343 Chapter 12 Software Support and Maintenance
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the types of Customer/User Support?
Non-defect support
Defect support
What is Non-Defect Support?
Usage questions/answers
General help (install, recovery, etc.)
Additional and supplemental functions (future releases)
What is Defect Support?
Report and track failure and defect
Recovery from failure
Work around
Fix releases
What kind of sophistication Defect support require?
Project the # of problems and problem arrival rate
Estimate and plan the needed support resources
Educate and build the defect support team
Defect reporting and tracking
Defect identification, fix, and release
During the period right after release, What is happens?
many problems are discovered and reported.
The amount of problems discovered eventually decreases, but what happens at the same time?
the nature of the problem discovered becomes more difficult to diagnose.
Is software support free?
no, Most charge an annual fee (e.g., 18% of product)
Why is software support not forever?
Most product goes through a number of releases
Each product release is only supported for a limited number of years
Customers/users are moved from back-level software to the current release as soon as possible
Usually support no more than two back levels of a software
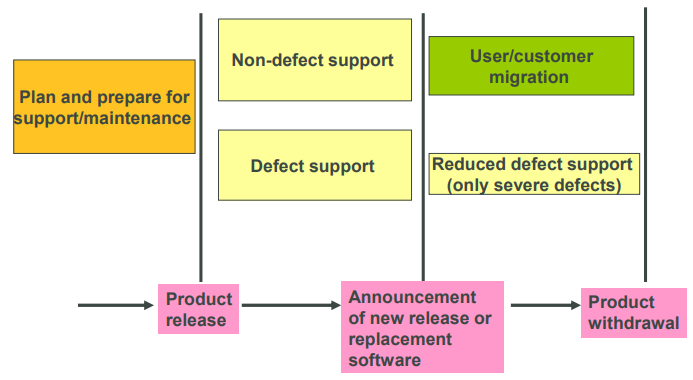
What is this?
Product Support Life Cycle
What happens when a product enters a “Sun-Setting” phase?
Stop any product’s additional feature and enhancement.
Fix only the high-severity problems.
Announce new replacement product.
Encourage new and existing customers to move to new product.
Notify all old users on the old product of the planned termination date.
Provide names of other vendors who are willing to support the old product to the customers who chooses to stay.
Terminate the customer product and withdraw the product from market.
What tiers do you organize the support groups into?
A direct customer contact tier to accept problems, prioritize the problems, record problem, solve the “easy” problems, and manage the problem-resolution cycle.
A higher tier of specialized resource that sometimes talk to customers to resolve more difficult problems with work arounds
A tier of experts that can fix and rebuild the code
What is a key parameter in keeping the customer satisfied?
Turn the problem fixes around within some reasonable time frame
What does fixing a problem require?
an understanding and a “contract” of service terms.
What is the contract on fix time depended on?
The types of problem based on some “prioritization” scheme.
Why doe customers not always install a fix release that is provided?
Choose and pick the fixes they want
Modified code and cannot apply the generic fix release
Stay on some past release because it “finally” works
Need to explain the potential serious problem?
Fix release related to other fix releases that customer care about in product fix situation (see next slide)
A released fix may have reworked over a previous “emergency” fix code area (see a later slide)
What should we encourage the user/customer to do?
To install the latest fix release and install the fix releases in sequence.
All problems reported need to be what?
Tracked through successful problem resolution with the customers.
A part of this control is to ensure that all changes, for fixes and for enhancements are what?
not arbitrary and capricious.
Change control is the mechanism used, just as in software development prior to release, to ensure that all changes are managed through what?
Change control process
Documented changes (change control form as an aid)
Change control committee
What is the work flow that manages the changes?
Origination of change request
Approval of change request
Monitoring the changes being made
Closing the completed change
What resource do we need to ensure the control process?
Change control board or committee
Automated workflow tool (using a change control form)