SCH4U - Unit Two Thermochemistry
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
heat
thermal energy in transfer

thermal energy
total of all energy in particles, not heat

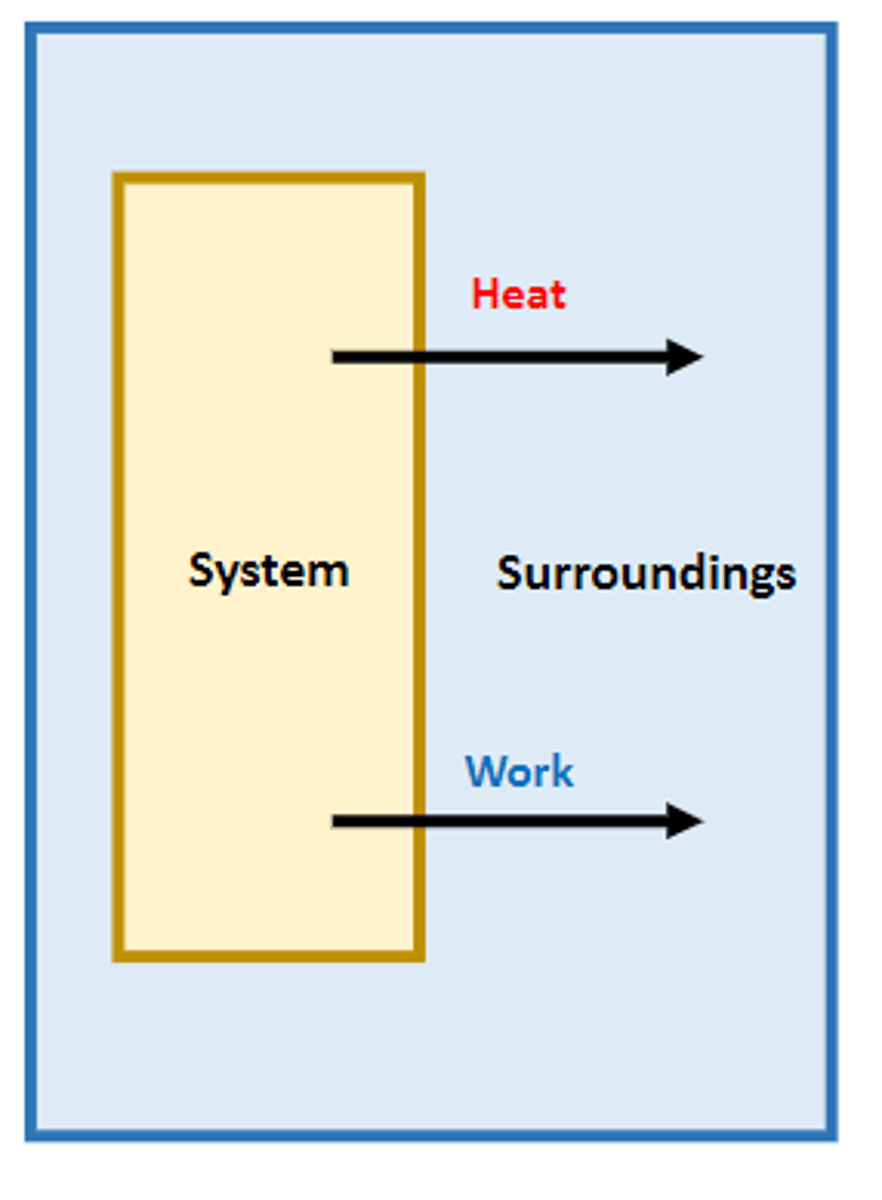
chemical system
a group of reactants and products being studied, typically a reaction

chemical surroundings
all matter around the system, can absorb or release thermal energy
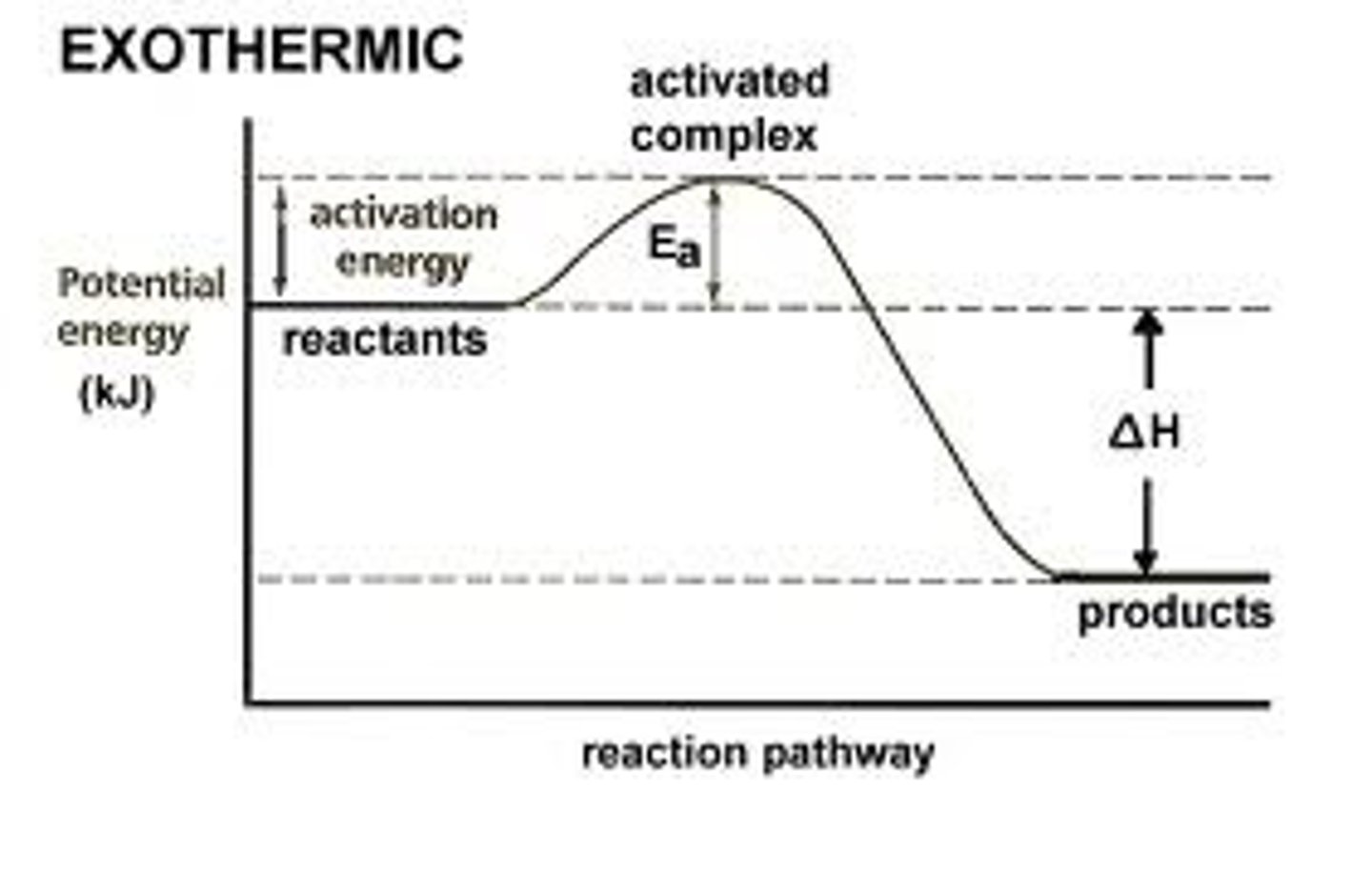
exothermic
