4 Lec 17 (Exam 3): Systemic diseases manifested in the jaws, Soft tissue calcifications and ossification
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, endocrine disorders will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, hyperparathyroidism will result in a ______ in bone density
both increase and decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, hypoparathyroidism will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, Cushing's Syndrome will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, metabolic diseases will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, osteoporosis will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, Rickets Disease will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, hypophosphatasia will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease
In terms of changes in bone density, hypophosphatemia will result in a ______ in bone density
decrease; increase rare
In terms of changes in bone density, Renal osteodystrophy will result in a ______ in bone density
increase
In terms of changes in bone density, Osteopetrosis will result in a ______ in bone density
Hyperparathyroidism
ID the pathology:
•'Salt and pepper' appearance of calvarium
•Granular
•Loss of diploic trabeculae
Demineralization/ thinning of cortical boundaries
•Loss of distinct lamina dura
• No demineralization of mature teeth
demineralization of mature teeth
All of the following are findings of a patient with Hyperparathyroidism EXCEPT:
- decrease bone density
- salt and pepper appearance
- cortical thinning
- demineralization of mature teeth
- Brown tumors
- loss of lamina dura
- ground glass appearance
salt and pepper appearance
All of the following are findings of a patient with Renal Osteodystrophy EXCEPT:
- decrease bone density
- salt and pepper appearance
- cortical thinning
- increase bone density
- Brown tumors
- loss of lamina dura
Brown tumors
This patient has hyperparathyroidism. What type of lesion is this?
Hyperparathyroidism
Radiograph shows patient with generalized decrease in bone density (except for mature teeth), loss of lamina dura, but no demineralization of mature teeth. Maxillary sinuses, inferior border of mandible and mandibular canal are demineralized, not distinctly visible. Trabecular bone has "salt and pepper" like appearance or "ground glass". Patient has high serum calcium, PTH and alkaline phosphatase. What is the diagnosis?
Hyperparathyroidism
Brown tumors are associated with _______
-Loss of bone mass: increased radiolucency
-Loss of distinct lamina dura
describe the changes in bone density from this pano:
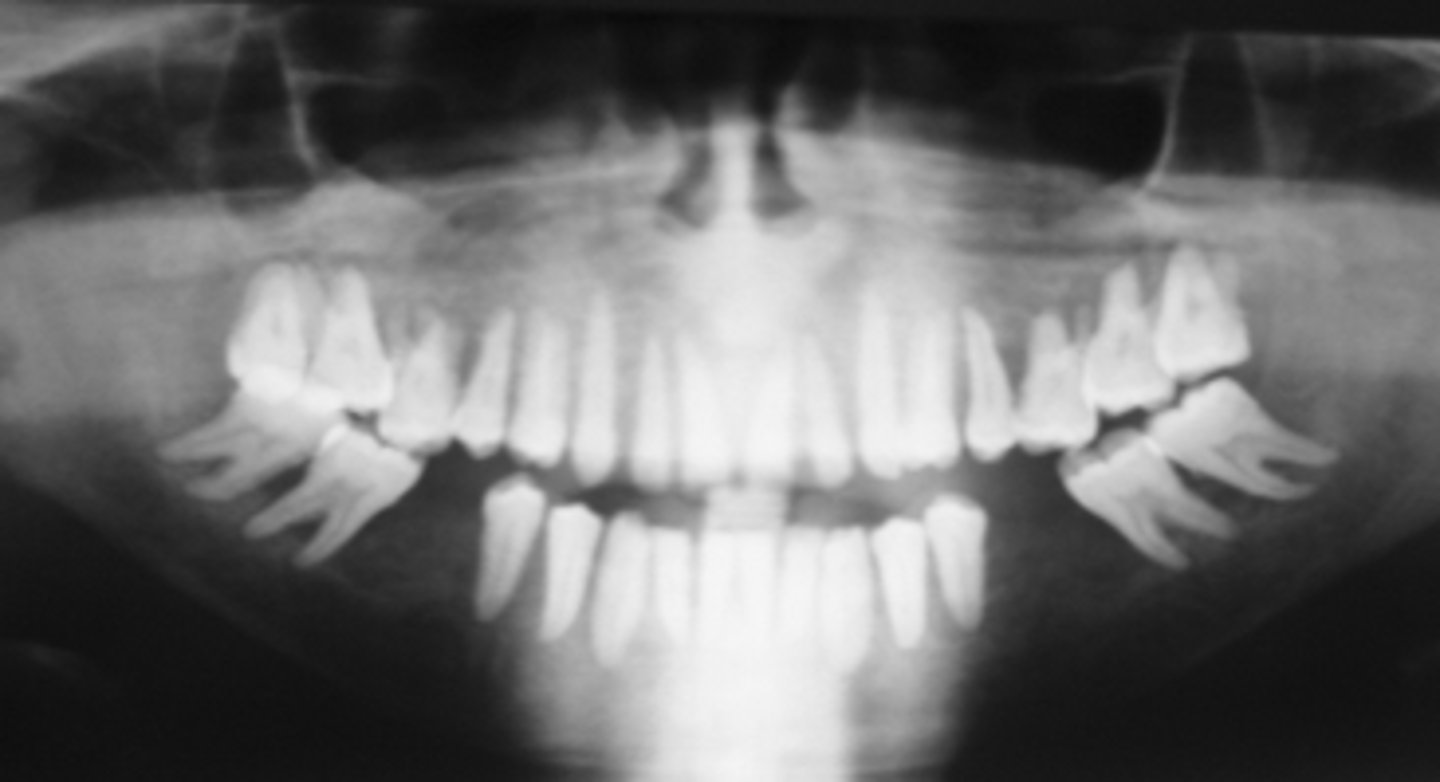
-Diffuse sclerotic bone pattern: increased radiopacity
-Loss of distinct inferior cortex of mandible
describe the changes in bone density from this pano:
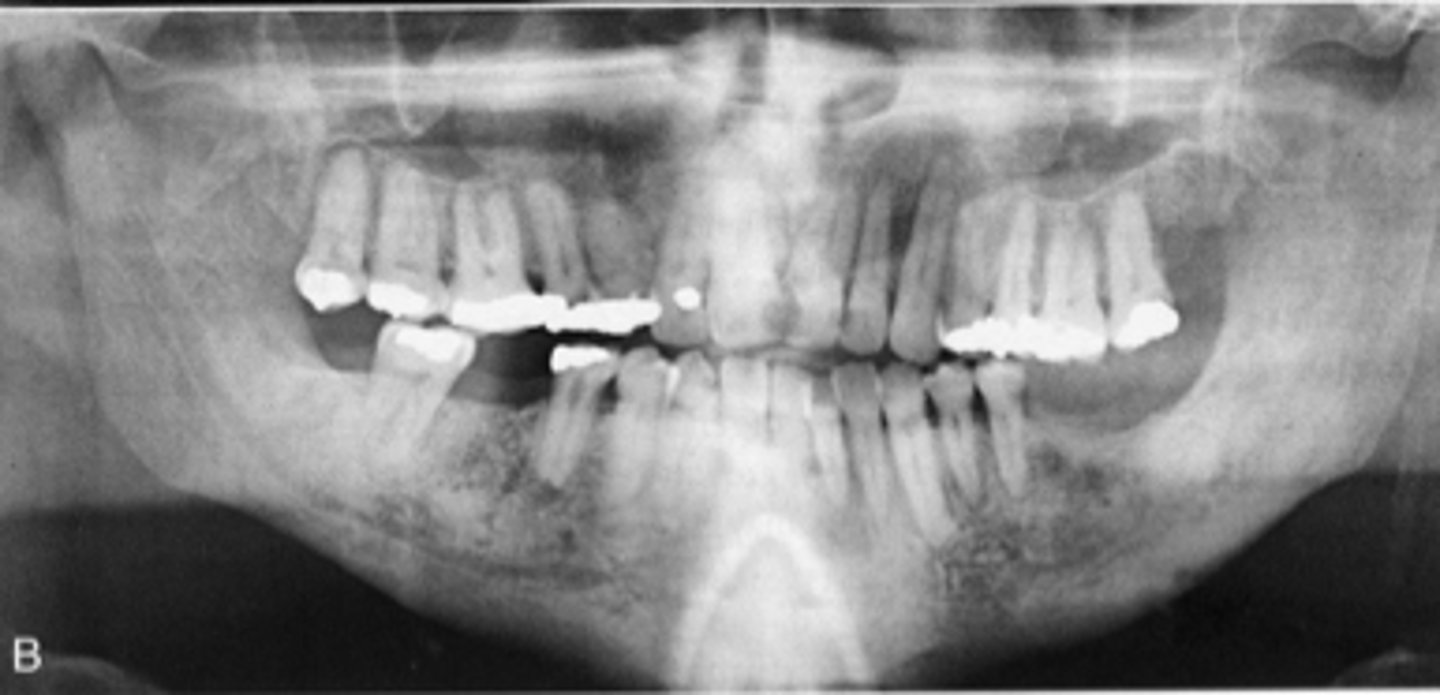
secondary hyperparathyroidism/renal osteodystrophy
These sclerotic changes around the roots is associated with :
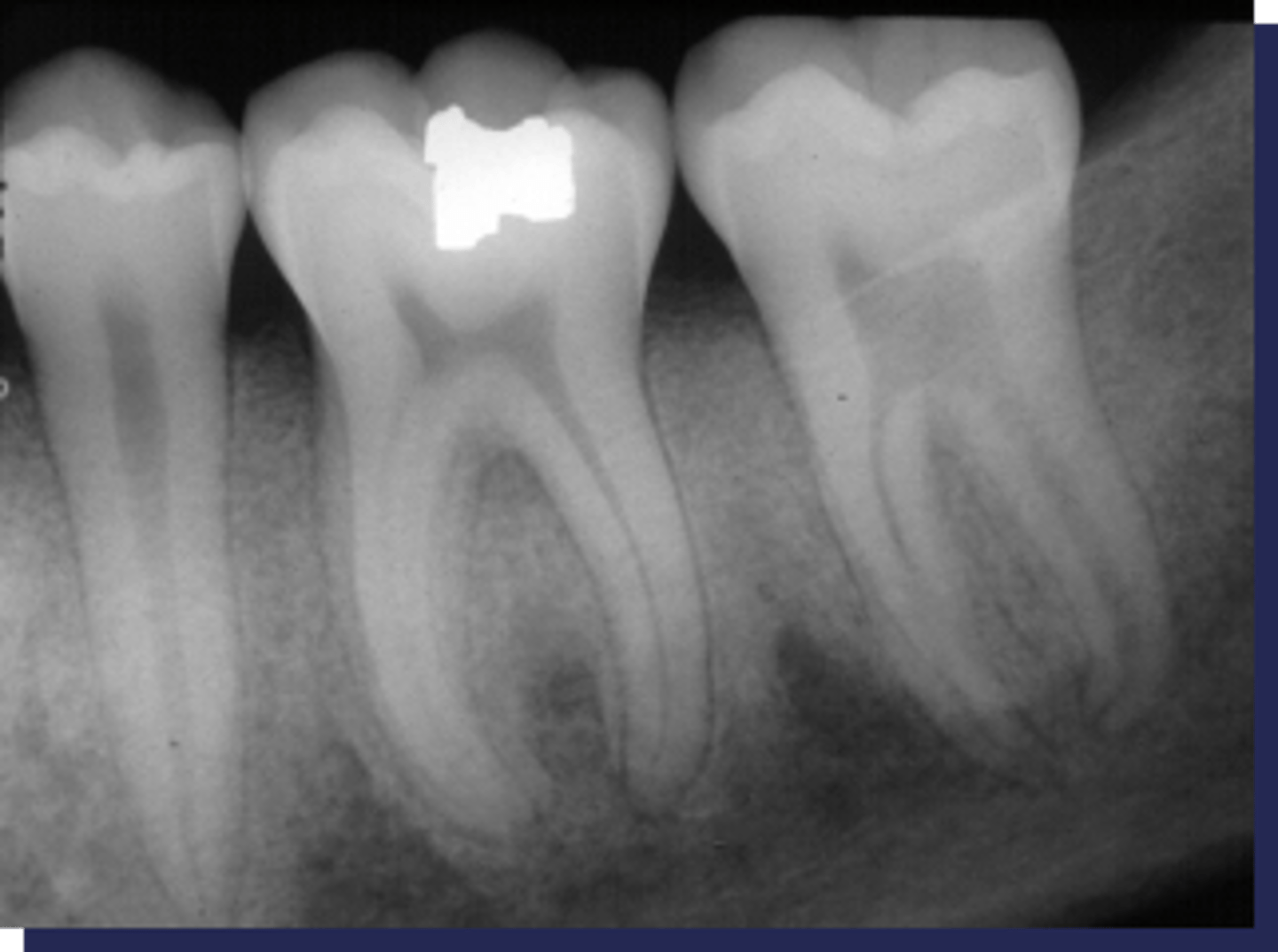
primary osteoporosis
Type of Osteoporosis due to age related changes in bone:
secondary osteoporosis
Type of Osteoporosis due to nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalance, corticosteroid or heparin therapy:
Brown tumors
All of the following are findings of a patient with Osteoporosis EXCEPT:
- decrease bone density
- cortical thinning
- Brown tumors
- reduced volume of trabecular bone
- thinning of lamina dura
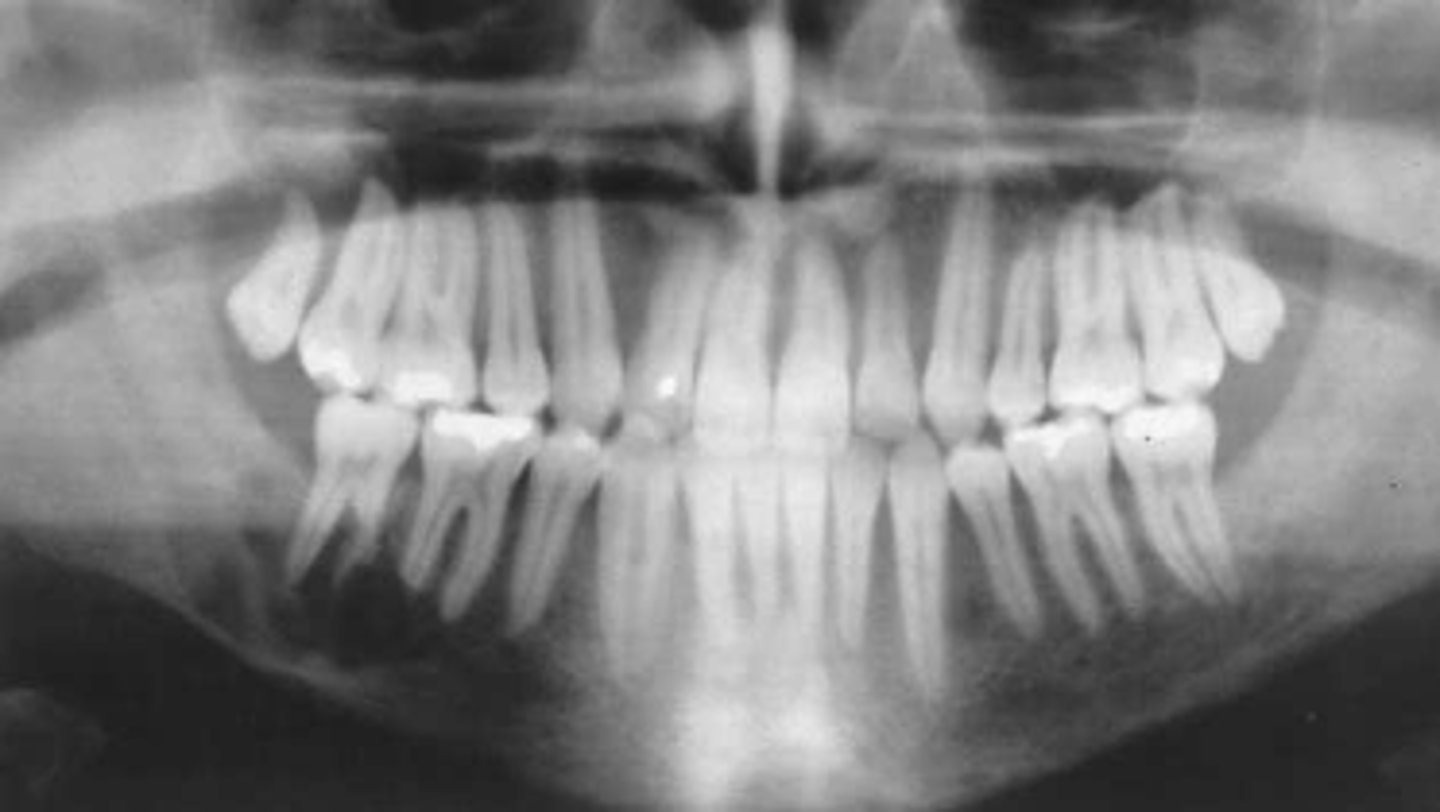
Osteoporosis
Patient's radiograph shows the following
•Overall reduction in density of bone.
