APK4125 Lab 8: Muscular Fitness
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Muscular fitness is a composite term including multiple facets of overall ?
muscular ability
The three main components of muscular fitness are:
-strength (health-related)
-endurance (health-related)
-power (skill related)
Strength is the ability of a muscle group to develop ? against a ? in a single contraction
-contractile force
-resistance
Endurance is the ability of a muscle group to exert ? for extended periods of time
submaximal force
Power is the ability of a muscle to exert force per ? or the ? of performing work
-unit of time
-rate
? is a major portion of the body
On average it makes up over ?% of an individual's bodyweight
-Skeletal muscle
-40%
There are over ? muscles that are vital to movement, metabolism, communication, posture, balance, heat production, breathing, and many other functions
600 muscles
In general, exercise that improves musclar fitness (i.e., resistance training) enhances the following: (5)
-bone mass
-glucose tolerance
-musculotendinous integrity
-activities of daily living
-FFM and RMR
Bone mass prevents against ?
ostoeporosis
Glucose tolerance prevents against ?
metabolic disorders
Musculotendinous integrity prevents ?
injury
FFM and RMR are related to ? when it comes to muscular fitness
weight management
Muscle performance adaptations to resistance training
-muscular strength:
-muscular endurance:
-muscular power:
-increases
-increases
-increases
Muscle enzyme adaptations to resistance training
-phosphagen system enzyme concentration:
-phosphagen system enzyme absolute levels:
-glycolytic enzyme concentrations:
-glycolytic enzyme absolute levels:
-may increase
-increase
-may increase
-increase
Muscle substrates adaptations to resistance training
-ATP concentration
-ATP absolute levels
-CP concentration
-CP absolute levels
-ATP and CP changes during exercise
-Lactate increases during exercise
-may increase
-increase
-may increase
-increase
-decrease
-decrease
Muscle fiber characteristics adaptations to resistance training
-Type I CSA
-Type II CSA
-% Type IIa
-% Type IIx
-% Type I
-increases (
-increases
-decreases
-no change
Body composition adaptations to resistance training
-% fat
-fat-free mass
-metabolic rate
-likely decreases
-increases
-likely increases
Neurological changes adaptations to resistance training
-EMG amplitude during MVC:
-Motor unit recruitment:
-Motor unit firing rate:
-Cocontraction:
-likely increases
-likely increases
-increases
-decreases
Structural changes adaptations to resistance training
-connective tissue strength:
-bone density/mass:
-likely increases
-likely increases
The extent to which a client sees individual adaptations to resistance training is dependent on the type of ? they perform
training (i.e. number of reps, the sets, % of load, rest time etc.)
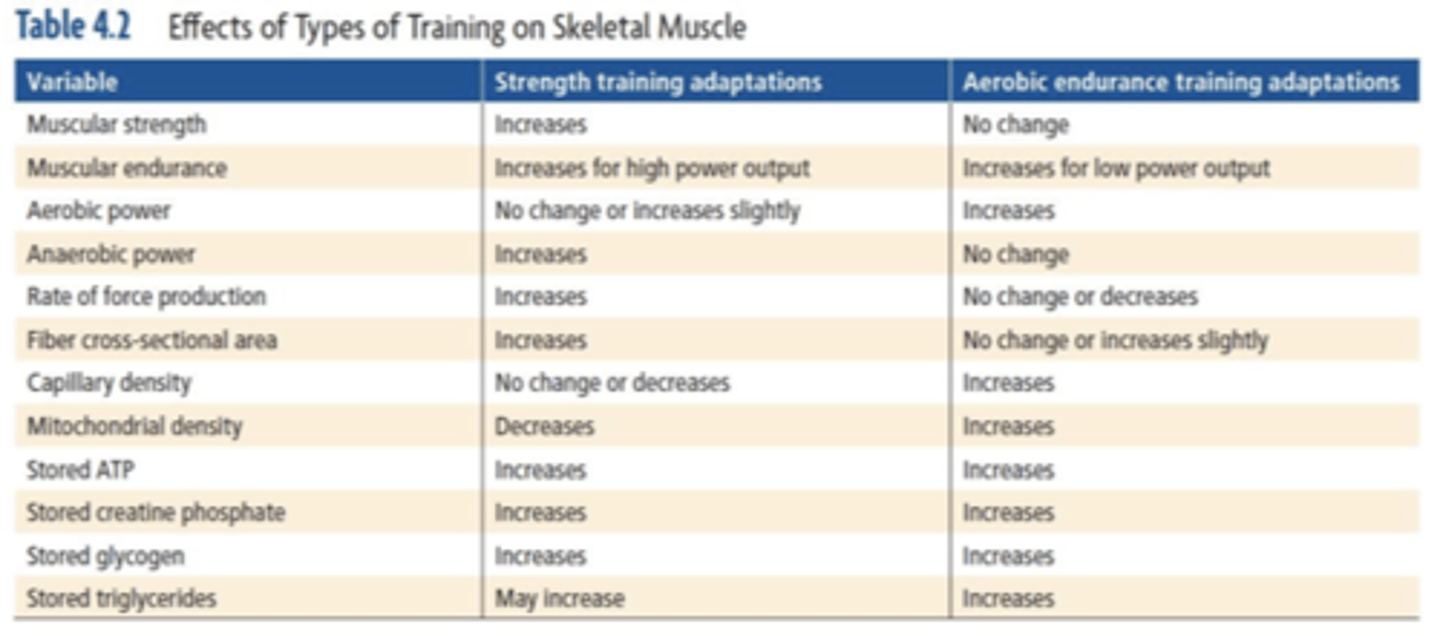
Difference between chronic aerobic training and chronic resistance training adaptations (table)
2 types of muscle contrations
-static (isometric)
-dynamic (includes both an eccentric and concentric component)