releases heat
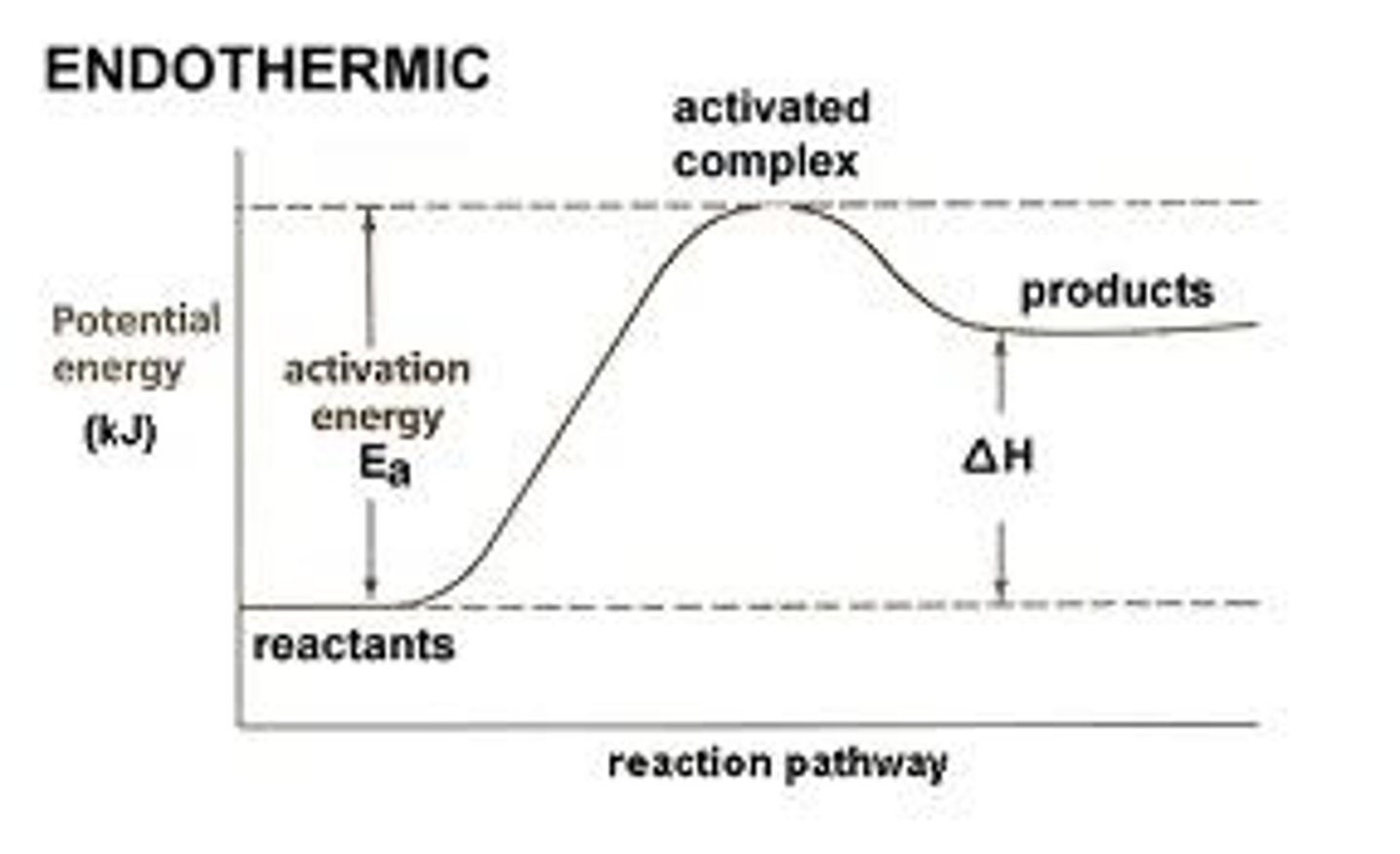
endothermic
absorbs heat
closed vs. isolated system
only energy can move between the system and the surroundings
enthalpy
total energy change of a system (delta H, kJ)
molar enthalpy
the energy change of one mole of a substance, (delta H of, kJ/mol)
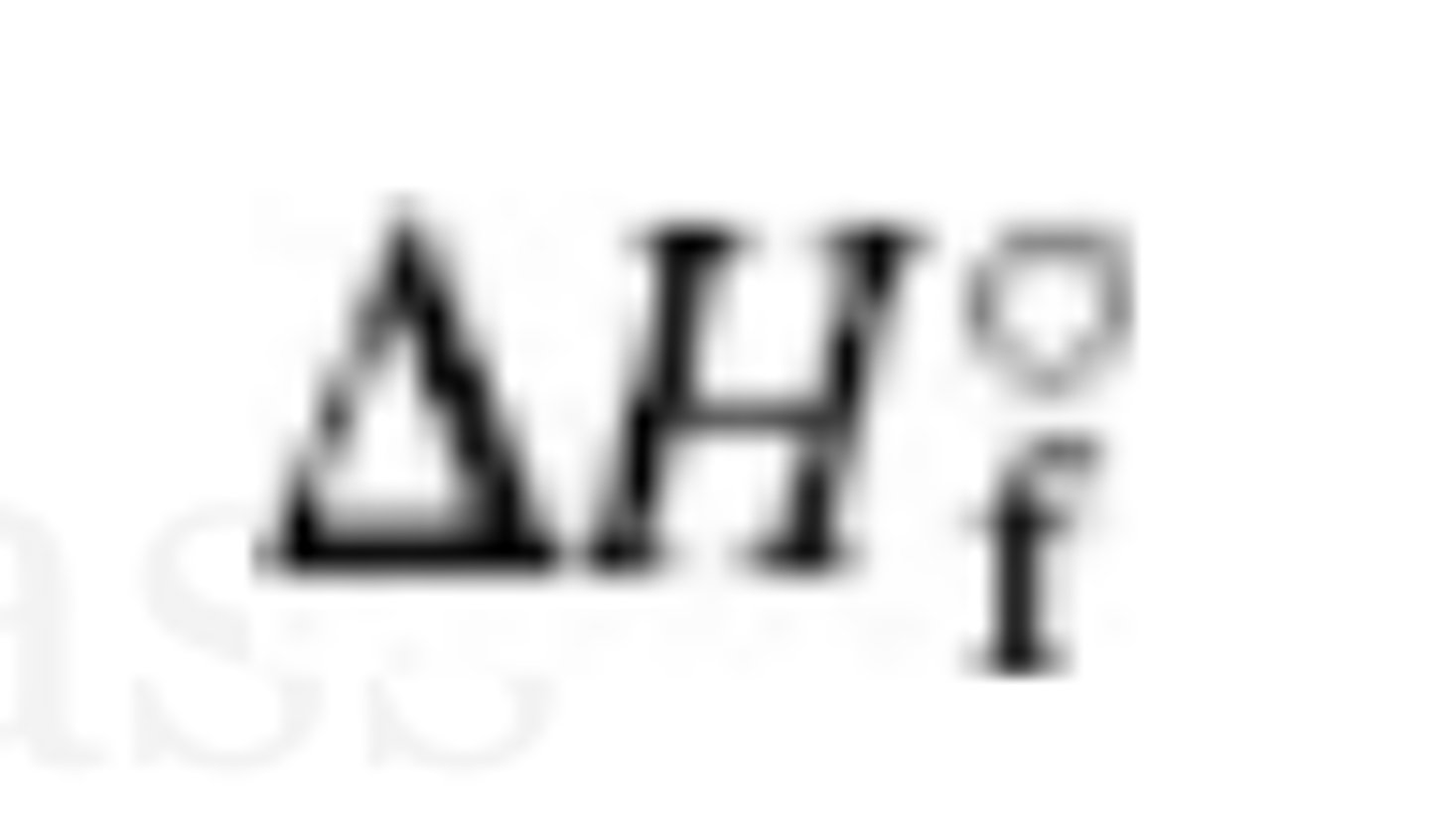
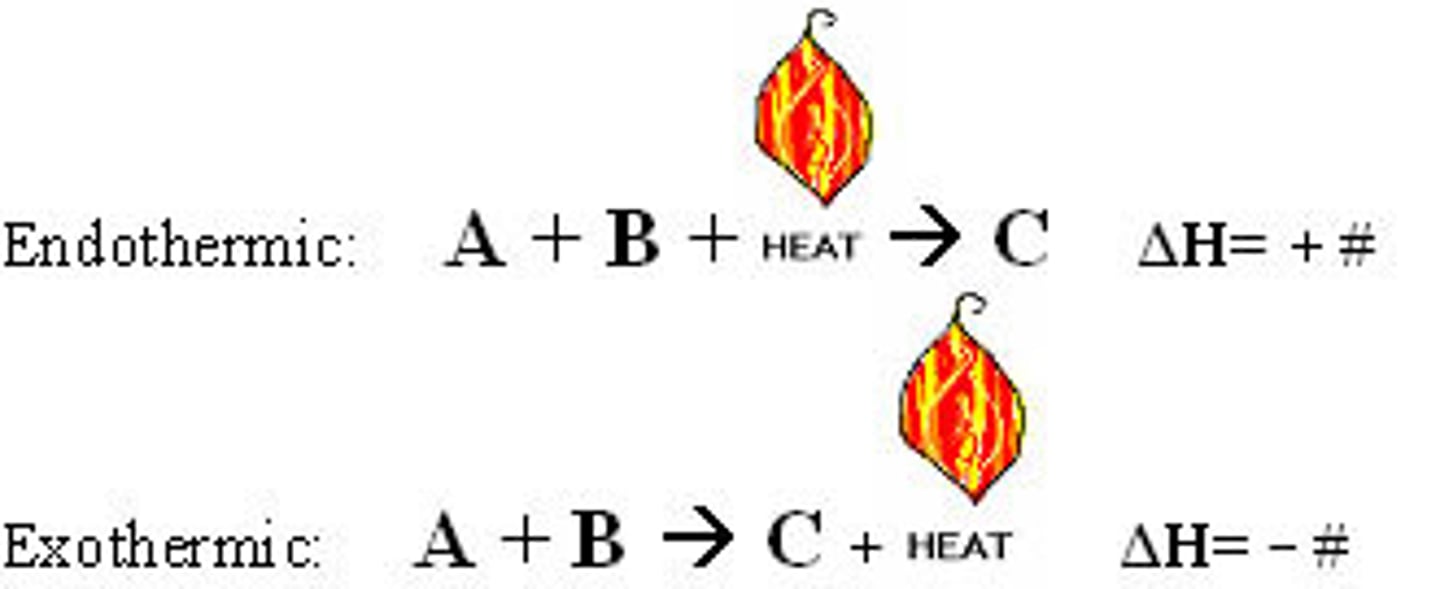
thermochemical equations
