NEUR200 exam1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
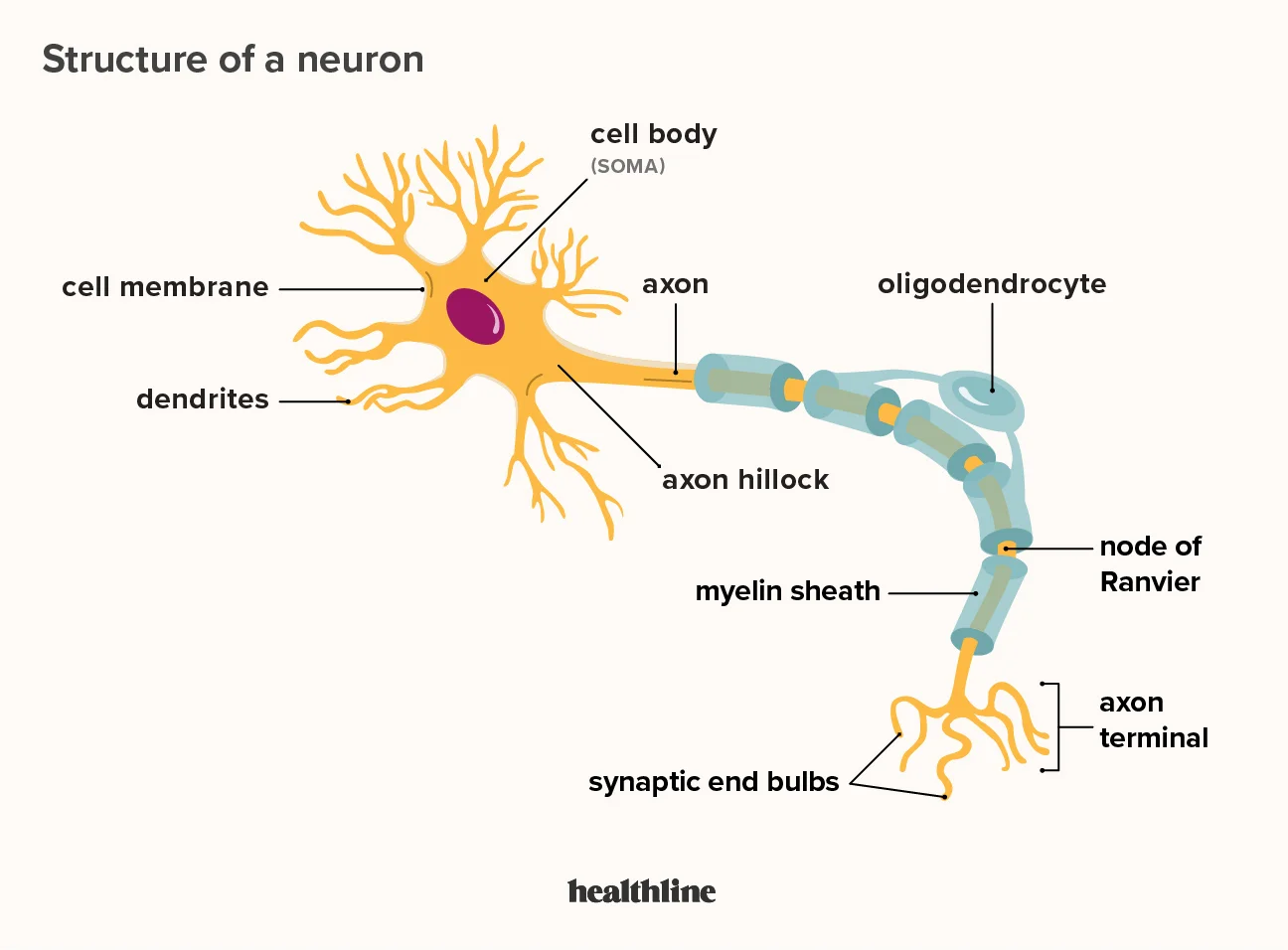
Neuron
A specialized cell that transmits nerve impulses.
Soma
The central part of a neuron where most of the cell's metabolism occurs. (cell body)
Dendrites
Fibers that surround the cell body and receive information from other neurons.