Dynamic muscle contraction can further be broken down into 4 categories
-auxotonic (dynamic constant external resistance (DCER))
-dynamic variable external resistance (DVER)
-isotonic
-isokinetic
Isometric is a muscular contraction in which the velocity is ? and the length of the muscle ?
-0
-does not change
Auxotonic is a muscular contraction against ? in which the velocity is ?, the length of the muscle ?, and the tension or force requires changes due to ? or ?
-resistance
-not constant
-changes
-increasing load or difference in leverage
Isotonic is a muscular contraction against ? in which the velocity is ?, the length of the muscle ?, and the tension or force required ?
-resistance
-not constant
-changes
-stays the same
Isokinetic is a muscular contraction against ? in which the velocity is ?, the length of the muscle ?, and the tension or force required ?
-resistance
-constant
-changes
-changes
Equipment options for static strength testing (3)
-isometric dynamometers
-cable tensiometers
-load cells
Equipment options for dynamic-constant resistance strength testing (2)
-free weights (e.g., dumbells)
-exercise machines
Equipment options for dynamic-variable resistance strength testing (2)
-exercise machines (depends)
-rubber bands
Equipment options for isokinetic strength testing (1)
-isokinetic dynamometer
Measure for static strength testing
max voluntary contraction (MVC) (kg)
Measure for dynamic-constant resistance strength testing
Force in newtons or 1-RM (lbs or kg)
Measure for dynamic-variable resistance strength testing
not recommended
Measure for isokinetic strength testing
peak torque (ft-lbs or Nm)
Biodex machines cannot do ? motions
compound
Isokinetic dynamometers
Provide accurate assessments of all components of muscular fitness (strength, endurance, and power)
With a biodex system 4 (isokinetic dynamometer), the speed is kept at a ? velocity
constant, preselected velocity
Any increase in muscular force (measured by the biodex) produces an increased ? rather than ? of the limb
-resistance
-acceleration
Isokinetic dynamometers have a range of velocity from ? to ? degrees per second
0 to 300
? ratios are easily measure with isokinetic dynamometers
agonist/antagonist
Historically, measures of ? between ? have been used to determine when an athlete can return to play
strength between limbs
(Isokinetic testing)
Speed setting for strength
30 or 60 degrees per second
(Isokinetic testing)
Speed setting for endurance
120-180 degrees per second
(Isokinetic testing)
Speed setting for power
120-300 degrees per second
(Isokinetic testing)
Protocol for strength
-? submax practice trials followed by ? max trials
-2 submax
-3 max
(Isokinetic testing)
Protocol for endurance
? maximal trial(s)
1
(Isokinetic testing)
Protocol for power
-? submax practice trials followed by ? max trials
-2 submax
-3 max
(Isokinetic testing)
Measure for strength
peak torque (ft-lb or Nm)
(Isokinetic testing)
Measure for endurance
number of repetitions until torque reaches 50% of initial torque
(Isokinetic testing)
Measure for power
peak torque (ft-lb or Nm)
The gold standard for measuring dynamic strength is with a ? and ?
