AP Biology Unit One - Organic Compounds (Vocabulary)
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering organic compounds and their major components and structures as outlined in the notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Organic compounds
Compounds that contain covalently bonded carbon; examples include lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.
Carbon versatility
Carbon has four valence electrons, enabling stable single, double, and triple bonds and serving as the backbone for diverse biomolecules.
CHON
The four most common elements in living organisms: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N).
Phosphorus and sulfur
Essential elements added to CHON; contribute to about 98% of body mass; others include Ca, Na, K, and trace elements.
Functional group
A specific group of atoms within a molecule that imparts characteristic chemical properties and reactivity.
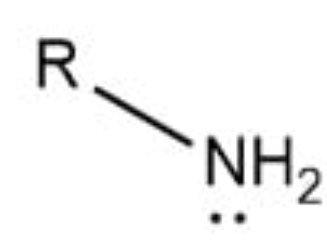
Amino group
–NH2; basic group found in amino acids and involved in peptide bond formation.
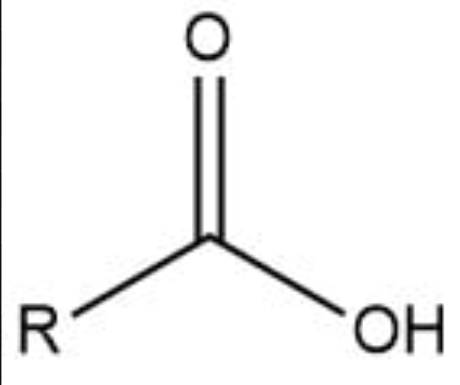
Carboxyl group
–COOH; acidic group found in amino acids and fatty acids.
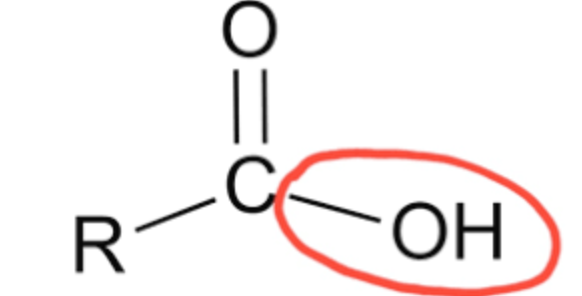
Hydroxyl group
–OH; polar group that forms hydrogen bonds, found in sugars and alcohols.
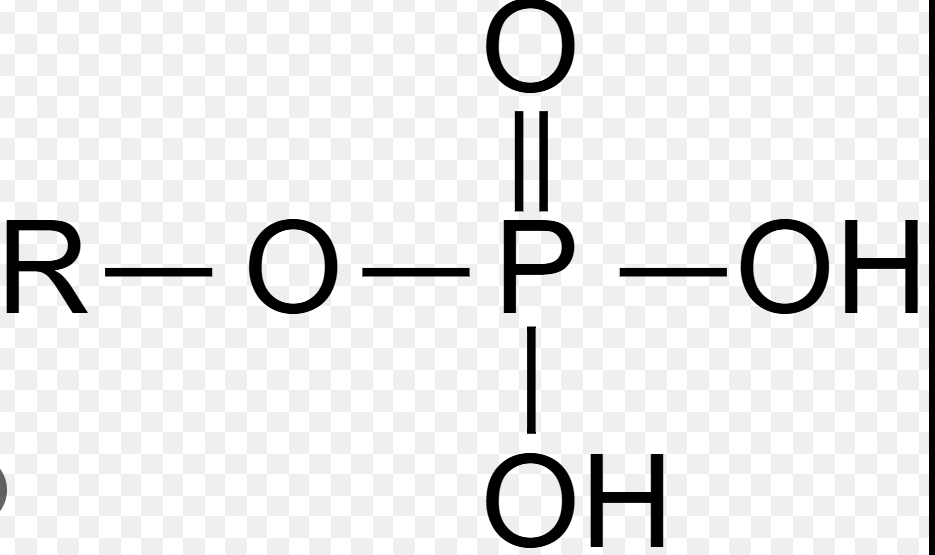
Phosphate group
–PO4; involved in energy transfer (ATP) and present in phospholipids; negatively charged.
