Global 1H Unit 4- Indus River Valley, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism
5.0(1)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Last updated 10:18 PM on 1/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Indus River Valley- Notes
1. In modern day Pakistan
2. Two major cities: Harappa
and Mohenjo-Daro
3. Developed on banks of Indus River and also benefited from monsoon rains
4. Few details known because
we do not know how to translate its
writing
5. Organized and well-constructed towns are evidence of complex government
6\.Evidence of trade with Mesopotamia (Textiles were very likely traded with Mesopotamia)
6. IRVC may have failed after natural disasters like earthquakes but no one knows for sure
2
New cards
IRVC- article
1. earliest known urban culture of the Indian subcontinent
2. herding animals from one place to another and growing a limited amount of food
3. The annual flooding, with its resultant deposit of silt, offered good prospects for growing food and other crops with a minimum of labor and tools
4. The chief crops grown were wheat, rice, dates, melons, green vegetables—primarily legumes, and cotton
5. animals raised by the Indus civilization were humped cattle, buffalo, sheep, goats, pigs, camels, dogs, cats, and domestic fowl
6. a number of stone sculptures, cast-bronze figures, and terra-cotta figurines. Most of these are unclothed females heavily laden with jewelry, but a few standing males have also been discovered. The figurines probably represent gods and goddesses, but many—such as animals and carts—are toys. It appears that the only painting was that done on pottery
7. It is widely assumed that there was a Great God and a Great Mother. These may have formed the basis for later Hindu belief in the god Shiva and his consort, Shakti.
8. animal cults devoted to the bull, the buffalo, and the tiger. Excavations at burial sites indicate belief in an afterlife. The number of household goods buried with a body suggest the hope that the individual would later need them
3
New cards
IRVC- homework
1. The Iranian plateau people and distant Mesopotamian cities had strong influences on the Indus River Valley civilization.
2. The annual floods helped to avert droughts while replenishing soil.
3. At the center of the Mohenio Daro was the famous great bath, which is assumed to have been used for public bathing rituals
4
New cards
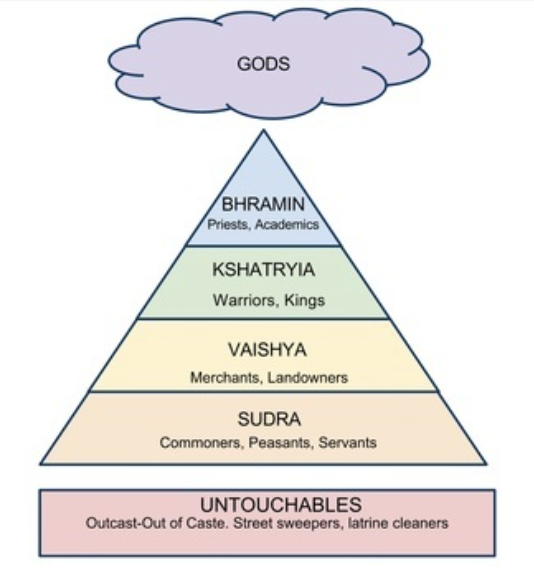
**HINDUISM- notes**
1. Roots in the Vedas (sacred text) of the Aryans
2. Three main gods: Brahma the Creator, Vishnu the Preserver, and Shiva the Destroyer plus countless other gods also worshipped
3. Aryan social classes evolves into thousands of castes\* based on profession and ethnic group (caste comes from Europeans in the 1600s)
4. Worship many gods but believe they are all avatars\* of one universal spirit called Brahman
5. Goal is to achieve moksha (a perfect understanding of all things) and joining your atman (individual soul) with Brahman
\*an avatar is an incarnation or form of a deity
6. MOKSHA-Reincarnation and karma (good karma is achieved when you follow your dharma (moral and religious duties that are expected of a person according to their caste)
all Hindus revere the Veda, an ancient body of sacred literature
Brahman is the source of all existence and is present in every thing and every place.
The human soul, called atman, is part of the universal Brahman. Hindus generally believe that when someone dies, the atman is reborn in another body.
A soul may return many times in human, animal, or even plant form. This idea is known as reincarnation, which Hindus believe the persons highest purpose is to BREAK this cycle
5
New cards
**HINDUISM- article**
1. Hindus revere the Veda, an ancient body of sacred literature
2. Brahman is the source of all existence and is present in every thing and every place
3. ahimsa, which means “nonviolence.”
4. god Vishnu is considered the protector and preserver of life’
5. god Shiva represents the forces that create life as well as those that destroy it
6. supreme goddess is most commonly called Shakti. Like Shiva, she can be either beneficial or fierce, depending on her form
7. Brahma (not to be confused with Brahman) is considered the creator of the universe
8. puja, Hindus pray for a god to enter a home or temple and then treat the god as an honored guest
9. Tantrism is the search for spiritual knowledge and for release from the cycle of rebirth
10. Pilgrimages, or journeys to holy places, have been common in Hinduism since ancient times
11. Diwali is probably the most widely observed Hindu holiday. It is a New Year celebration that lasts for five days in late October or early November.
12. Holi. It is a spring festival. People throw colored water and powder on one another, and traditional roles are reversed.
13. In reaction to foreign rule, Hinduism underwent a revival. It helped unify Indians against the British
14. Mahatma Gandhi. He brought the idea of ahimsa into politics. He helped win India’s independence from Britain using only nonviolent methods.
6
New cards
**HINDUISM- hw**
1. Rakshasas are evil creatures
2. **CQ: What does this myth about what some Hindus value in their heroes and/or leaders?** It shows how they value persistence and justice, with Rama saving Sita and eventually killing her kidnapper. This also shows how they value justice, as Rama killing Sita wasn’t seen as an evil or unjust act.
3. A group of people who did the dirty jobs were a new social class known as the “untouchables”.
4. People began to challenge traditional beliefs, as well as gain more knowledge and establish wealth and/or skill to gain higher status.
5. Ascetic: A belief or a person who rejects material things and physical pleasures.
7
New cards
**JAINISM- notes**
1. Jainism (founded c. 500
BCE)
2. Do not believe in any gods
3. Seek enlightenment through five principles: no violence, no lying, no stealing, no possessions, and chastity
4. All are vegetarians and the most dedicated follow philosophy
of ahimsa (“no hurt”), believing any killing is wrong and sweeping the path in front of them to avoid killing any living creature
8
New cards
**JAINISM- article**
1. The name of the religion derives from the term Jina, meaning “victor” or “conqueror.” The goal of Jainism explains this term. It is the spiritual progress of the individual through a succession of stages until he is able to conquer and renounce dependence on the world and the self. Thereby the individual is freed from all contamination by the material world.
2. There is a center containing a region of souls in which all living things—people, animals, gods, and devils—exist
3. The means of liberation for the soul is yoga, a discipline of self-control and meditation
4. It aims at these goals through knowledge of reality, faith in the teachings of religious leaders who are called Tirthankaras, and doing no evil
5. ahimsa, or reverence for life, the principle of nonviolence and noninjury toward all living things. This principle has led to a belief in the equality of all souls and to the freedom to associate with anyone. Because of ahimsa, the social distinctions prevalent in the Hindu caste system never became firmly established in Jainism (see Hinduism)
6. monks and lay followers. The monks lead a far more austere life than do lay members because they devote their whole lives to the stages of spiritual perfection. Monks must adhere scrupulously to the principle of ahimsa and avoid such sins of Jainism as lying, stealing, sexual intercourse, and eating meals at night (for fear of inadvertently killing an insect or other small creature
7. Lay members are expected to refrain from eating certain foods, limit their possessions, be content with their spouses, and avoid violence, lying, and stealing
8. Temple worship plays a major role in Jainism. There is a large pantheon of lesser gods, goddesses, demons, and other divinities.
9. Jainism was founded in the 6th century bc by Vardhamana Mahavira
9
New cards
**JAINISM- hw**
1. “doctrine of ahimsa”: Being known as the doctrine of no hurt, it taught that every life mattered, so if you were to “hurt” or kill any being even as small as an ant, it would result in unfavorable rebirth.
2. Jainism became a religion of city dwellers and traders because they were the jobs that could easily allow people to respect the religion’s beliefs of not harming any type of being/insect.
10
New cards
**BUDDHISM- notes**
1. Siddhartha Gautama AKA the Buddha (c. 500 BCE)
a. Born Hindu prince in
India/Nepal c. 500 BCE
b. Left his riches to search for
the meaning of life
c. Achieved enlightenment while meditating under a tree
2. Four Noble Truths of Buddhism
a. All life is suffering
b. Suffering is caused by the desire for things
c. The way to eliminate suffering is to eliminate desire
d. To overcome desire, follow the Eightfold Path
3. The Eightfold Path video
a. right views
b. right intentions
c. right speech
d. right conduct
e. right livelihood (or job)
f. right effort
g. right mindfulness
h. right meditation
4. Buddha believed in karma/reincarnation but not caste system
5. Goal is to reach nirvana (the release from pain and suffering achieved after enlightenment) video
11
New cards
**BUDDHISM- article**
1. The first truth is that life is made up of pain and suffering.
2. The second is that all suffering is caused by one’s desires.
3. The third is that one can be free of these desires. The freedom from desire is called nirvana.
4. The fourth truth is the Eightfold Path, which explains eight ways to achieve nirvana.
5. Buddhism has three main parts.
1. These parts are called the Triratna, or “the three jewels.”
1. They are: the Buddha, or the teacher; the dharma, or the teaching; and sangha, or the community of believers
6. Two major groups: Theravada, meaning “Way of the Elders,” Mahayana. Zen Buddhism comes from Mahayana Buddhism
7. Buddha, which means, “enlightened one.”
12
New cards
**BUDDHISM- hw**
1. Mara was an evil demon, who was a challenger of Siddhartha becoming the Buddha.
2. “wealth, race, gender and family background” were ignored by Buddha and his followers
3. Buddha said that his disciples should follow nobody as their leader.
13
New cards
Brahmin
**social caste, religious leaders**
14
New cards
Brahma
**powerful god**
15
New cards
Brahman
**universal spirit**
16
New cards
caste
European term for the hereditary social classes in Hinduism that restrict the occupation of their members and their association with the members of other castes
17
New cards
arnas
literally “color”; the four ranked social groups within early Vedic (Indian/South Asian) society
18
New cards
jatis
literally “birth”; subgroups within the Hindu caste system usually based on kinship and profession
19
New cards
avatar
an incarnation or form of a deity
20
New cards
moksha
a state of perfect understanding of all things
21
New cards
atman
the individual soul of a living being
22
New cards
reincarnation
the process by which a soul is reborn
23
New cards
karma
the totality of the good and bad deeds performed by a person
24
New cards
dharma
in Hinduism, the moral and religious duties that are expected of a person according to their caste
25
New cards
ahimsa
literally “no hurt”; nonviolence
26
New cards
ascetic
a person who practices severe (strict) self-discipline and abstention (the giving up of pleasurable things)
27
New cards
enlightenment
in Buddhism, a state of perfect wisdom in which one understands basic truths about the universe
28
New cards
nirvana
in Buddhism, the release from pain and suffering achieved after enlightenment