linear transducer and force plates
*however, these pieces of equipment are expensive and not practical
The most common method of dynamic testing is the ?
one repetition maximum (1-RM)
A 1-RM is the max weight that can be lifted for ? of the movement through the ?
-one complete repetition
-full range of motion
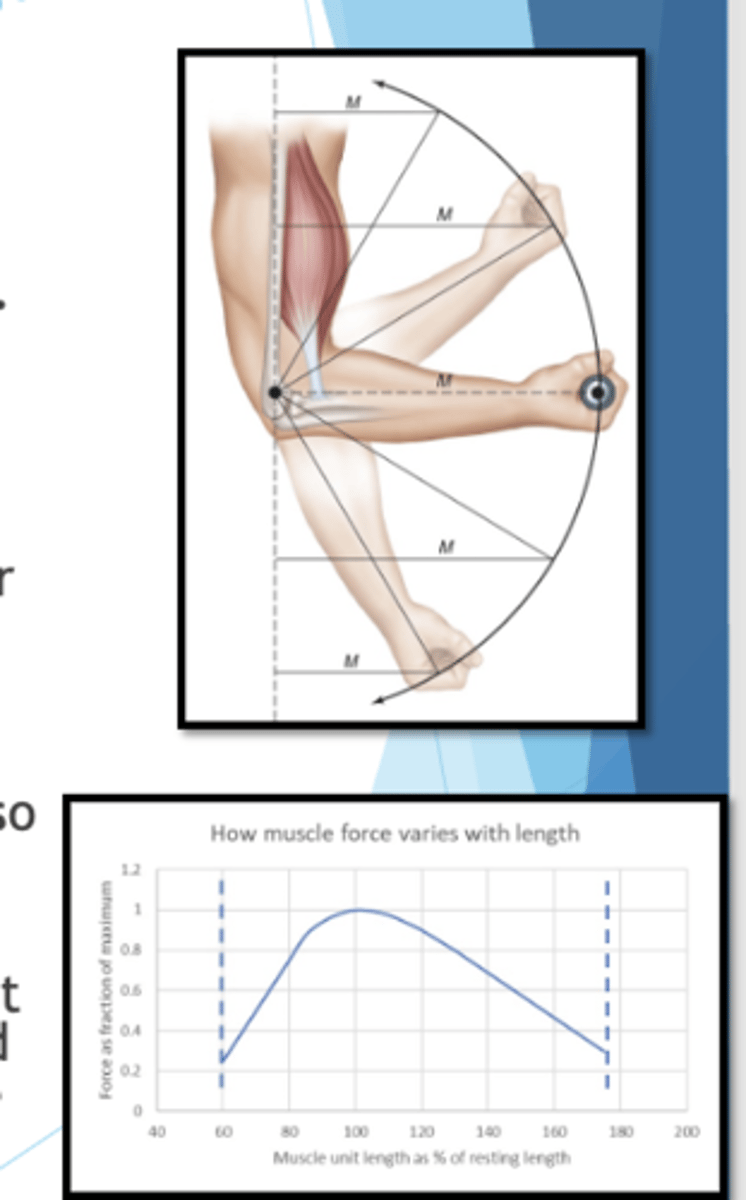
A 1-RM truly only measures the maximum strength at the ? in the ROM, this point also coincides with what is labeled the ?
