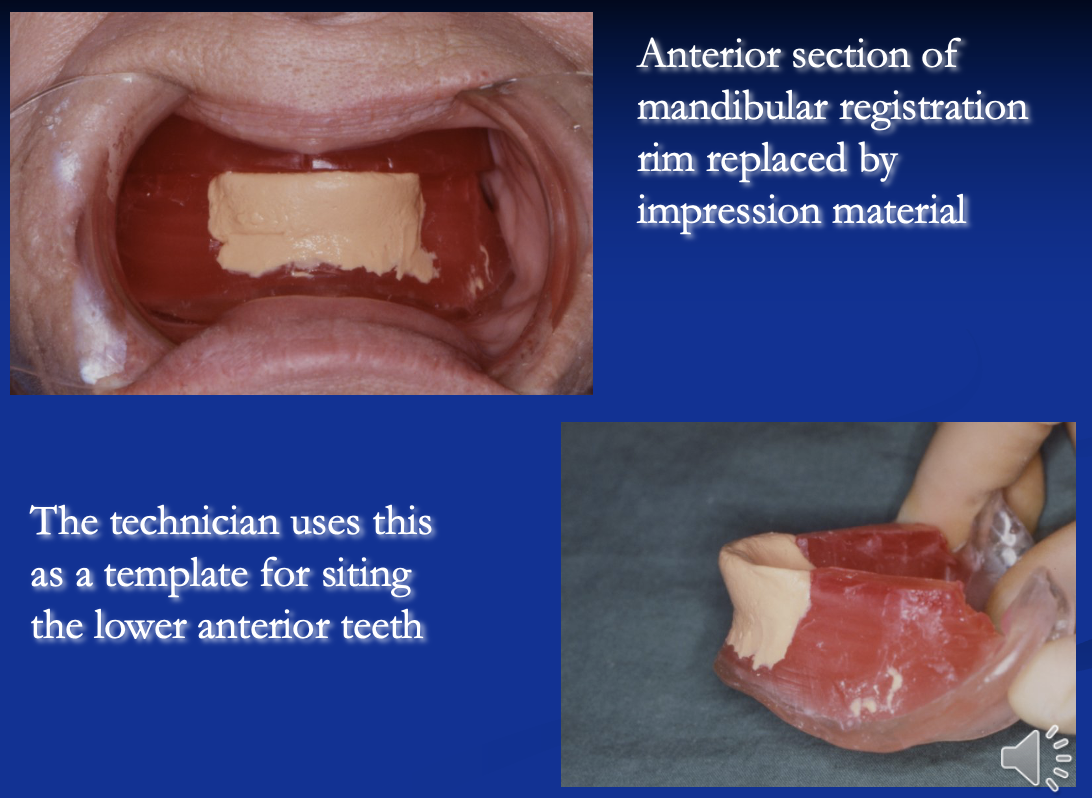
what is a common reason for lower dentures moving whilst in function
lower anterior teeth not being in the neutral zone
how can the issue of lower anteriors not being in the neutral zone be fixed
get patient to move their lip and tongue
this moulds the impression material into a shape where you can set the anteriors in the best position
what anatomical feature can preserve alveolar bone
retained roots
outline the use of polycarbonate
polycarbonate is a plastic
reduces the likelihood of a midline fracture
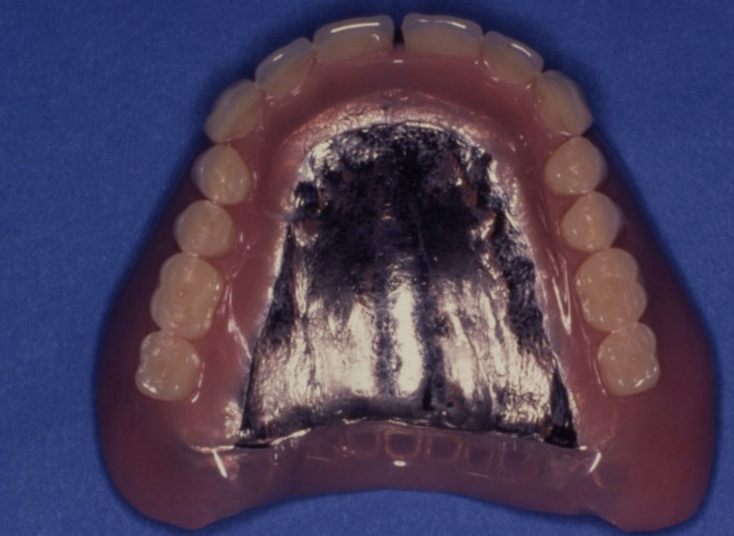
what does this image show and what is a disadvantage of it
chrome palate
makes denture heavy so not really opted for
outline the use of soft liners in prosthodontics
cushions the effect of dentures on the mental foramen
processed onto denture in laboratory
lasts 6-12 - 3yrs
what are some disadvantages of soft liners
soft liners sacrifice a bit of retention
sometimes not as permanent as we would like
the material can dry out quickly so even after as little as 6 months it may need to be replaced
what surgical options are there to improve denture retention
implants - usually provided in lower 3 area
sulcus deepening surgery
ridge augmentation