ANT 201 -class 5 Brain Basics -9/17/2024 -
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are the 3 parts of the Peripheral Nervous System:
1. Spinal Nerves
2. Cranial Nerves
3. Autonomic Nervous System
Where do the Cranial Nerves Go?
The head or neck region.
How many Cranial Nerves are there?
12
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
Control functioning of organs and things we are not generally aware of.
What are the 2 parts of the Autonomic Nervous System?
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic.
What is the difference between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous is Involved in fight or flight while the parasympathetic is on how the body works in rest and recovery.
What is the Triune Brain Model?
There are different layers of the brain reptilian, paleomammalian, and neomamalian that came about from evolution.
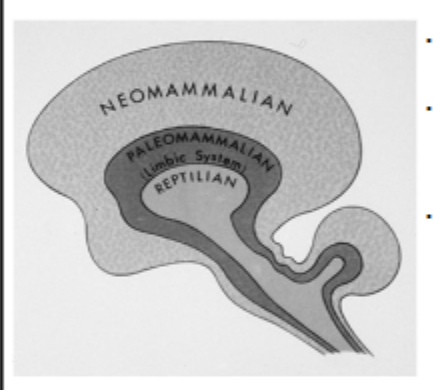
What is the characteristics of the Reptilian Brain?
- Highly stereotyped, instinctive behaviors
- Sex, aggression and food getting.
What is the characteristic of the Paleomammalian Brain?
- Characteristic of early mammals
- Involved in experience and expression of emotions
- Social attachment
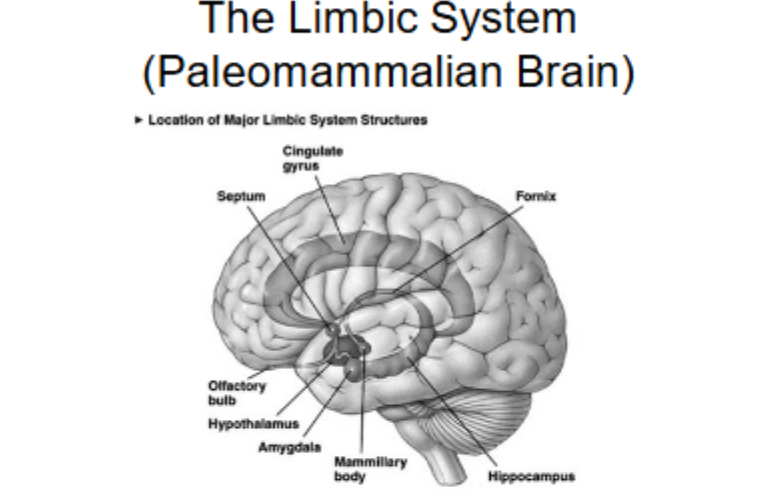
What is another name for the Paleomammalian Briain?
- Limbic System.
What are the characteristic of neomammalian Brain?
- Characteristic of higher mammals
- Thinking and reasoning
- Suppression/regulation of instincts and emotions
What does the Reptilian Brain look like in humans and what does it include?
Brainstem and Basial Ganglia
What does the Paleomammalian Brain look like in humans and what does it include?
The limbic system
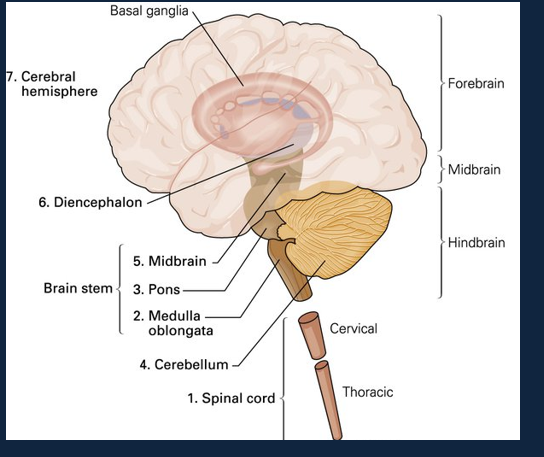
What does the developmental subdivisions of the Brain look like?