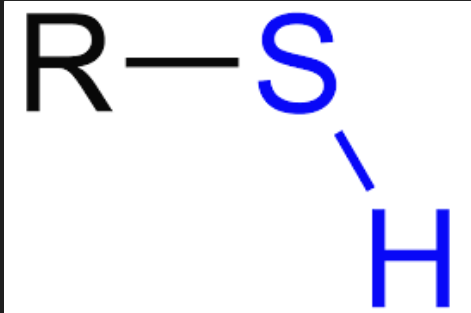
Sulfhydryl group
–SH; forms disulfide bonds that stabilize protein structure.
Lipids
Non-polymer molecules (~C, H, O, sometimes P/N) used for long-term energy storage, waterproofing, and insulation.
Fats and oils (triglycerides)
Glycerol backbone with three fatty acids; energy-dense storage; fats are typically saturated, oils unsaturated.
Saturated fat
Fat with only single C–C bonds; solid at room temperature; common in animals.
Unsaturated fat
Fat with one or more C=C double bonds; kinked tails; liquid at room temperature; common in plants.
Phospholipids
Glycerol + two fatty acids + one phosphate group; form cell membranes; hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads.
Phospholipid bilayer
Two-layer membrane with hydrophobic interiors and hydrophilic exteriors, forming cell membranes.
Steroids
Lipids with a ring structure; includes cholesterol and various hormones.
Cholesterol
A steroid component of animal cell membranes; serves as a precursor to steroid hormones.
Carbohydrates
Sugars and their polymers used for energy and structure; monomers are monosaccharides; include disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharide
Simple sugar; common example: glucose.
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis (e.g., sucrose, maltose, lactose).
Starch
Plant storage polysaccharide; polymer of glucose.
Glycogen
Animal storage polysaccharide; highly branched glucose polymer used for short-term energy storage.
Chitin
Structural polysaccharide in fungal cell walls and invertebrate exoskeletons; contains N-acetylglucosamine.