-weakest point
-sticking point
The weakest points in the ROM are the product of ? for a muscle and the ? it moves and then the changes in the ? throughout the range of motion
-length tension relationship
-joint
-moment arm
When performing dynamic strength assessments, they can be performed with ? or ?
free weights or machines
Free weights pros and cons
-require more ? to stabilize body parts and maintain ?
-? needed
-less ? in testing because of the greater amount of ? to control
-not ideal for ?
-ideal for client who want to improve at ?
-require more neuromuscular coordination to stabilize body parts and maintain balance
-spotter(s) needed
-less reliability in testing because of the greater amount of variables to control
-not ideal for beginners
-ideal for client who want to improve at a specific exercise
Dynamic constant resistance exercise machines pros and cons
-no ? needed
-limit ? and ?
-? weight increments...potentially less accurate
-not useful for individuals with very ? limbs or very ? limbs/body circumferences
-no spotter(s) needed
-limit joint ROM and plane of movement
-large weight increments...potentially less accurate
-not useful for individuals with very short limbs or very large limbs/body circumferences
The primary role of the spotter is to help protect the lifter from ?
injury
Free-weight exercises that require one or more spotters include...(4)
-bar moving over the head
-on the back
-in front of the shoulders
-passing over the face (e.g. bench press, squats, lying tricep extension)
The spotter should be at least as ? and at least as ? as the client performing the exercise