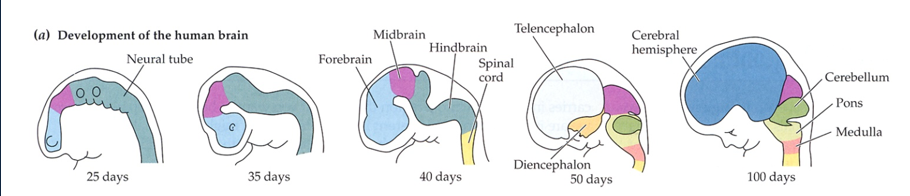
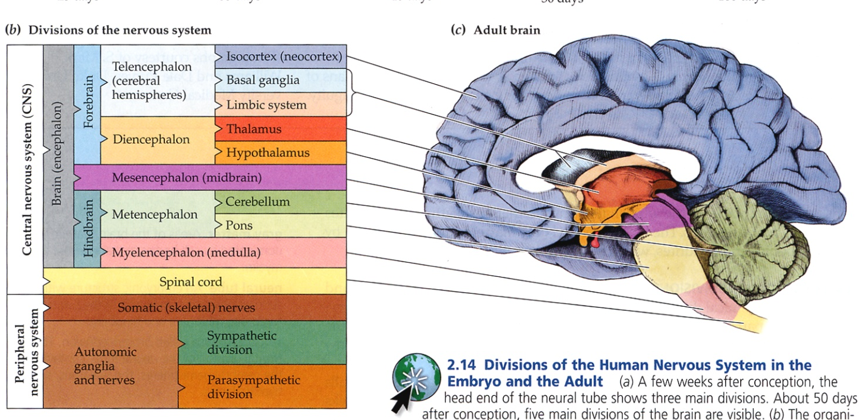
What does the divisions of the brain look like?
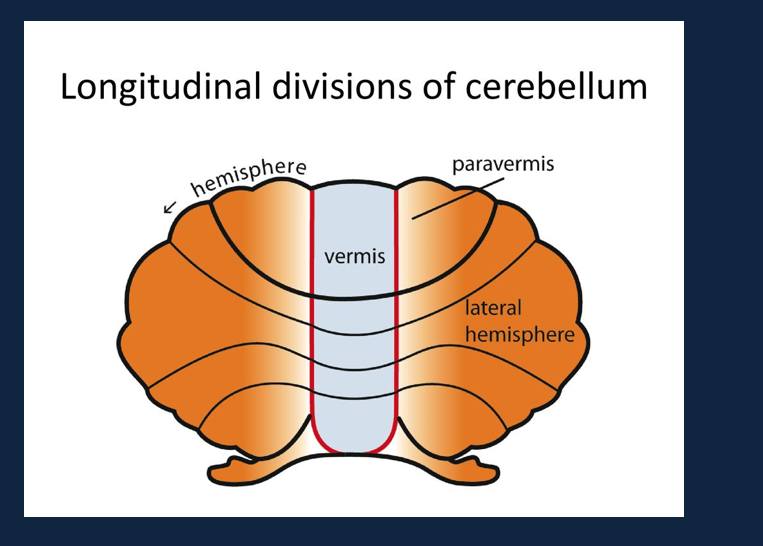
What are the 3 sturctures of the hind brain?
Medulla, Pons and Cerebellum
What does the Medulla do?
- Involved in functions that are critical to survival, heart rate, blood pressure, respiration etc.
- Carries information
What does the Pons do?
- Blood pressure regulation and other survival stuff
- Relay station for information between the Cerebellum and Cerebral Cortex
What does the Cerebellum do?
- Cerebellum vermis (middle area) good for balance and posture
- Lateral hemisphere more involved in fine motor coordination and advanced cognitive functions
What are the structures of the Midbrain and what do they do?
Include image
- Tectum: vision and hearing
- Tegmentum:
a. Dopamine Neurons
b. Cranial Nerve Nuclei in the Brain Stem
What are the structures of the Forebrain?
Diencephalon
Telecehpelon
What are the structures of the diencephalon and what do they do?
