Module 11 Reversible Reactions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Acid
A substance that increases the hydronium ion concentration in a solution by donating a hydrogen ion to water
Base
A substance that decreases the hydronium ion concentration in a solution by stealing a hydrogen ion from hydronium
Hydronium Ion
H₃O+
-formed when a hydrogen ion combines with water
Hydroxide Ion
OH-
-formed when a hydrogen ion is removed from water
pH
- log (the molar concentration of hydronium ions)
Molarity
-the number of moles of a substance per liter of solution
-metric unit of concentration
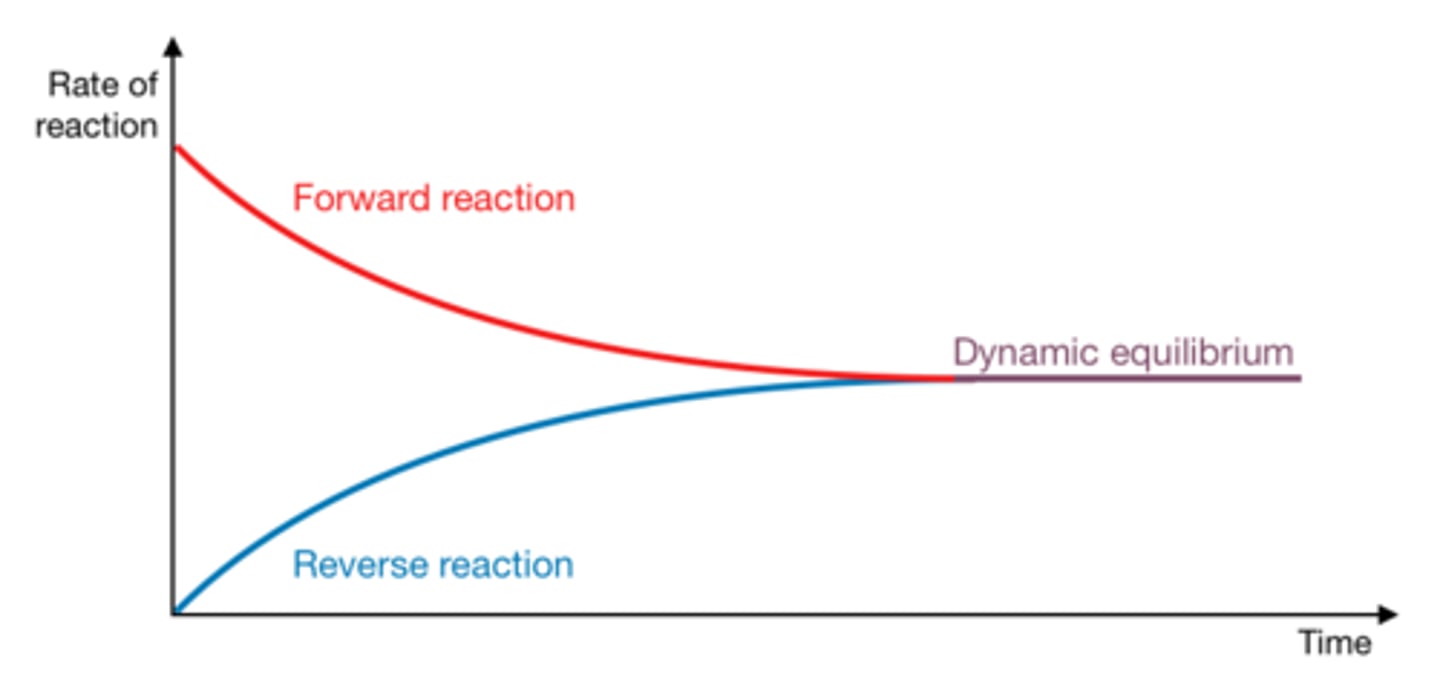
chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, the state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, so that the relative concentrations of the reactants and products do not change with time.