•Reduced density and thinning of inferior mandibular cortex
•Reduction of volume of trabecular bone
•Lamina dura may appear thinner than normal
Patient is currently on heparin therapy for pulmonary emboli. What is the diagnosis?
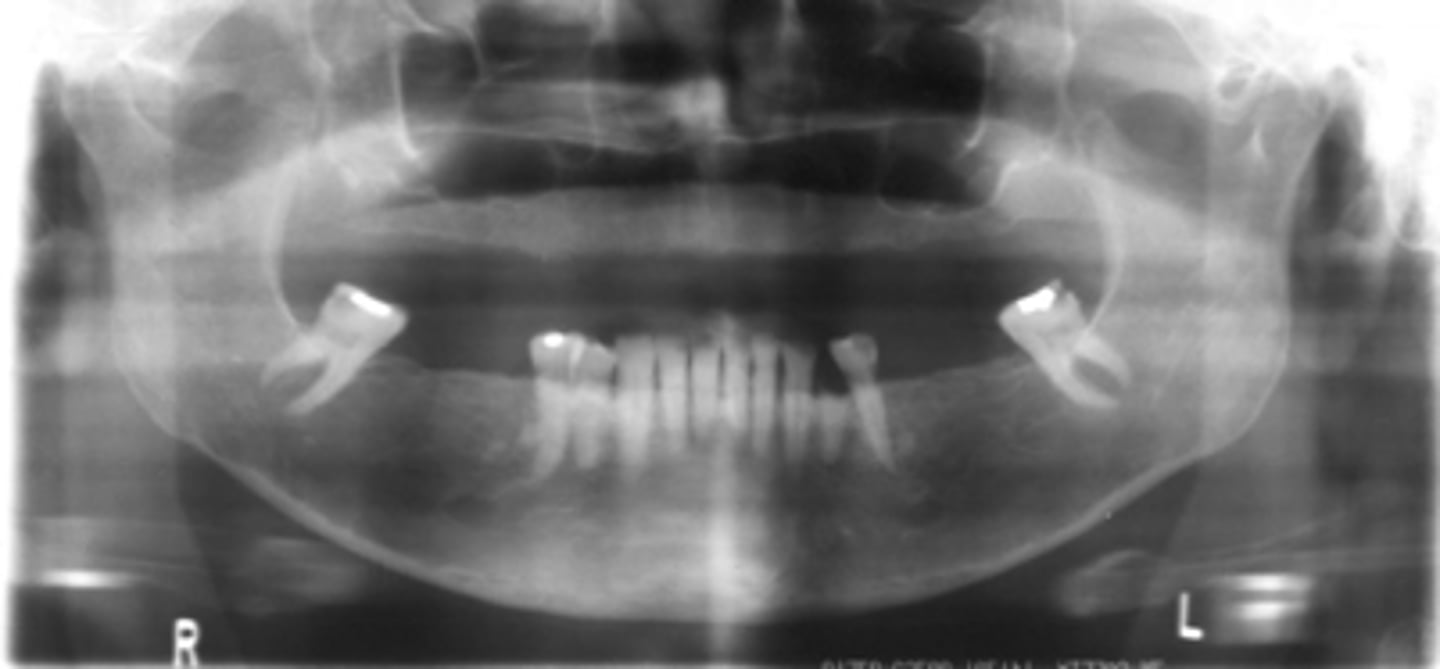
cortical thinning of inferior mandibular cortex
All of the following are findings of a patient with Rickets EXCEPT:
- decrease bone density
- cortical thinning of inferior mandibular cortex
- reduced volume of trabecular bone
- thinning of lamina dura
- hypoplasia of enamel
- retarded tooth eruption
Rickets
Patient's radiograph shows the following:
•Reduction in bone density
•Thinning/missing lamina dura/cortex of tooth follicles
•Hypoplasia of enamel
•Retarded tooth eruption
Patient has a Vit-D deficiency due to malabsorption. What is the diagnosis?
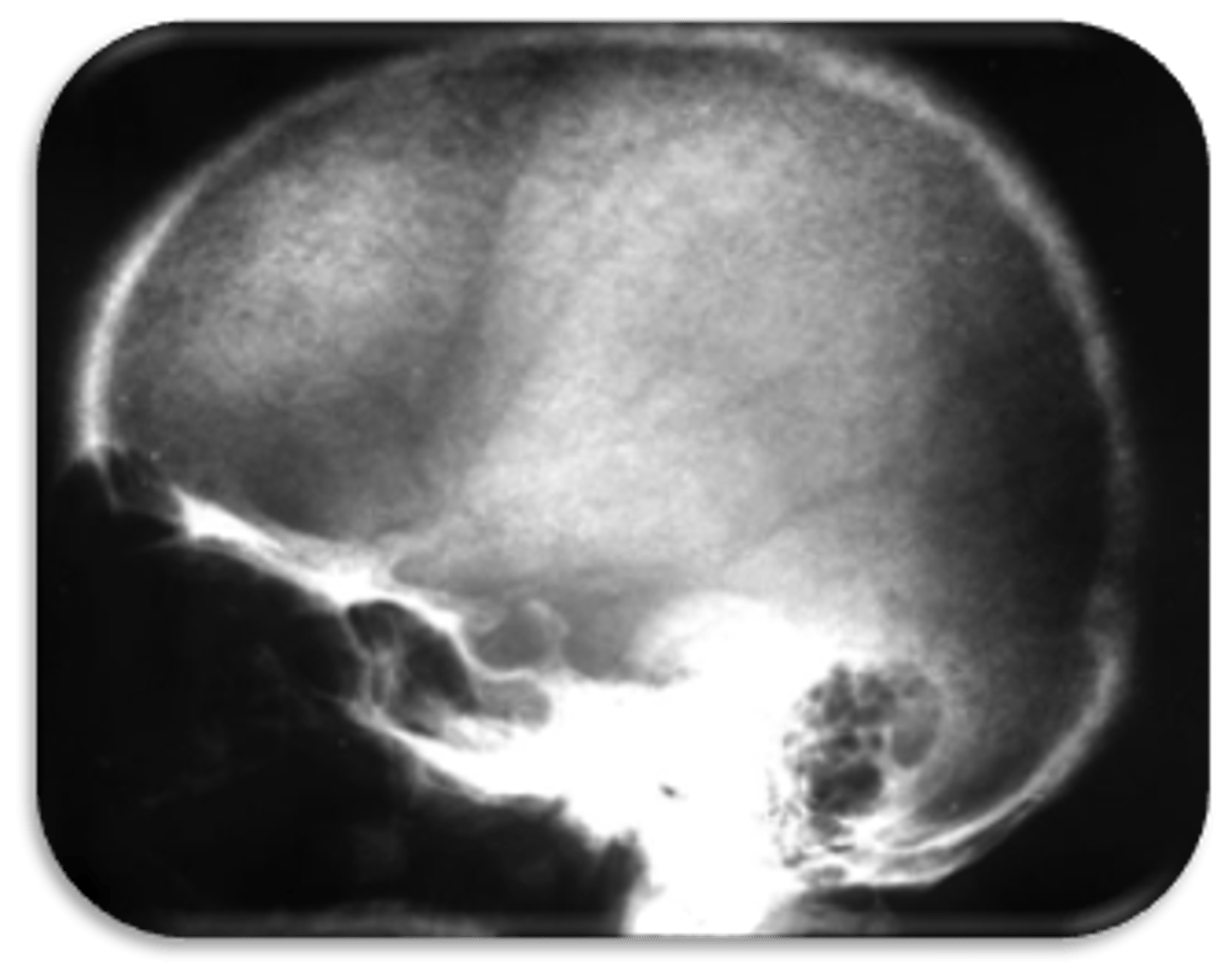
Hypophosphatasia
First clinical sign of this disorder is premature loss of primary teeth and delayed eruption of permanent teeth:
increase bone density
All of the following are findings of a patient with Hypophosphatasia EXCEPT:
- premature loss of primary teeth
- delayed eruption of permanent teeth
- Premature closure of skull sutures
- increase bone density
- Gyral/ convolutional markings on skull resembling ‘beaten metal’
- decrease bone density
- Thin enamel
- large pulp chamber and root canal
- thinning of lamina dura
Hypophosphatasia
Patient presents with the following radiographic features:
-Premature closure of skull sutures
- Gyral/ convolutional markings on skull resembling ‘beaten metal’
- generalized decrease bone density
- Thin enamel
- large pulp chamber and root canal
- thinning of lamina dura