Thalamus - decides if information received gets passed on to cortex and what we’re consciously aware of
Hypothalamus - appetite, sexual behavior, emotions, endocrine function
What are the parts of the Telencephalon
Basal Ganglia - movement/motivation and reward
Limbic System - emotion
Cerebral Cortex - perception reason, and movement
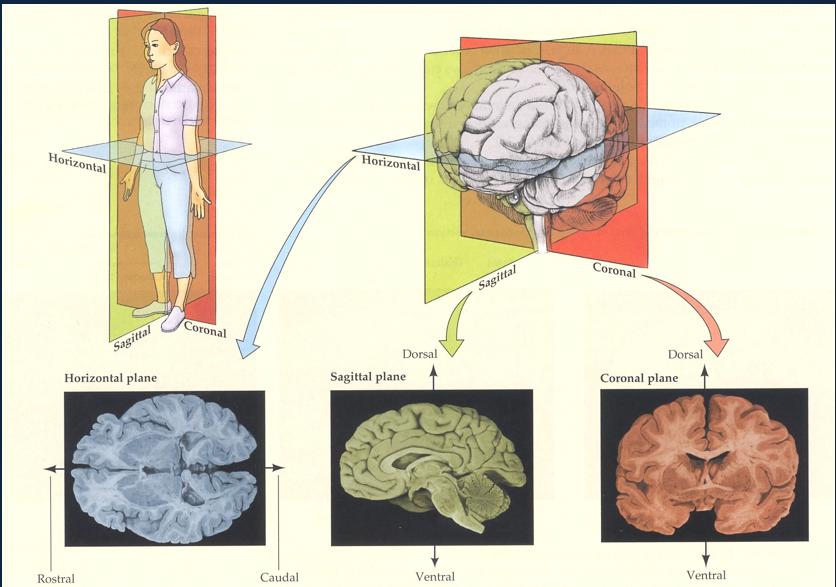
What are the Planes of Section for slicing brain and what are the terms for the positions?
Horizontal
Sagittal Plane
Coronal Plane
What are characteristics of the Cerebral cortex ?
It gets wider not thicker
Sulci - inward fold: Central sulcus and Lateral sulcus
Gyri - Outward fold
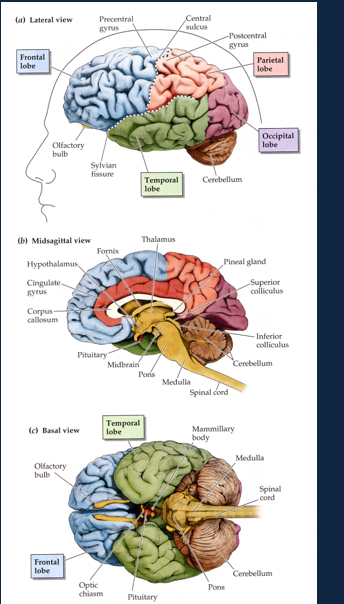
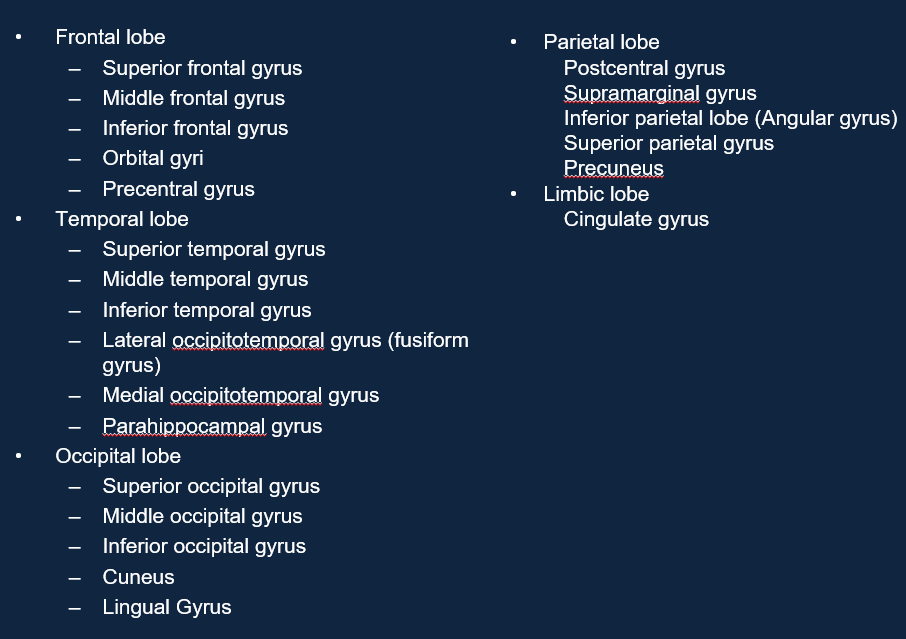
What are the main parts of the cerebral cortext?
