ANATOMY OF THE HEAD, FACE AND NECK
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Paired
○ Parietal (2)
○ Temporal (2)
What are the paired bones under neurocranium?
Unpaired
○ Frontal (1)
○ Occipital (1)
○ Sphenoid (1)
○ Ethmoid (1)
What are the unpaired bones under neurocranium?
Paired
○ Maxilla (2)
○ Zygomatic (2)
○ Palatine (2)
○ Lacrimal (2)
○ Nasal (2)
○ Inferior concha (2)
Paired bones under viscerocranium?
Unpaired
○ Mandible (1)
○ Vomer (1)
Unpaired bones under viscerocranium?
Pterion
Thinnest/softest part of the lateral aspect of skull?
Unossified membranous intervals
○ Anterior fontanelle - 18 months
○ Posterior fontanelle - 12 months
Unossified membranous intervals
○ Anterior fontanelle - __ months
○ Posterior fontanelle - __ months
Skin
Connective tissue
Aponeurosis
Loose Areolar Tissue
Pericranium
Layers of the SCALP?
Blood Supply to the Scalp
Arteries and Veins:
○ Supratrochlear artery and vein
○ Supraorbital artery and vein
○ Superficial temporal artery and vein
○ Posterior auricular artery and vein
○ Occipital artery and vein
Olfactory Nerve
1st cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Sensory
Function: Smell
What is the nerve type and function of the 1st nerve?
Optic Nerve
2nd cranial nerve?
Nerve type: Sensory
Function: Vision
What is the nerve type and function of the 2nd nerve?
Oculomotor
3rd cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Motor
Function: Most eye movement
What is the nerve type and function of the 3rd nerve?
Trochlear
4th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Motor
Function: Moves eye outer and lower
What is the nerve type and function of the 4th nerve?
Trigeminal
5th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Both
Function: Face sensation, mastication
What is the nerve type and function of the 5th nerve?
Abducens
6th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Motor
Function: Abducts the eye
What is the nerve type and function of the 6th nerve?
Facial