-strong
-tall
Overhead exercises and exercises where the bar is placed on the? or in front of the ? should ideally be performed inside a ?
-back
-shoulders
-power rack
When spotting over-the-face exercises, use an ? grip that is ? than the client's when grasping the bar to lift or lower it
-alternated
-narrower
When spotting heavy loads, establish a stable ? and a ?-back position
-base of support
-flat-back
For dumbbell exercises, spot at the ? instead of spotting at the ? for pressing and pushing exercises
-wrists
-elbows
When spotting, don't assist the lift until the ? velocity is ? and starting to move ?, or the lifter asks for help
-concentric velocity
-0
-eccentrically
General procedures for a 1-RM assessment

If you are testing a client for overall fitness and health and they are planning on doing extensive ? training you may want to perform a ? battery
-resistance training
-multi-1RM test
Vivian Heyward proposed a 6-test battery including:
benchpress
bicep curl
lat-pull down
leg extension
leg curl
leg press
With multi 1-RM tests, a max is determined in each lift and then ?-to ?-mass ratios are calculated for each lift
strength-to-body
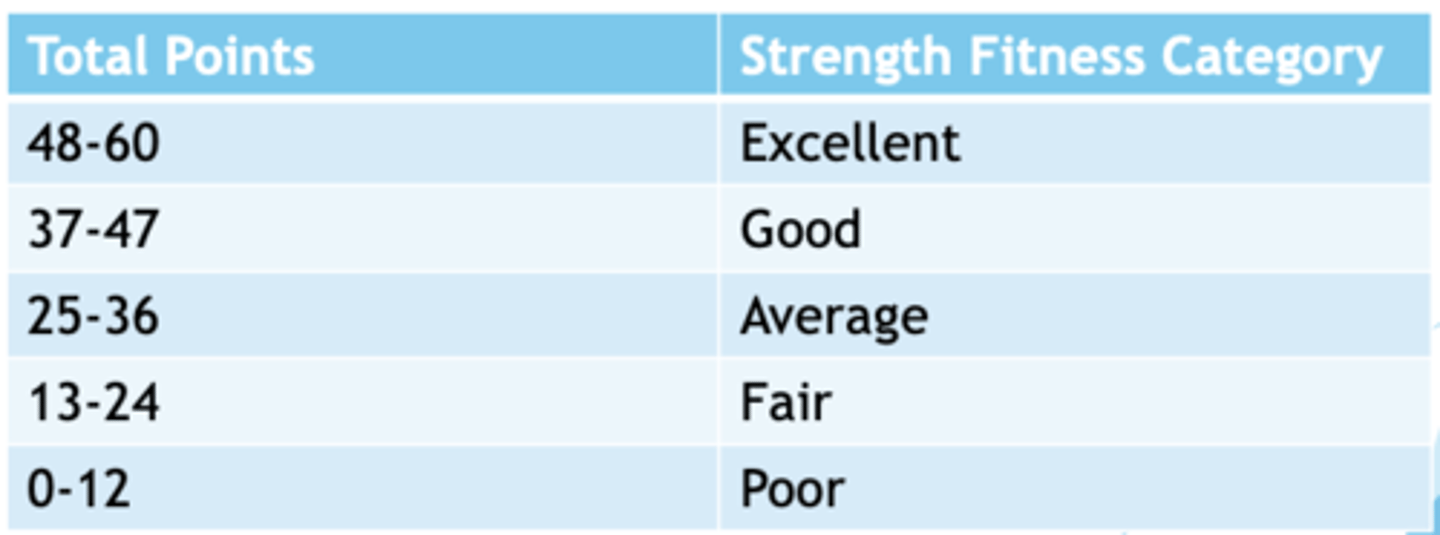
Multi 1-RM Test battery categorization chart
Dynamic muscular endurance testing tests the ability of a muscle group to:
-execute ? contractions over a period of time sufficient to cause ? fatigue
-maintain a specific % of the ? or ? for a prolonged period of time
-repeated
-muscular fatigue
-MVC
-1-RM
There are multiple studies that show a strong relationship between muscular ? and muscular ?