show the enthalpy changes, endothermic is the reactants, and exothermic is the products
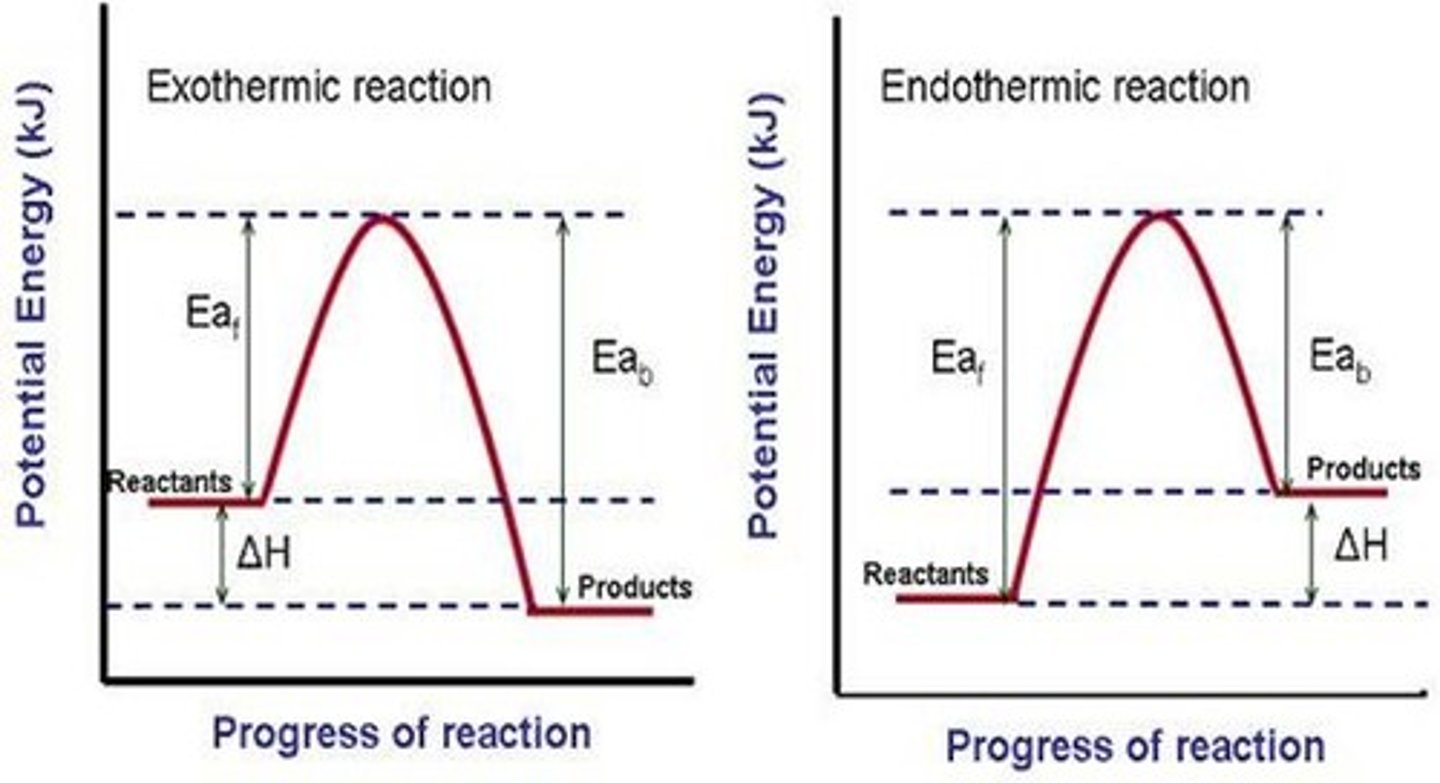
potential energy diagram
a diagram that shows the changes in potential energy
calorimetry limitations
not useful when reactions are too slow, temperature changes are too small to measure, and when reactions occur too fast and dangerous
hess law
the overall enthalpy in a reaction will be the sum of all enthalpy changes in the steps taken