….
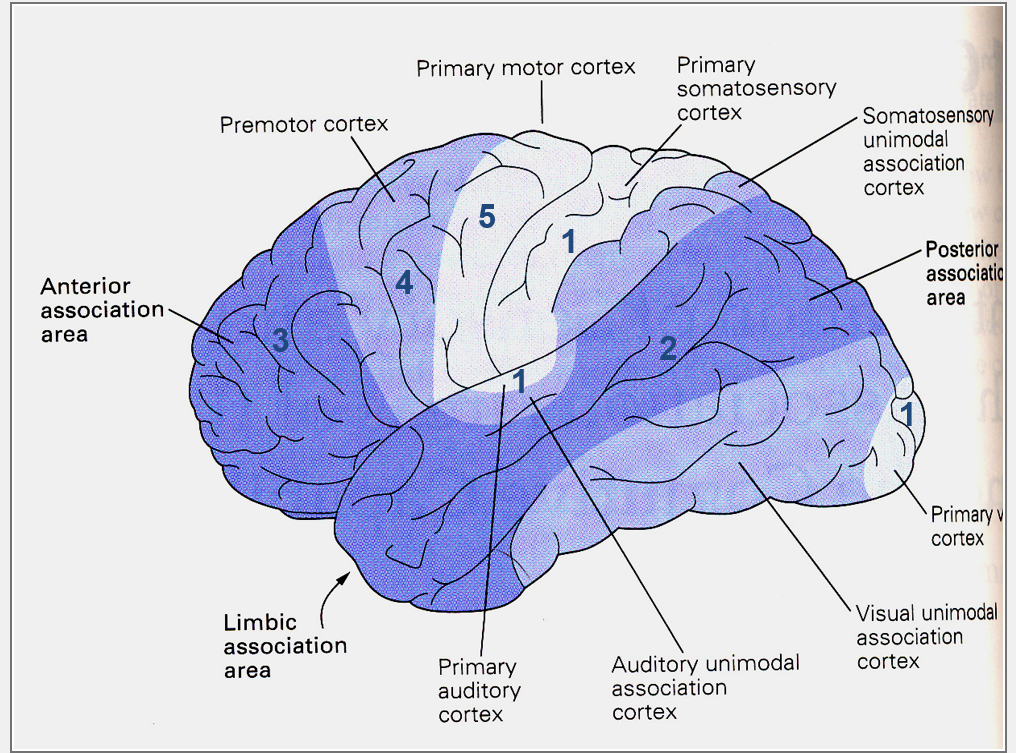
What is the Motor cortex and what does it do
moving muscles
What is the somatosensory cortex?
…
What does the horizontal slice view of cerebral cortex look like and what does it contain?
Neuron cell bodies are concentrated in gray matter (cortex and nuclei)
Axons are concentrated in white matter
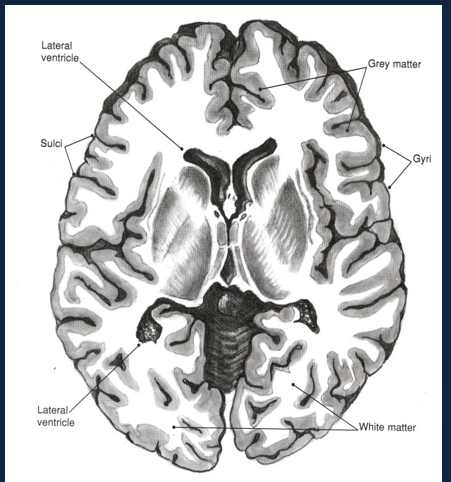
What is white matter in cerebral cortex made of?