strength and endurance
Both muscular strength and endurance rely on ? metabolism, strong and coordinated ?
-anaerobic
-neuromuscular recruitment
Aerobic endurance uses ? metabolism and is a measure of ?
-aerobic
-the entire body
Muscular endurance uses ? metabolism and is ? specific
-anaerobic
-muscle/joint
There is a much stronger relationship between muscular ? and muscular ?, than muscular ? and aerobic ?
-muscular strength and muscular endurance
-muscular endurance and aerobic endurance
When performing dynamic muscular endurance, it can be measured in two categories: ?
absolute muscular endurance and relative muscular endurance
Absolute muscular endurance is the number of reps performed at ?
a given resistance
ex: YMCA bench press test
Relative muscular endurance is the number of reps performed at ?
a % of max (pre and post-testing)
ex: dynamic muscular test battery (7 exercises with load prescribed based off bodyweight of client, maximum number of 15 repetitions performed for each exercise)
The YMCA bench press test is an ? muscular endurance test that is ? bearing
-absolute
-non-weight
The YMCA bench press test uses a standard bench press, a ? pushing exercise used for developing muscular fitness in the ?, ?, and elbow ? muscles
-multi-jointed
-chest
-anterior shoulder
-elbow extensor muscles
This test can be beneficial for assessing ? and can be correlated to ? even estimating bench press 1-RM with equations
-upper body muscular endurance
-upper body muscular strength
YMCA bench press 1-RM estimation equations
Males: 1-RM (kg) = (1.55 x YMCA bench press test reps) + 37.9