Patient has a history of premature loss of primary teeth and delayed eruption of secondary teeth. What is the diagnosis?
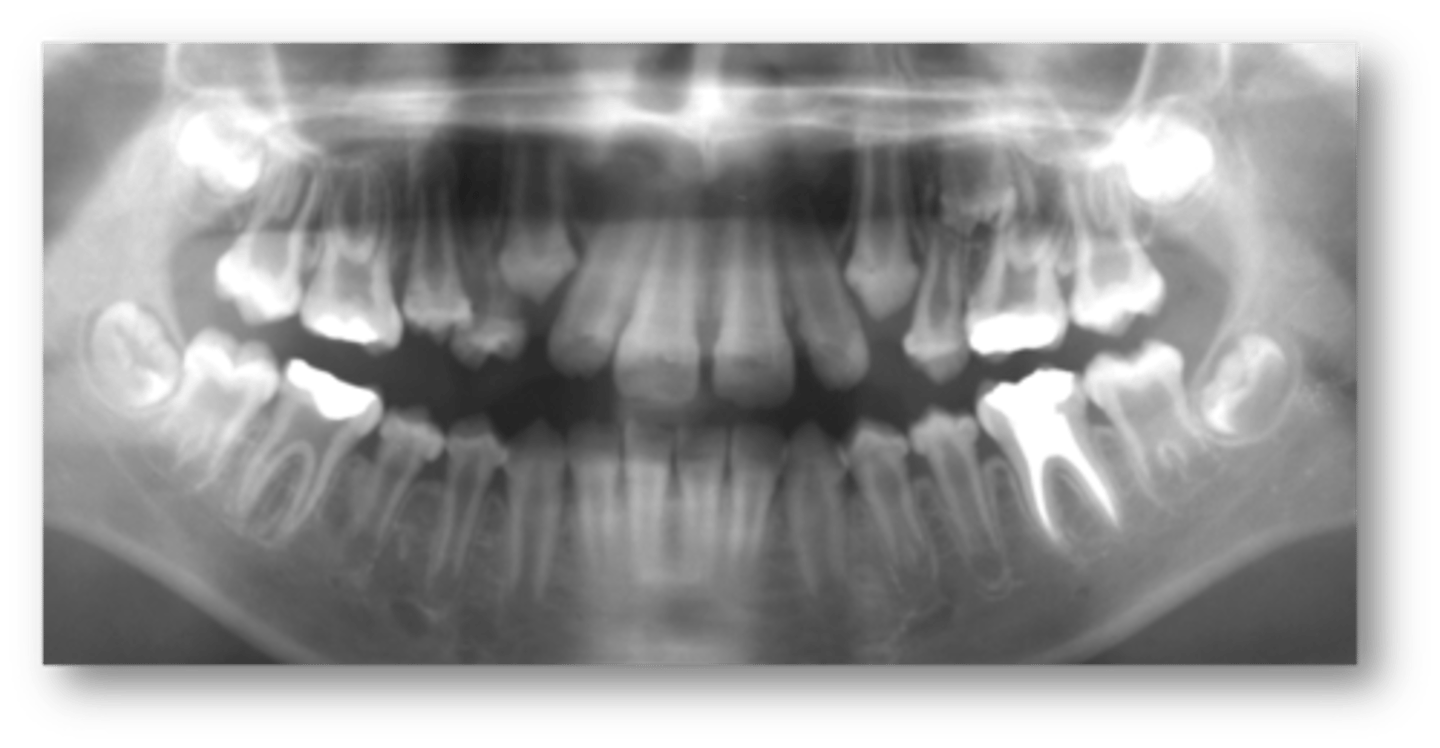
Hypophosphatasia
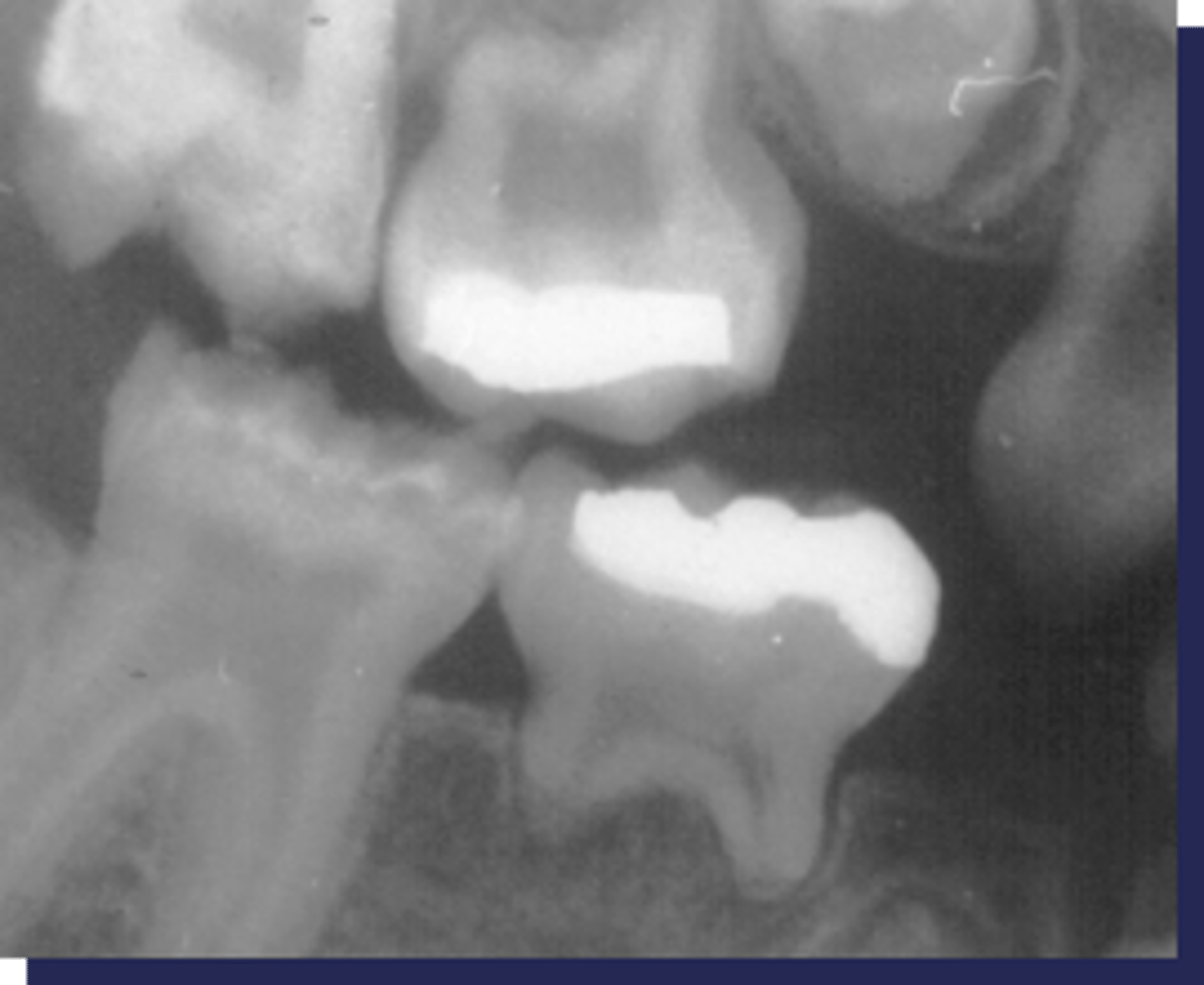
A large pulp chamber and root canal with apical displacement of pulpal floor is associated with:
Hypophosphatasia
Gyral/ convolutional markings on skull resembling ‘beaten metal’ is associated with:
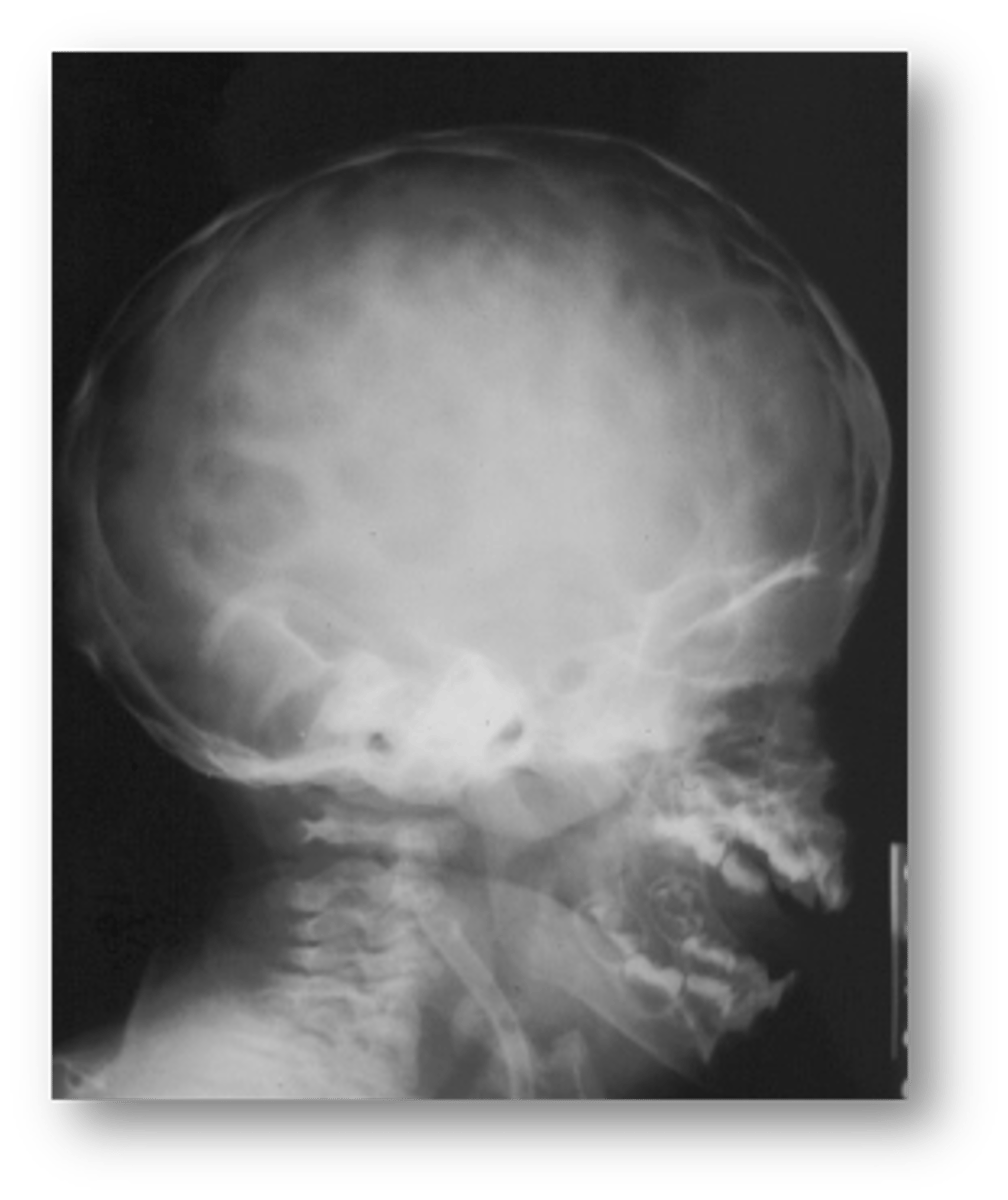
Hypophosphatasia
ID the pathology:
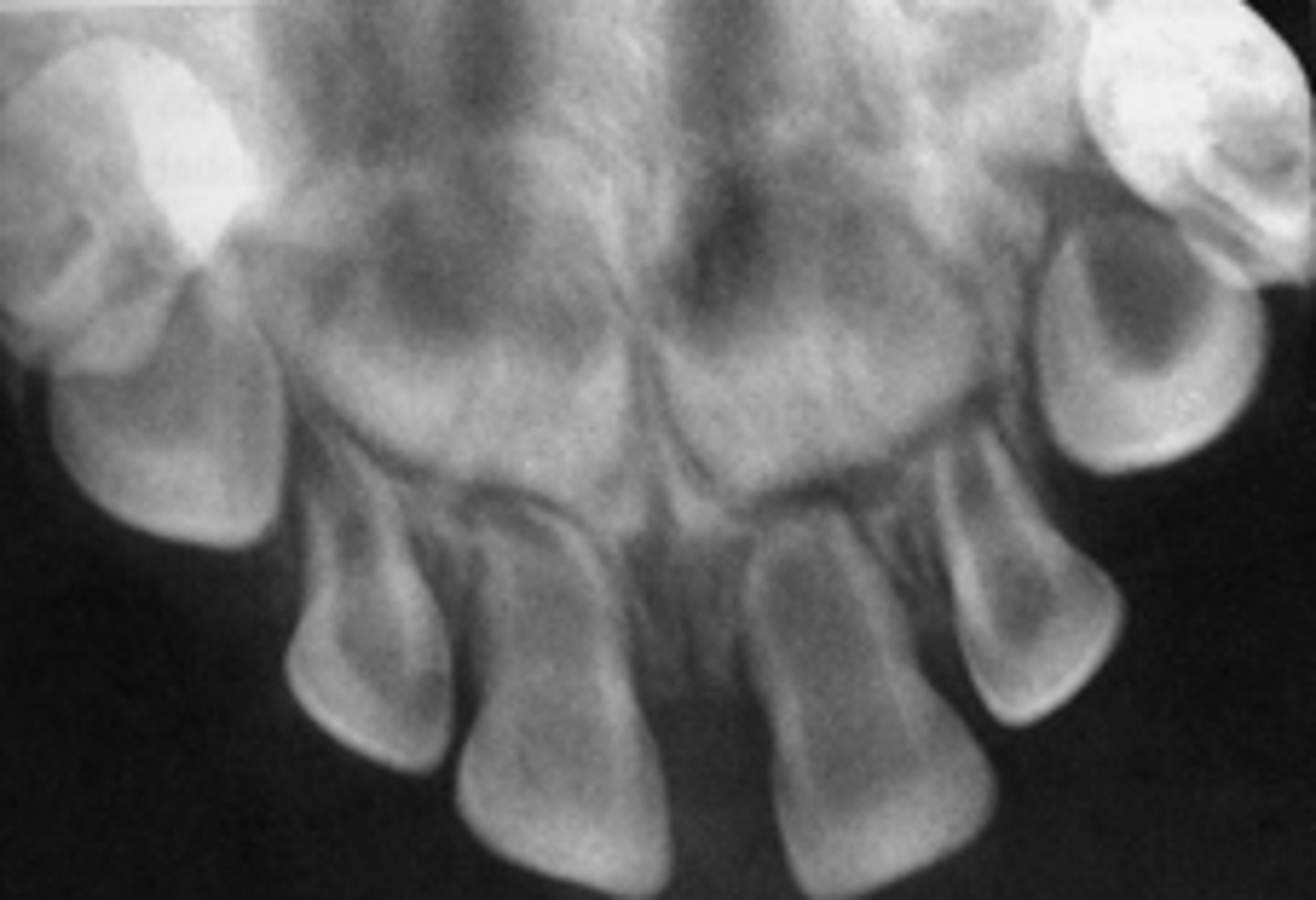
Osteopetrosis
This condition is known as a "Marble" bone disease:
Osteopetrosis
Patients with this condition have a predisposition to osteomyelitis resulting from dental/periodontal disease:
'beaten metal’ appearance
All of the following are findings of a patient with Osteopetrosis EXCEPT:
- increase bone density
- symmetric enlargement of bone
- ‘beaten metal’ appearance
- marble bone appearance
- obliteration of bone marrow
- neural compression
Osteopetrosis
Patient's radiograph presents with a diffuse, symmetric increase in bone density and enlargement of bone (marble bone appearance). Patient experiences neural deficits in the face. What is the diagnosis?
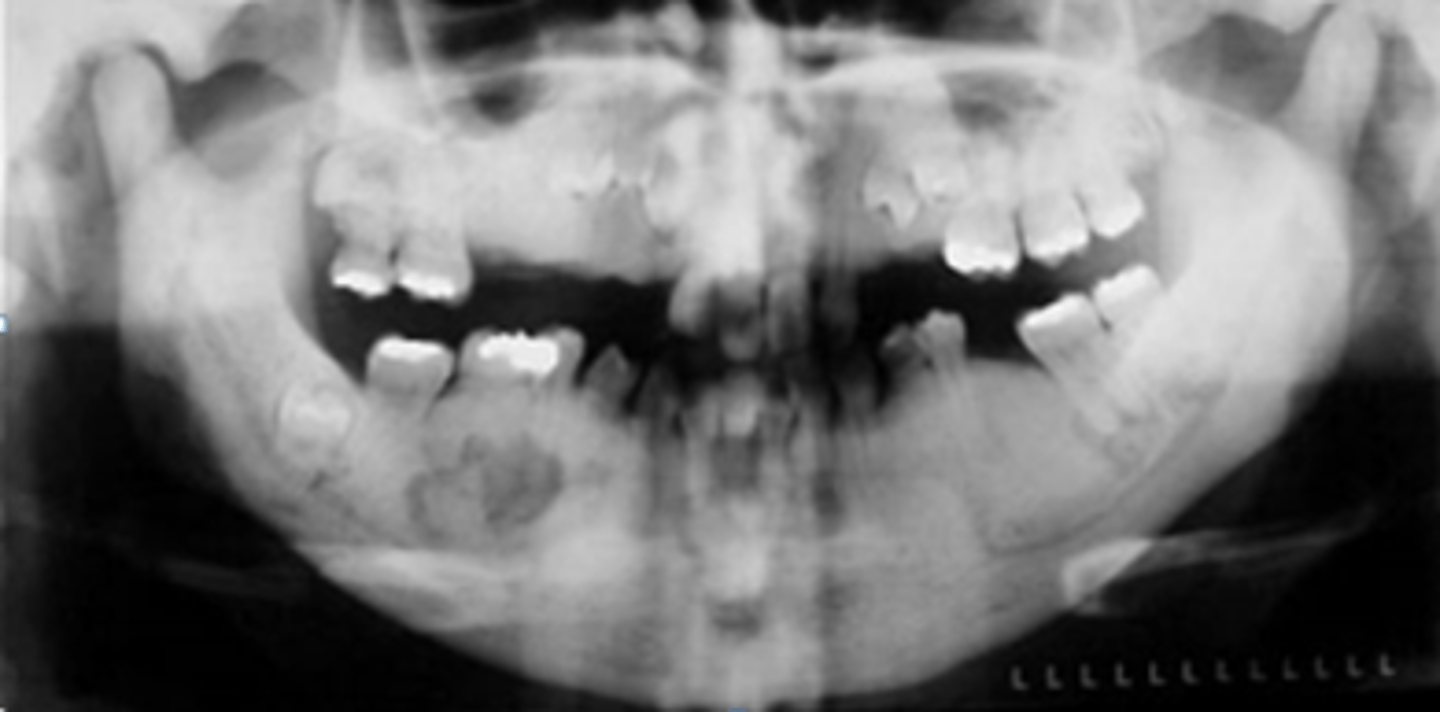
Osteopetrosis
ID the pathology:
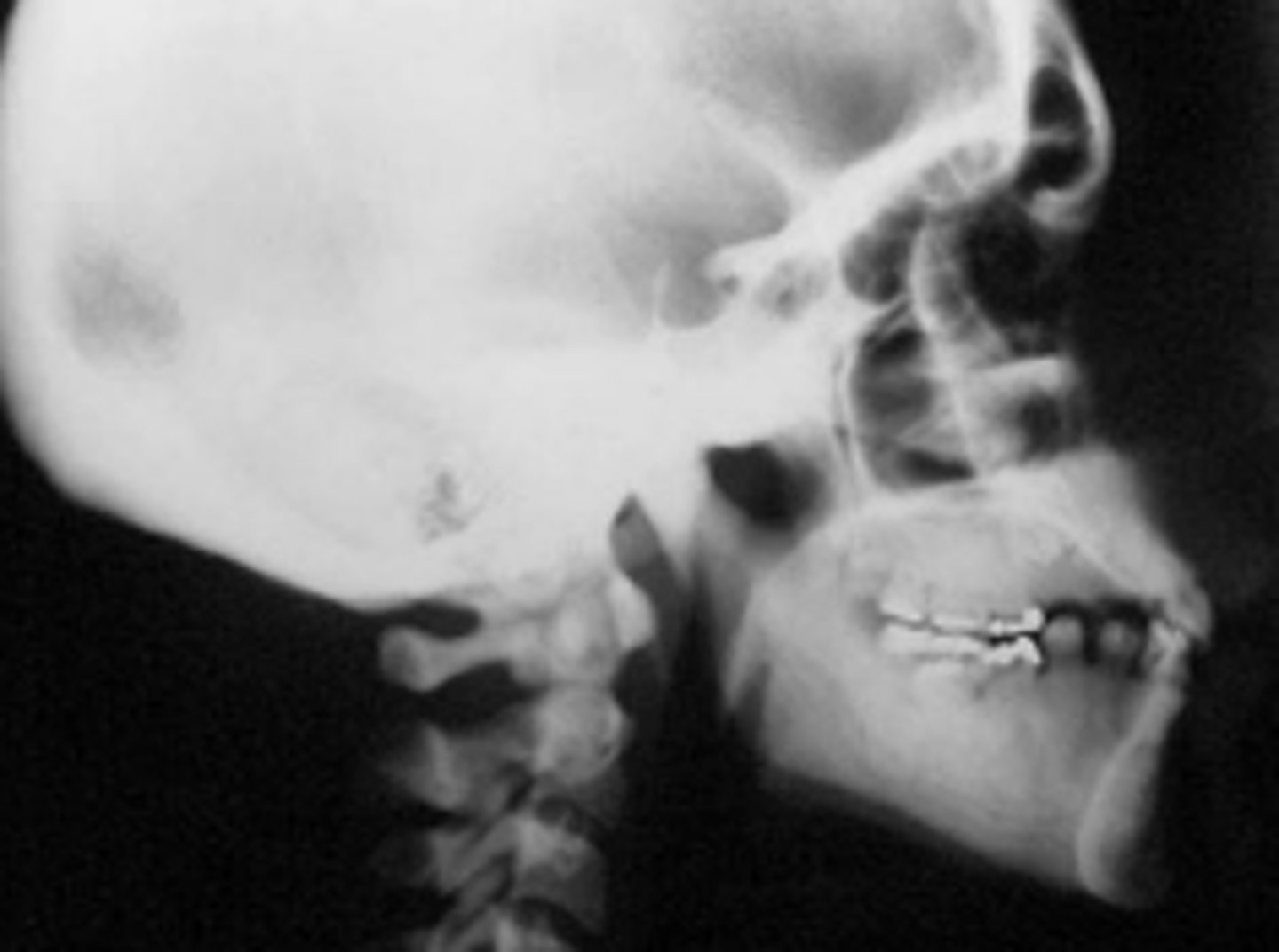
Langerhans' Cell Histiocytosis
patient's radiograph shows multiple, defined, radiolucent areas with irregular outlines-punched out lesions in the skull. In the alveolar bone, there is saucer-shaped destruction/scooping out of alveolar process that make the teeth appear to be floating in space. Patient is young but experiences abnormal tooth mobility and tooth loss. What is the diagnosis?