Axon
A long fiber that conveys impulses toward other neurons, organs, or muscles.
Presynaptic Terminal
Releases chemicals at the synapse, facilitating communication between neurons.
Multipolar Neuron
A neuron with many dendrites and one axon.
Unipolar Neuron
A neuron with an axon and no dendrites that branches into two directions.
Bipolar Neuron
A neuron with one dendrite and one axon.
What are Spindle Neurons
A type of bipolar neuron that help us with communications between frontal lobe, frontal cortex, etc., and impact our empathy, morality, and emotional regulation
Motor neurons
Its soma is in the spinal cord (conducts impulses along its axon to a muscle). Efferent, carries information out
Sensory neurons
(Light, sound, or touch) soma is located on the trunk. Afferent brings information in
Intrinsic Neurons
(Inside the structure) Neurons that communicate within a structure
What are the two types of neurons?
Presynaptic and postsynaptic
Presynaptic neurons
Release neurotransmitters
Post synaptic neurons
Receive neurotransmitters
COMT Gene
A gene linked to the degradation of dopamine and impulsivity.
MOA
Can elevate serotonin, aggression, and dopamine
Higher levels can lead to impulsivity, (but for males a decrease in it can lead to impulsivity)
Glial Cells
Supporting cells in the brain that provide firmness and structure.
Glial cell functions?
It helps with the migration of neurons
Myelin formation (oligodendrocytes in CNS and Schwann cells in PNS)
Synapse formation/maintenance
What are the types of glial cells?
Macroglial and microglial
Oligodendrocytes
A type of Macro-Glial cells that contribute to the myelin sheath in the central nervous system.
Myelin sheath
Insulate axons with fats and proteins provided by oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwan Cells (PNS). Increase the speed of action potentials by preventing the need for regeneration along the axon
Astrocytes
Star-shaped macro-glial cells that are nutritive to oligodendrocytes and remove death neurons after brain injury. Also maintain white matter integrity
Function of astrocytes mental health
Since they provide nutrients to oligodendrocytes (which produce myelin sheath), the disruption of communication between the two leads to myelin disorders like schizophrenia and psychosis
Blood-Brain Barrier
A selective barrier that protects the brain from fluctuations in blood composition. Keeps out most toxic products
Is there a single barrier in the blood brain barrier?
There is not a single barrier; there are many different systems that exist for excluding substances from blood to brain
Action Potential
The process of releasing a neurotransmitter into the synapse so that neurons can communicate with other neurons.
Under what conditions does an axon produce an action potential?
Whenever the membranes potential reaches the threshold
Hyperpolarization
The membrane potential is further away from the threshold (below -70 mV) so the neuron can’t fire. Before resting potential
Resting Potential
The electrical charge difference across the neuronal membrane when at rest. The inside of the neuron is more negative than outside, typically at around -70 millivolts (mV). Sodium Na+ is more concentrated outside
Depolarization
The process of reducing the polarization of a neuron, leading to action potential. When the threshold (-55 mV) is reached by the neurotransmitters, Na+ channels open, allowing sodium ions to flow into the neuron, resulting in a rapid action potential.
All-or-None Law
The principle that action potentials occur fully or not at all.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between myelin sheaths where sodium ions enter the axon through saltatory conduction
Saltatory Conduction
The process by which action potentials jump from one node of Ranvier to another.
Optogenetics
A technique for brain stimulation that uses light to activate or inhibit neurons using light-sensitive proteins. An optical fiber is implanted to deliver light to the targeted neurons.
Electrical Recording
Methods like EEG, MEG, and iEEG for measuring brain activity through electrical signals.