Axons covered in myeline sheath.
What are the layers of the cerebral cortex.
Layer IV - Afferent cortical inputs
Layer V - Efferent Cortical outputs
Layer I, II, III
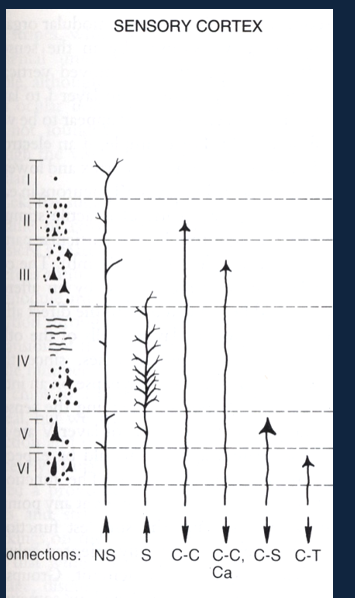
What is the cellular architecture of the cortex like
The cellular architecture varies across space
There are about 52 areas
This matched up better with function than comparing gyri
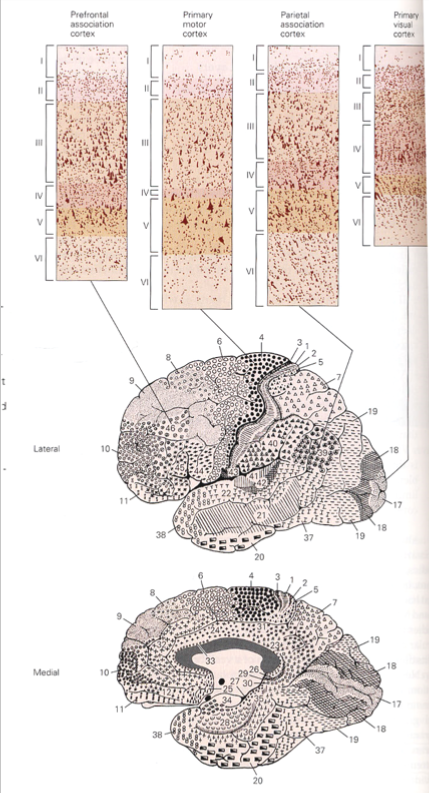
What is a cortical Column and what does it contain?
How neurons are arranged in the cortex
Within a column there are about 50 - 100 neurons that are strongly connected to each other and have similar response properties
What gyri should we be identify on a 3d surface view of a brain?
What are white matter tracks and what are the different types?
Projection Fibers - –Connect cerebral cortex to brainstem and gray matter nuclei
Commissural Fibers - –Connect gray matter in two cerebral hemispheres
Association fibers - –Link cortical regions within the same cerebral hemisphere
These area a collection of the myelinated axons
What is the Cortical limbic system and what is the specific region its found?
The interaction of cognition and emotion and in the Orbitofrontal Cortex.
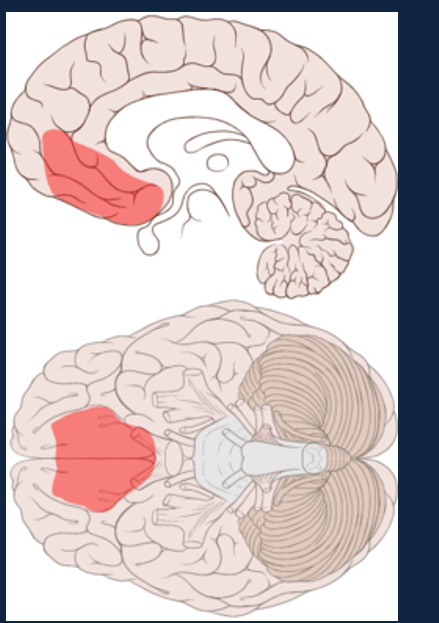
What was the event that happened to Phineas Gage and how did it affect him.