7th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Both
Function: Facial expression, taste
What is the nerve type and function of the 7th nerve?
Vestibulocochlear
8th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Sensory
Function: Hearing, Balance
What is the nerve type and function of the 8th nerve?
Glossopharyngeal
9th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Both
Function: Taste, gag reflex
What is the nerve type and function of the 9th nerve?
Vagus
10th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Both
Function: Gag reflex, parasympathetic innervation
What is the nerve type and function of the 10th nerve?
Accessory
11th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Motor
Function: Shoulder shrug
What is the nerve type and function of the 11th nerve?
Hypoglossal
12th cranial nerve?
Nerve Type: Motor
Function: Swallowing, speech
What is the nerve type and function of the 12th nerve?
Eye muscles
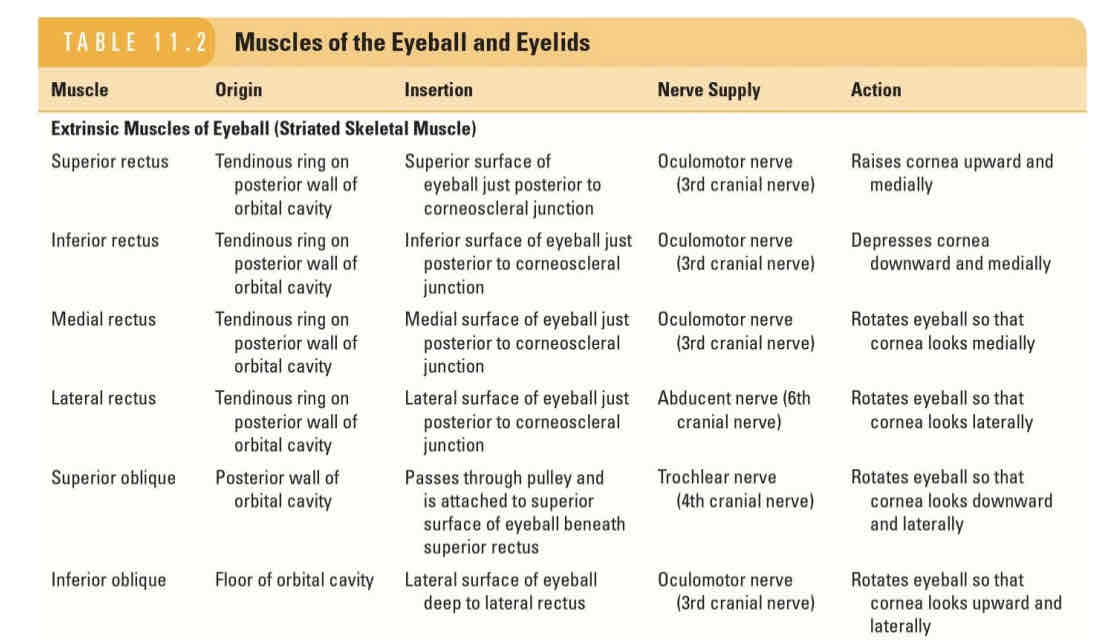
Occipitofrontalis (surprise)
Surprise

Levator palpebrae superioris (eye opening)
Eye opening

Orbicularis oculi (eye closing)
Eye closing
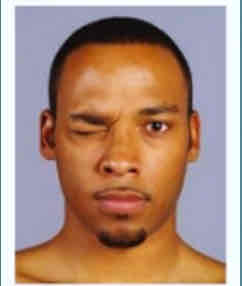
Corrugator supercilli (frowning)
Frowning

Procerus (wrinkling the bridge of the nose)
Wrinkling the bridge of the nose
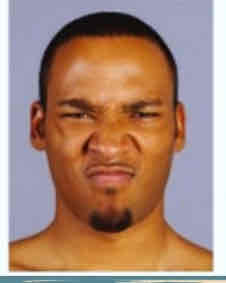
Orbicularis oris (lip closing and kissing)
Lip closing and kissing

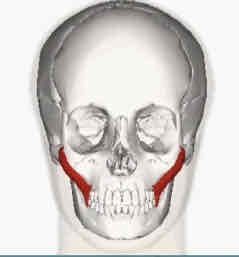
Buccinator (cheek compression)
Cheek compression
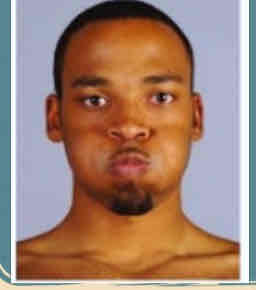
Levator anguli oris (sneering)
Sneering
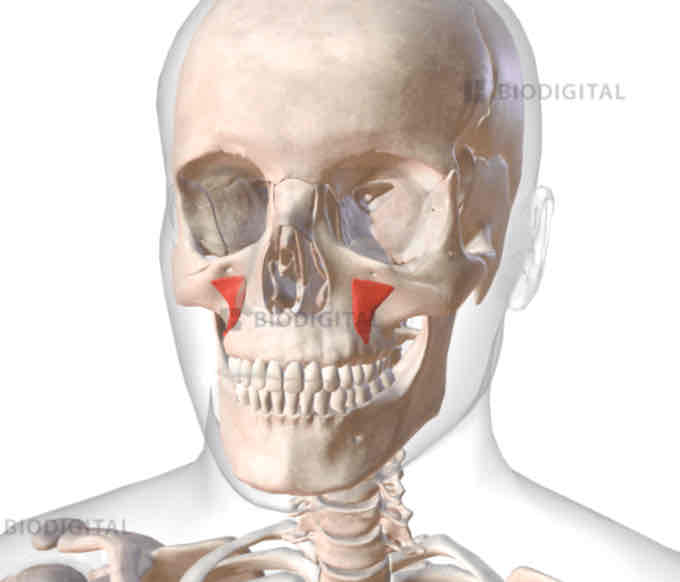
Levator labii superioris
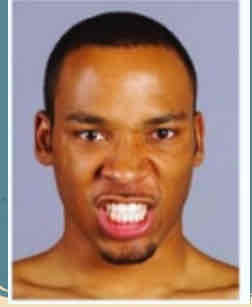
Zygomaticus major and minor (smiling)
Smiling
Mentalis (pouting)
Pouting

Depressor anguli oris (sadness)
Sadness
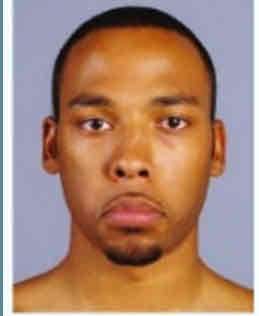
Platysma (egad)
Egad
Risorius (grinning)
Grinning

Depressor labii inferioris (melancholy/irony)
Melancholy or irony

Facial artery and vein
Superficial temporal artery
2 blood supply to the face?
