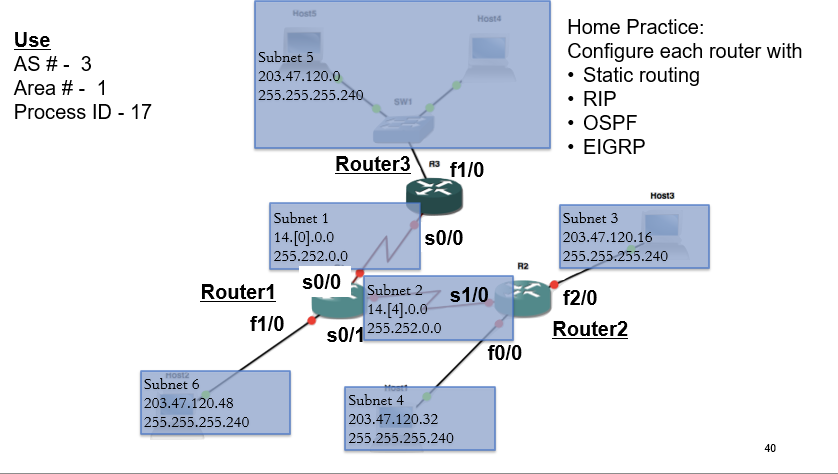
Quiz Routers andSwitches
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the difference between a routing protocol and a routed protocol?
A routing protocol determines the best path for data to travel across a network (e.g., OSPF, RIP), while a routed protocol is a protocol that can carry data over the network and be routed by routers (e.g., IP, IPv6).
What information does a router need to find the best path?
Destination address
Neighbouring routers so it can learn about remote networks
Possible routes to all remote networks
Best route to each remote network
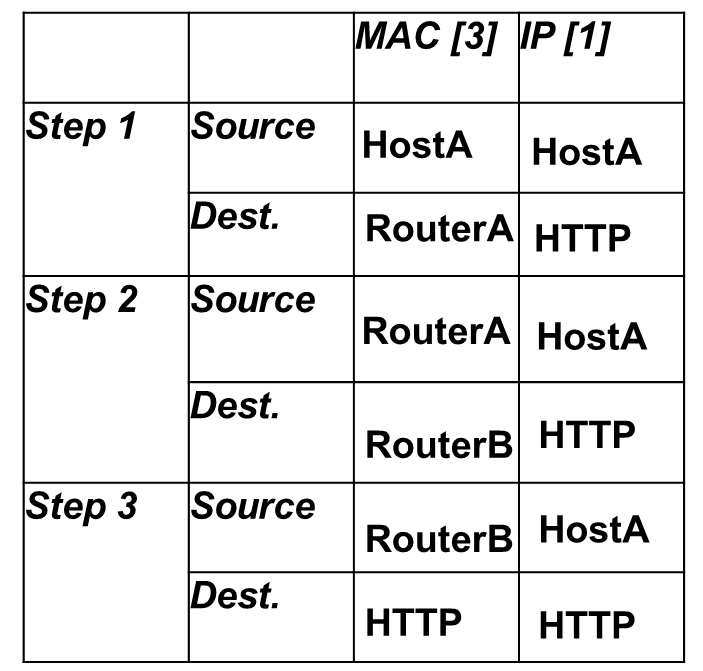
![<p>Fill in the Chart</p><table style="min-width: 100px"><colgroup><col><col><col><col></colgroup><tbody><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:43.22pt;width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>MAC [3]</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>IP [1]</em></strong></span></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="2" style="height:83.2pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Step 1</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Source</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:39.98pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Dest.</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="2" style="height:99.18pt;
width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Step 2</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Source</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:48.26pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Dest.</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="2" style="height:86.12pt;
width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Step 3</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Source</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:43.13pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Dest.</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr></tbody></table><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5d4c3cad-45ef-4bf4-8d36-b886f7b4f463.png)
Fill in the Chart
MAC [3] | IP [1] | ||
Step 1 | Source | ||
