ASTR1220 Midterm (night sky - gravity)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what unit of distance do we use
Kilometers!
inner planets of solar systems are…
Rocky (terrestrial) and small e.g. Venus, Mercury, Earth, Mars
Outer planets are…
gas giants (made of mostly hydrogen) e.g. Jupiter, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn
Astronomical Unit (AU)
Average distance between Earth and Sun. 1 AU = 150 mil km
Light Year
UNIT OF DISTANCE that light can travel in one year. Speed of light is always constant and light is the fastest thing in the universe. 1 ly = 9.5 trillion km
how long does it take light to travel to earth?
8 mins from the sun to get to us on earth. 1 AU = 8 light minutes
When we look at an object that's 1,000 ly away, we see it...
As it was 1,000 years ago
Explanation: bc ly describes a unit of distance NOT time, but when sometimes is so so far away, time eventually gets involved because we don't see it instantly as it is not close. Something that is 1,000 ly away takes 1000 years to travel to Earth
how do we measure the size of astronomical objects?
using trigonometry (do some practice problems with it)
earth rotates around its axis once a day
this gives us night and day
celestial sphere
the location of stars onto the surface and we view the celestial sphere form the inside unlike an Earth globe
North celestial pole
point in space directly over Earth’s north pole
altitude
how high in degrees above the horizon
why do the stars appear to move?
bc of Earth’s rotation. the stars themselves aren’t moving rather it’s Earth that’s rotating causing stars trail
polaris
north star that lies near the north celestial pole. you can see it in the northern hemisphere
in what direction does earth rotates? what direction do stars move?
counter clock wise from east to west. so all stars also move in arcs across the sky from east to west
how does astrology work?
The sun is in front of a zodiac sign each month (we can't see that zodiac in the night sky for that month until 6 months later when that constellation appear directly opposite of another constellation)
+ e.g. In Jan, the sun is in front of Capricorn. 6 months later you'll see Capricorn directly on the other side of the axis
ecliptic plane
earth’s orbital path around the sun
how do we get seasons?
earth’s rotational axis which is tilted 23.5 degrees in the ecliptic plane. the more extreme the tilt, the more extreme the seasons (90 degrees most extreme season & 0 degrees = no seasons bc every place on earth would receive the same amount of sunlight year round and everywhere except the poles would have the same 12 hours of day and night)
in the northern hemisphere, earth’s tilted rotational axis cause north pole to be pointed where in the summer? in winter?
polaris is pointed towards the sun in the summer. polaris is pointed away from the sun in the winter (helpful to draw it out to visualize)
define:
summer solstice
spring equinox
fall equinox
winter solstice
summer solstice: longest day of the year, we get the most daylight bc sun’s path is the highest on Earth and rise to the most extreme north of due east and west
spring equinox and fall equinox: 12 hours of day and night so that’s split evenly
winter solstice: shorter day of the year, we get the least daylight and the longest night bc sun’s path is the lowest on earth and set at the most extreme south of due east and west
(helpful to draw it out)
rank earth’s distance from the sun with respect to the seasons (in northern hemisphere)
closest to the sun= winter. earth is closest to the sun during the winter. in the northern hemisphere we get winter while the southern hemisphere enjoys summer due to earth’s rotational axis as polaris points away from the sun (in the northern hem)
Spring
Fall
furthest to the sun = summer. in the northern hemisphere earth is furthest from the sun in the summer bc polaris is pointed to the sun, we enjoy warmer season. the southern hemisphere would get winter
rank how much time the person spends in daylight from most to least daylight based on Earth's tilt:
1. 23.5 degrees tilt (facing towards the sun)
0 degree tilt
23.5 degrees tilt (facing away from the sun)
45 degrees tilt
90 degrees tilt --> experience least daylight where only half the world enjoying daylight and night all the time
what happens when earth’s tilt is 90 degrees? 0 degrees?
90 degrees = Each hemisphere (north and south) would take turns pointing at the sun for half a year. 6 months of winter in the northern hemisphere and 6 months of summer in the southern hemisphere, vice versa. most extreme season
uranus gets the most extreme season due to most tilt
0 degrees = no seasons. north and south hem would experience same amount of day and light
jupiter gets no season due to having least tilt
What makes planets so special?