Females: 1-RM(kg) = (0.31 x YMCA bench press test reps) + 19.2
YMCA bench press test protocol

For YMCA bench press test, men use ?lbs and women use ?lbs
-80lbs for males
-35lbs for females
For YMCA bench press test, set the metronome cadence at ? beats/min to establish a rate of ? repetition per minute
-60 beats/min
-30 repetitions per minute
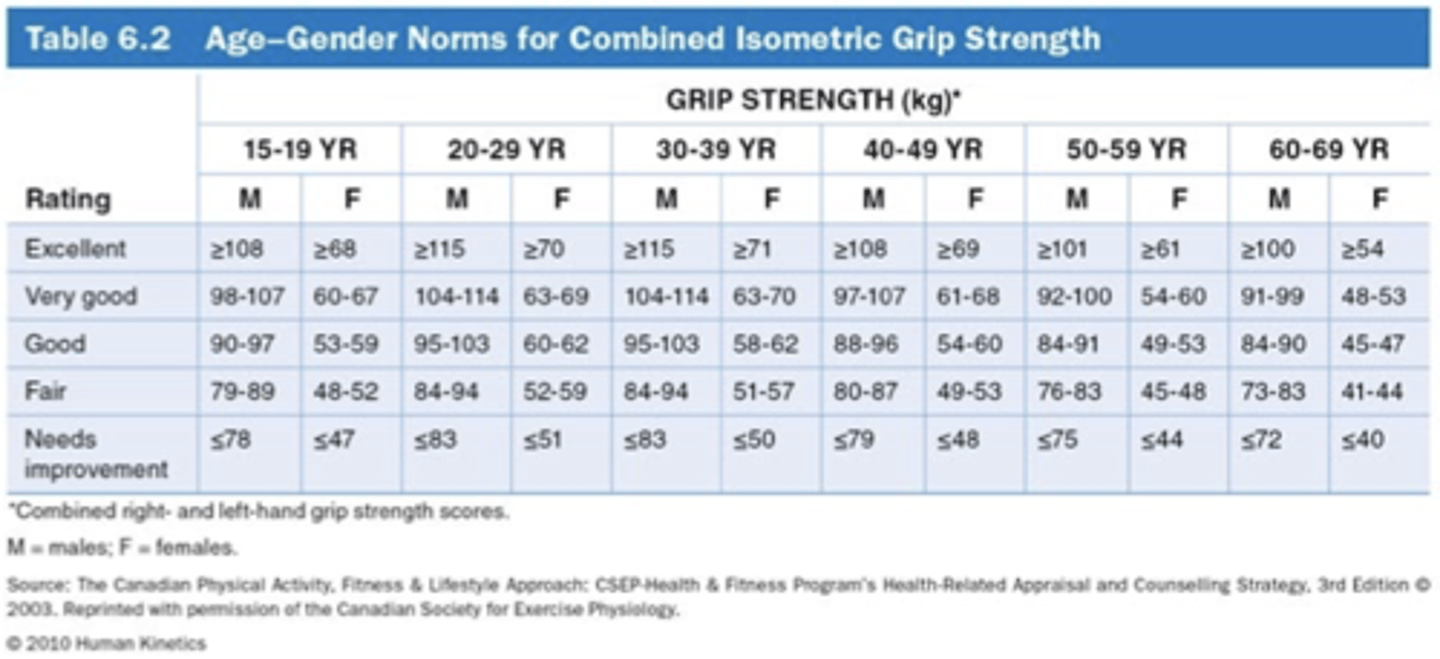
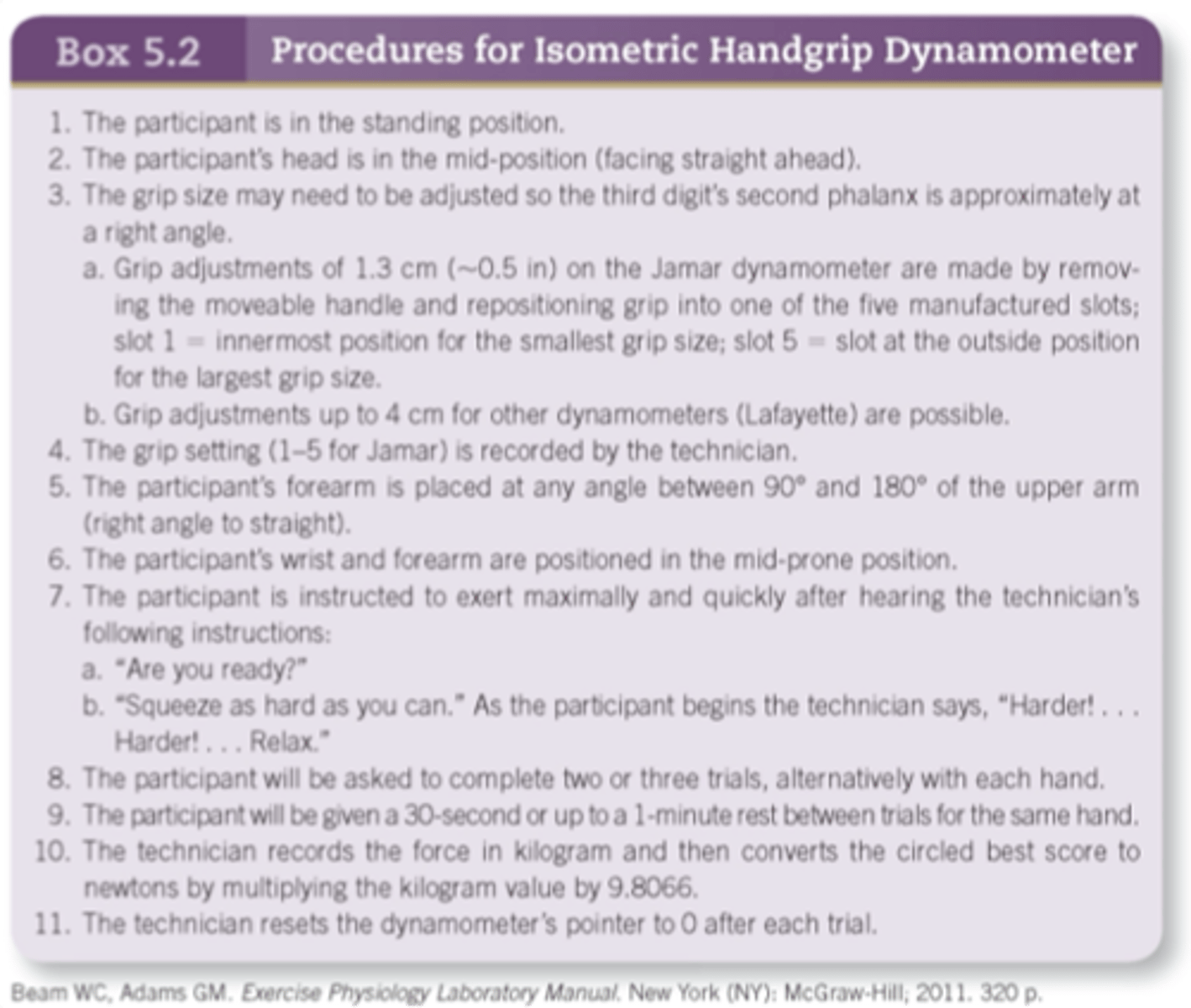
The most typical piece of equipment when performing isometric testing is a ?
spring-loaded handgrip dynamometer
Spring-loaded handgrip dynamometer typically ? and ?kg
0 and 100kg
With spring-loaded dynamometers, as force is applied to the instrument, a spring is ? and moves an ?
-compressed
-indicator needle
Studies have shown a correlation between ? strength and ? muscular strength tests
-hand-grip
-dynamic
Anatomical landpoint for spring-loaded handgrip dynamometers is ?
second phalanx
Body position for assessing strength using a handgrip dynamometer
-adjust ? size
-individual ?
-shoulder ? and ? rotated
-elbow ? or flexed at ?
-forearm in ? position
-adjust handgrip size
-individual stands
-shoulder adducted and neutrally rotated
-elbow straight or flexed at 90
-forearm in neutral position
Squeeze hand dynamometers as hard as possible using one brief ? contraction and NO ?
-maximal
-extraneous body movement
With a handgrip dynamometers, do ? trials per hand, with ? min rest between trials
-3 trial
-1 min rest
Use ? value as ? strength when using a handgrip dynamometer
-best value
-static
Protocol for handgrip dynamometer
Isometric grip strength norms