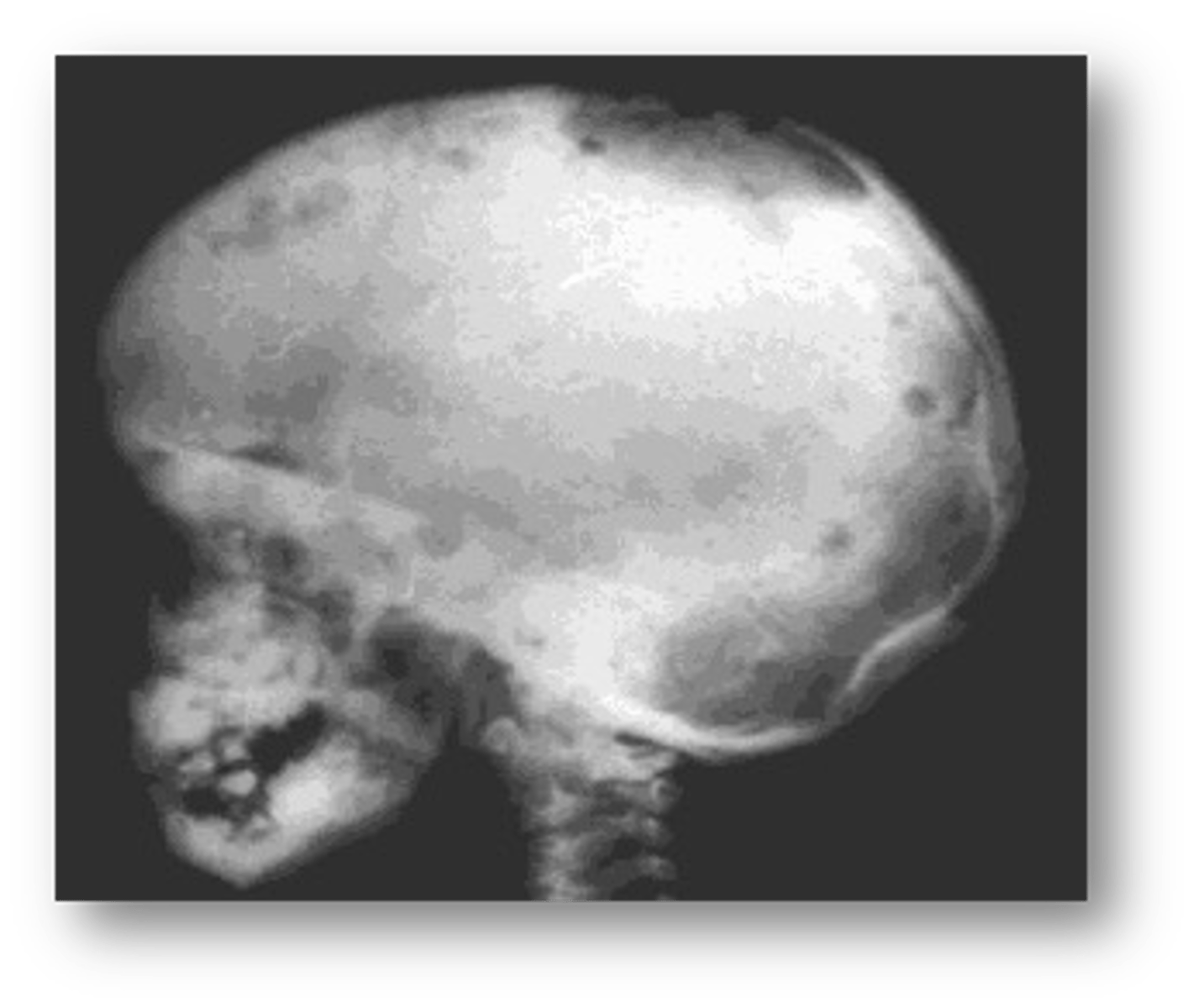
Langerhans' Cell Histiocytosis
ID the pathology:
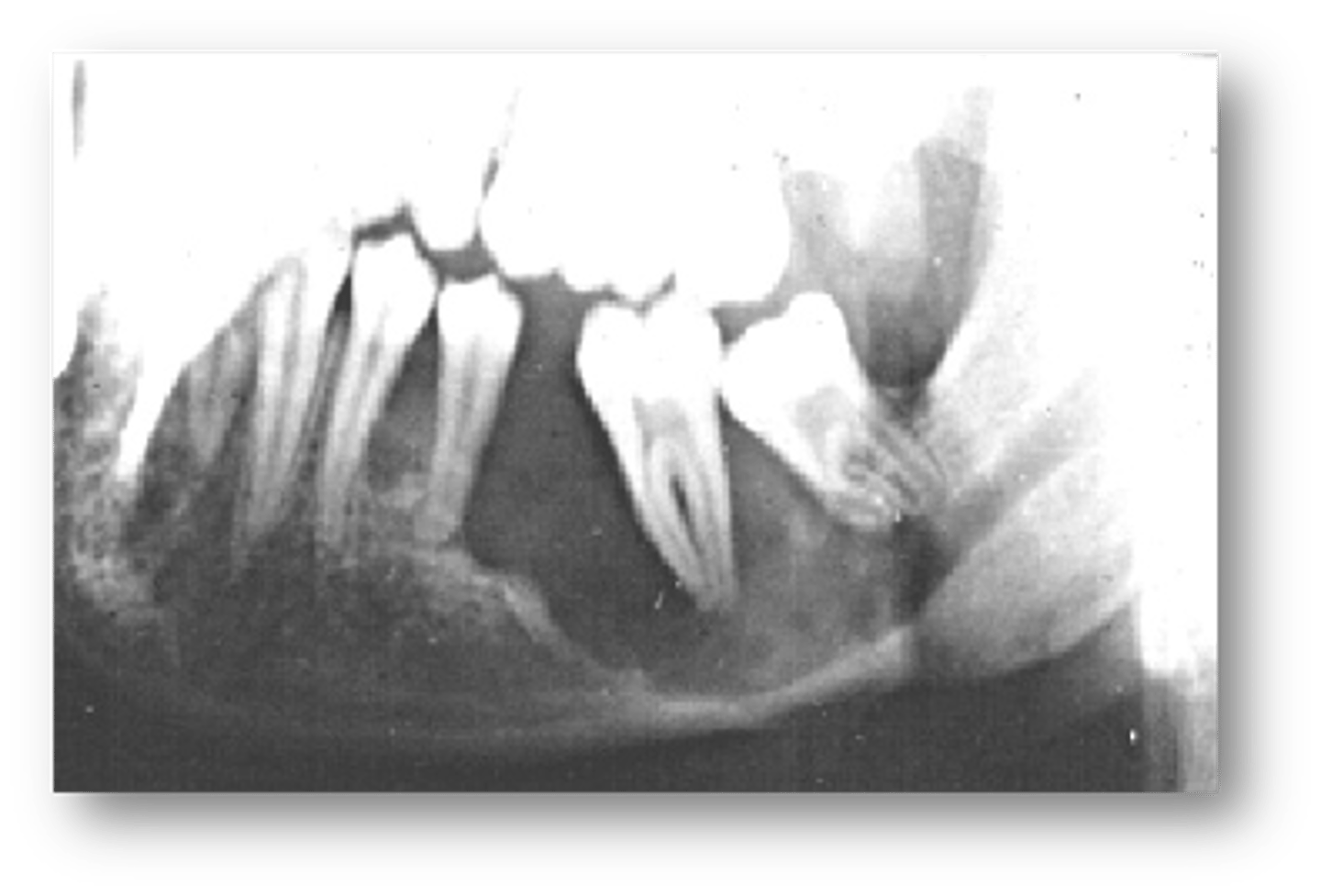
'beaten metal’ appearance
All of the following are findings of a patient with Langerhans’ Cell Histiocytosis EXCEPT:
- ‘beaten metal’ appearance
- punched out lesions in the skull
- Saucer-shaped destruction/scooping out of alveolar process
Saucer-shaped destruction/scooping out of alveolar process
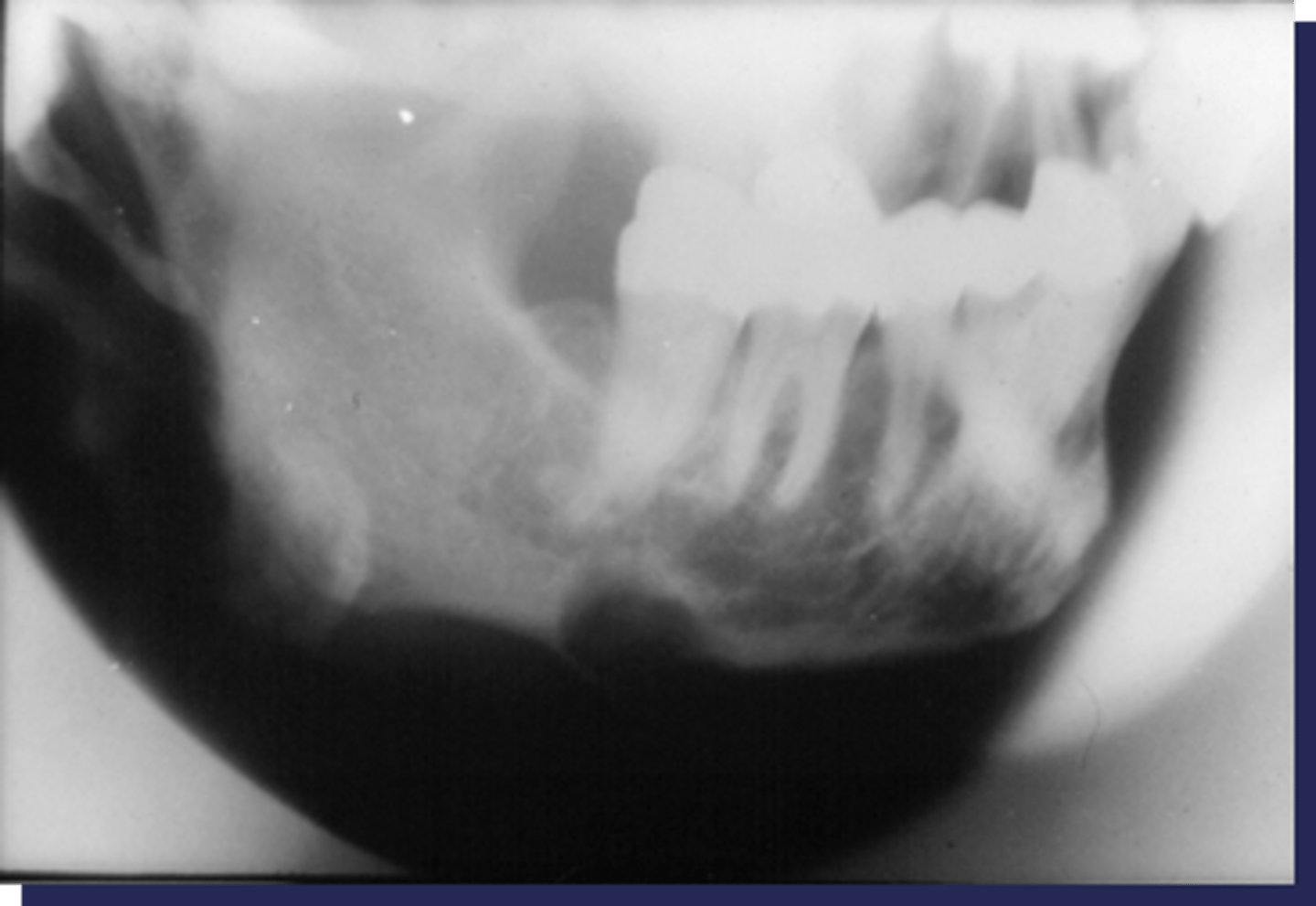
All of the following are findings of a patient with Progressive systemic sclerosis (Scleroderma) EXCEPT:
-Mandibular erosions at regions of muscle attachments: angles, coronoid process, condyles
- Saucer-shaped destruction/scooping out of alveolar process
- Decreased mouth opening
- Xerostomia
- Uniform widening of PDL space around the teeth
- Deep periodontal pockets
- Increased number of decayed, missing / filled teeth
Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
patient's radiograph shows the following features:
-Mandibular erosions at regions of muscle attachments: angles, coronoid process, condyles
- Decreased mouth opening
- Xerostomia
- Uniform widening of PDL space around the teeth
- Deep periodontal pockets
- Increased number of decayed, missing / filled teeth
What is the diagnosis?
