AP Psychology: Topic 3.8 - Operant Conditioning
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
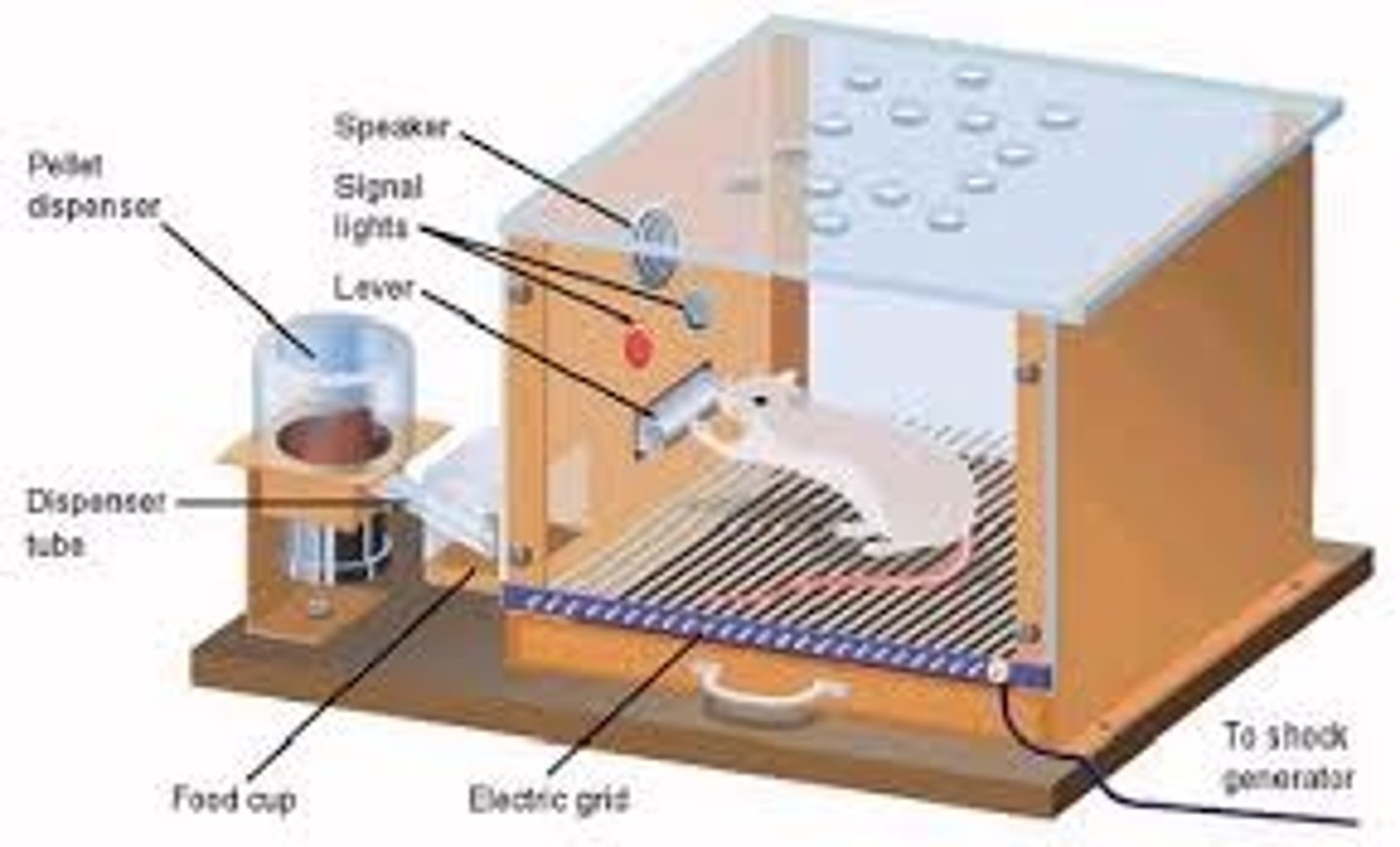
Operant conditioning
a method of learning that uses rewards and punishment to modify behavior
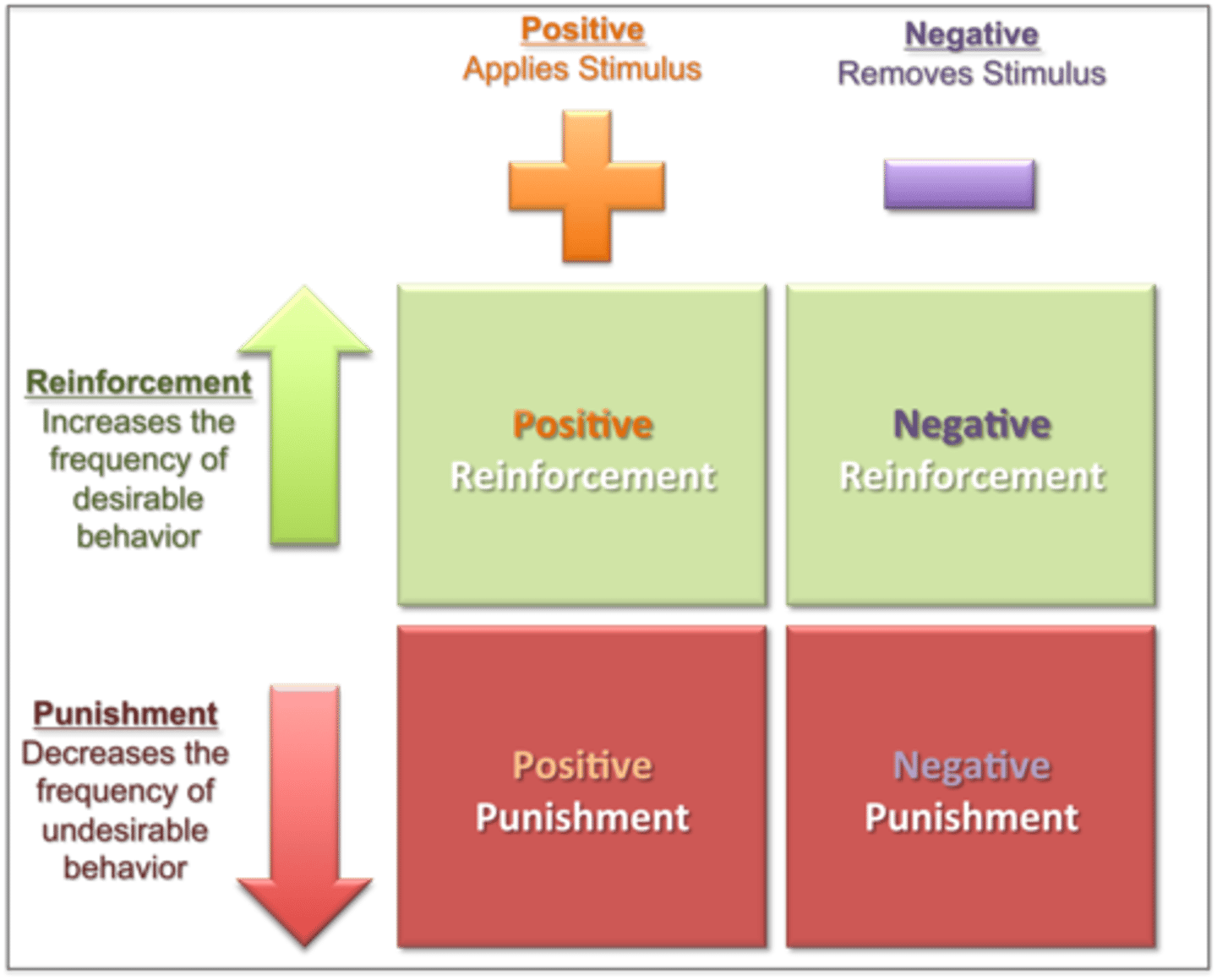
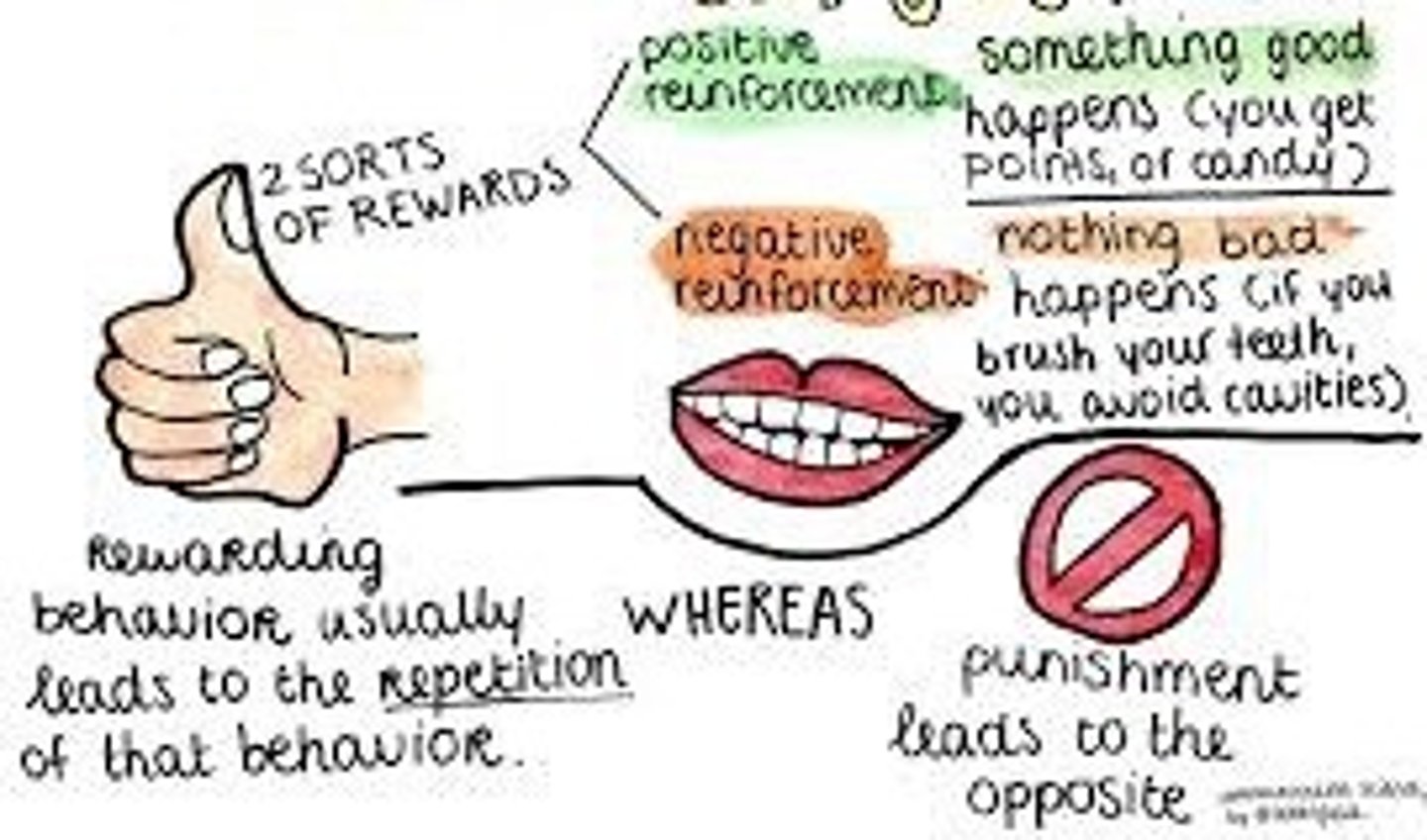
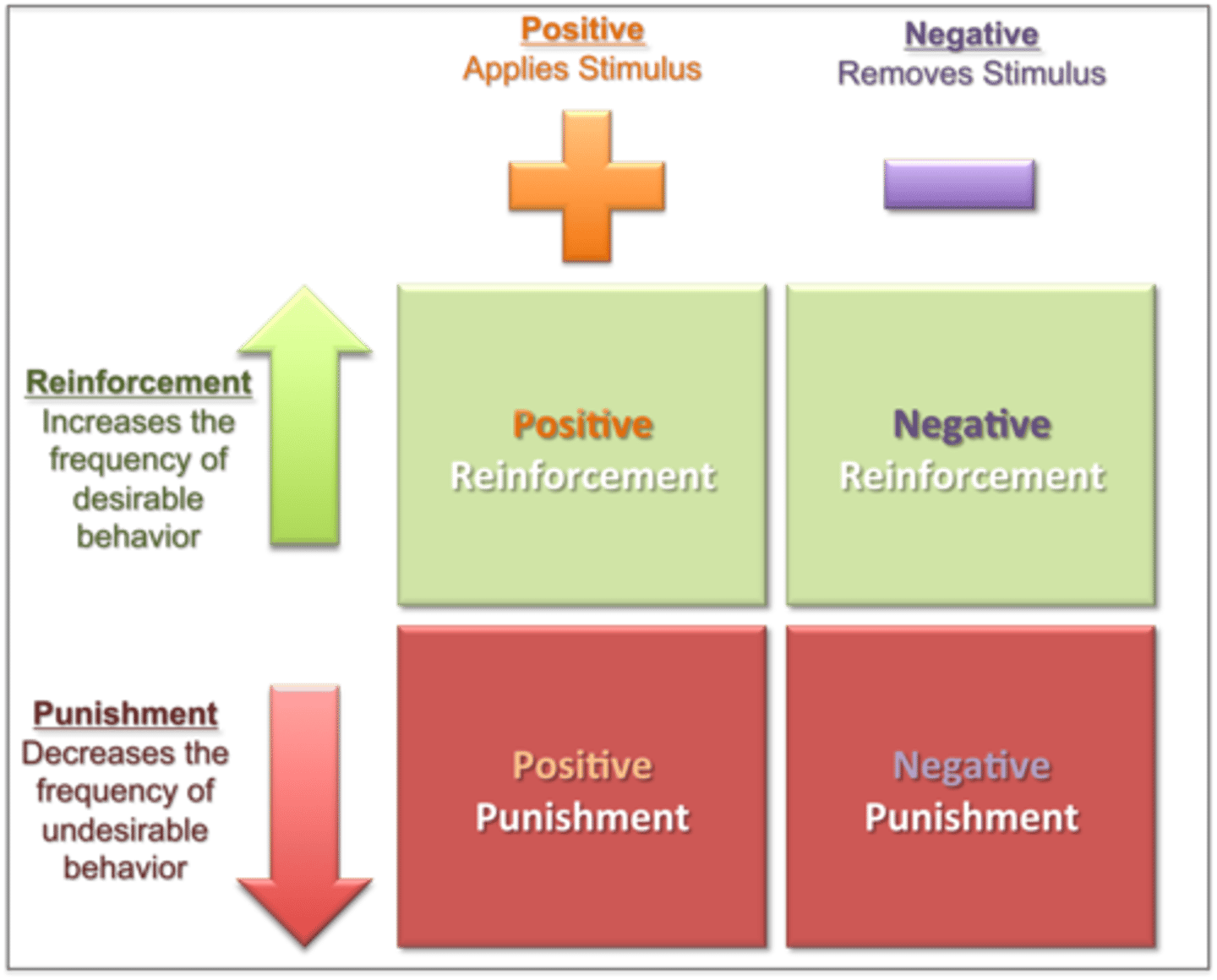
Reinforcement