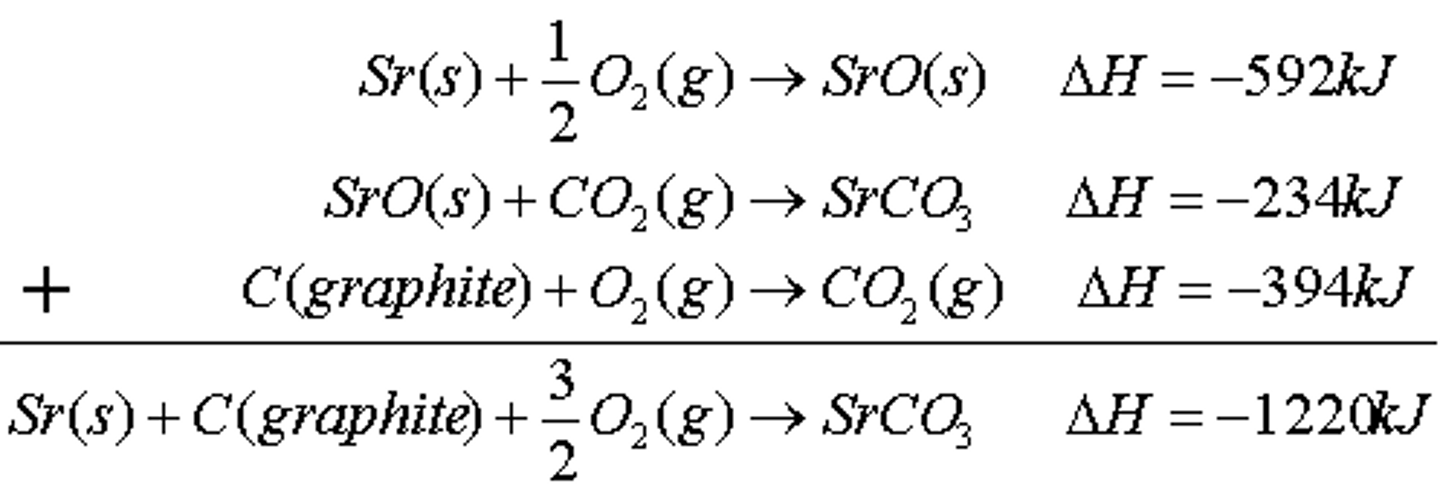
rules for enthalpy changes
if chemical reaction is reversed, you must reverse the sign of delta H,
if coefficient is multiplied, all others and enthalpy change value must be done by same number
formation equations
equations that show the production of a compound from its elements
standard enthalpy of formation
the change when one mol of a compound is formed from its elements, all of which are in standard states (e.g O2(g))