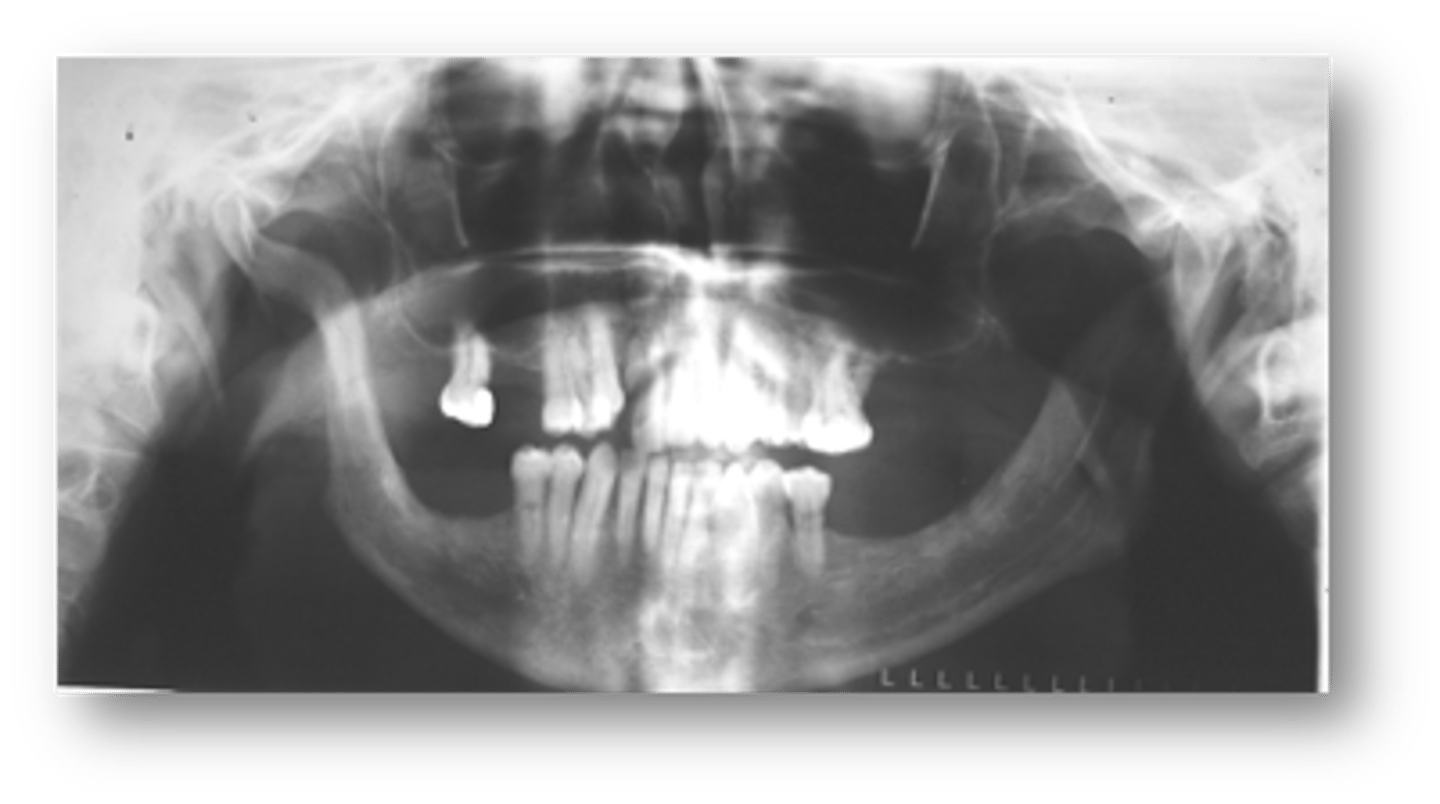
Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
Uniform widening of PDL space around the teeth is associated with what condition?
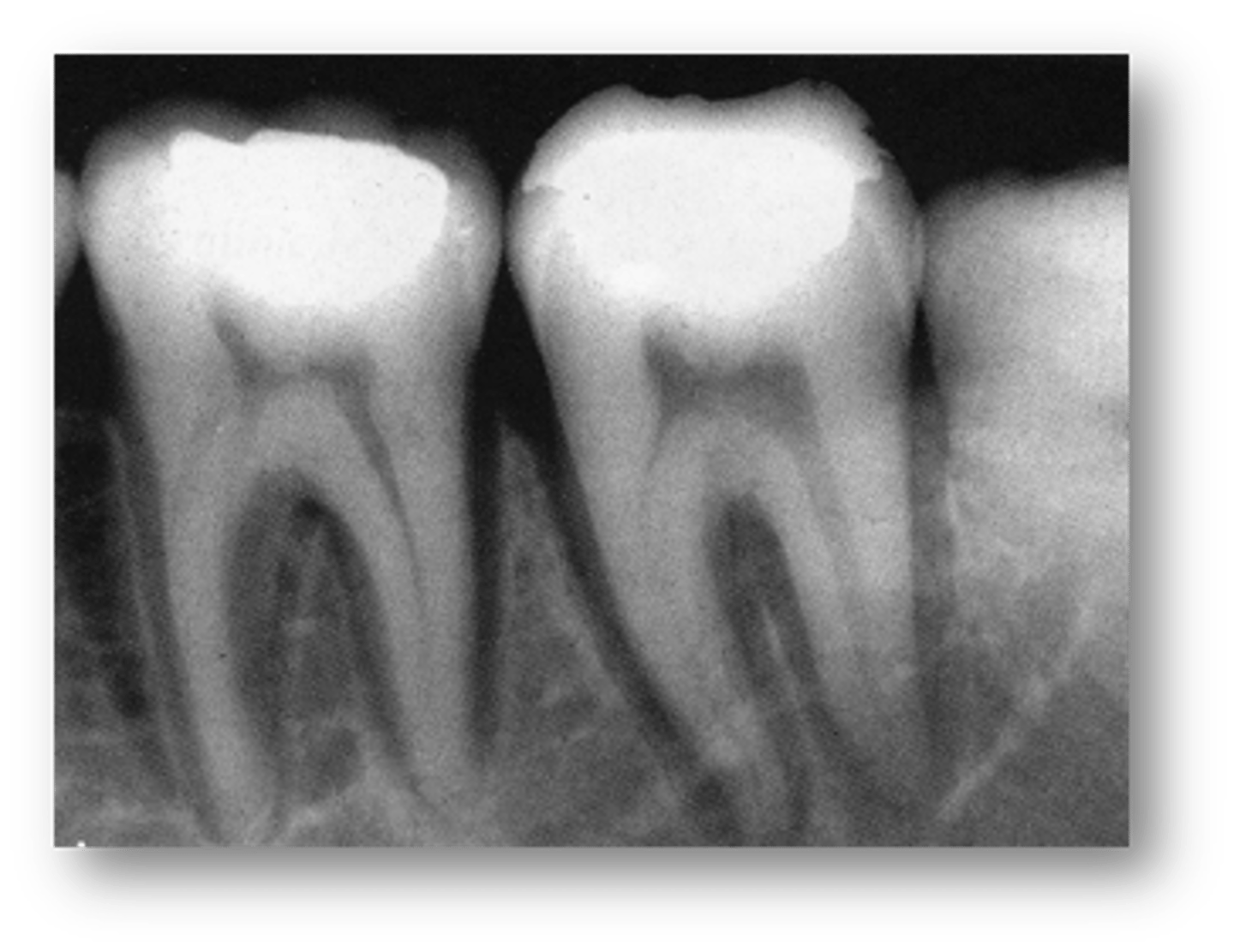
Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
Mandibular erosions at regions of muscle attachments: angles, coronoid process, condyles is associated with what condition?
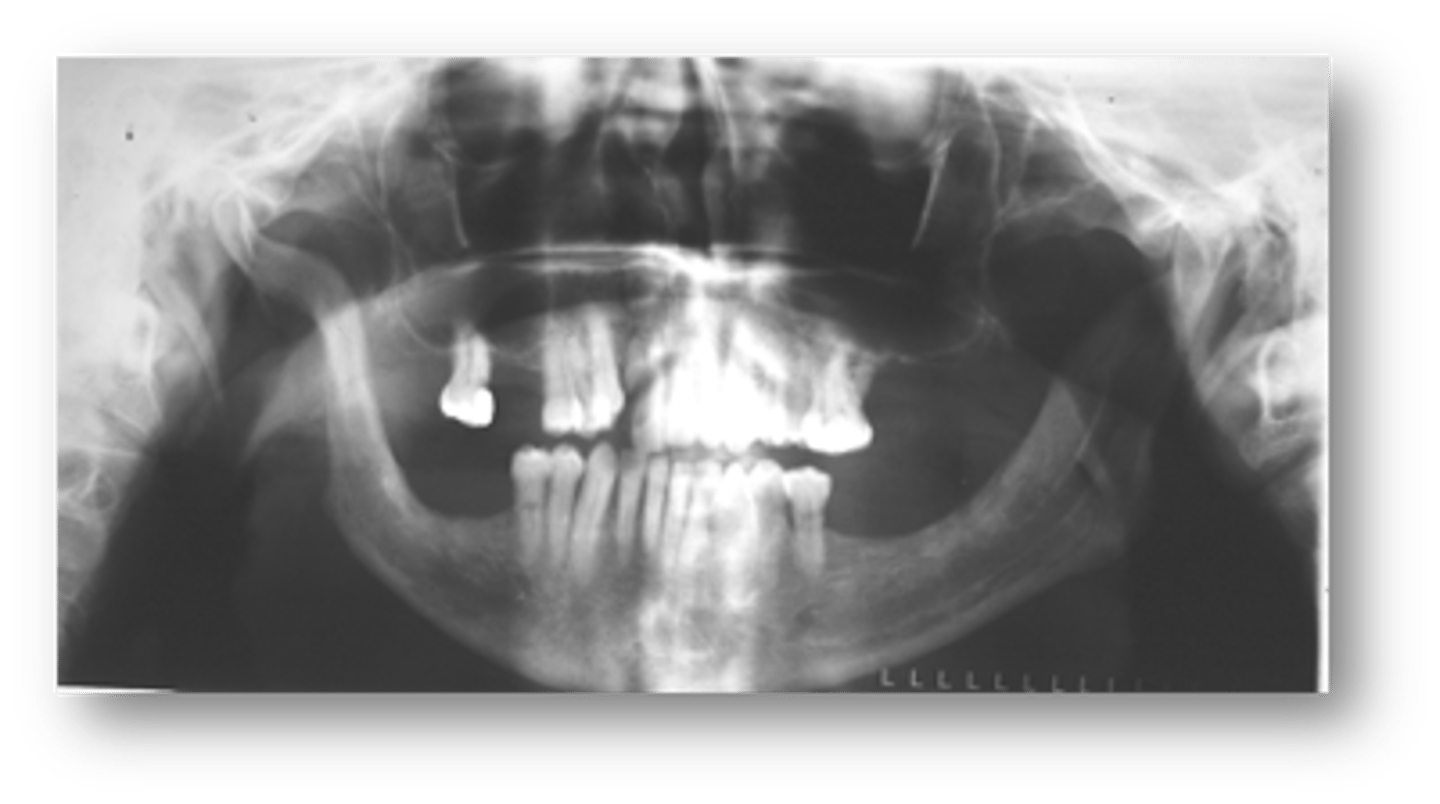
Blood dyscrasias (Sickle Cell Anemia, Thalassemia)
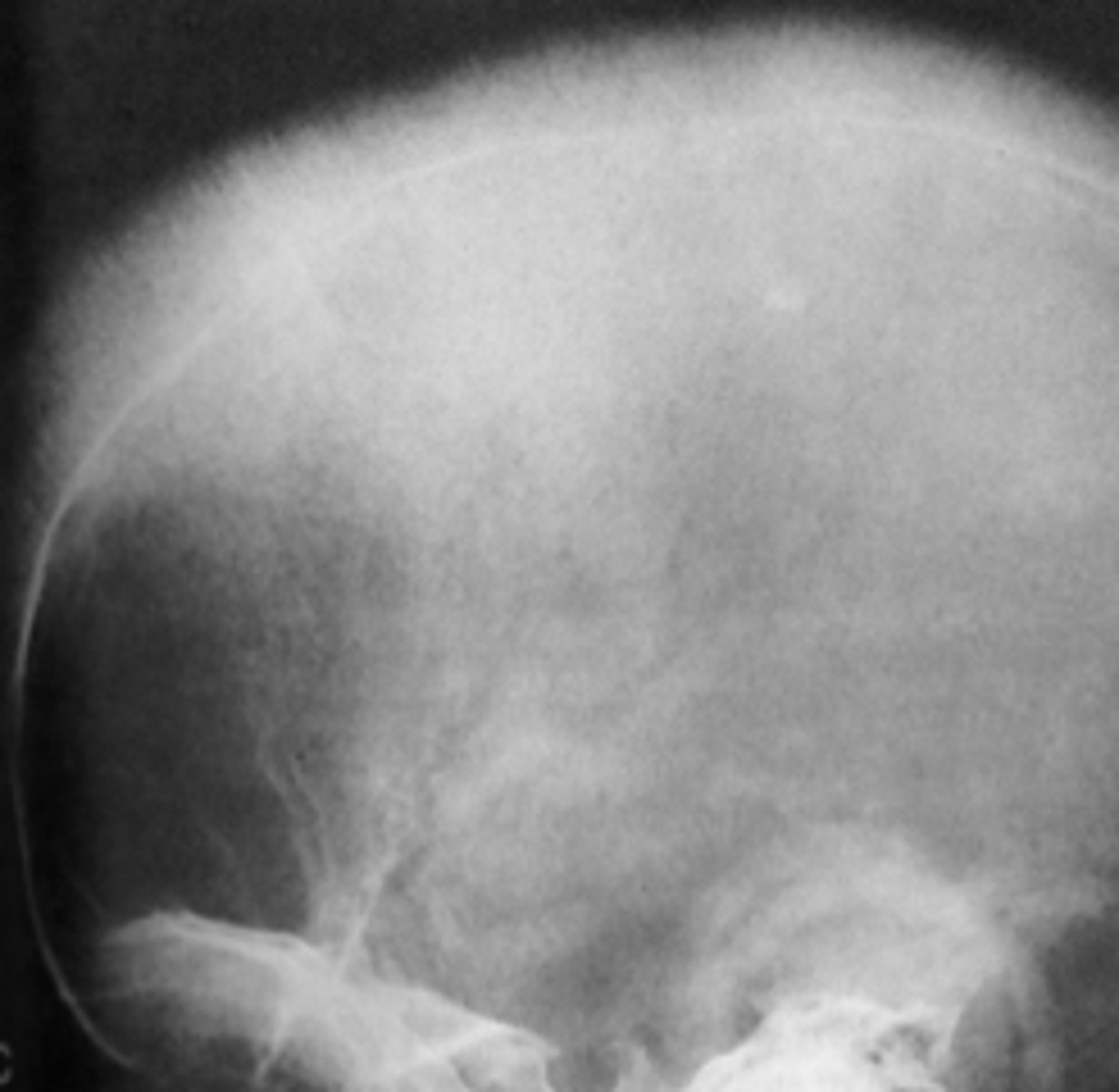
A hair-on-end appearance of the skull is associated with what condition?