an event or stimulus that strengthens the behavior it follows
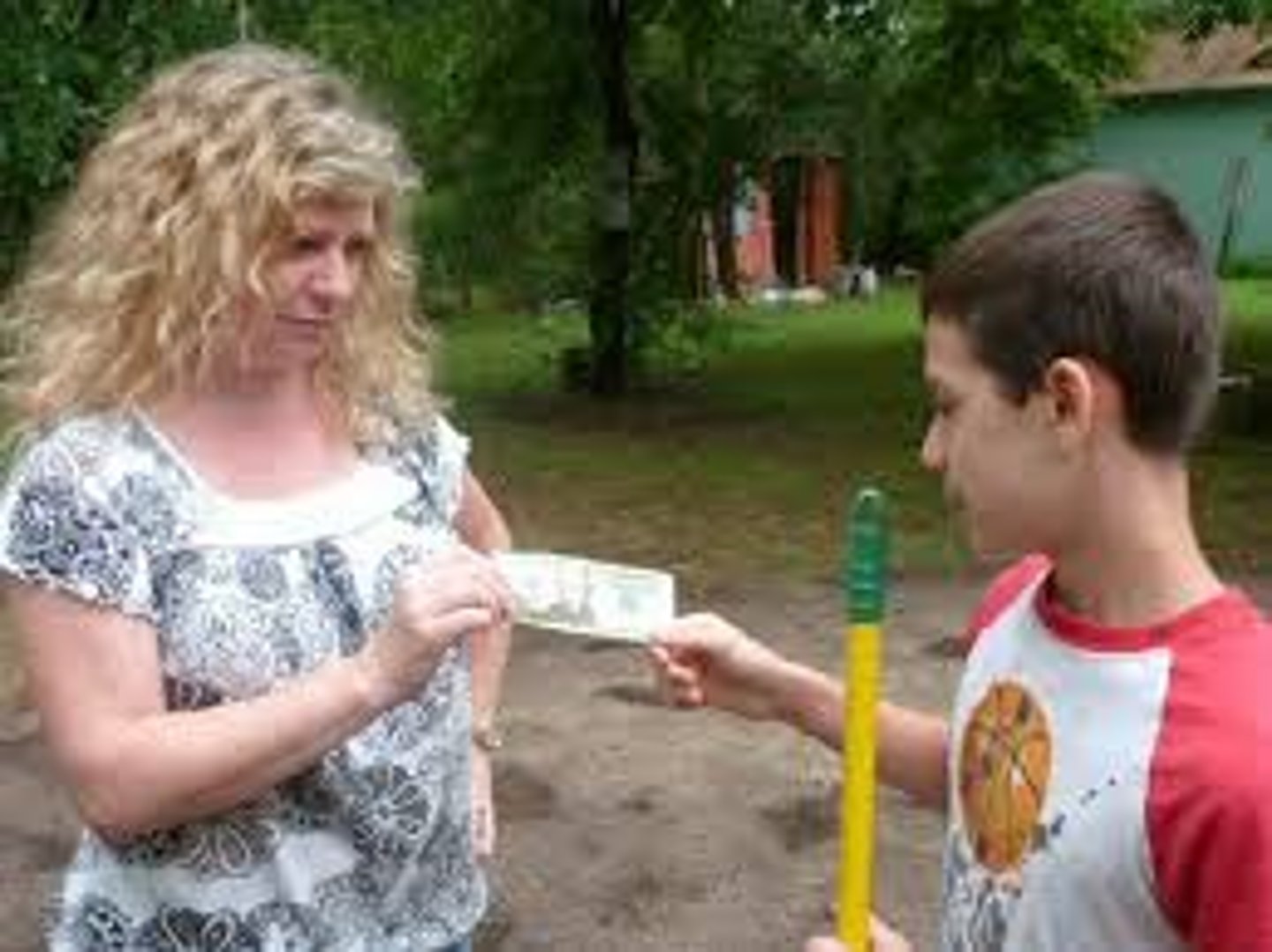

Punishment
an event or stimulus that decreases the behavior it follows
Secondary reinforcer
a stimulus that reinforces a behavior after it has been associated with a primary reinforcer, such as giving a dog a treat (primary reinforcer) and also telling him "good boy" (secondary reinforcer)

Reinforcement discrimination
reinforcing a behavior in the presence of one stimulus but not others

Reinforcement generalization
when a behavior that has been reinforced in a specific context is also exhibited in similar contexts

Shaping
reinforcement of successive steps that lead to a final desired behavior

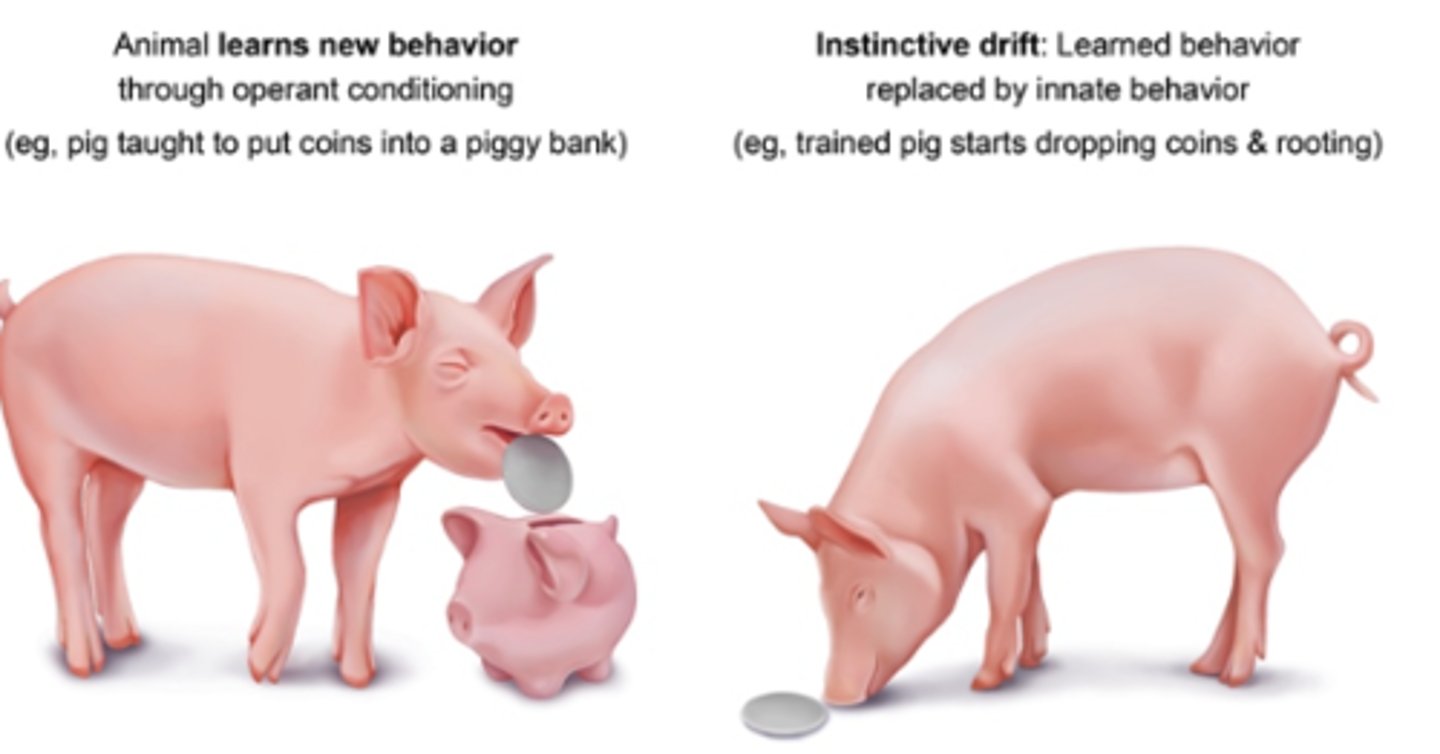