remember P4(s) and S8(s)
at SATP
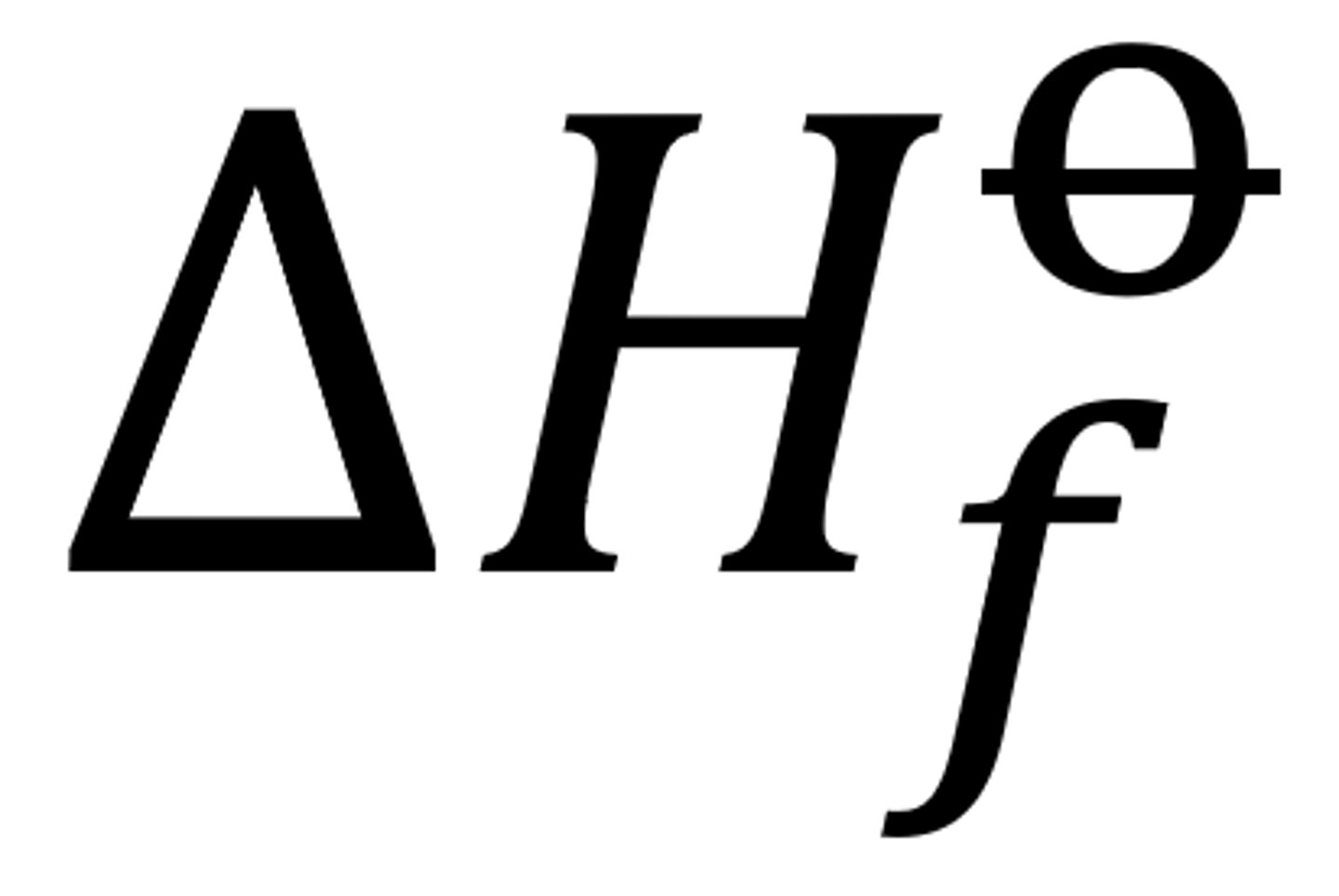
standard state enthalpy
standard enthalpy of formation of an element already in its standard state is zero (kJ/mol)
equation for standard enthalpy of formation
n x deltaH (products) - n x deltaH (reactants)
collision theory
for a reaction to occur, the particles must collide, they must collide with the appropriate orientation, and with sufficient energy.

