C1: States of Matter
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IGCSE chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

What is the state of matter of these particles?
Solid

What is the state of matter of these particles?
Liquid

What is the state of matter of these particles?
Gas
Describe the particle arrangement/movement in a solid and its properties
Particles are close together, arranged in a regular pattern, and they vibrate on the spot. They have their own shape and a fixed volume
Describe the particle arrangement/movement in a liquid and its properties
Particles are close together, arranged irregularly, and they move around each other slowly. They take the shape of the container and have a fixed volume
Describe the particle arrangement/movement in a gas and its properties
Particles are far apart in a random arrangement, moving quickly in all directions. They take the shape of the container and have no fixated volume
Define molecule
A group of 2 or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Define atom
The smallest particle of an element that retains its chemical properties
Define ion
An atom or molecule with an electric charge
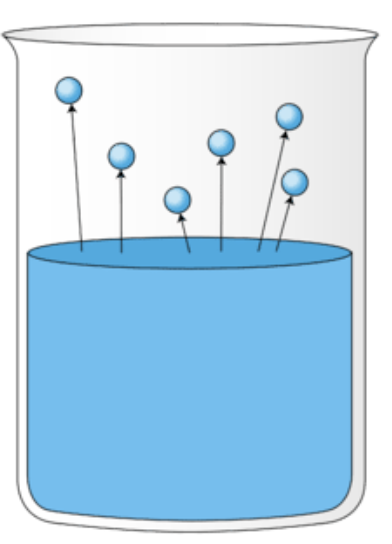
What is happening in this image?
Evaporation
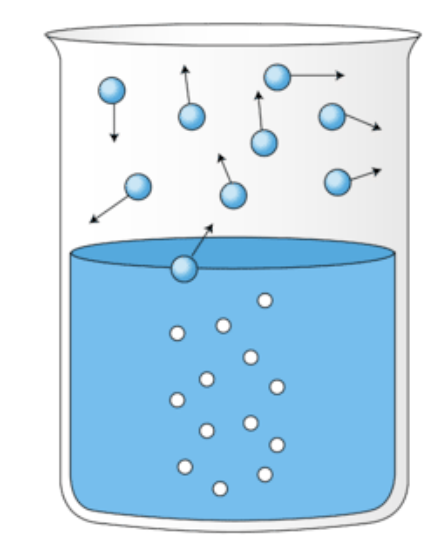
What is happening in this image?
Boiling
In terms of energy + particles, what happens during condensation?
Particles lose KE, making them move slower and go to a more structured form
In terms of energy + particles, what happens when something evaporates?
Particles gain KE, moving faster and further apart, breaking free from the liquid’s surface and being released into the atmosphere
In terms of energy + particles, what happens when something freezes?
Particles lose KE, making them slow down and move from a disorderly liquid state to a fixed solid state
In terms of energy + particles, what happens when something melts?
Particles gain KE, breaking the intermolecular bonds holding them in a fixed solid structure, and they move more freely, transitioning from a solid to a liquid
In terms of energy + particles, what happens when something boils?
Particles gain KE, overcoming the forces holding them together, making them move faster and further apart, and transitioning from a liquid to a gas
Define Charle’s Law
When the temperature of the gas increases, the volume increases proportionally and vice versa
Provide an example for Charle’s Law
Gases in a container exert pressure as the gas molecules are constantly colliding with the walls of the container because of their high amount of KE, which makes them move faster in a random direction
Which are the endothermic (require heat) changes of state?
Melting, evaporation, and sublimation
Which are the exothermic (release heat) changes of state?
Freezing, condensation, and deposition
What is sublimation?
The change of state from a gas to a solid or a solid to a gas
What is melting?
The change of state from a solid to a liquid
What is freezing?
The change of state from a liquid to a solid
What is evaporation?
The change of state from a liquid to a gas
What is condensation?
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
Define Boyle’s Law
When the temperature is held constant, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure, meaning that if pressure is increased and temperature is held constant, the volume decreases and vice versa
Define diffusion
The movement of particles in a liquid or a gas from a region of high concentration to low concentration
Give an example for diffusion
A sock can be smelled across the room because sweat particles spread out evenly across the room.
How does particle size/mass affect the rate of diffusion?
The bigger/more mass a particle has, the slower it will diffuse