Arteries and veins:
Temporomandibular Joint
Articulation: Occurs between the articular tubercle and the anterior portion of the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone above and the head (condyloid process) of the mandible below
● Type of joint: Synovial joint
● Movements: Mandibular depression, elevation, protrusion and retrusion and rotation
Mouth/Jaw Closing
MASTICATION MUSCLES
○ Temporalis
○ Internal/Medial pterygoid
○ Masseter
Mouth/Jaw Opening
MASTICATION MUSCLES
○ External/Lateral pterygoid
○ Digastric
○ Mylohyoid
○ Geniohyoid
Mouth/Jaw Retraction
MASTICATION MUSCLES
○ Temporalis
Mouth/Jaw Protrusion
MASTICATION MUSCLES
○ External/Lateral pterygoid
○ Internal/Medial pterygoid
○ Masseter
Lateral excursion/deviation
MASTICATION MUSCLES
○ Ipsilateral
■ Temporalis
■ Masseter
○ Contralateral
■ Medial pterygoid
■ Lateral pterygoid
7 vertebrae
How many vertebrae does cervical region have?
Atlas
Axis
C7
What are the 3 atypical vertebrae?
C1 (Atlas)
(-) body, pedicle, lamina and spinous process
C2 (Axis)
(+) odontoid process/dens
C7 (Vertebral prominens)
Spinous process is not bifid
Long, slender similar to thoracic vertebra
Anterior atlanto-occipital membrane
● Continuation of the ALL, which runs as a band down the anterior surface of the vertebral column
● The membrane connects the anterior arch of the atlas to the anterior margin of the foramen magnum
● Limits extension
Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
● Similar to the ligamentum flavum and connects the posterior arch of the atlas to the posterior margin of the foramen magnum
● Limits flexion
Apical Ligament
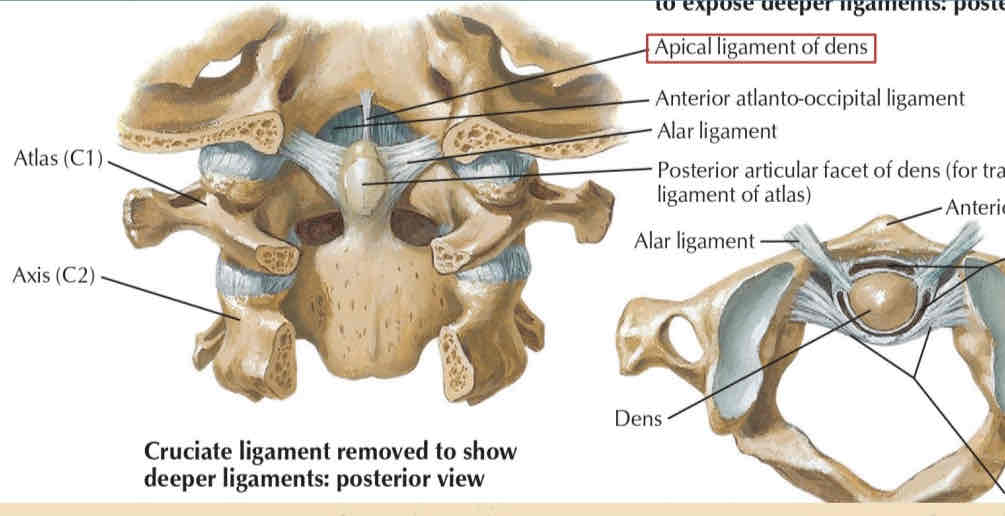
Alar Ligament
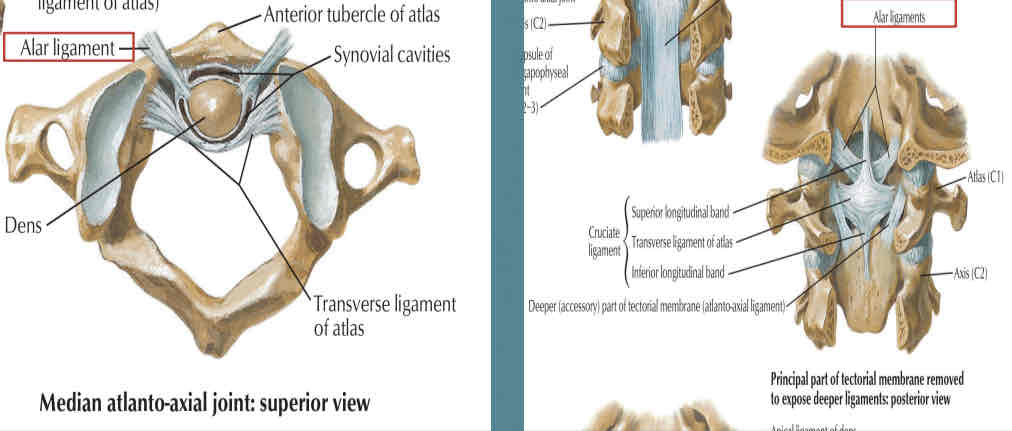
Vertical part
CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
○ runs form the posterior surface of the body to the axis to the anterior margin of the foramen magnum.