Move with respect to fixed stars
Change in brightness
Change speed
Some planets (Mars) appear to undergo retrograde motion
heliocentric model
Earth is not the center, rather all planets revolve around the sun (theorized and developed by Copernicus; later supported by Galileo)
define:
Speed
Velocity
Acceleration
speed- how fast an object moves over time.
speed = 100 miles / hr
velocity- involves speed and direction
velocity = 25 km/hr towards the northwest
acceleration- the changes in speed OR direction over time
speed up from 0 to 60km/hr
changing direction
acceleration is caused by an applied force
Kepler’s laws
describe the patterns and relationships that predict the positions and motions of the planets
kepler’s 1st law
Orbit of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus point. Circle has an eccentricity of 0 (e=0). the bigger the eccentricity the more elliptic it is.
higher eccentricity = longer ellipse
lower eccenticity = closer it appears to a circle
what is the eccentricity of earth?
close to zero (e=0) as earth’s orbit around the sun is close to a circle
kepler’s 2nd law
as planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times. this means:
as a planet orbit further from the sun, it travels slower; as planet orbit closer to the sun, it travels faster. but both sweeps out equal areas as they are all in the same orbit (helpful to draw it out)
kepler’s 3rd law
more distant planets orbit the sun at slower average speeds
p^2 = a^3
p= orbital period (in years)
a= avg. Distance from sun (in AU)
This is an empirical relationship but it is not a real law
The size of the orbit determines the orbital period; planets that orbit near the sun orbit with shorter periods than planets that are far from the sun (e.g. Mars orbit sun slower so 1 year in Mars is longer than Earth which orbits the sun faster as it’s closer)
the planet’s mass does not matter here bc it only depends on the object’s orbit’s distance from the sun
Does earth or mars have higher orbital velocity?
Earth have higher orbital velocity because it is closer to the sun than Mars. Making Earth orbit the sun at a higher speed than Mars
what is the explanation for Mars Retrograde motion?
when one planet that goes fast (Earth) overtakes the slower planet (Mars) which makes it looks like Mars is "going backwards" but it's really Earth going faster and overtaking Mars in the orbital space due to Kepler's third law
Specific explanation of Kepler's 2nd and 3rd law
2nd law tells us what one particular planet does when it orbits a star (sun)
3rd law tells how the orbital periods are related to the orbital distances for all the planets in the solar system
Planets that are in an orbit located near the sun have short orbital periods
Planets that are in an orbit located farther will have longer orbital periods
According to Kepler's second law, a planet with an orbit like Earths would:
Experience very little change in orbital speed over the course of the year
If a small weather satellite and a large international space station are orbiting earth at the same altitude above earth's surface, what is true?
Each has the same orbital period. Why? Bc mass of the objects does not matter when it comes to determining whether their orbital period is longer/shorter. If they are orbiting earth at the same altitude above earth's surface, then that means they are all in the same orbital period
define:
mass
density
size
weight
Mass: the amount of matter in an object
Density: mass/volume = density
Size: how much space the object takes up
Weight: gravitational force that acts upon an object's mass. You will have different weight on Earth vs Moon but same mass
Mass DOES NOT CHANGE but weight does depending on gravity
Weight of astronaut = 1200N of force on Earth; weight of astronaut = 200N on Moon
Newton’s 1st law of motion
An object moves at constant velocity (or remains at rest) unless a force act on it to change its speed or direction
A hockey puck glides across the ice at constant speed until it hits something
An astronaut will coast in space along a straight line at constant speed (unless a force acts on it)
Newton’s 2nd law of motion
Force = mass x acceleration
if mass goes down, then acceleration goes up.
if force goes up so does acceleration
Throwing a football harder will make it go faster; given the same force, a smaller mass will be given more acceleration (bc it is lighter)
Newton’s 3rd law of motion
For any force, there is always an equal and opposite reaction force
Sitting still, you're exerting the same amount of force on your chair as it's exerting on you. No motion means forces are balanced (equal and opposite)
A rocket is propelled upward by force equal and opposite to the force with which the gas is being expelled
Newton's Universal Law of Gravity
Every mass attracts every other mass
Attraction is increases as the product of their masses (M1 * M2)
Attraction decreases as the square of the distance between their centers
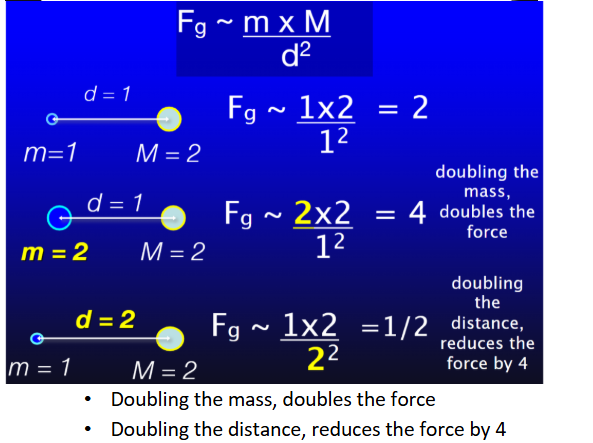
which laws are universal: Newton’s or Kepler’s?
Newton’s. Kepler’s describe a pattern or observation instead
make sure to do practice prob with universal law of gravitation!
is the force the earth exerts on you larger, smaller, or the same force you exert on it?
earth and I exert equal and opposite forces on each other