Dest. | |||
Step 2 | Source | ||
Dest. | |||
Step 3 | Source | ||
Dest. |
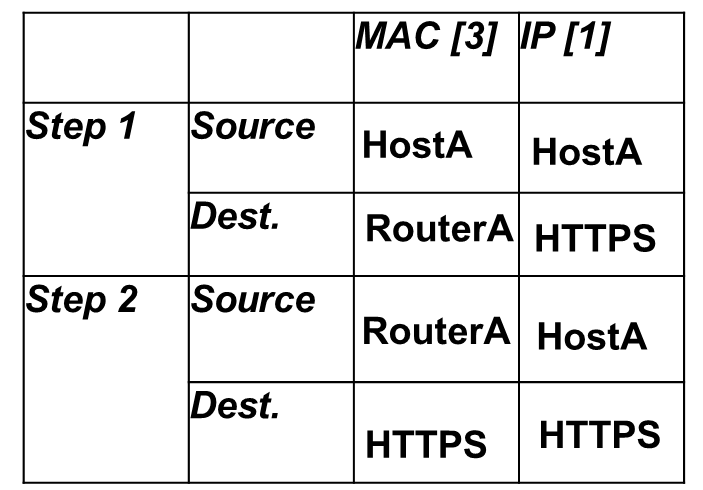
![<p>Fill in the Table </p><table style="min-width: 100px"><colgroup><col><col><col><col></colgroup><tbody><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:43.22pt;width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>MAC [3]</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>IP [1]</em></strong></span></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="2" style="height:83.2pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Step 1</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Source</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:39.98pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Dest.</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="2" style="height:99.18pt;
width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Step 2</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Source</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="height:48.26pt;width:79pt"><p><span><strong><em>Dest.</em></strong></span></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="width:79pt"><p></p></td></tr></tbody></table><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/da061ce7-28a0-4e45-a240-3faab44b7ba6.png)
Fill in the Table
MAC [3] | IP [1] | ||
Step 1 | Source | ||
Dest. | |||
Step 2 | Source | ||
Dest. |
Host 4 sends out an ARP broadcast request for the default gateway. How will the devices in the topology respond?
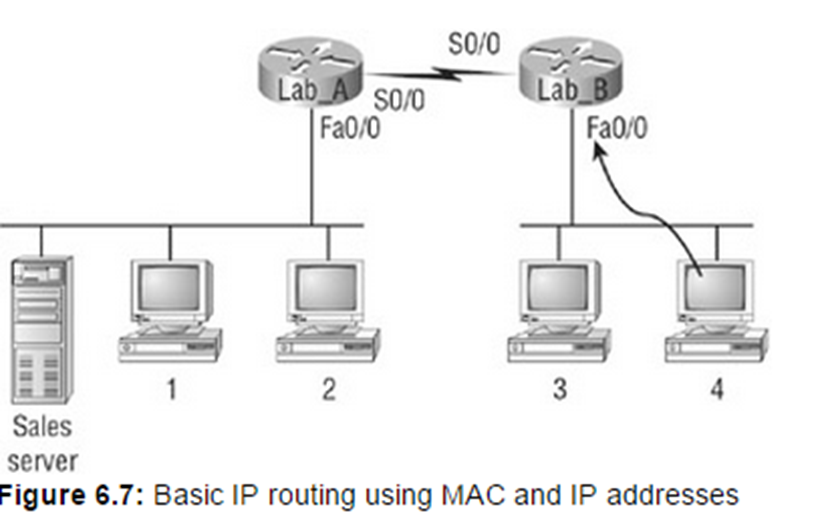
Only Lab_B will respond the ARP request (it is the default gateway in that segment of the network)
How would Host 4 be displaying two documents from the sales server at the same time?
It would use two different ports to display two different pages (that’s the point of the port address!)
It would use two different ports to display two different pages (that’s the point of the port address!)
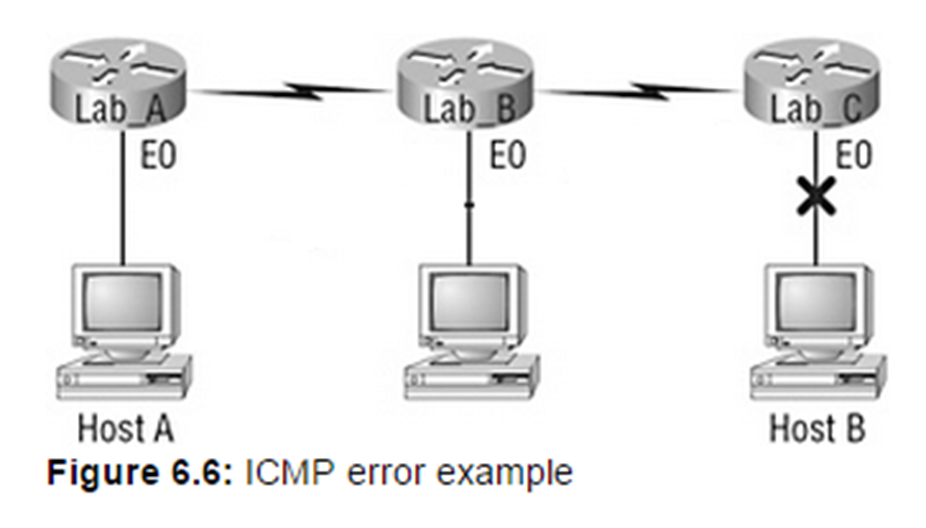
If the routing information has been updated then Lab_A can tell host A that the connection is down, otherwise Lab_C will be the one to inform Host A that the destination is unreachable.