Instinctive drift
the tendency of some trained animals to revert back to instinctual behaviors
Law of Effect
Thorndike's rule that behaviors which have positive outcomes tend to be repeated
Superstitious behavior
an irrational behavior based on a false belief that a specific action can cause a particular outcome

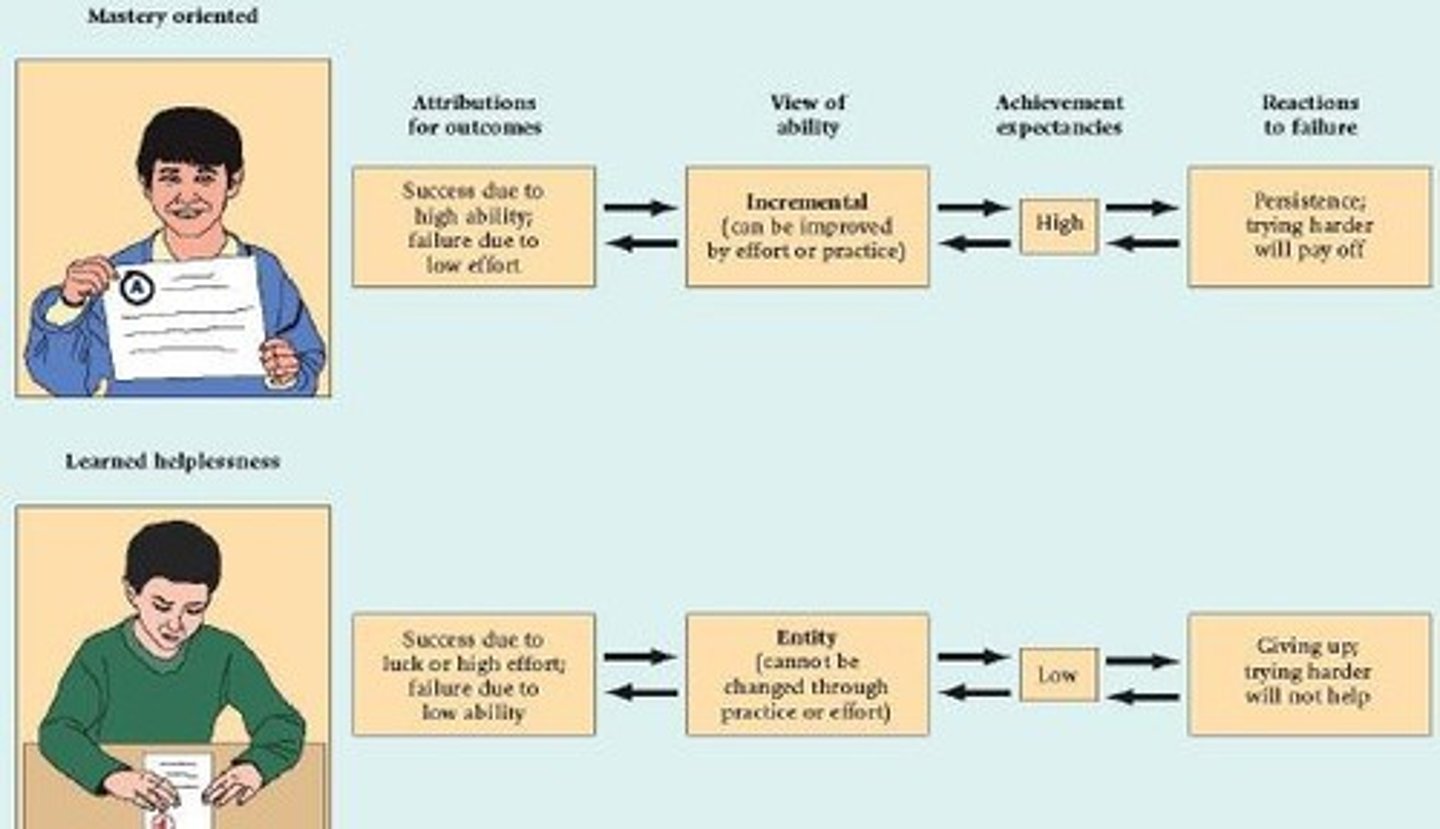
Learned helplessness
the tendency to fail to act to escape from a situation because of a history of repeated failures in the past
Positive reinforcement
a desirable or pleasant stimulus following a behavior that makes it more likely the behavior will reoccur

Negative reinforcement
a stimulus that, when removed after a behavior, strengthens the behavior
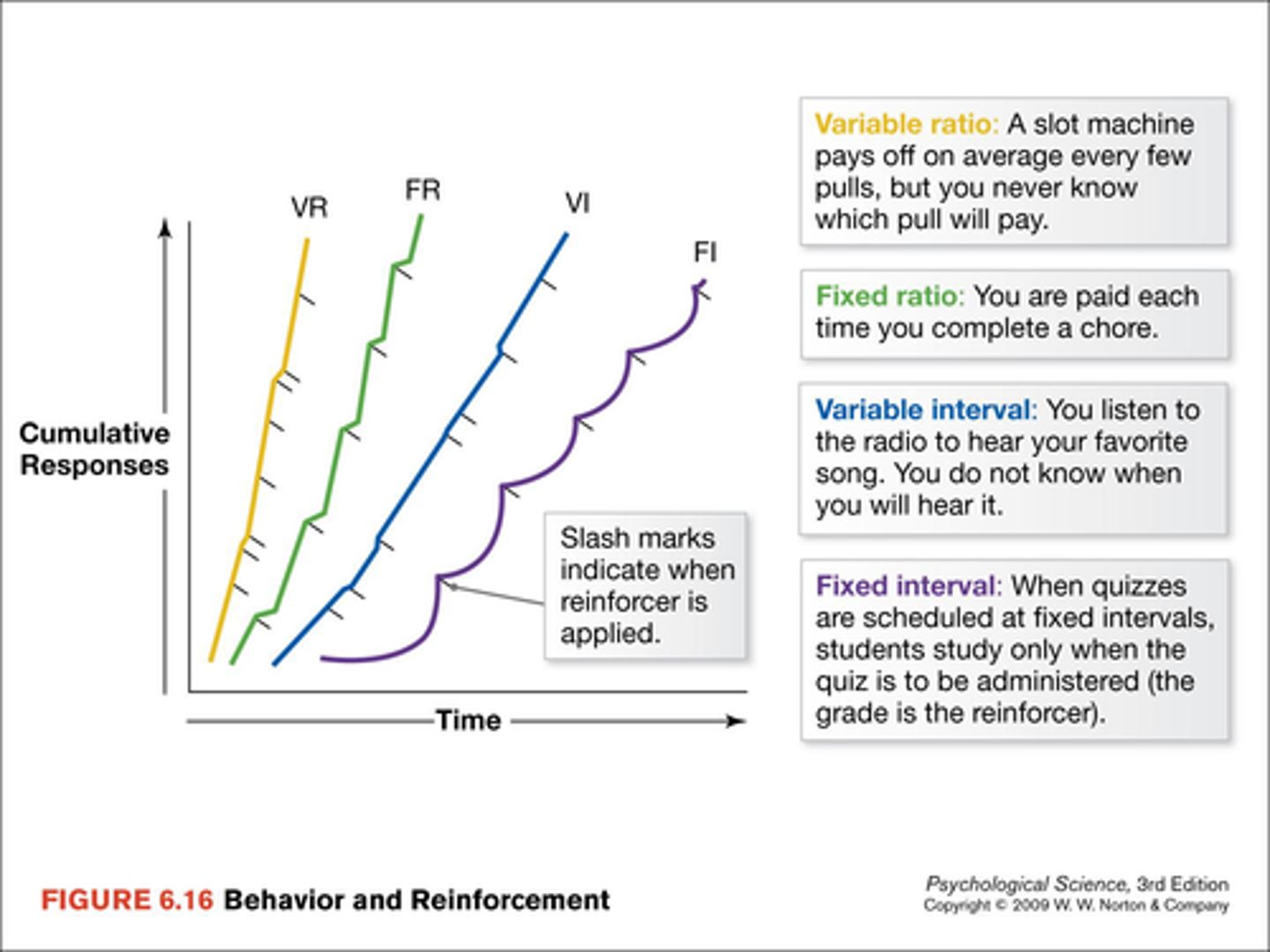
Reinforcement schedules
rules that control when and how often reinforcement is given during operant conditioning
Continuous reinforcement
reinforcing a desired response every time it occurs

Partial reinforcement
reinforcing a response only part of the time (results in slower acquisition but also greater resistance to extinction)

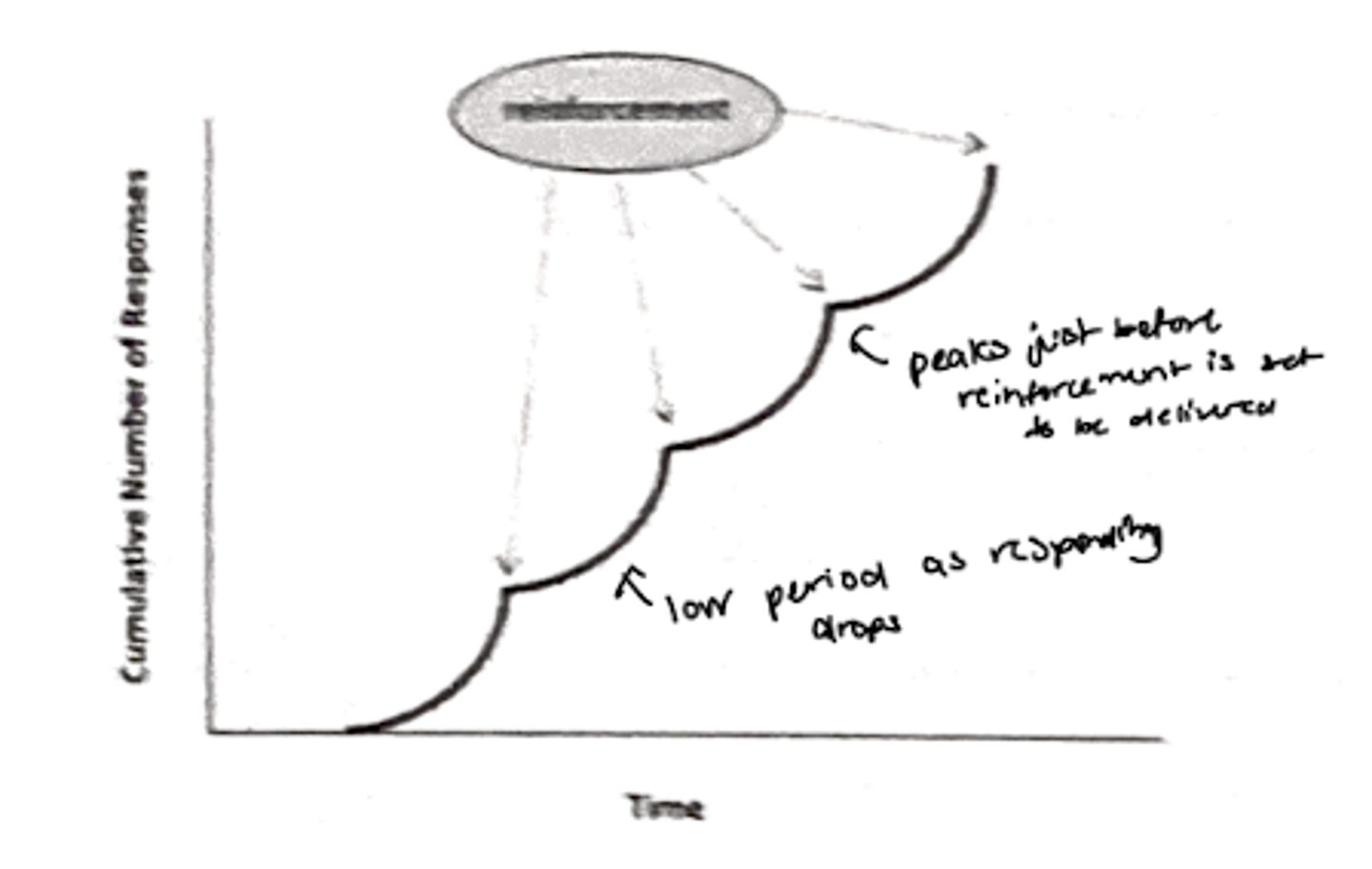
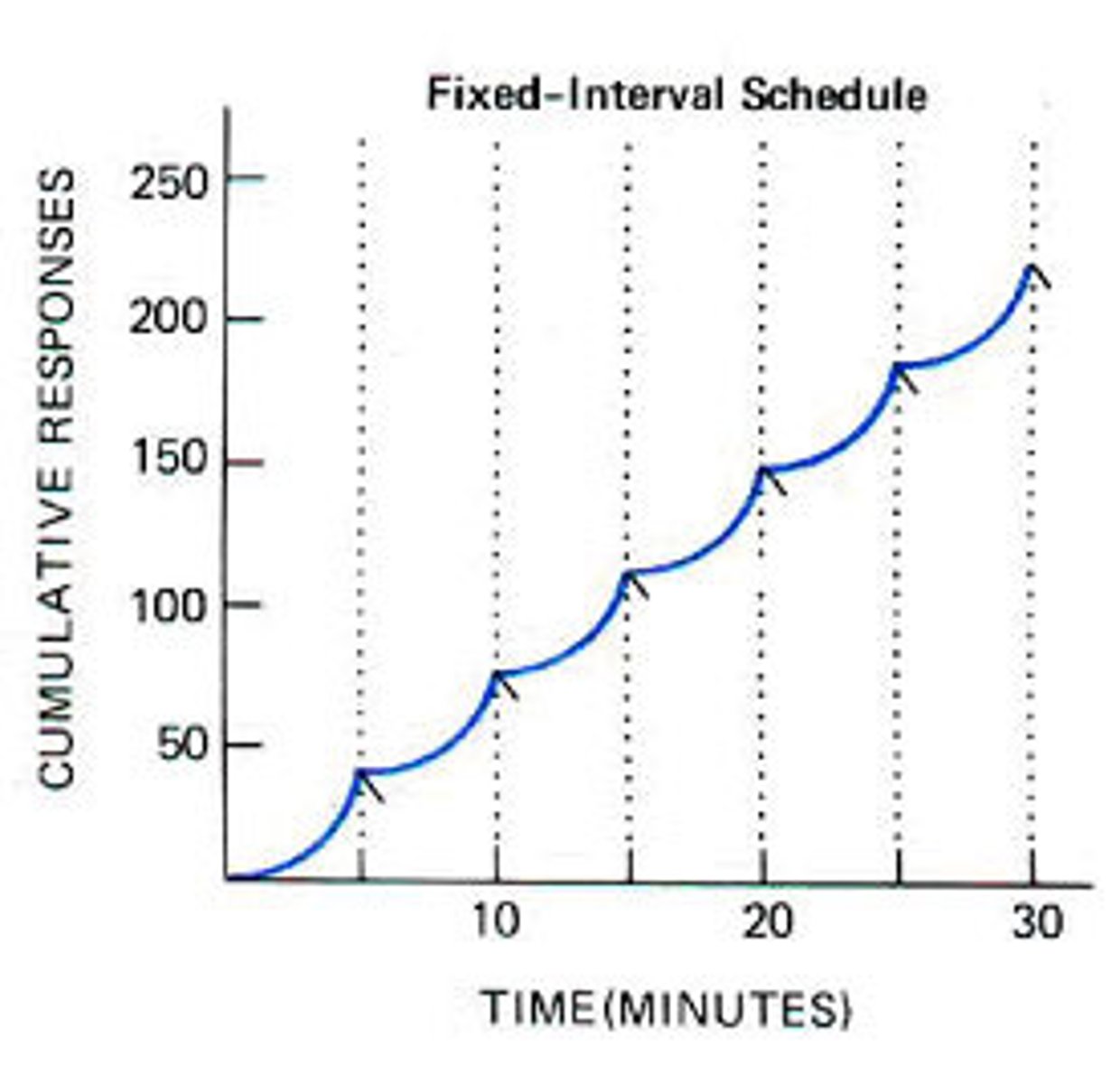
Fixed interval
reinforces a response only after a specified amount of time has elapsed
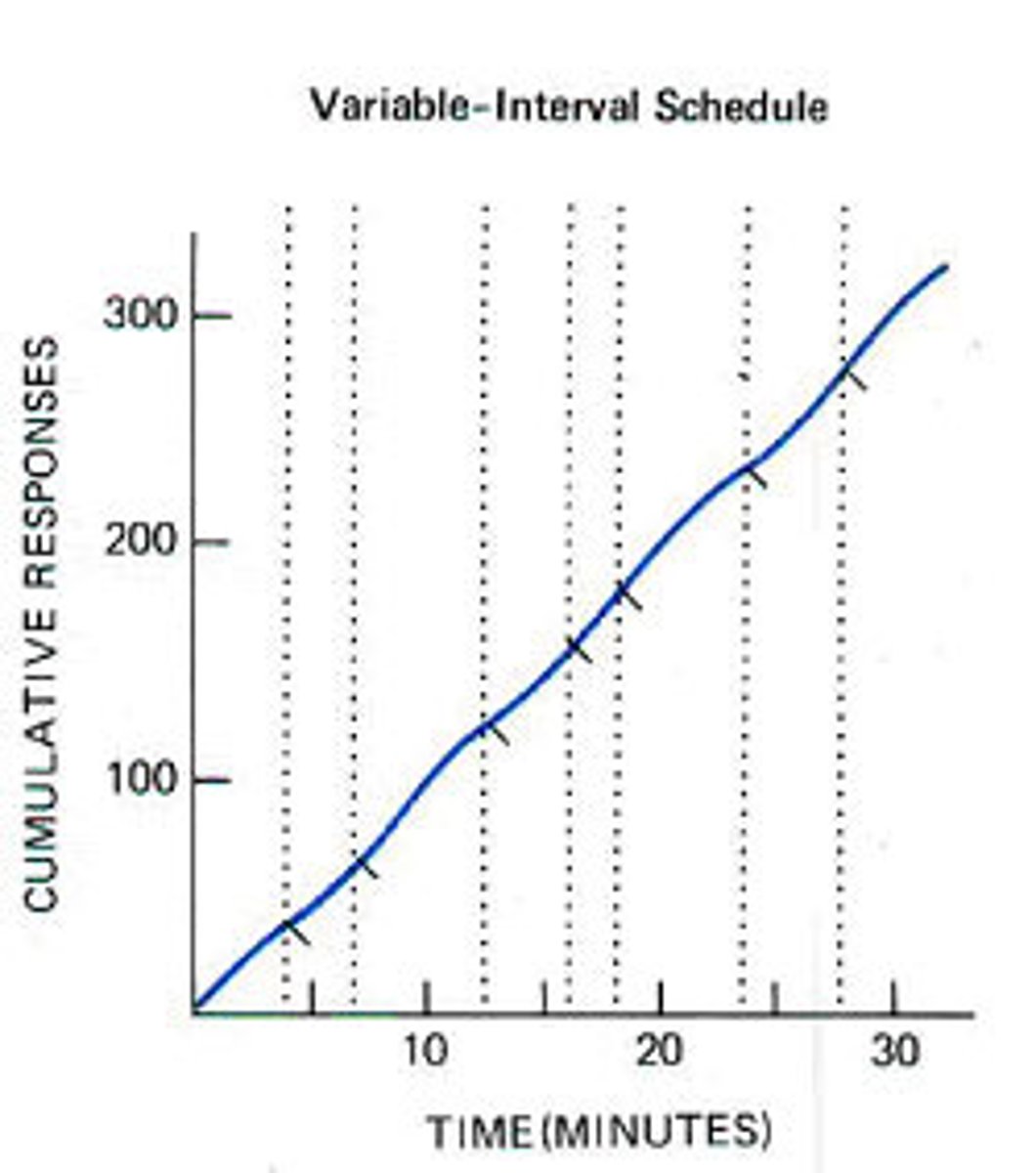
Variable interval
reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals
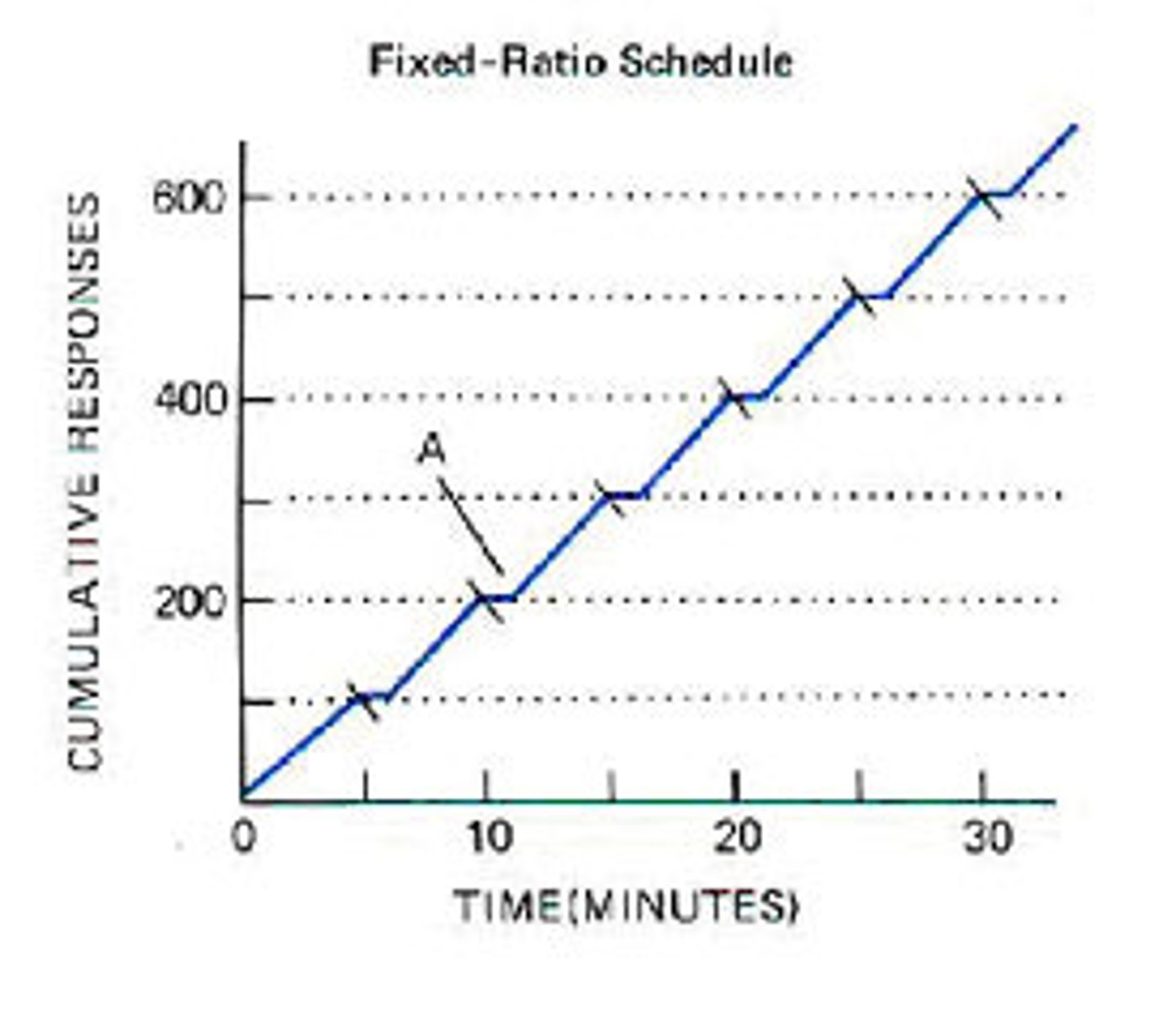
Fixed ratio
reinforces a response only after a specific number of responses
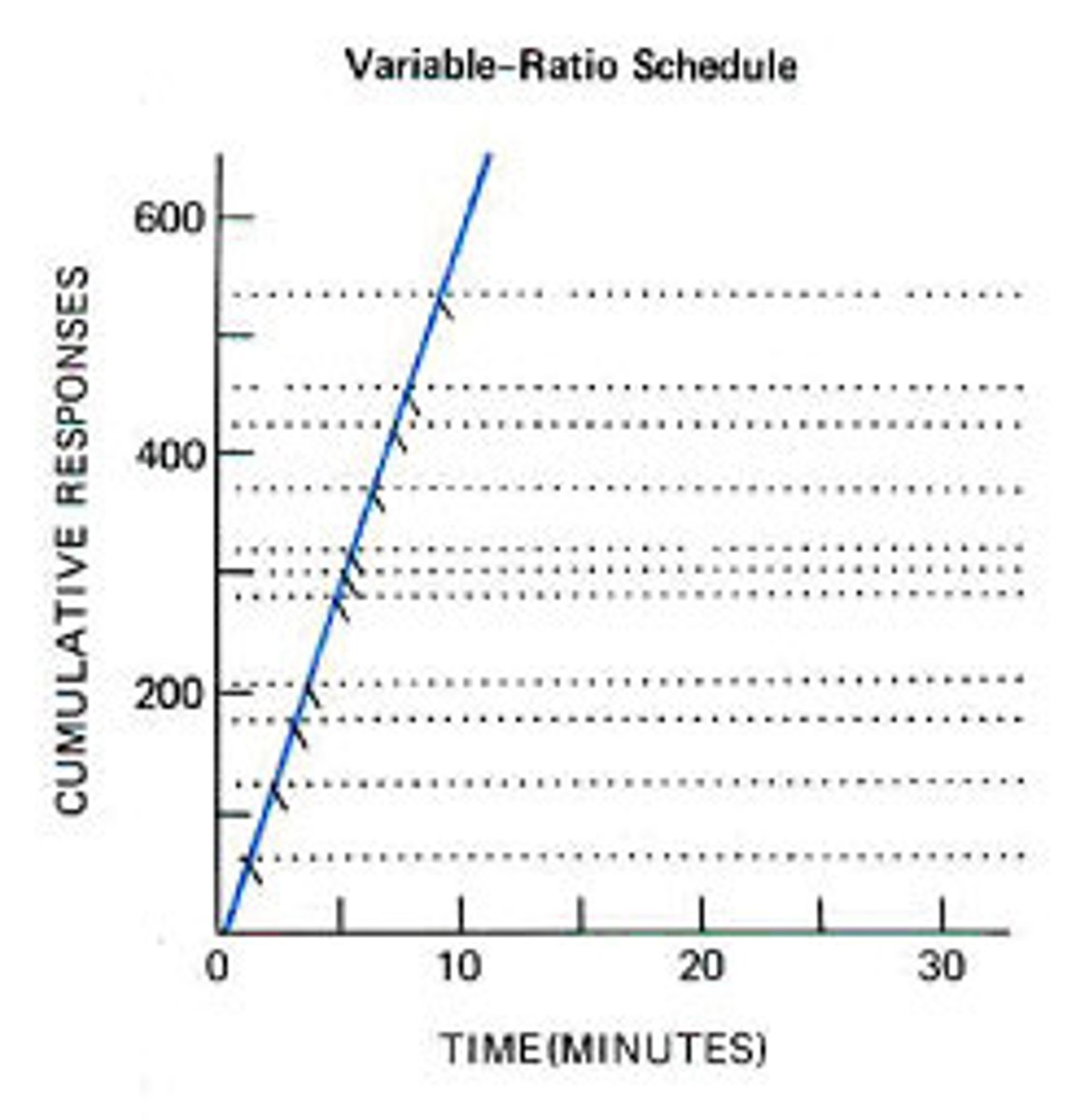
Variable ratio
reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses
Scalloped graph
the pattern that appears on a cumulative response graph of a fixed-interval reinforcement schedule (shows that the subject only begins making a response as the time for the available reinforcements draws near)