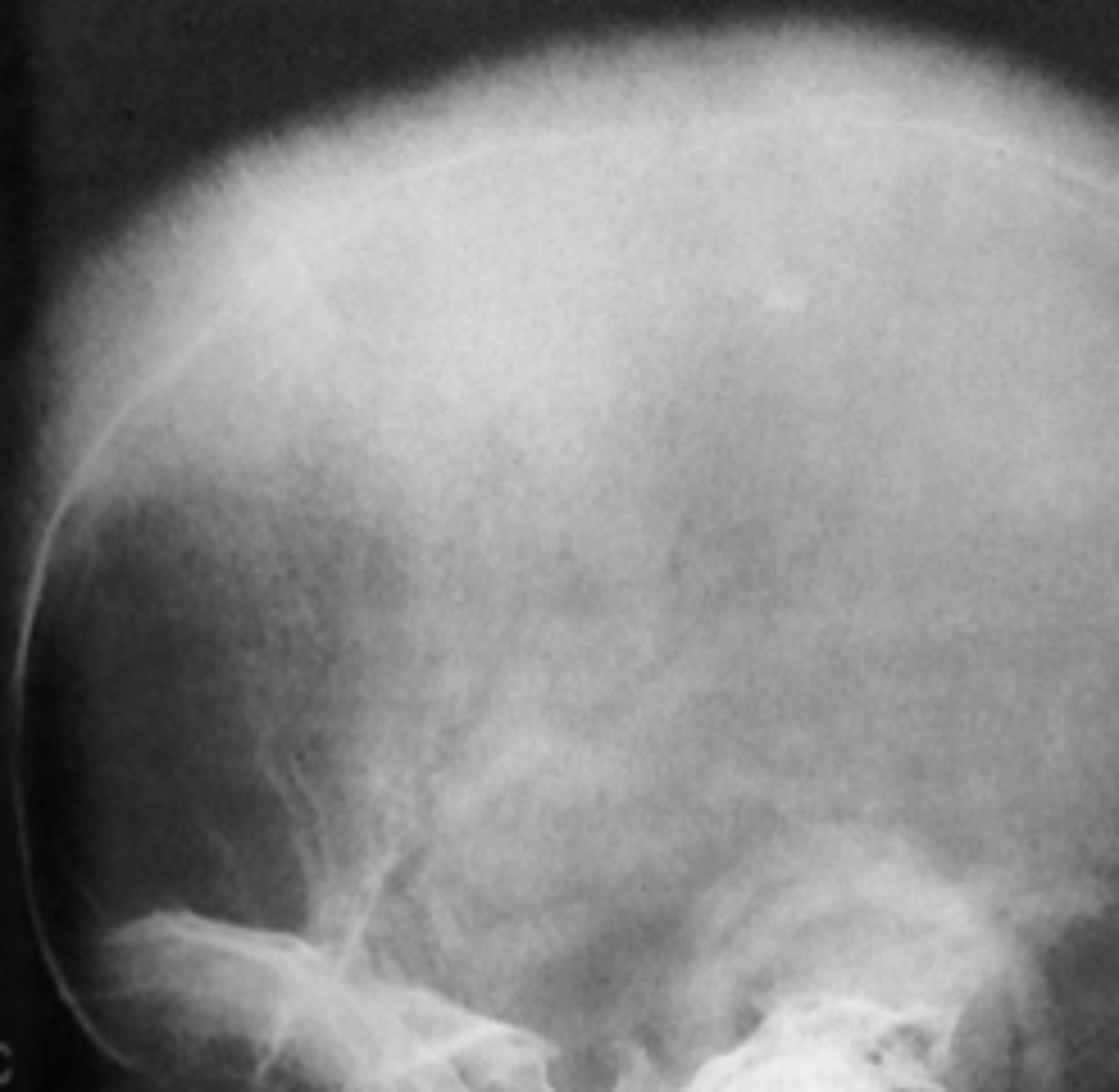
Uniform widening of PDL space around the teeth
All of the following are findings of a patient with Blood dyscrasias (Sickle Cell Anemia, Thalassemia) EXCEPT:
- generalized reduction in density of long bones
- thinning of cortical borders
- widening of diploic space
- Hair-on-end appearance of outer table
- Generalized osteoporosis
- Fewer and coarser trabeculae
- Uniform widening of PDL space around the teeth
- Large marrow spaces
Blood dyscrasias (Sickle Cell Anemia, Thalassemia)
Patient's radiograph shows:
- Hair-on-end appearance of outer table
- Generalized osteoporosis
- Fewer and coarser trabeculae
- Large marrow spaces
What is the diagnosis?
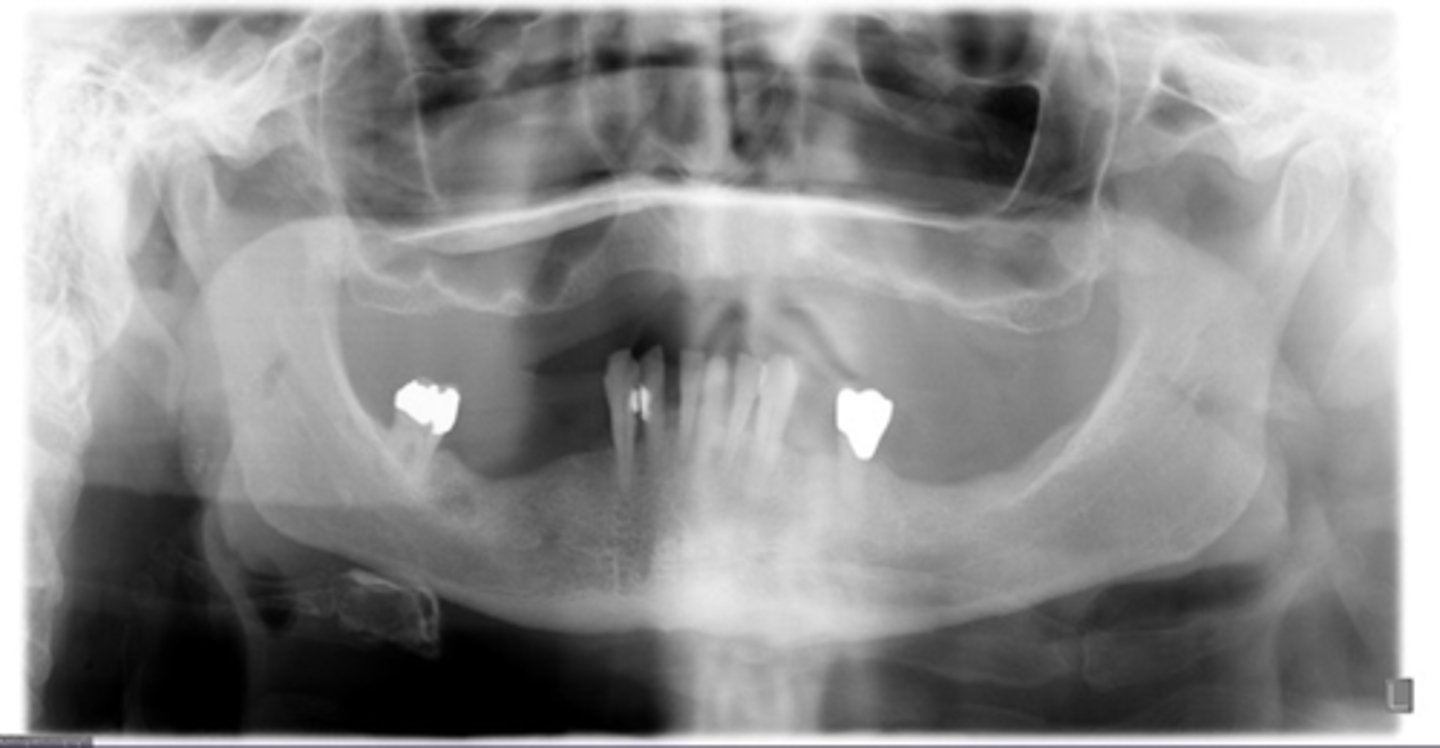