If you’re using static routes then it won’t be until Router C that the packet will realize the destination is unavailable. Dynamic routing protocols will update the routing tables of A and B and in those cases router A will be able to tell Host A that the destination is unreachable
What is Dynamic routing?
In dynamic routing a protocol is run on all the routers and if a change is detected the protocol informs all the routers in the network
What is Static Routing?
In static routing the administrator is responsible for updating all changes by hand into the routers
Write the Static Routing Command
ip route 172.16.30.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0
Define Distance Vector
Every time a packet goes through a router it is called a hop. The route with the fewest hops is the best route (RIP or IGRP)
What is a Link State?
Link state knows the entire topology and knows what all the routers are connected to.
What is Hybrid?
Uses both aspects
Which of these paths is faster?
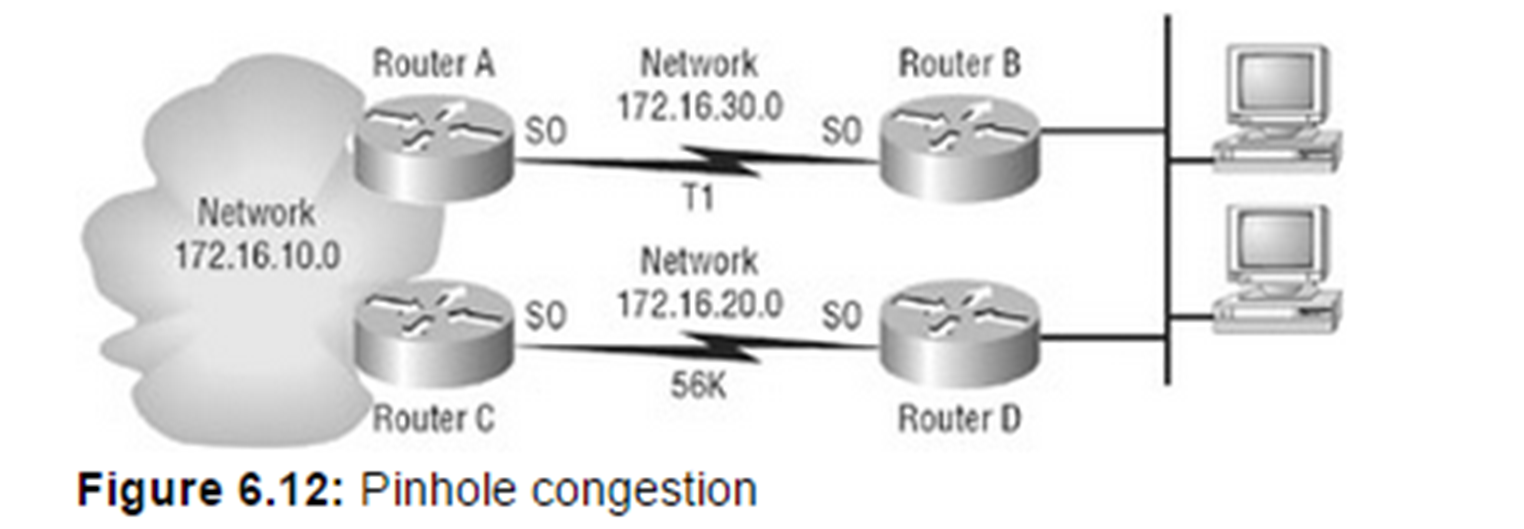
They are both the same ( 1 hop)
How do you fix a routing loop?
Set a maximum hop count
What is the command for Dynamic Routing -RIP?