Cellulose
Structural polysaccharide in plant cell walls; polymer of glucose with beta linkages.
Proteins
Macromolecules made of amino acids; perform diverse functions: enzymes, transport, signaling, receptors, structure.
Amino acid
Monomer of proteins; contains an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a variable R group.
Peptide bond
Covalent bond formed by dehydration synthesis between amino acids, building a protein.
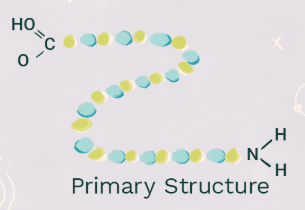
primary structure
amino acid polymer made at the ribosome; peptide bonds. think pool noodles in a line
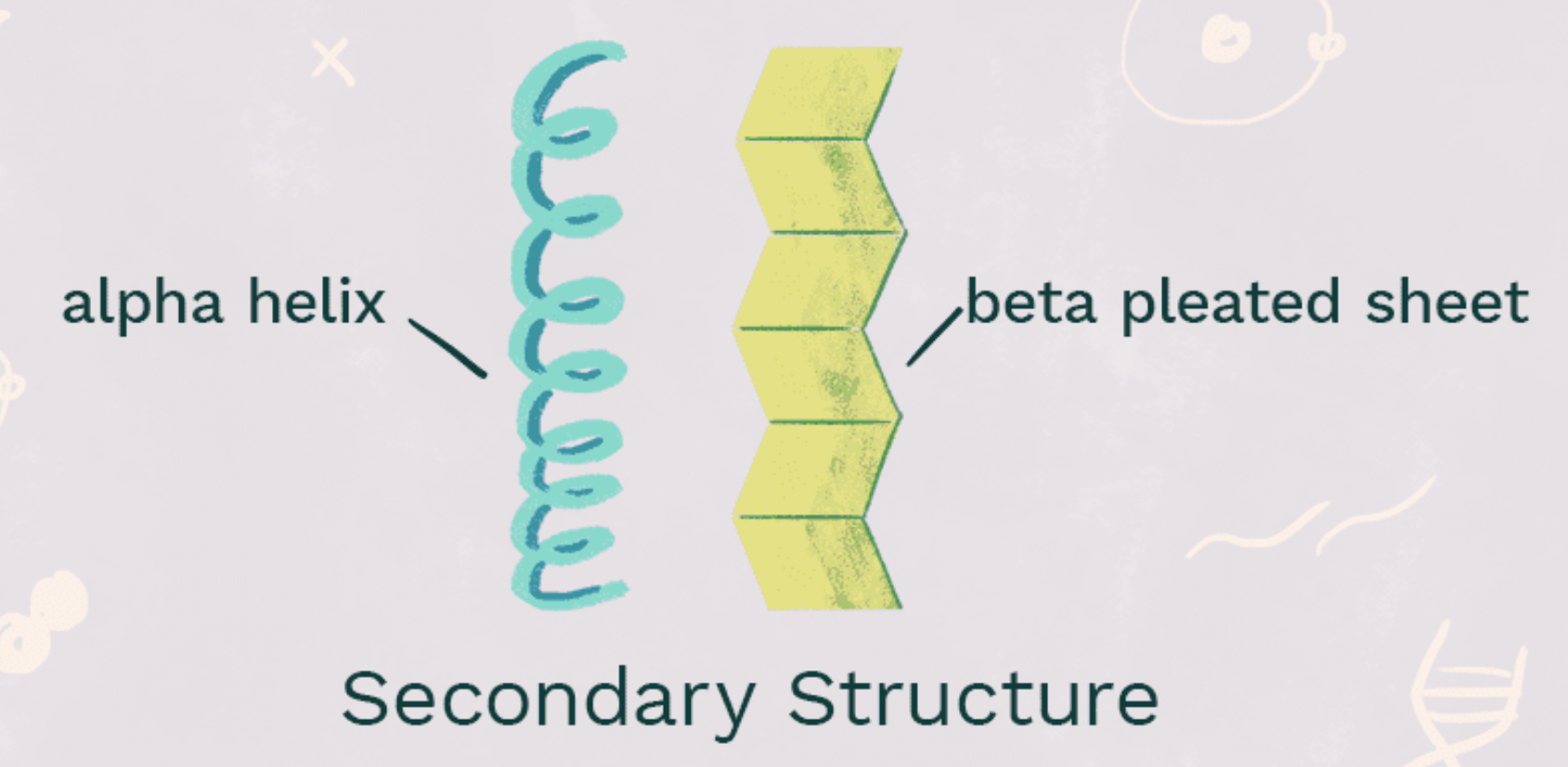
secondary structure
beta pleats or alpha helices; stabilized by hydrogen bonding along the backbone. think people standing back to back (like the spine)
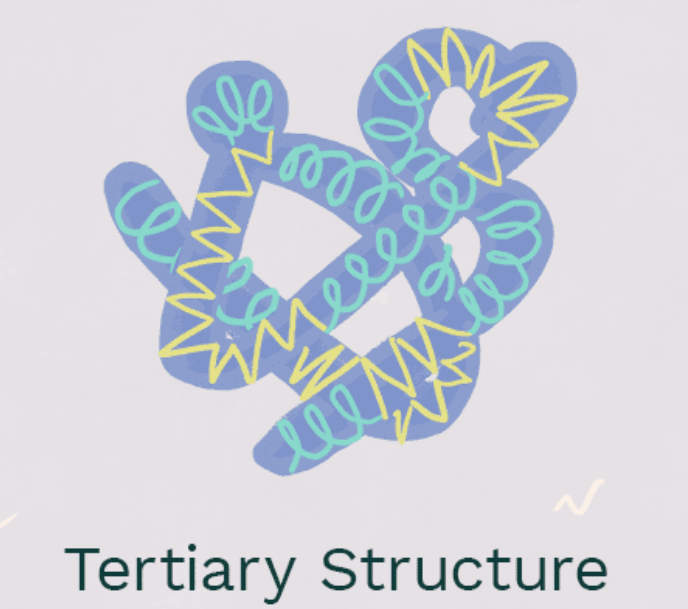
tertiary structure
interactions between the side chains (R groups) of the amino acids, hydrogen bonding, van der Walls forces, ionic interactions, disulfide bonding, hydrophobic interaction. think of AP bio 102 people tangled with the pool noodles.
Quaternary structure
interactions with other separate polymer chains, stabilized by same interactions as tertiary except disulfide. think AP bio 102 is tangled and then joins by hydrogen bonds with AP bio 101.
basic pH
above 7
acidic pH
below 7
Endergonic reaction
reaction that requires energy input (feels cold); makes bonds
Exergonic reaction
reaction that gives off energy (feels hot); breaks bonds
cohesion
water sticks to water
adhesion
water sticks to other surfaces
high specific heat
thermoregulation
solubility
bc it’s polar