Better Plant Tax SG 2
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What feature is a synapomorphy of the eudicots?
Triaperature pollen
Are the leaves of Ranunculaceae pinnately or palmately lobed?
Palmately
What is the count of stamens and carpels in the Ranunculaceae family?
Numerous
The carpel of Ranunculaceae are apocarpous, which means what?
Their ovaries are separated
What type of fruits do members of the Ranunculaceae manufacture?
Aggregate fruits → can be berries, drupes, etc.
What is often found merosity of the Ranunculaceae family?
5-merous
Members of the Ranunculaceae are likely to have showier petals or sepals?
Sepals - many have lost their petals and made the sepals showy
Members of Papaveraceae are STRICTLY what habit type?
Herbaceous
What substance do members of Papaveraceae produce?
Latex - which is toxic and alkaloid rich
What is so unique about producing latex?
It’s expensive to produce because of the presence of Nitrogen which is a limiting nutrient in most soils
The sepals of Papaveraceae can be described as what term? And what does that term mean?
Cauducous - early deciduous
What specific fruit type is unique for the Papaveraceae family?
Poricidal capsule
T/F: The numerous tiny seeds of the Papaveraceae family is similar to Orchidaceae, in which they lack endospermatic tissue.
FALSE - they’re just numerous and tiny seeds
T/F: The Papaveraceae family is much larger in size compared to the Ranunculaceae family.
FALSE - much smaller (825 v. 2500)
The Crassulaceae family’s habit can best be described as what?
Succulent
Think of CAM plants = desert = succulence (normally)
The Crassulaceae family often has a suffrutescent which is ….
being woody at the base and herbaceous above ground
What type of photosynthesis do members of the Crassulaceae family undergo?
CAM - Crassulacean Acid Metabolism = stomata open at night
Members of the Crassulaceae family have 5 ______ ovaries.
Apocarpous
What type of fruit does members of the Crassulaceae family produce?
Aggregate of follicles
T/F: Compared to the Papaveraceae family, the Crassulaceae family is larger in size.
TRUE
Succulence on a plant is (normally) a good indication of what type of photosynthesis?
CAM
Describe the leave for members of the Saxifragaceae family.
They are mostly basal leaves in rosettes
What is unique about the gynoecium found in Saxifragaceae?
It is fused and lobed
Similar to onions, Saxifragaceae members have a ______ present.
Scape
What is the stamen count for members of the Saxifragaceae?
10 stamens
What is the petal AND sepal count for members of the Saxifragaceae?
5 of each → perianth = 10 total
T/F: The Saxifragaceae family is smaller in size (like Papavers) compared to the Crassulaceae family.
TRUE
What are 3 features of the Caryophyllales ORDER?
Free central placentation
Curved embryos
Betalains
T/F: Betalains are easy for plants to produce.
FALSE - they require Nitrogen = limiting nutrient in most soils
What is characteristic of the nodes of the Caryophyllaceae family?
They are swollen
What is the merosity found in the Caryophyllaceae family?
5-merous
What is the specific fruit type found in Caryophyllaceae?
a) Capsules
b) Follicles
c) Loculicidal capsules
d) Denticidal capsules
d) Denticidal capsules
Describe the petals of the Caryophyllaceae family.
The petals are often notched to fringed, and contain a claw (which is a narrowing/tapering region)
Teeth number on the denticidal capsule of Caryophyllaceae is normally 1-2 times the….
style or carpel number
The habit of the Cactaceae family can be best described as what?
Succulent
What type of ovary and fruit type can be found in the Cactaceae family?
Inferior → berry
Members of the Cactaceae family have short axillary shoots with congested “leaves” called…
areoles
On the areoles of the Cactaceae family, barbed trichomes called ______ can be found.
glochids
Many cacti will actually make leaves, but these leaves are characteristically what?
a) Large
b) Caducous
c) Small
d) A & B
e) B & C
e) Caducous and small
Give the modified plant tissue/part that produces the following pointy structures:
Spines
Thorns
Prickles
Spines → modified leaves
Thorns → modified stems/branches
Prickles → modified epidermal tissue
What type of fruit does members of the Amaranthaceae family form?
Achenes → specifically an utricle
What is distinct about members of the Amaranthaceae family?
a) Caducous leaves
b) Farinose/salty covering
c) 3 sided achene
b) Farinose covering - the saltbushes
T/F: The Amaranthaceae family is rather small, on the same level as Papaveraceae and Saxifragaceae.
FALSE - rather large at ~2500 species
What is characteristic of the Polygonaceae family?
a) 3 sided achene
b) ochrea
c) swollen nodes
d) all of the above
d) ALL OF THE ABOVE
What is this thing?

An ochrea
What is unique about the fruit type of the Polygonaceae family?
They form 3 sided achenes
What inflorescence do members of the Polygonaceae form?
Inflorescence of fascicles
T/F: Members of the Polygonaceae family often have 6 tepals.
TRUE
If ovary position or leaf attachment is not mentioned, we can infer it is _______ & ________ respectively.
superior & alternate
Members of the Nyctaginaceae have what type of leaf arrangement?
a) Opposite
b) Alternate
c) Whorled
a) Opposite
What is the structure of showy bracts that forms a ring, found in the Nyctaginaceae family?