activation energy
minimum amount of energy a reactant must have for a collision to be effective
transition state
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed
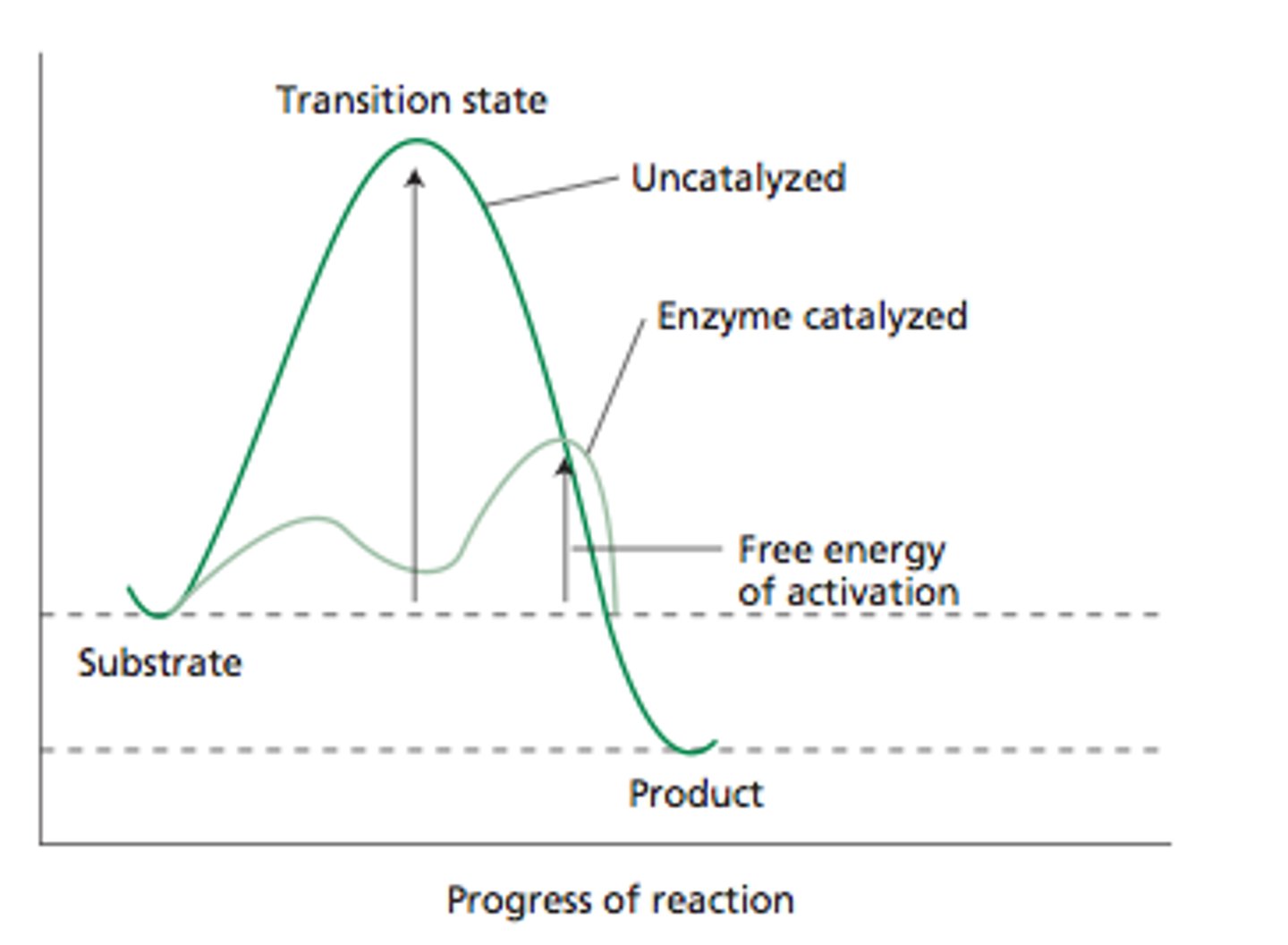
rates of reaction
dependent on concentration, as reactants are used up the reaction will get slower and slower
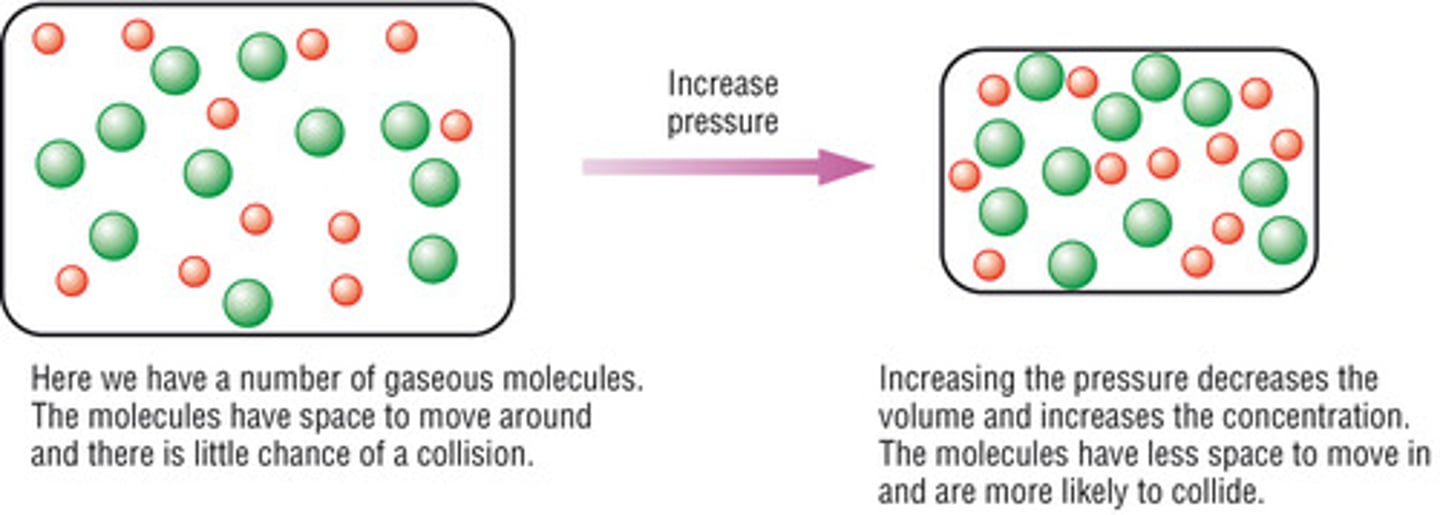
concentration increase
collision frequency increases, effectiveness does not
surface area increase
collision frequency increases, effectiveness does not