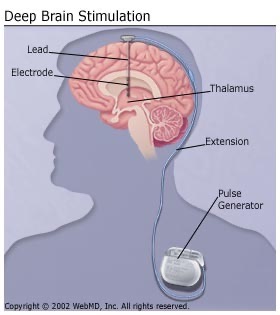
Deep Brain Stimulation
A surgical procedure that involves implanting a neurostimulator to send electrical impulses to specific brain regions, used when medications are ineffective. Used for treatment
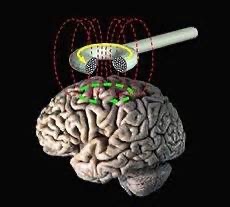
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
A non-invasive brain stimulation technique that applies magnetic stimulation to a portion of the scalp to stimulate neurons beneath. Activates or inactivates neurons below the magnet. can create temporary brain activity and effective only for cortex
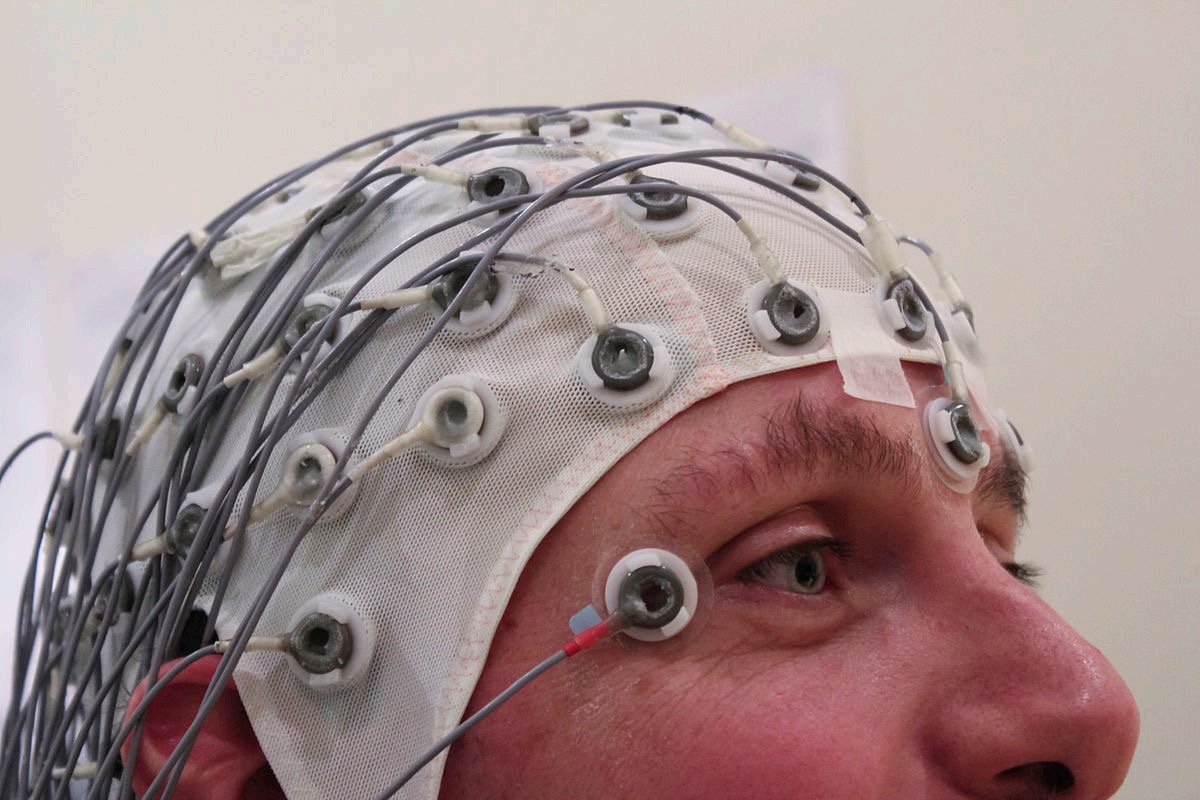
Electroencephalography (EEG)
A method for recording electrical activity of the brain by placing electrodes on the scalp. When many neurons are active at the same time, the current generated is strong enough to be detected on the surface of the scalp with sensitive electrodes. Bad spatial resolution. Very good time resolution (milliseconds). Can see changes in consciousness
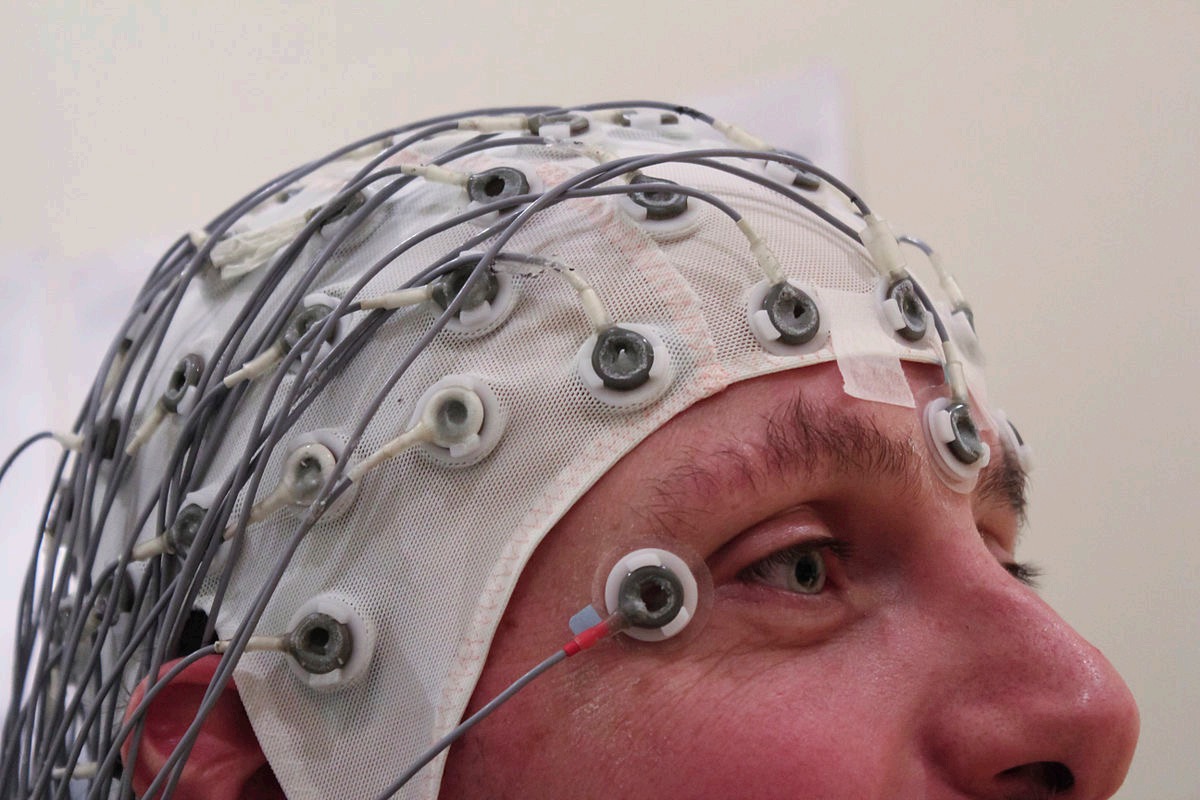
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Similar to EEG, a technique for mapping brain activity by measuring the magnetic fields produced by neuronal activity. Bad spatial resolution. Very good time resolution (milliseconds). Can see changes in consciousness
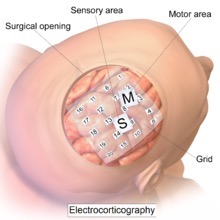
Intracranial EEG (ECOG)
A invasive recording of electrical activity. Electrodes are placed directly on the brain. Good spatial and temporal resolution. Only used with patients who are going through brain surgery
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A neuroimaging technique that produces structural images of the brain (anatomy) using strong magnetic fields. avoids X-rays. Poor temporal resolution (~2 seconds). Good spatial resolution.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
An imaging technique thats used to investigate brain function by measuring the oxygen content in the blood flow in each region of
the brain (relies on the magnetic properties) Poor temporal resolution (~2 seconds). Good spatial resolution.
Resting-State fMRI
Assesses brain connectivity without task performance. Particularly useful for exploring the default mode network in the brain.
Roman y Cajal
Made drawings of neurons contributing to the understanding of the nervous system. After golgi technique. Discovered the nervous system is composed of separate cells
Golgi
Developed the Golgi silver staining technique which enabled visualizing neurons