Buffering
when pH of a solution remains stable due to a chemical equilibrium between an acid, base and water
LeChatelier's Principle
if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift to reduce the stress and move the system back towards the original equilibrium
Stress
change in the concentration of a chemical, change in temperature, change in pressure
Exothermic reaction
a reaction which releases energy in the form of heat
Endothermic reaction
A reaction that ABSORBS energy in the form of heat
weak base
a salt composed of metal ions and negatively charged polyatomic ions that are not hydroxide
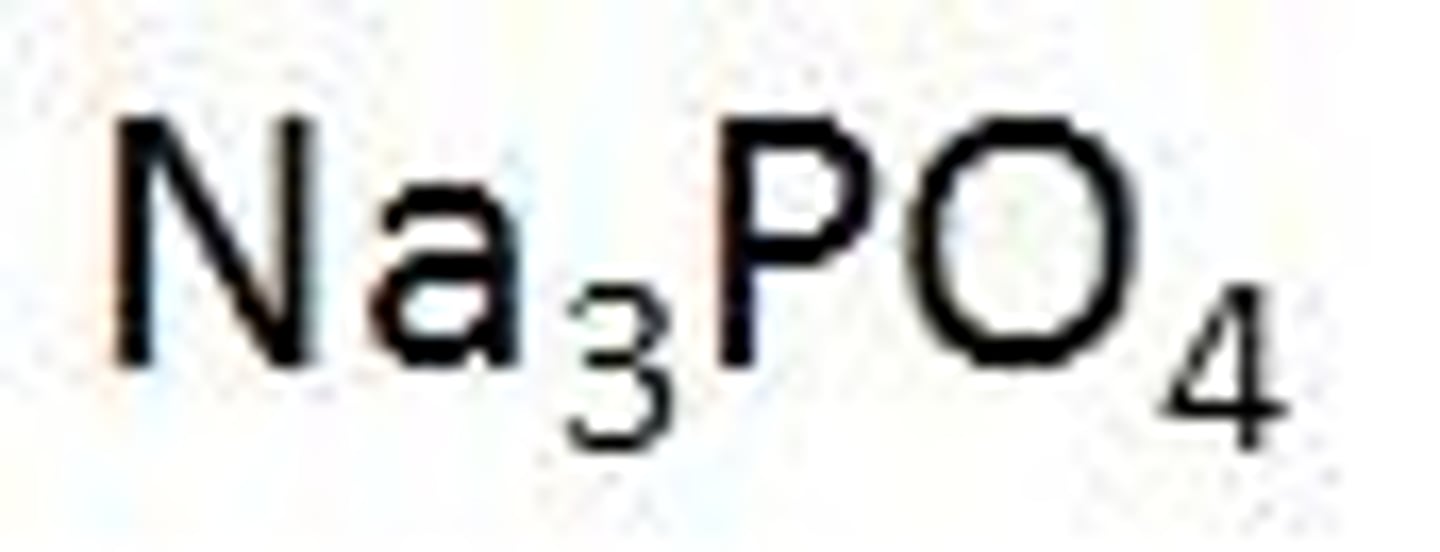
weak acid
an substance composed of hydrogen and negatively charged polyatomic ions