Transverse part
CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
○ attached on each side to the inner aspect of the lateral mass of the atlas and bind the odontoid process of the anterior arch of the atlas.
Tectorial Membrane
An upward continuation of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)?
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)
Runs continuous from anterior surface of the vertebral column from skull to sacrum.
Limits extension
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)
Runs continuous band down the posterior surfaces of the vertebral column form the skull to the sacrum
Limits flexion
Supraspinous Ligament
Runs between the tips of adjacent spine?
Interspinous Ligament
This connects the adjacent spine?
Ligamentum Flavum
Connects the laminae of the adjacent vertebrae.
Continuation of tectorial membrane
Joints of the Neck
Intervertebral joints
Zygapophyseal joints
○ Facets are oriented 45 degrees to the transverse plane/ frontal plane
○ Inferior facets face: anteriorly and inferiorly
○ Superior facets face: posteriorly and superiorly
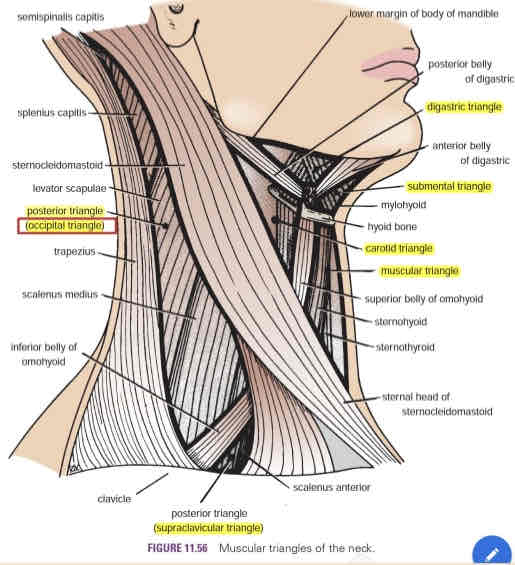
Anterior triangle
Carotid triangle
Digastric triangle (Submandibular)
Submental triangle
Muscular triangle
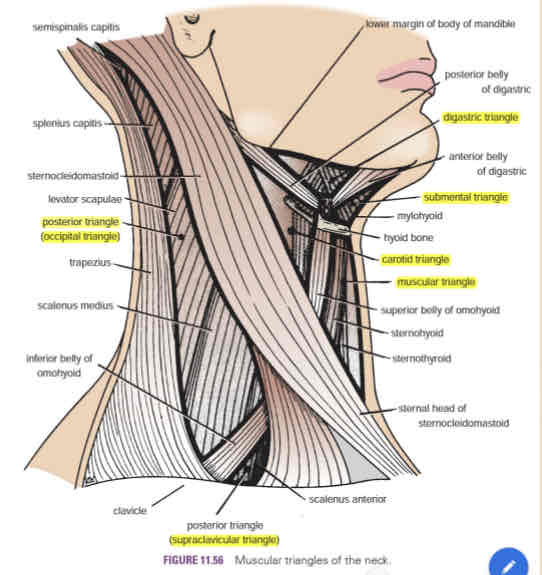
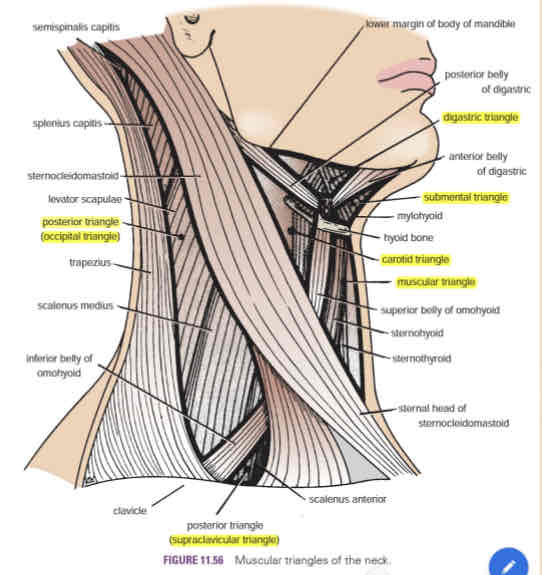
Posterior triangle
Occipital triangle
Supraclavicular triangle
Carotid triangle
Contains the carotid arterial system (common carotid artery, IJV and vagus nerve)
The carotid pulse can be palpated in this are
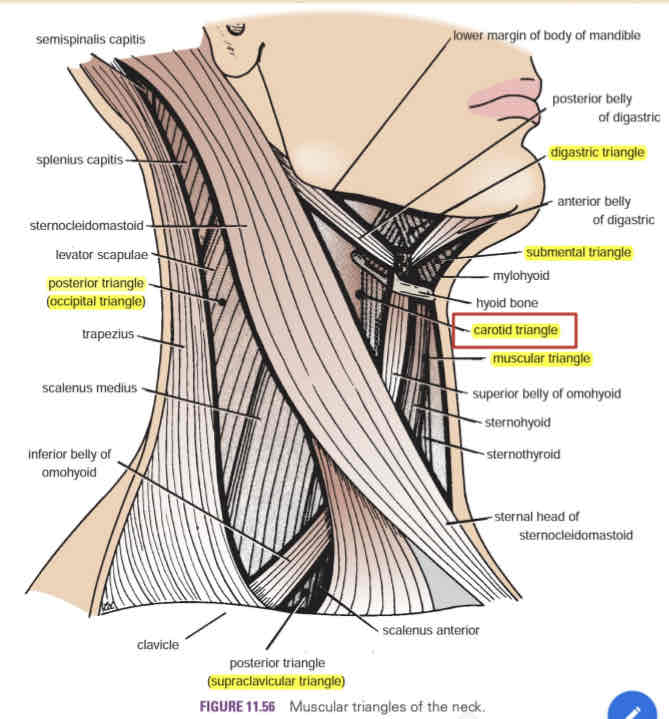
Digastric triangle
AKA submandibular triangle
Contains the submandibular gland and submandibular lymph nodes