Router rip
version 2
If class A (first octet 0-126)
Network x.0.0.0
If class B (first octet 128-191)
Network x.x.0.0
If class C (first octet 192-223)
Network x.x.x.0
What command do you use to verify a RIP configuration?
sh ip
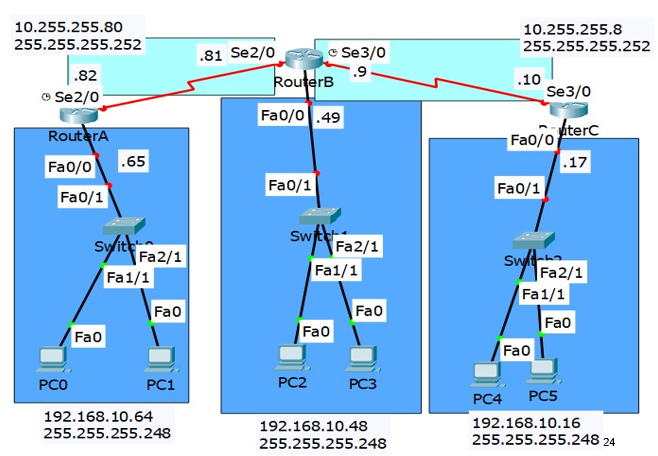
Configure using Static Routing, and Router RIP
Static
Router A
config t
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s2/0
RouterB
config t
ip route 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.258 s2/0
ip route 192.168.10.16 255.255.255.258 s3/0
RouterC
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s3/0
Router Rip (same for all 3 routers because all 3 are connected to the same subnets)
config t
router rip
version 2
network 10.0.0.0
network 192.168.10.0
What is feasible distance?
The route distance you find in the routing table as it’s considered the best path
What is Advertised Distance?
The distance reported to a destination by the neighbouring routers
What is the feasible distance to router 4 (from Router 0)
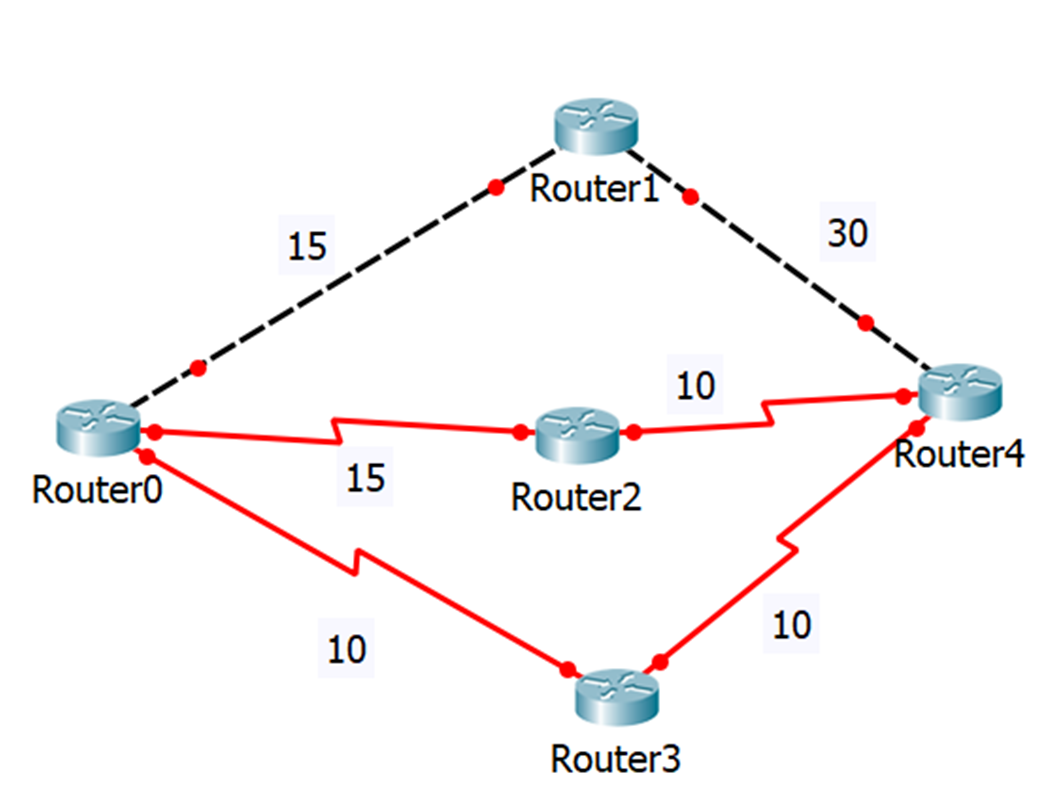
The path through Router 3
What are the advertised distances?

Router0 to Router1: 15
Router0 to Router2: 15
Router0 to Router3: 10
Router2 to Router4: 10
Router3 to Router4: 10
Router1 to Router4: 30
What are the 3 main features of EIGRP
Efficient Neighbour discovery
Communication via reliable transport protocol (declares neighbours as dead if needed, includes a sequence number for packets sent)
Best path selection using DUAL (uses Bellman-Ford Algorithm)
What is a Hello Message?
a hello message is a packet sent between routers at regular intervals to establish and maintain neighbor relationships, ensuring that routers are active and reachable.
What is an autonomous system?
is a collection of IP networks and routers under the control of a single organization that presents a unified routing policy to the internet or other networks, identified by a unique Autonomous System Number (ASN).
What is the command for Dynamic Routing (EIGRP)?
(You will always be given an “AS number”)
Router-eigrp <AS Number>
no auto-summary
If class A (first octet 0-126)
network x.0.0.0
If class B (first octet 128-191)
network x.x.0.0
If class C (first octet 192-223)
network x.x.x.0
What is a discontinguous network?
Two classful networks connected together by a DIFFERENT classful network
why would you want to stop EIGRP from sending hello messages? How would you stop EIGRP from sending hello messages?
Why: so the router doesn’t become neighbours with an external router
How: making the interface a passive interfaced
What is an AREA in OSPF?
A grouping of continguous networks and routers
What is a Neighbour in OSPF?
Two or more routers that have an interface on a common network
What is a Adjacency in OSPF?
A relationship that permits routers to exchange routing information (not all neighbours exchange info in OSPF)
What is the Hello Protocol in OSPF?
Addressed to 224.0.0.5 and provides neighbour discovery and maintains neighbour relations in the topological database
Define Designated Router
A router that is elected to send and receive information for all the other routers on the broadcast network (topology tables are synched)
Define Backup Designated Router
Receives routing updates but doesn’t send out updates unless the designated router fails
Define Link
Network or router interface assigned to a given network (each link will have a state up/down and an IP address
How do you determine the Designated Router?
determined by the router with the highest Router ID
What is a Loopback Interface?
A loopback interface is a virtual, logical interface on a router or switch that is always up and used primarily for testing, management, or as a stable IP address for identifying the device in routing protocols.
What is the command for Dynamic Routing OSPF
(You will always get the area number and process ID)
router ospf <process ID>
If class A (first octet 0-126)
network x.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area <area#>
If class B (first octet 128-191)
network x.x.0.0 0.0.255.255 area <area#>
If class C (first octet 192-223)
network x.x.x.0 0.0.0.255 area <area#>
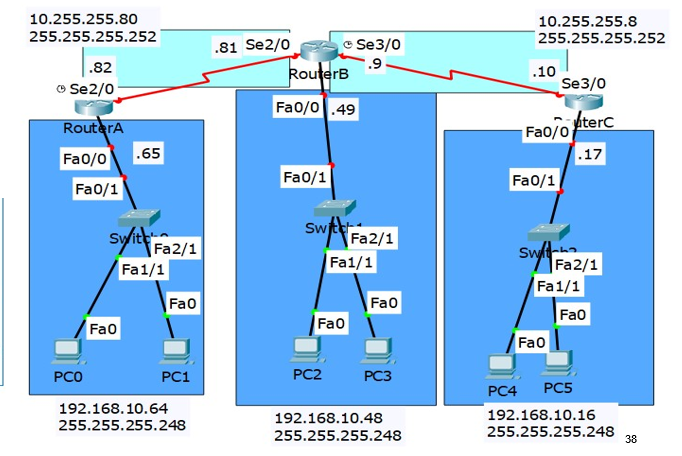
For OSPF use process ID 10 and area 0
OSPF configuration: class method (same for all routers)
config t
router ospf 10
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
We could again omit the 192 line since there’s no routers down there
OSPF: specific configuration
RouterA
config t
router ospf 10
network 10.255.255.82 0.0.0.0 area 0
I’m saying the IP must be exactly 82 to send hellos out here (which is just the one interface)
RouterB
config t
router ospf 10
network 10.255.255.9 0.0.0.72 area 0
-72 is so I get the range from .9 to .81 which will send hellos out both interfaces in a single line (in fact it will send out hellos of any IPs between the range of 9 to 81 so you have to be a bit careful)
Router C
config t
router ospf 10
network 10.255.255.10 0.0.0.0 area 0