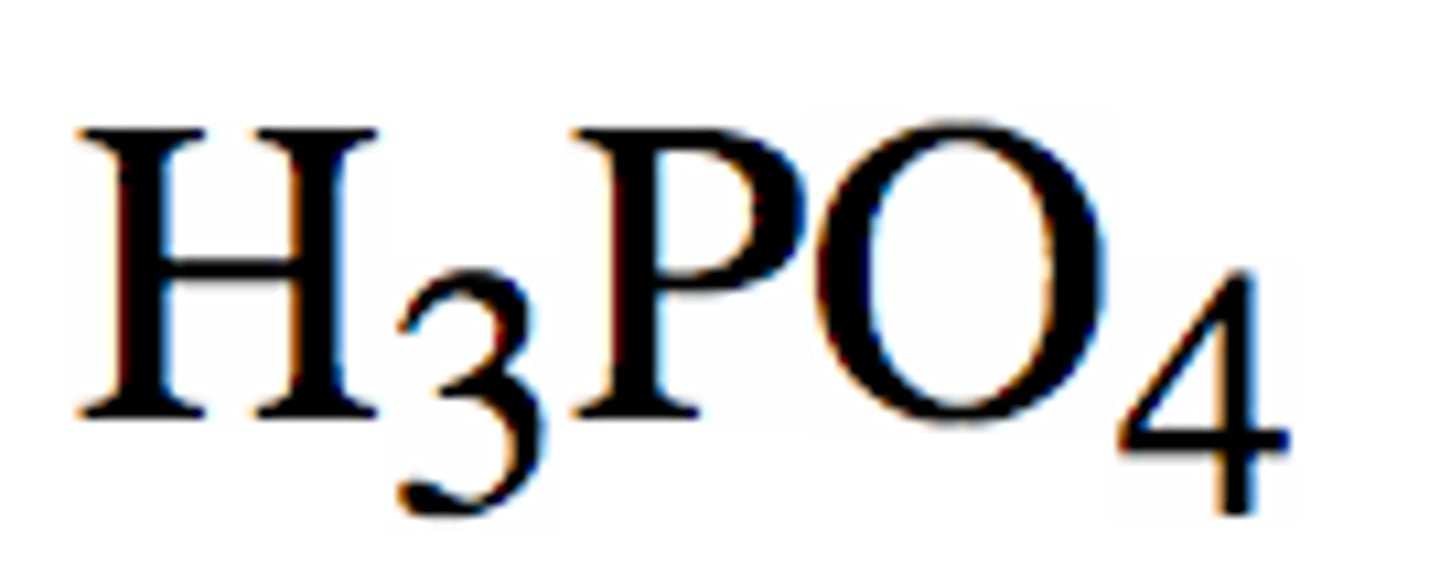
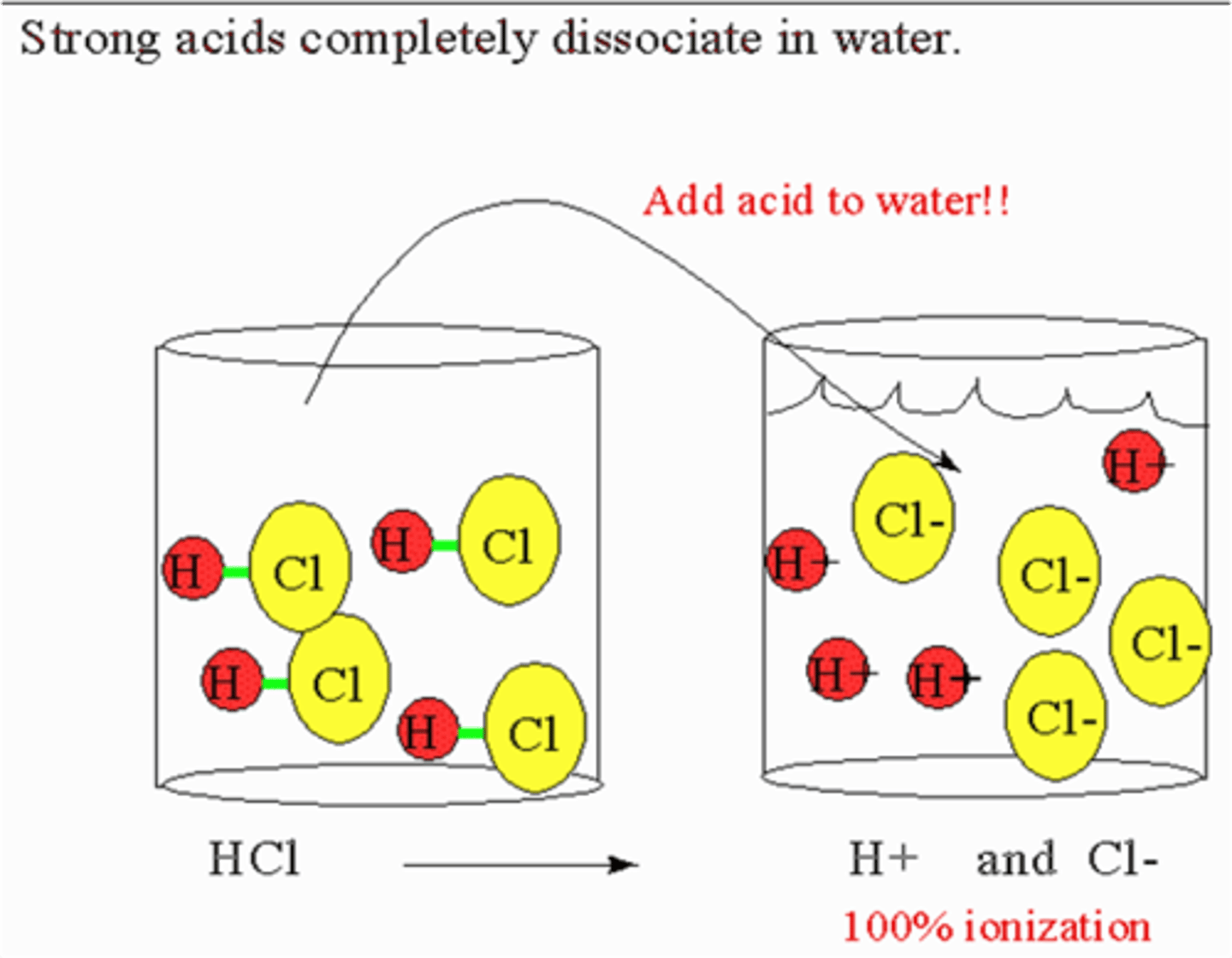
strong acid
a substance that donates hydrogen ions to water, but does not create a conjugate base (HCl, HF, HBr......)
strong base
a base that completely dissociates into metal ions and hydroxide ions in water
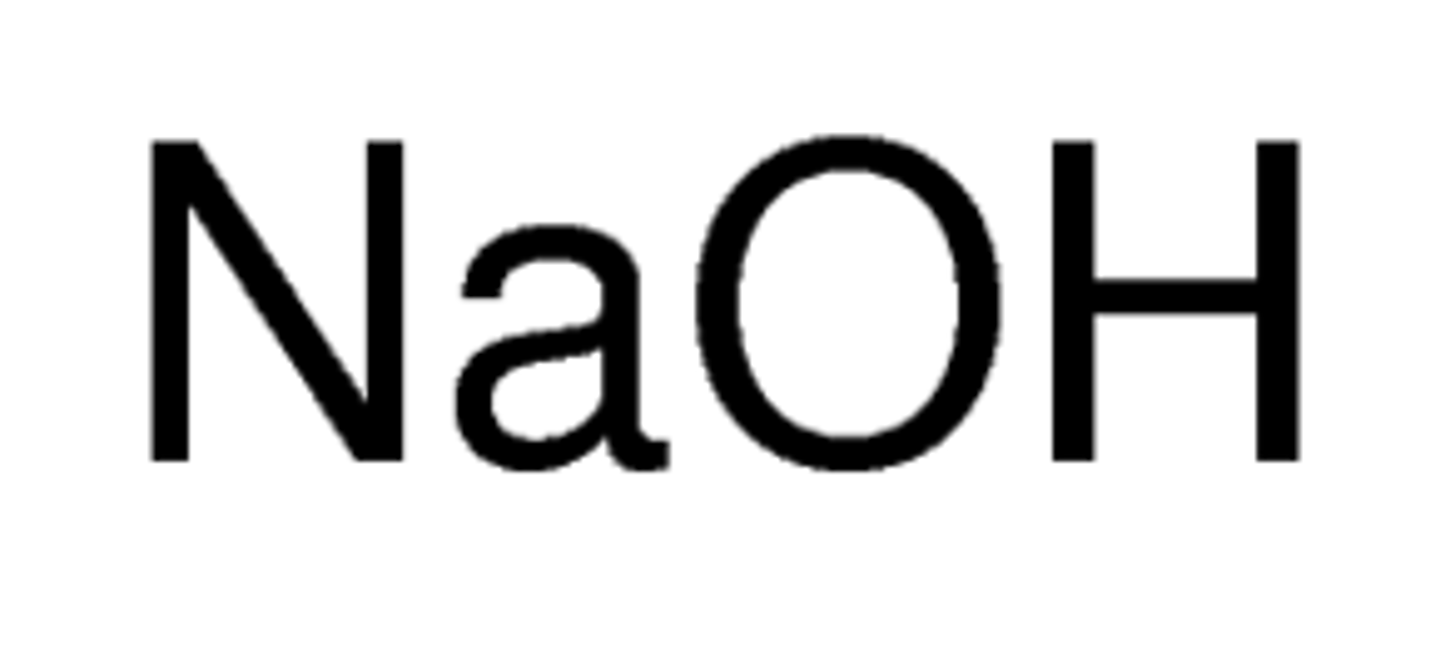
Collision theory
For a reaction to occur, the particles must collide, they must collide with the appropriate orientation, and they must collide with sufficient energy.
Five factors that increase the rate of a reaction
1. shrink the container or increase concentration
2. speed up particles by adding heat
3. break up clumps into individual particles
4. increase the number of particles
5. use a catalyst
How do catalysts work?