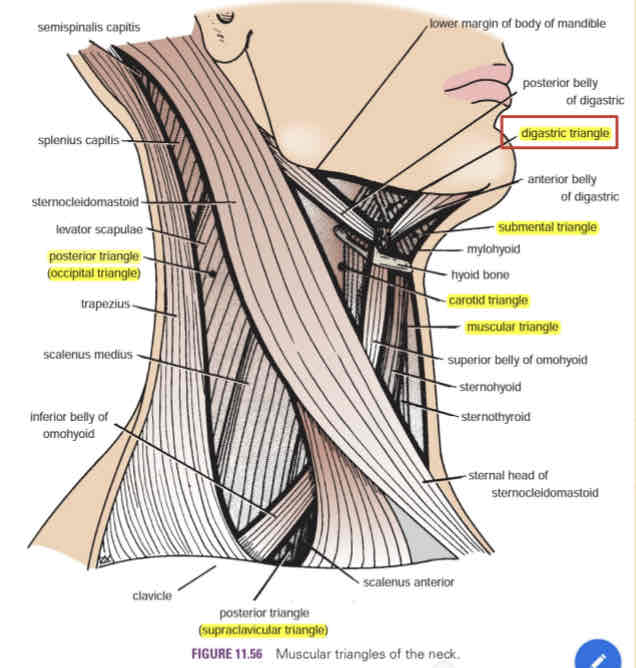
Submental triangle
Contains submental lymph nodes
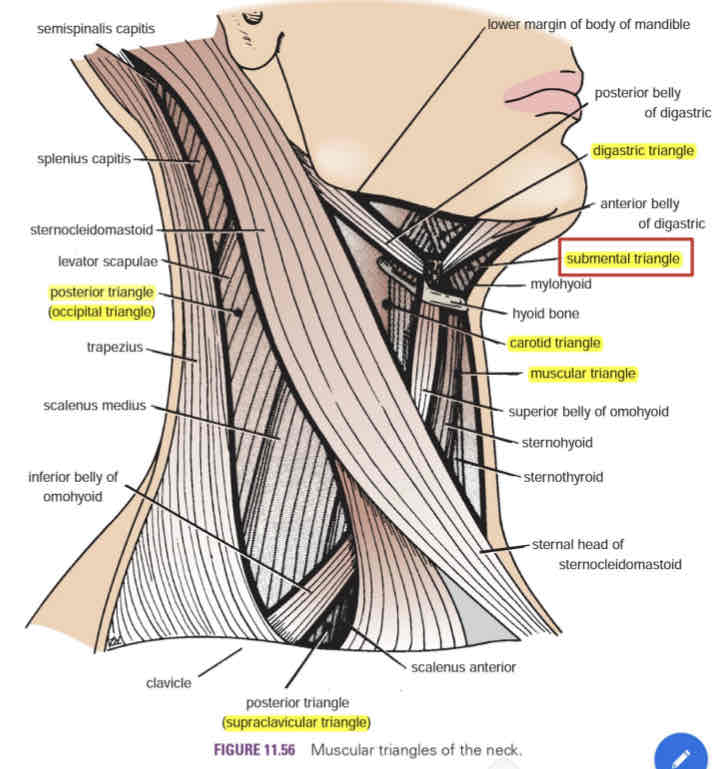
Muscular triangle
Anterior border of the SCM
Floor of the triangle composed of:
○ Sternohyoid
○ Sternothyroid
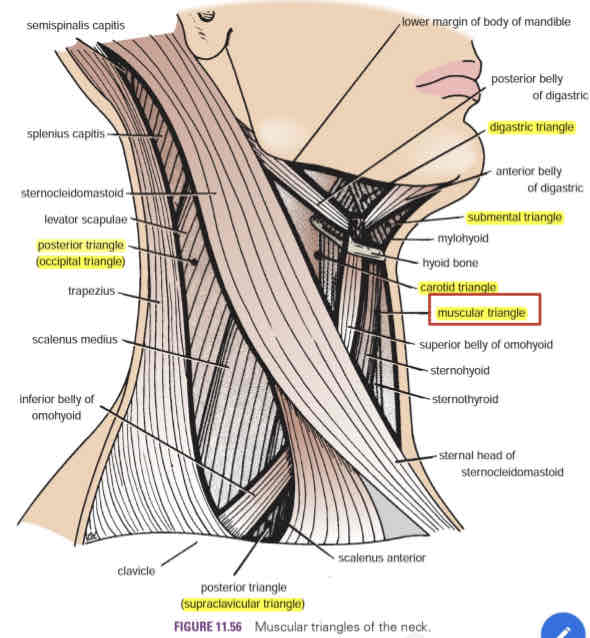
Occipital triangle
Superior to the omohyoid muscle
Contains the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI), cutaneous branches of cervical nerves (C2-C4) and cervical lymph nodes
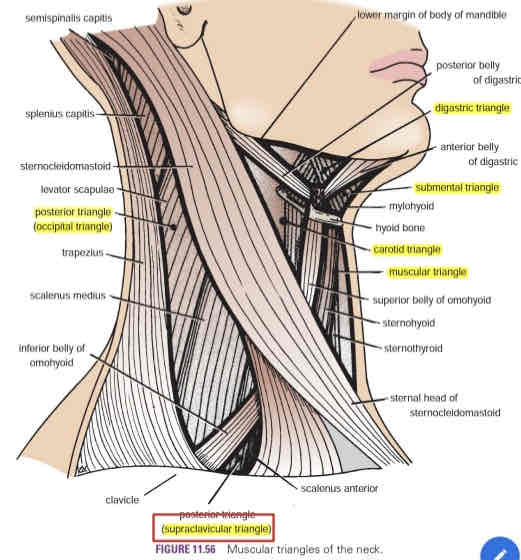
Supraclavicular triangle
AKA omoclavicular triangle
Supraclavicular fossa (subclavian arterial pulse)
Subclavian artery
Bell’s Palsy
Injury to the facial nerve (CN VII) or its branches produces paralysis of some or all facial muscles on the affected side
The affected area sags, and facial expression is distorted, making it appear passive or sad