An involucre
T/F: The petals are persistent in members of the Nyctaginaceae, but are often not showier than the involucre of bracts.
FALSE - they are ABSENT (the showier part is true though)
T/F: The Nyctaginaceae family is rather small, with about 405 species.
TRUE
What is the habit of the Euphorbiaceae family?
Succulent
What do members of the Euphorbiaceae produce, similar to other families covered?
Latex
What is the inflorescence type of the Euphorbiaceae family?
Cyathium - mini cyme that LACKS A PERIANTH
The ovaries of Euphorbiaceae are ___ carpellate ovaries.
3
T/F: The Euphorbiaceae family is a pretty small family with less than 1k species.
FALSE - Euphorbiaceae has nearly 7k species
What are the 2 flower types of Violaceae and describe what they mean?
Chasmogamous = opening up at maturity
Cleistogamous = staying closed through maturity
Members of the Violaceae family have a nectar spur which indicates what?
Bilateral symmetry (AKA zygomorphic)
Describe the androecium and gynoecium of the Violaceae family.
They have 5 connivent stamens & 3 carpellate ovaries
What placentation type is characteristic of the Violaceae family?
Parietal placentation
Members of the Violaceae family produce a ________ capsule.
Loculicidal
What is the reason for cleistogamy in Violaceae?
They self pollinate and they are also the earliest flowering plants so no pollinators are out in the first place
What genus consists of over half of the Violaceae family?
Viola
The stipules of the Violaceae family are found where on the plant?
At the nodes
What is the habit of the Salicaceae family?
Riparian shrubs to trees
Are leaves of the Salicaceae family simple or compound? What about their attachment?
Simple and Alternate
What are the characteristic glands found on the tips of the leaf margins for members of the Salicaceae?
Salicoid teeth
Describe the flowers of the Salicaceae family.
They are unisexual and small, lacking a perianth
What type of inflorescence do members of the Salicaceae family have?
Catkins
Describe the seeds found in the Salicaceae family.
They are comose seeds with tufts of coma
Describe the difference between Salix and Populus genera in the Salicaceae family.
Salix = upright catkins & ONLY 1 bud scale
Populus = pendulous catkins & 2+ bud scales
ALL members of the Fabaceae have what 4 characteristics?
Stipules
Compound leaves
Legume fruits
Root nodules
T/F: The Fabaceae family is the 3rd largest family in the world with 19,500 species, but less than the Orchidaceae family.
TRUE
What about the leaves are characteristic in the Mimosoid subfamily of the Fabaceae?
Bi-pinnately compound
What inflorescence does the Mimosoid subfamily produce?
Heads → bottlebrushes"
What type of floral symmetry does the Mimosoid subfamily have?
Radial
What are the Beltian bodies found in the Acacia genus?
These are protein bundles found on the secondary leaflets that act as “ant food”; the Acacia and ants have a symbiotic relationship where the Acacia provides food and the ants deter herbivory
Label the correct parts of the diagram.
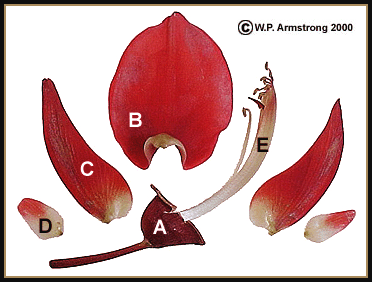
A = calyx
B = banner (1)
C = keel (2 fused petals)
D = wings (2)
E = diadelphous stamens
What are diadelphous stamens?
A cluster of stamens broken into 9 fused stamens + 1 free one
What is the largest genus on Earth that is found in the Faboid subfamily?
Astragalus
What is characteristic of the stipules in Rosaceae?
The stipules are fused
What is the merosity of the Rosaceae family?
5-merous
What structure is common in members of Rosaceae?
Hypanthium
What is a hypanthium?
Fusion of petals, sepal, and androecium
What are some similarities and differences between Rosaceae and Ranunculaceae?
Similarities = apocarpous gynoecium, numerous stamens
Differences = stipules found in Rosaceae, no hypanthium in Ranunculaceae
Every rose has its……
PRICKLE
A pome is known as an ________ fruit.
accessory
What is the fleshy part of the pome?
Mostly hypanthium or receptacle tissue
What fruit type do members of Rosaceae mostly form?
Aggregate of achenes
ALSO pomes and drupes
What do members of Moraceae produce to reduce herbivory?
Latex
T/F: ALL members of Moraceae are strictly woody.
TRUE
Do members of Moraceae have strictly compound or simple leaves?
Strictly simple leaves
What fruit type do members of Moraceae form?
Multiple fruit of achenes
What type of inflorescence do members of Moraceae have?
heads to catkins
What genus makes up nearly 75% of Moraceae?
Ficus = figs
Members of the Regoniacae family have what type of leaf bases?
Asymmetric
How many tepals are found in members of Regoniacae? Hint: Male and female are different
Male = 4
Female = 5
Describe the ovary of the Regoniacae family.
It is a winged inferior ovary