By lowering a reaction's activation energy
activation energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started
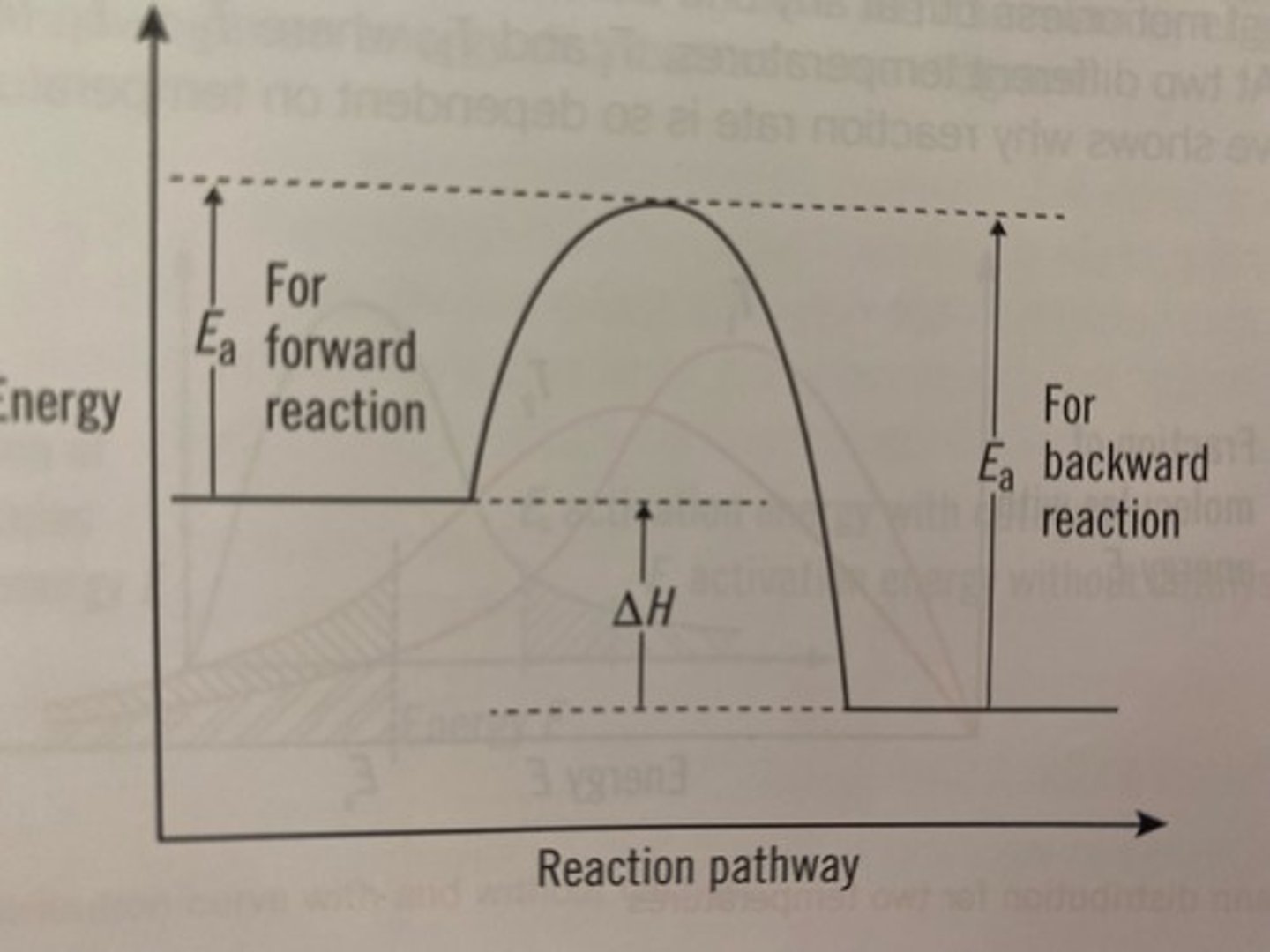
reaction rate
The change in concentration of reactants per unit time as a reaction proceeds
-moles per liter per unit time or (M/s)
Trick to predicting the direction of change
the reaction that will be fastest is the one that has the most collisions
Increasing the temperature of an exothermic reaction
increases the backwards (reverse) rate

Decreasing the temperature of an exothermic reaction
favors the forwards rate

Increasing the temperature of an endothermic reaction
favors the forwards rate

Decreasing the temperature of an endothermic reaction
favors the backwards (reverse) rate

decreasing the pressure
increase the rate of the reaction with the least moles of gases and eventually increases the number of moles in the container

increasing the pressure
increases the rate of the reaction with the most moles of gasses and eventually decreases the number of moles in the container

increasing the concentration of a reactant
favors the forwards rate

decreasing the concentration of a reactant
favors the backwards (reverse) rate

increasing the concentration of a product
favors the backwards (reverse) rate

decreasing the concentration of a product
favors the forwards rate

reversible reaction
a chemical reaction in which the products can react to re-form the original reactants
pOH
-log (molar concentration of hydroxide ions)
carbonic acid
H₂CO₃ - an acid created by dissolving carbon dioxide in water