Iron rod shot up through his skull
Cognition was fine
Personality change - rude, impulsive, emotional reregulation
Made decision for the short term good but long-term detriment
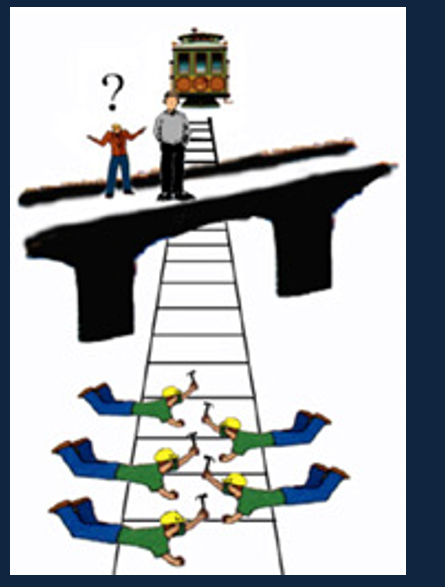
What is the Footbridge Dilemma and how does it affect people with damaged orbitofrontal Cortex’s
A train is coming, do you push the person off the bridge and save 5 workers or not and kill 5 workers.
They are more likely to choose pushing him.
Therefore, they are more ok with the idea of violating people’s right for the most good to the most people because they don’t really get the somatic marker to feel bad about it.

How does a neuron decide whether or not to fire an action potential?
Excitatory - Increase the likelihood of firing an action potential
Inhibitory - decrease the likelihood to fire action potential
Since neurons is connected to 10,000 neurons on average of excitatory and inhibitory, makes decisions from them at the axon terminal which is the integration zone .
What is neuro transmission like?
Action potential causes synapses to dump neurotransmitters in the cleft which then allows it to bind to receptors on the post - synaptic dendrite.
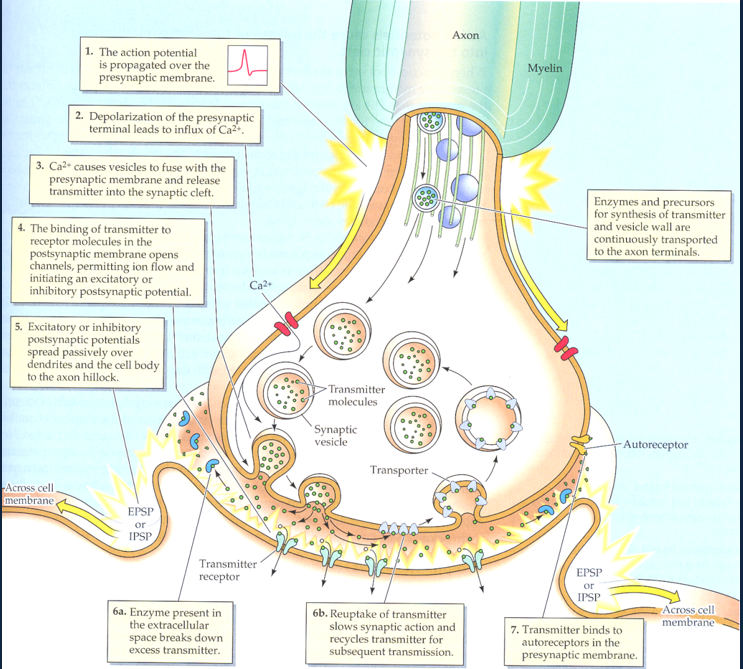
What are the main important neurotransmitters?
Excitatory: Glutamate
Inhibitory: GABA; gamma - Aminobutyric acid
What neuromodulatory neurotransmitters are not as important as the main to but have nuclei in the brain stem that releases throughout the brain?
–Serotonin - A prosocial neurotransmitter
–Dopamine - reward
–Norepinephrine - Stress response