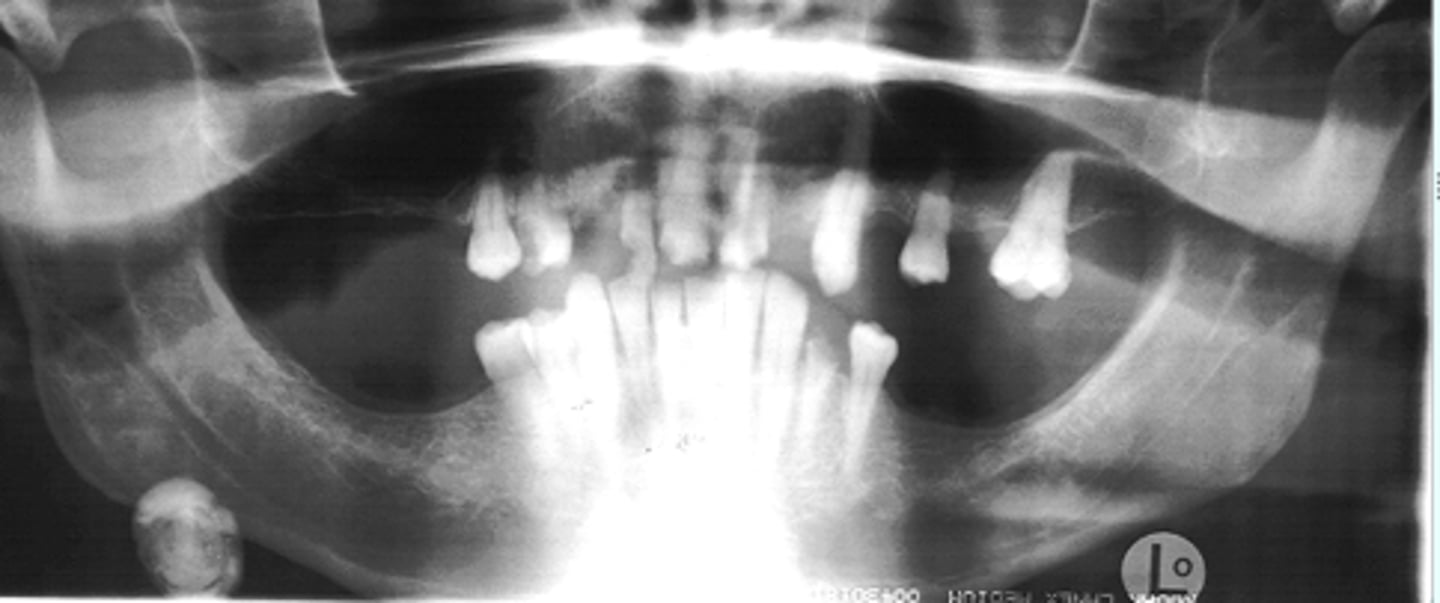
Sialolith
ID the calcified abnormality:
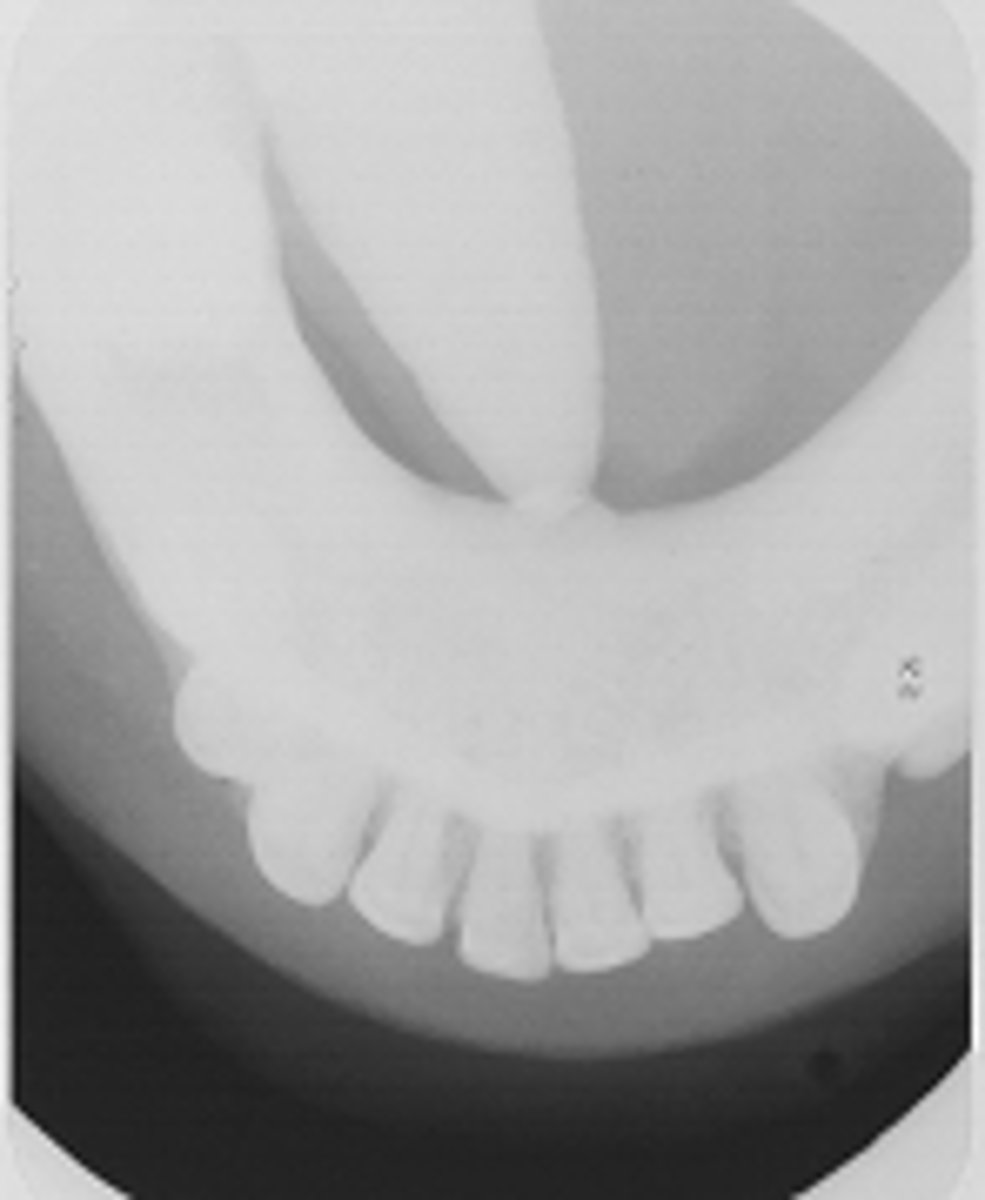
Sialolith
ID the calcified abnormality:
Calcified carotid atheromatous plaque
ID the calcified abnormality:
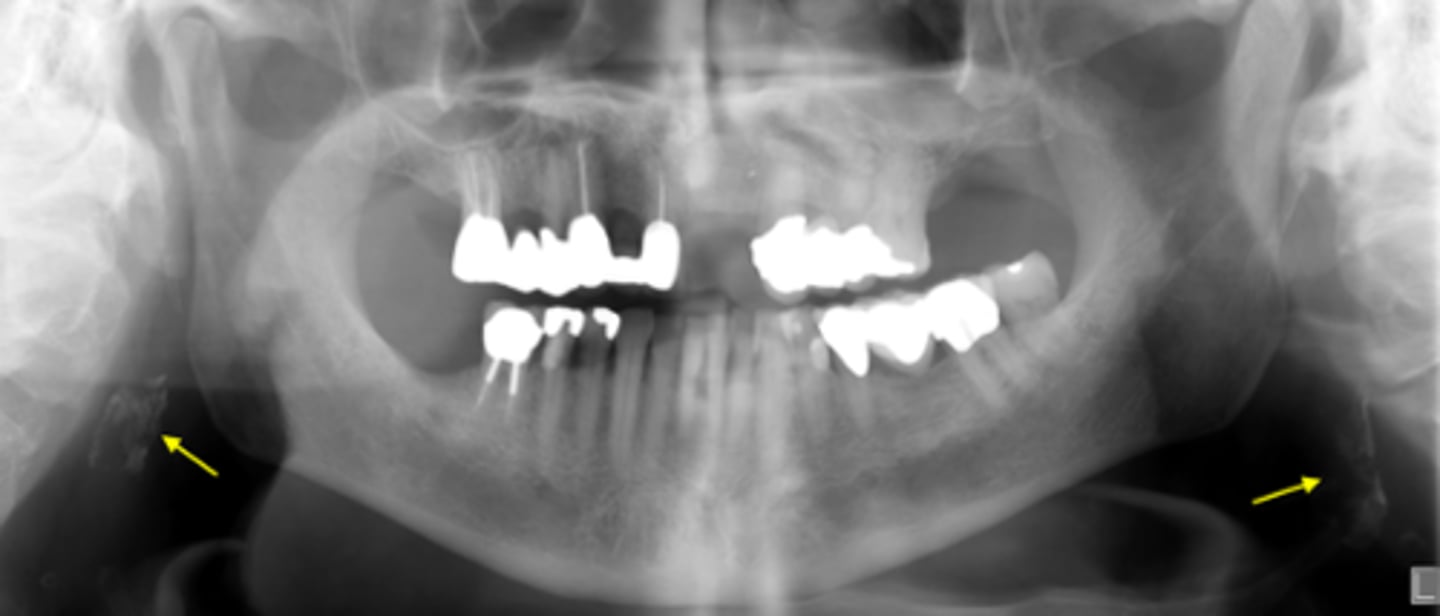
Calcified carotid atheromatous plaque
ID the calcified abnormality:
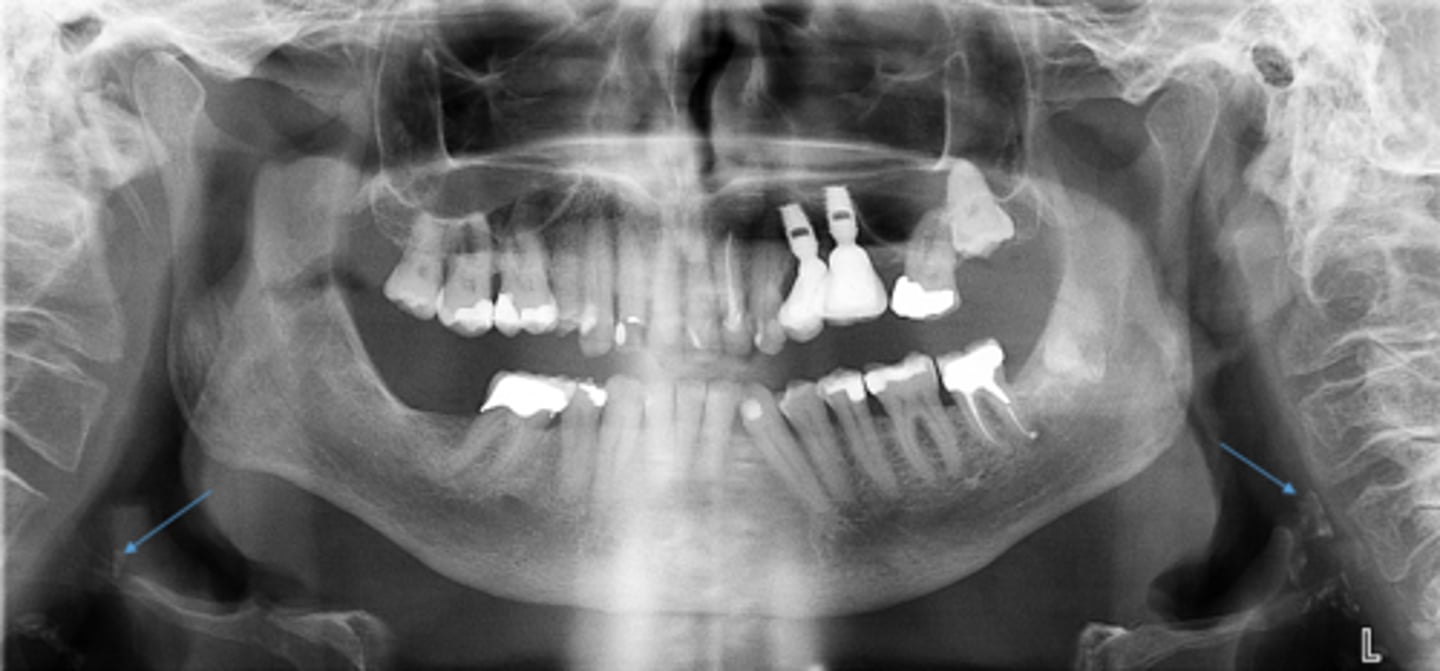
Ossified Stylohyoid Ligament
ID the calcified abnormality:
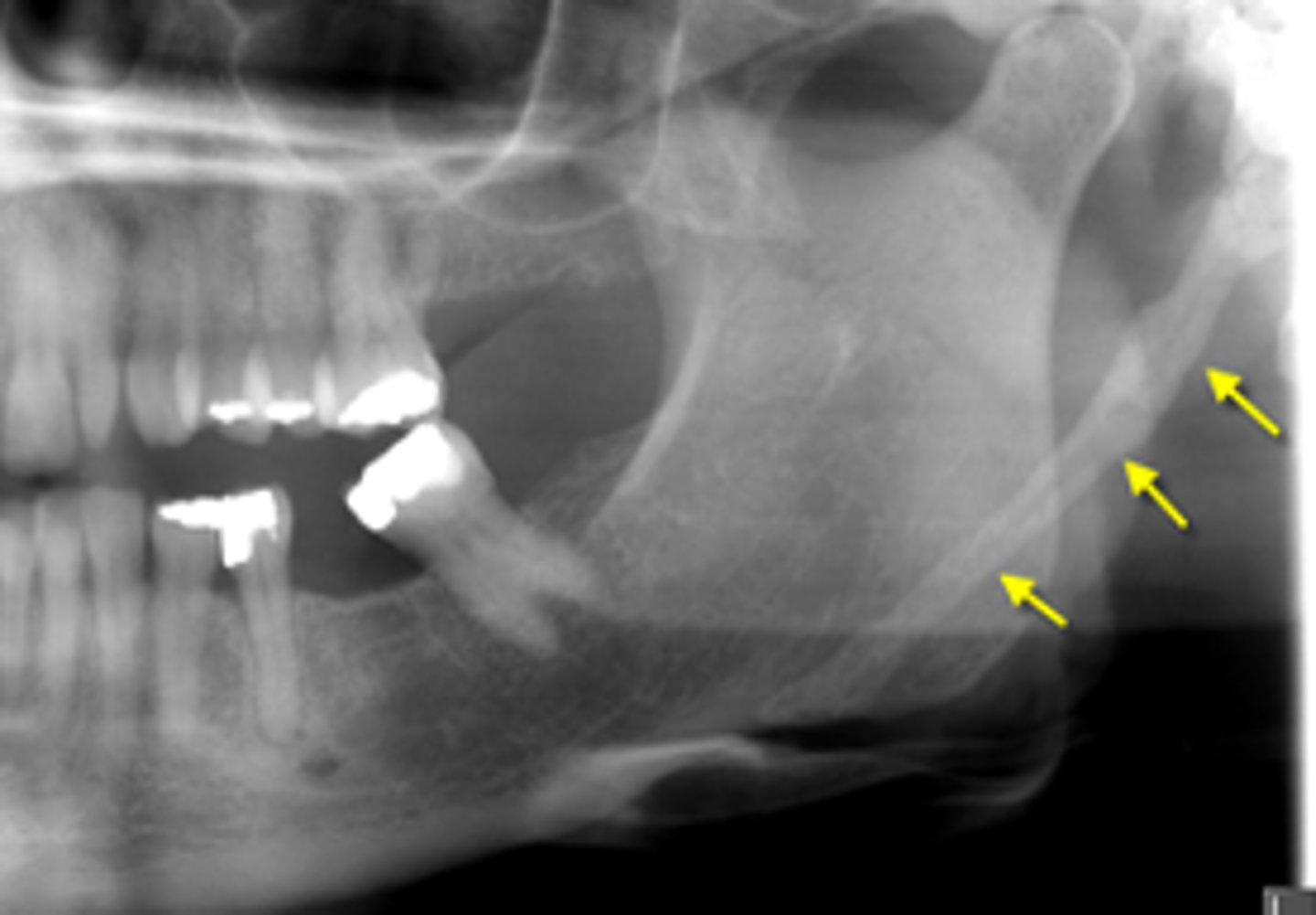
Ossified Stylohyoid Ligament
ID the calcified abnormality:
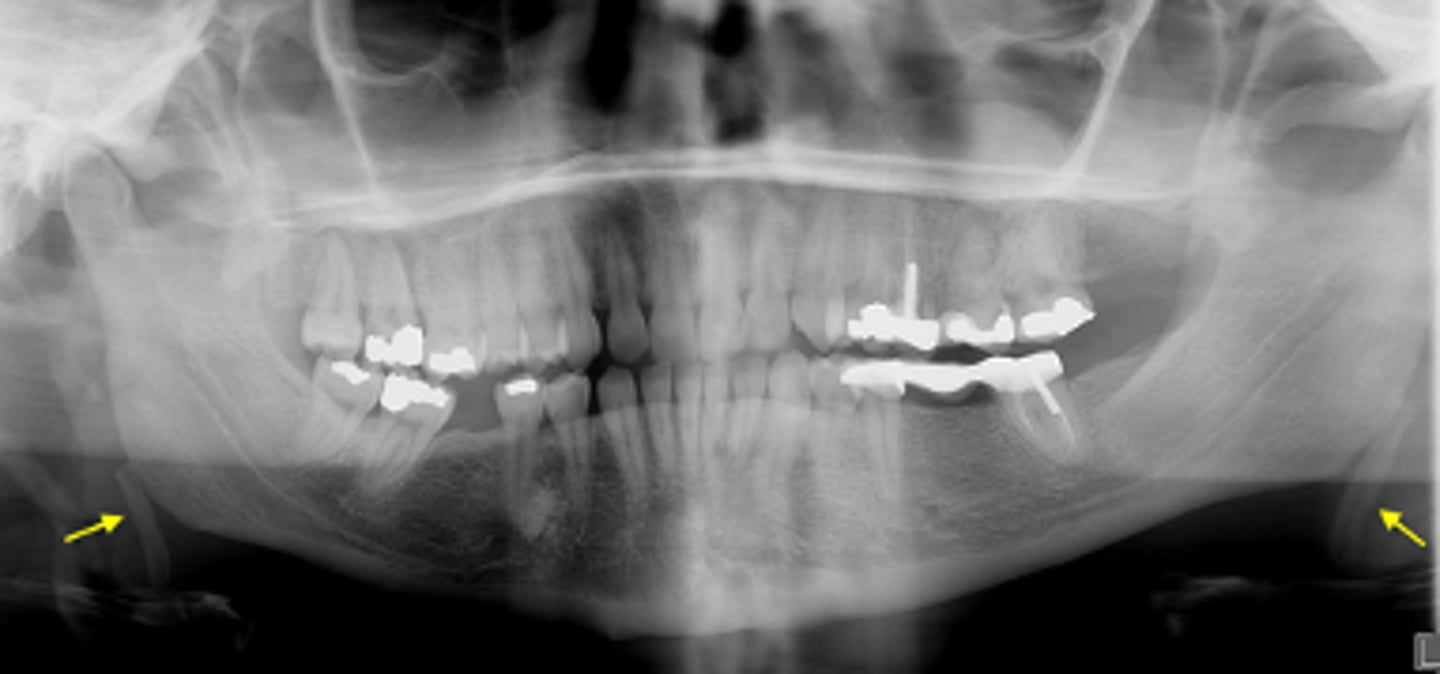
Antroliths
ID the calcified abnormality:
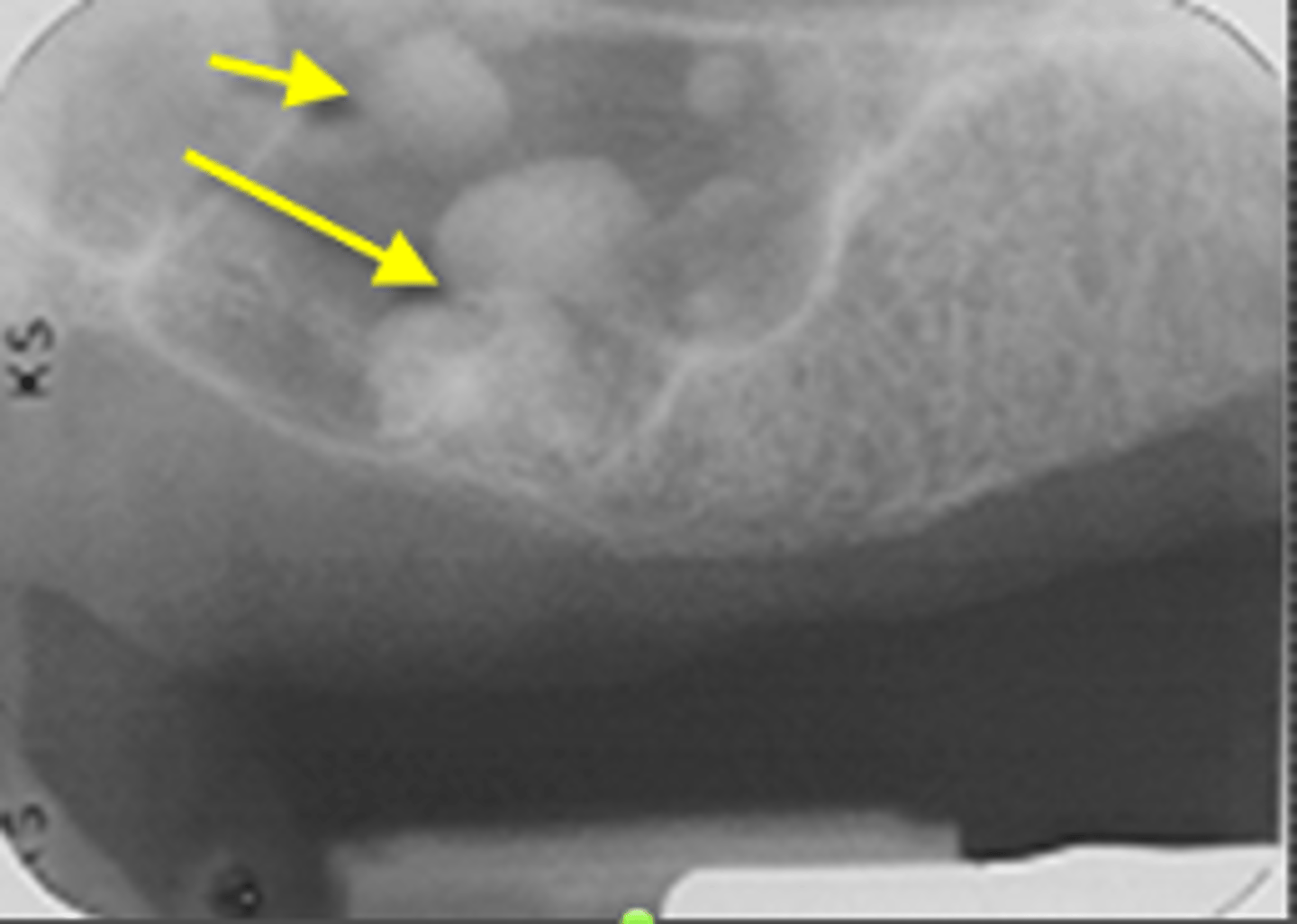
Antroliths
ID the calcified abnormality:
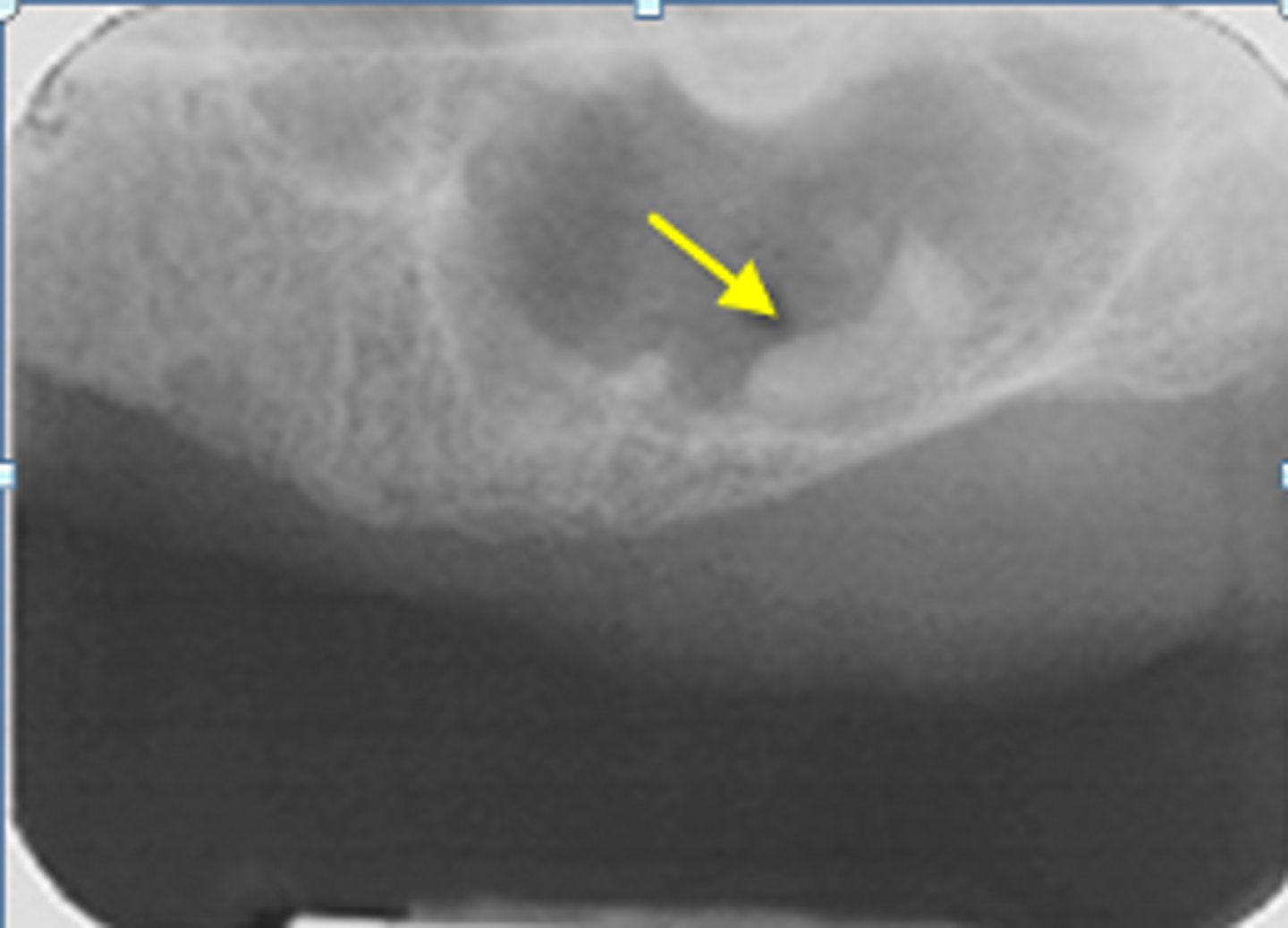
Lymph node calcification
ID the calcified abnormality:
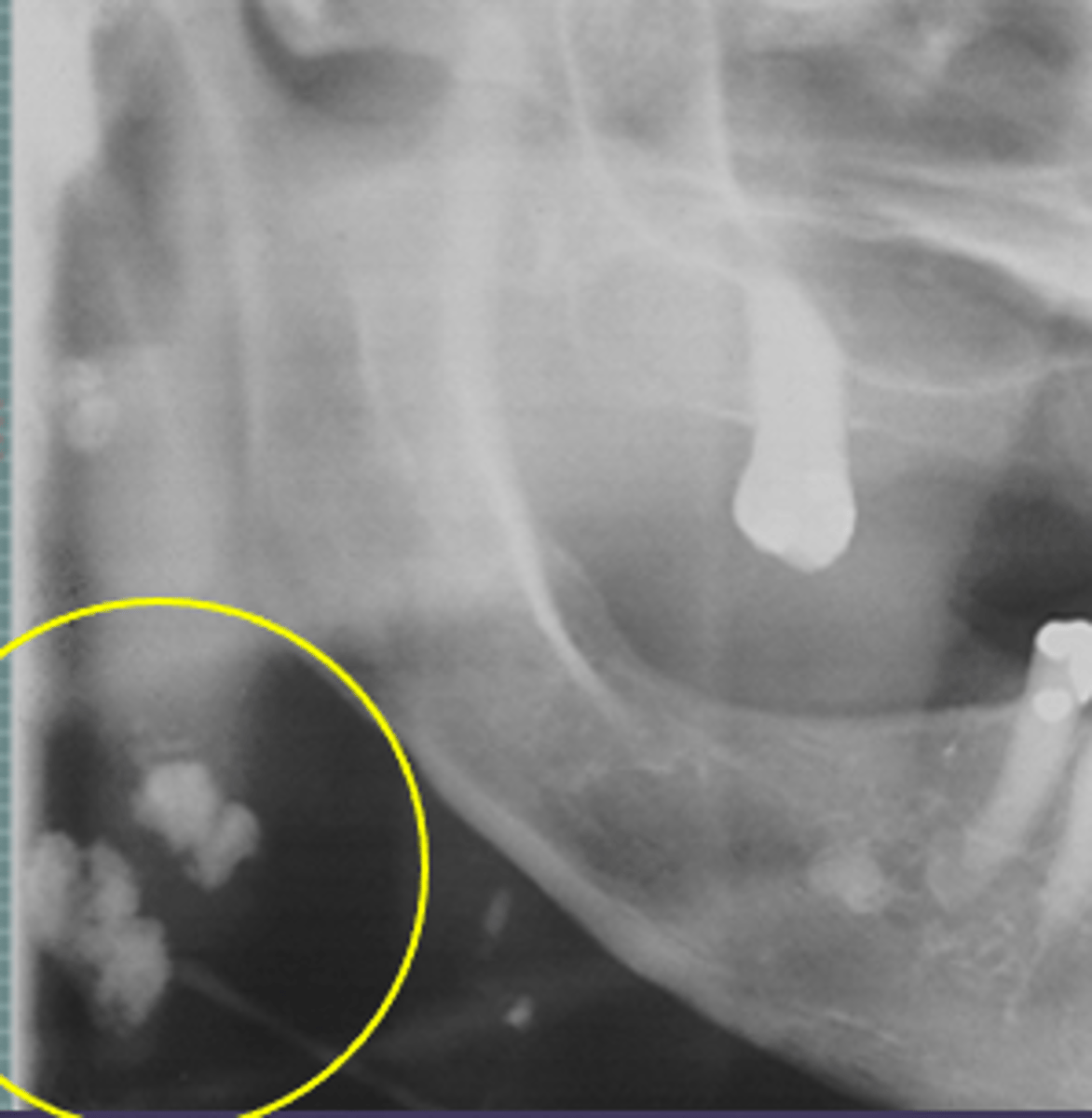
Lymph node calcification
ID the calcified abnormality:
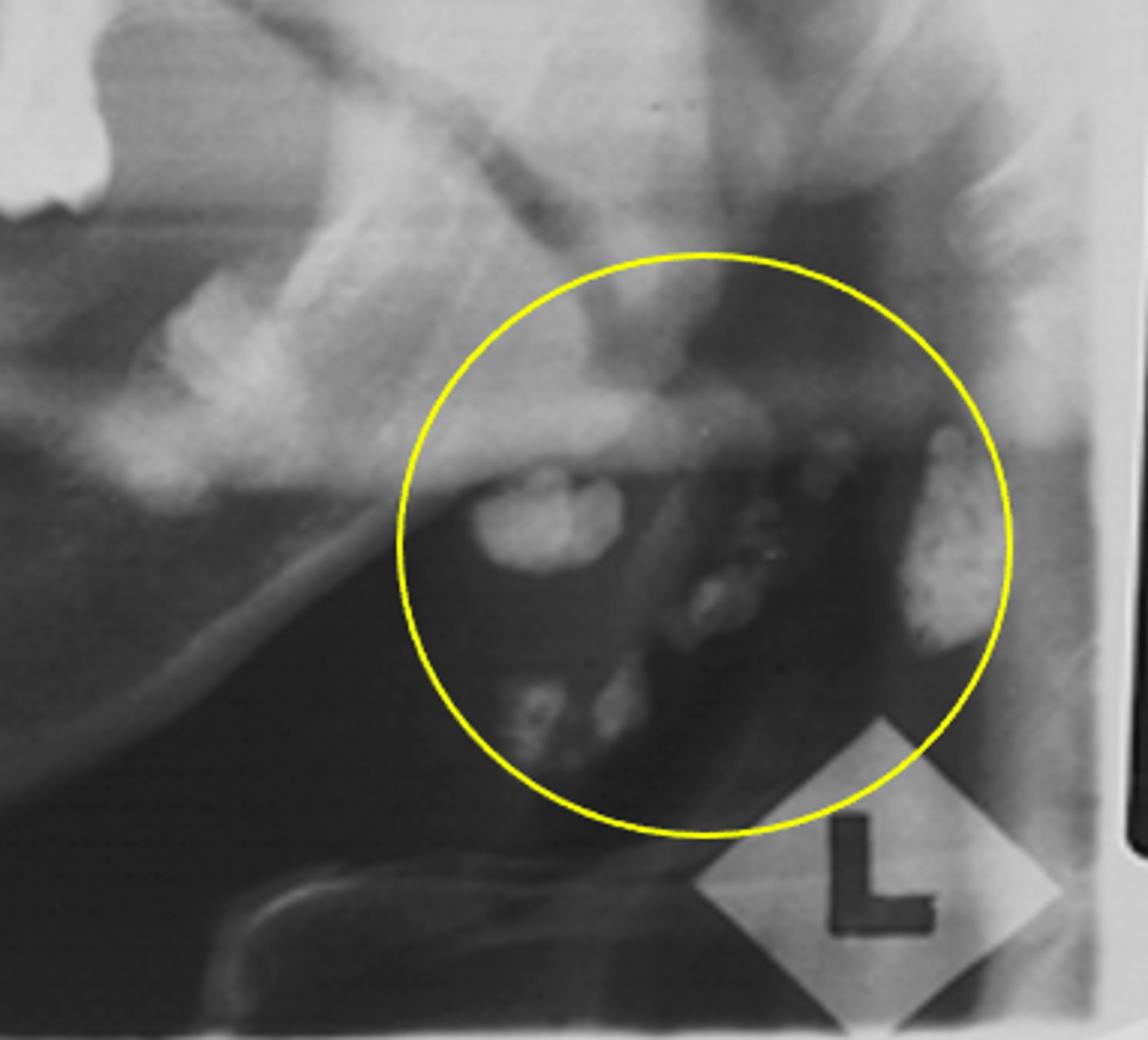
Tonsilliths/tonsilloliths
ID the calcified abnormality:
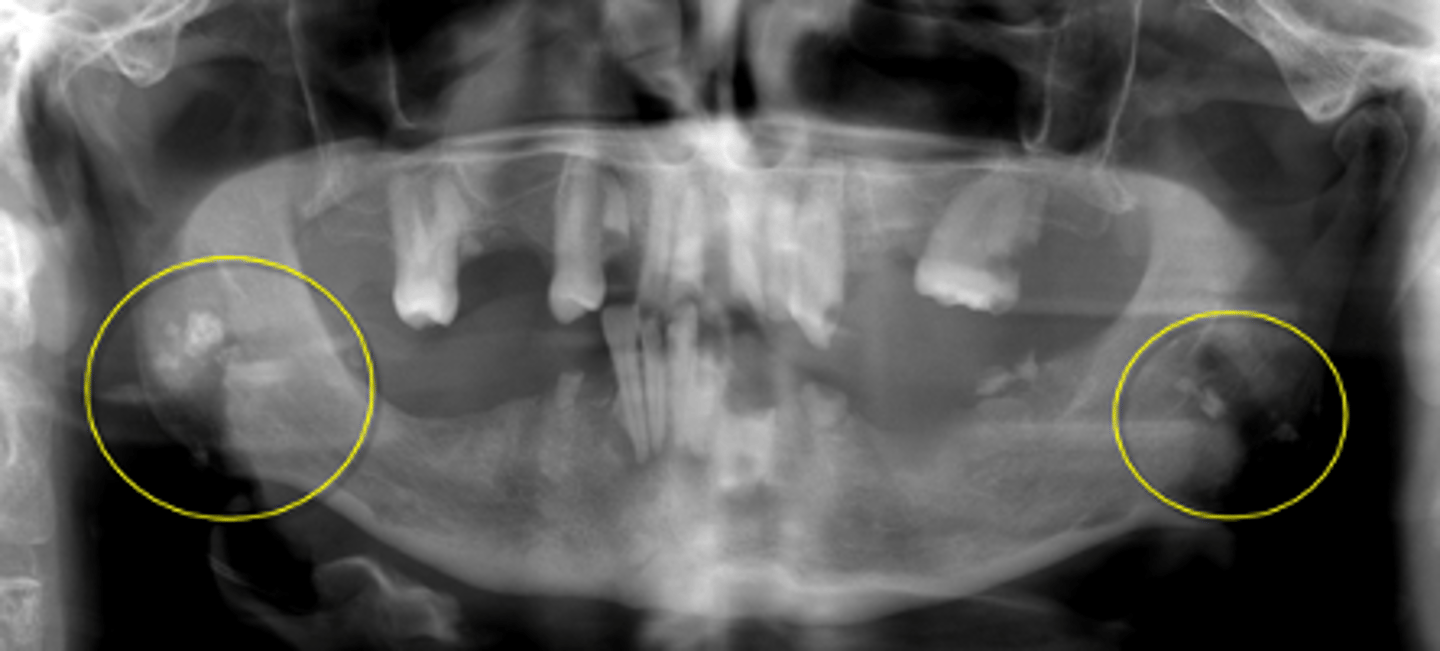
mid-ramus
Tonsilliths/tonsilloliths can appear radiographically as a cluster of radiopaque calcifications superimposed over what region?
Thyroid cartilage ossification
ID the calcified abnormality:
below the hyoid bone
Thyroid cartilage ossifications can appear radiographically as a cluster of radiopaque calcifications in what region?
Triticeous cartilage ossification
ID the calcified abnormality: