AP Physics 1 Study Guide: Key Vocabulary & Concepts
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of key vocabulary and concepts for AP Physics 1, covering topics such as kinematics, dynamics, energy, momentum, rotational motion, and electricity.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
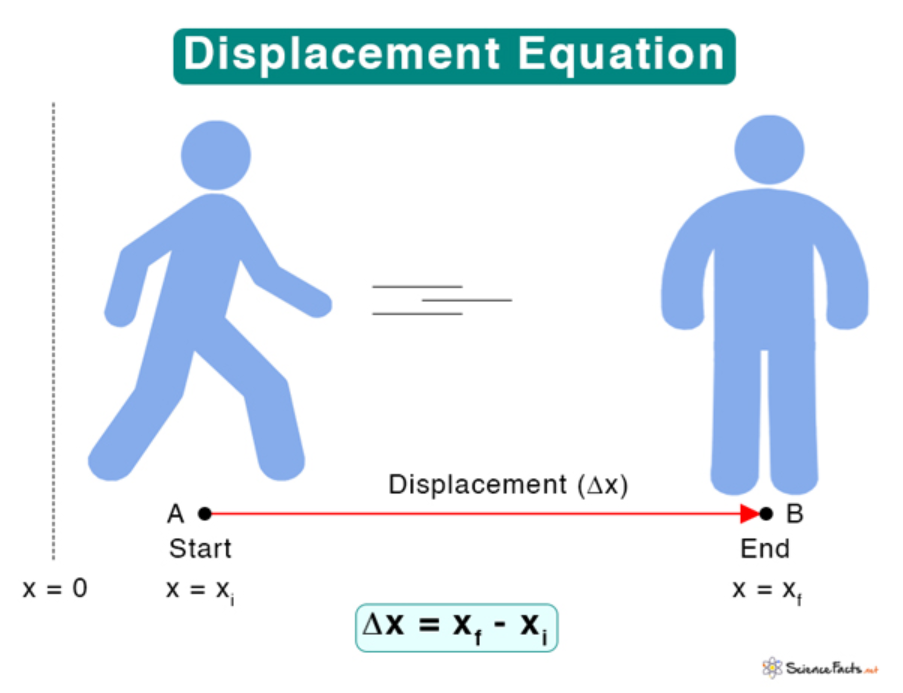
Displacement
Change in position of an object.
Velocity
Speed with direction; can be average or instantaneous.
Examples:
A car traveling at 60 miles per hour north .
A person walking 3 miles per hour east .
Throwing a ball 10 feet per second upwards .
A plane flying 500 miles per hour south .
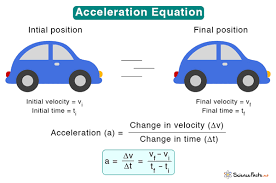
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity.
Free Fall
Motion under gravity alone.

Projectile Motion
Motion in two dimensions under gravity.
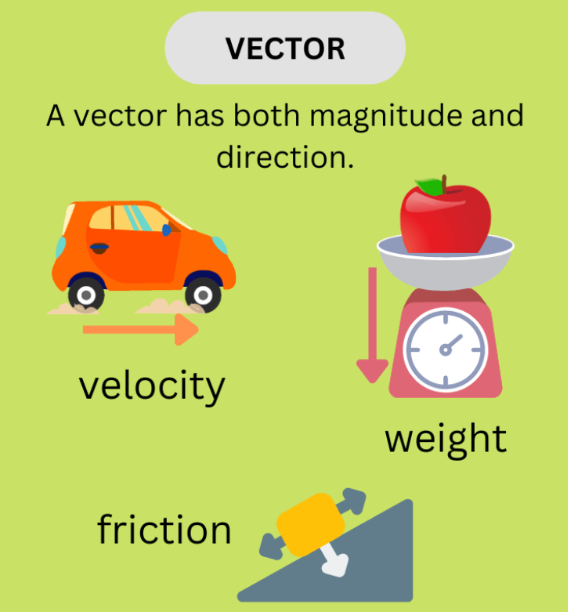
Vector
Scalar

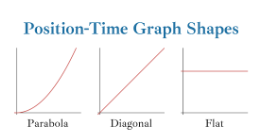
Position-Time Graph
Graph that shows motion over time.
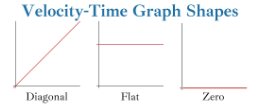
Velocity-Time Graph
Graph that shows acceleration and displacement trends.
Force
A push or pull acting on an object.
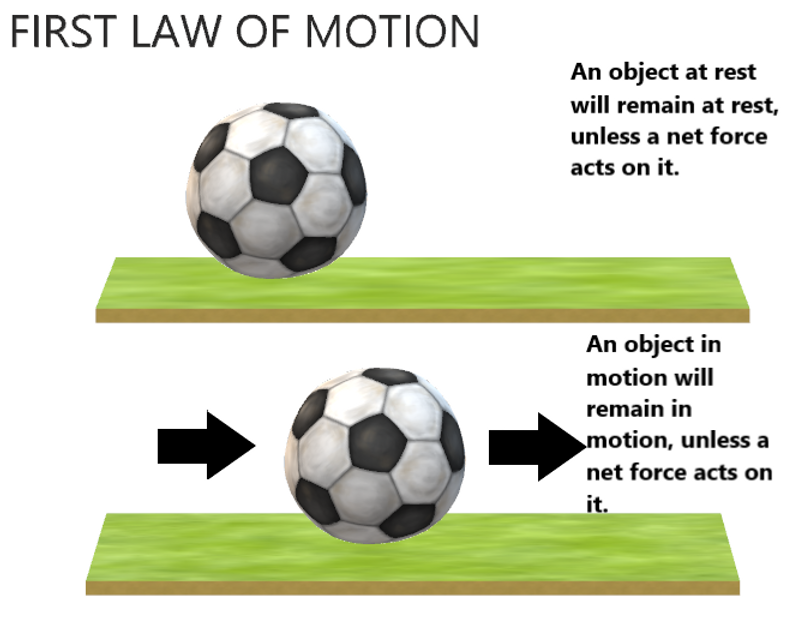
Newton’s 1st Law
Objects stay in motion/rest unless acted upon.
Newton’s 2nd Law

Newton’s 3rd Law

Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
Weight
The force due to gravity acting on an object.
Normal Force
Perpendicular force from a surface.
Examples:
When you stand on the floor, the normal force is the force exerted by the floor pushing up against your feet, counteracting gravity.
If a box is resting on a table, the normal force is the force exerted by the table pushing up against the box.
Friction
Resistance between surfaces (static & kinetic).
Tension
Force in a string or rope.
Free-Body Diagram
Diagram showing all forces acting on an object.
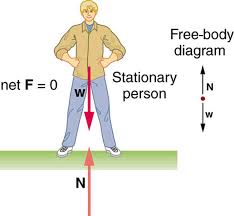
Equilibrium
State where net force is zero.
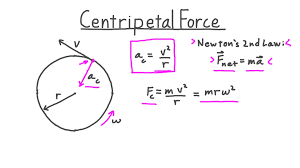
Centripetal Acceleration
Acceleration toward the center of a circular path.
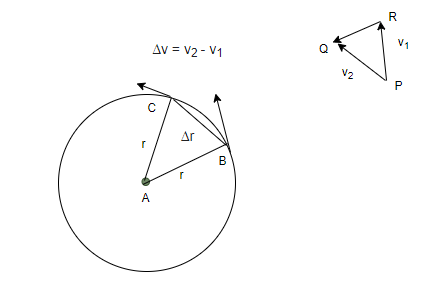
Centripetal Force
Net force keeping an object in circular motion.
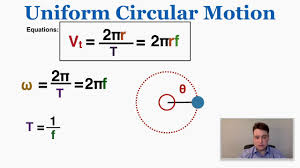
Uniform Circular Motion
Constant-speed motion in a circle.
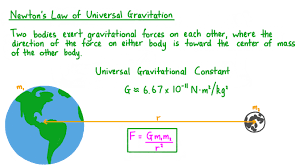
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
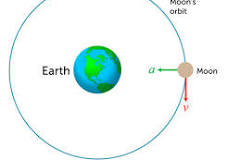
Orbital Motion
Motion of planets and satellites.
Gravitational Field
Force per unit mass due to gravity.

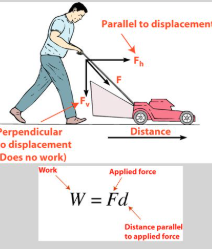
Work
Force applied over a distance.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion (KE = 1/2 MV²).
Potential Energy
Stored energy.

Mechanical Energy
Sum of kinetic and potential energy.

Conservation of Energy
Total energy remains constant.

Power
Formula : P=W/T
Power is a measure of how quickly work is done or energy is transferred over time.
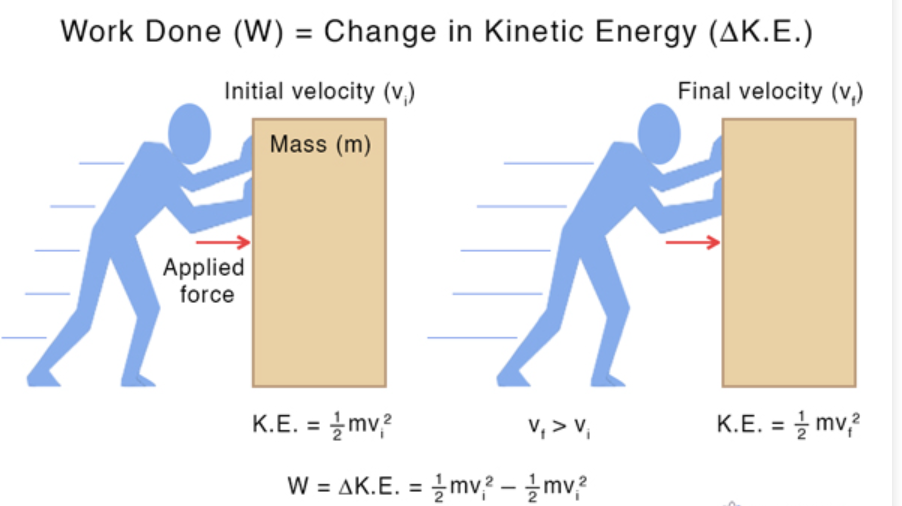
Work-Energy Theorem
Work done changes kinetic energy.
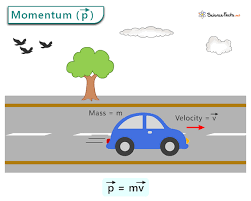
Momentum
Mass times velocity.
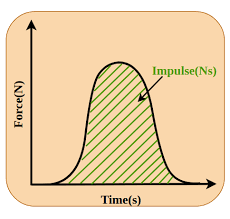
Impulse
Change in momentum.
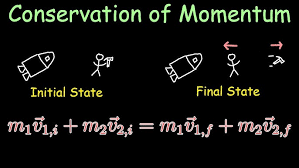
Conservation of Momentum
Momentum remains constant in an isolated system.
Elastic Collisions
Collisions that conserve kinetic energy.
= | mass object 1 | |
= | initial velocity object 1 | |
= | mass object 2 | |
= | initial velocity object 2 | |
= | final velocity object 1 | |
= | final velocity object 2 |
Inelastic Collisions
Collisions that do not conserve kinetic energy.
= | mass object 1 | |
= | initial velocity object 1 | |
= | mass object 2 | |
= | initial velocity object 2 | |
= | final velocity of objects |
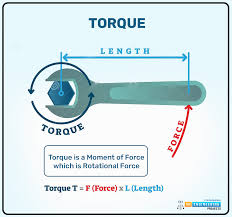
Torque
Rotational force.
Moment of Inertia
Resistance to rotational motion.
= | inertia | |
= | angular momentum | |
= | angular velocity |
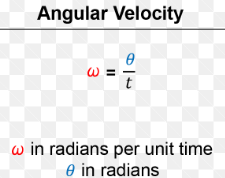
Angular Velocity
Rate of rotational change.
Angular Acceleration
Change in angular velocity.
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Energy of rotation.
Angular Momentum
Rotational equivalent of momentum.
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Angular momentum remains constant in a closed system.
Period
Time for one cycle.
Frequency
Cycles per second.
Amplitude
Maximum displacement.
Restoring Force
Force directing toward equilibrium.
Hooke’s Law
Force in a spring is proportional to displacement.
Charge
Property of matter causing electrical interaction.
Current
Flow of electric charge.
Voltage
Electric potential difference.
Resistance
Opposition to current.
Ohm’s Law
V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
Series Circuit
Circuit where components share current.
Parallel Circuit
Circuit where components share voltage.
Kirchhoff’s Laws
Laws regarding the conservation of charge and energy in circuits.
Wave
A disturbance that transfers energy.
Frequency (Waves)
Number of waves per second.
Wavelength
Distance between crests of a wave.
Period (Waves)
Time for one wave cycle.
Amplitude (Waves)
Maximum wave displacement.
Constructive Interference
When waves combine to increase amplitude.
Destructive Interference
When waves combine to decrease amplitude.
Doppler Effect
Change in frequency due to motion.
System
Defined set of objects under analysis.
Isolated System
A system with no external forces or energy exchanges.
Open System
Exchanges energy and matter.
Closed System
Exchanges only energy.
Center of Mass
Point where mass is balanced.
Dimensional Analysis
Checking equations by analyzing units.
Scalar Quantity
A quantity that only has magnitude.
Vector Quantity
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.