temperature increase
both collision frequency and effectiveness increases
higher temperature means faster moving particles, and there is more kinetic energy (collision theory)
presence of a catalyst
collision frequency does not increase, but effectiveness does
rate law
equation that connects speed of reaction with concentration, determined empirically
order
the exponent held to concentration value
elementary step
a step involving entity collisions, either one, two, or three
rate determining step
the slowest step in a reaction mechanism, larger activation energy
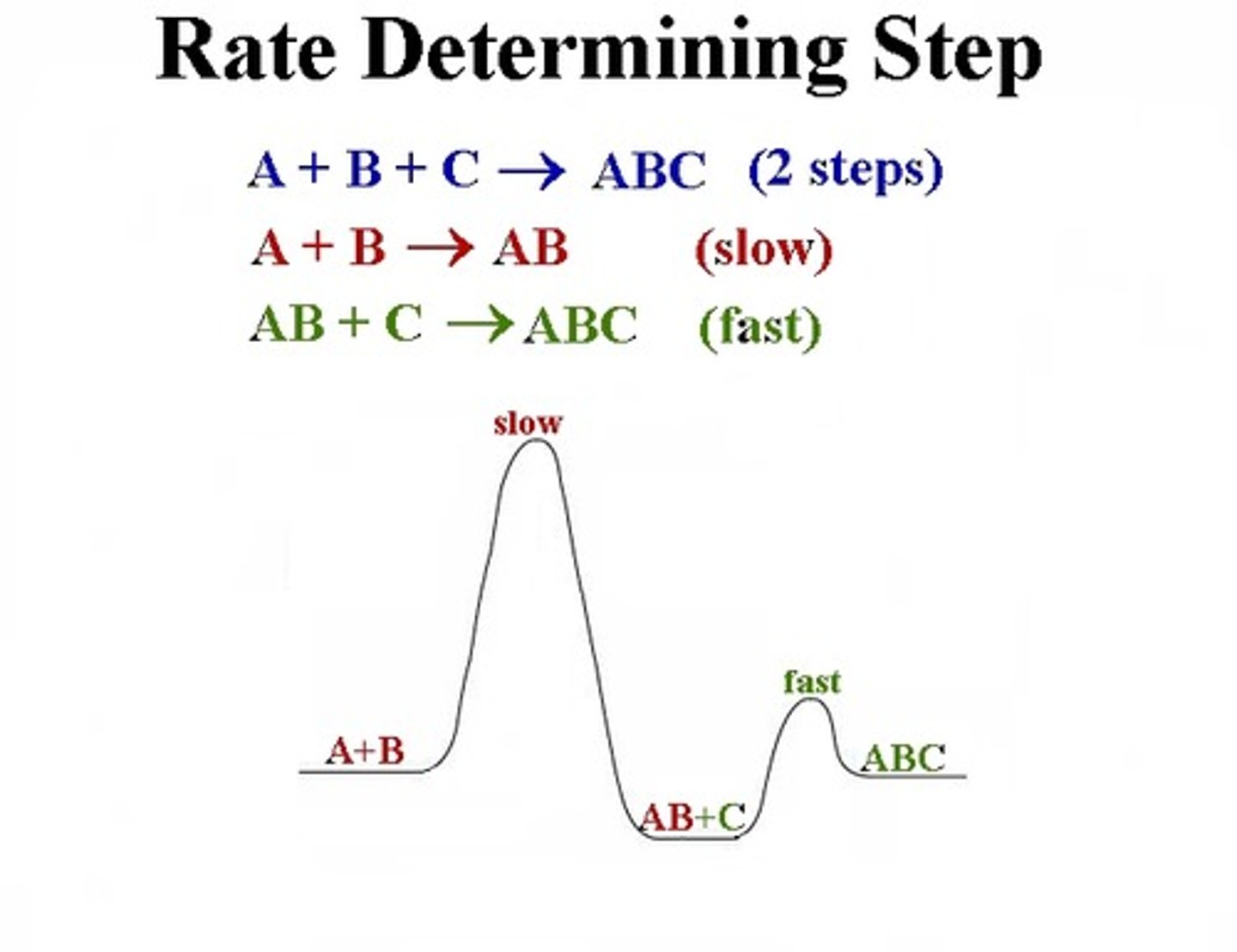
reaction intermediate
forms in one elementary step and is consumed in another
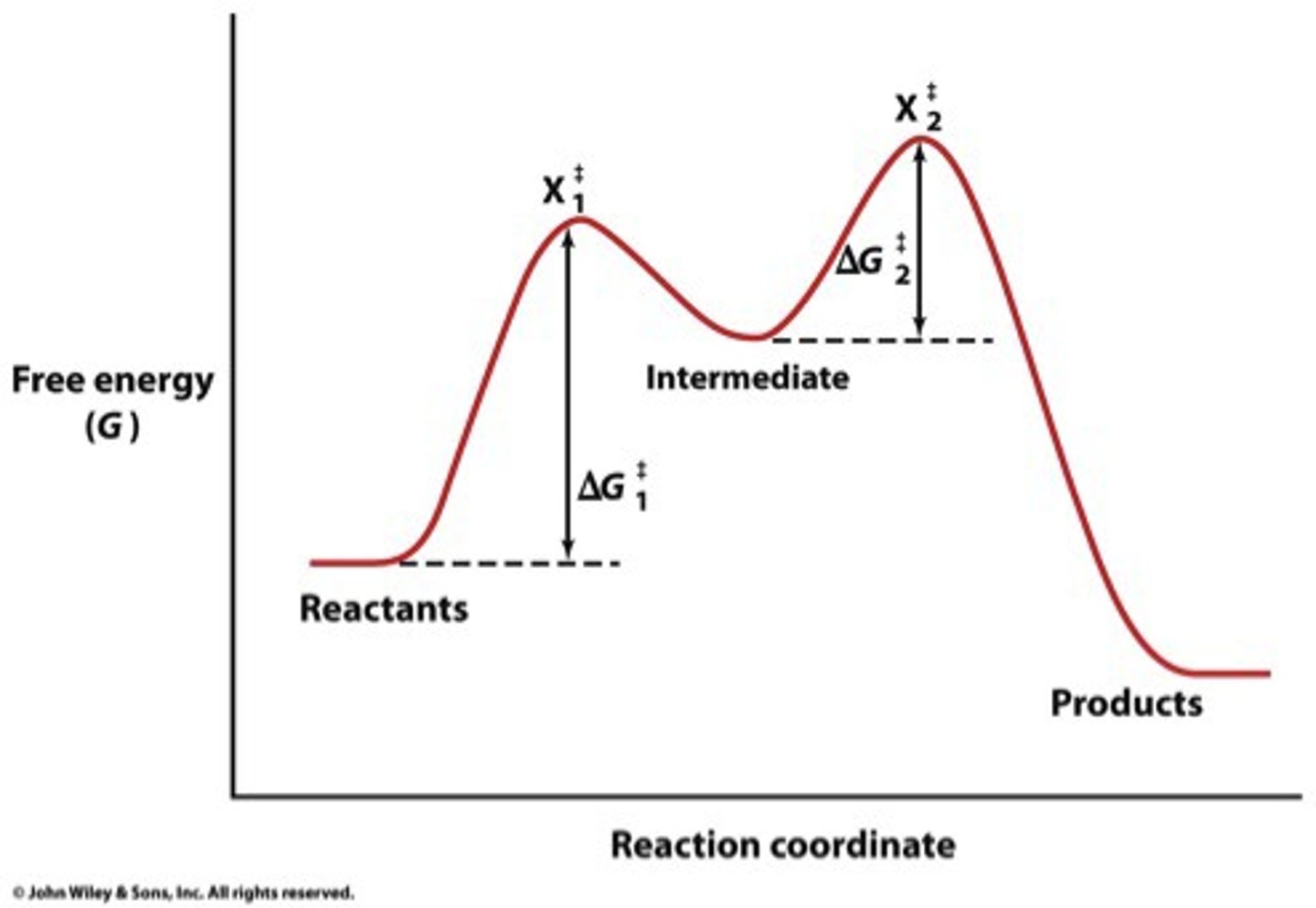
requirements to satisfy mechanism
elementary steps must add to overall balanced, mechanism must agree with rate law of overall (slow step)
1st law of thermodynamics
energy may change forms, but the total energy stays the same
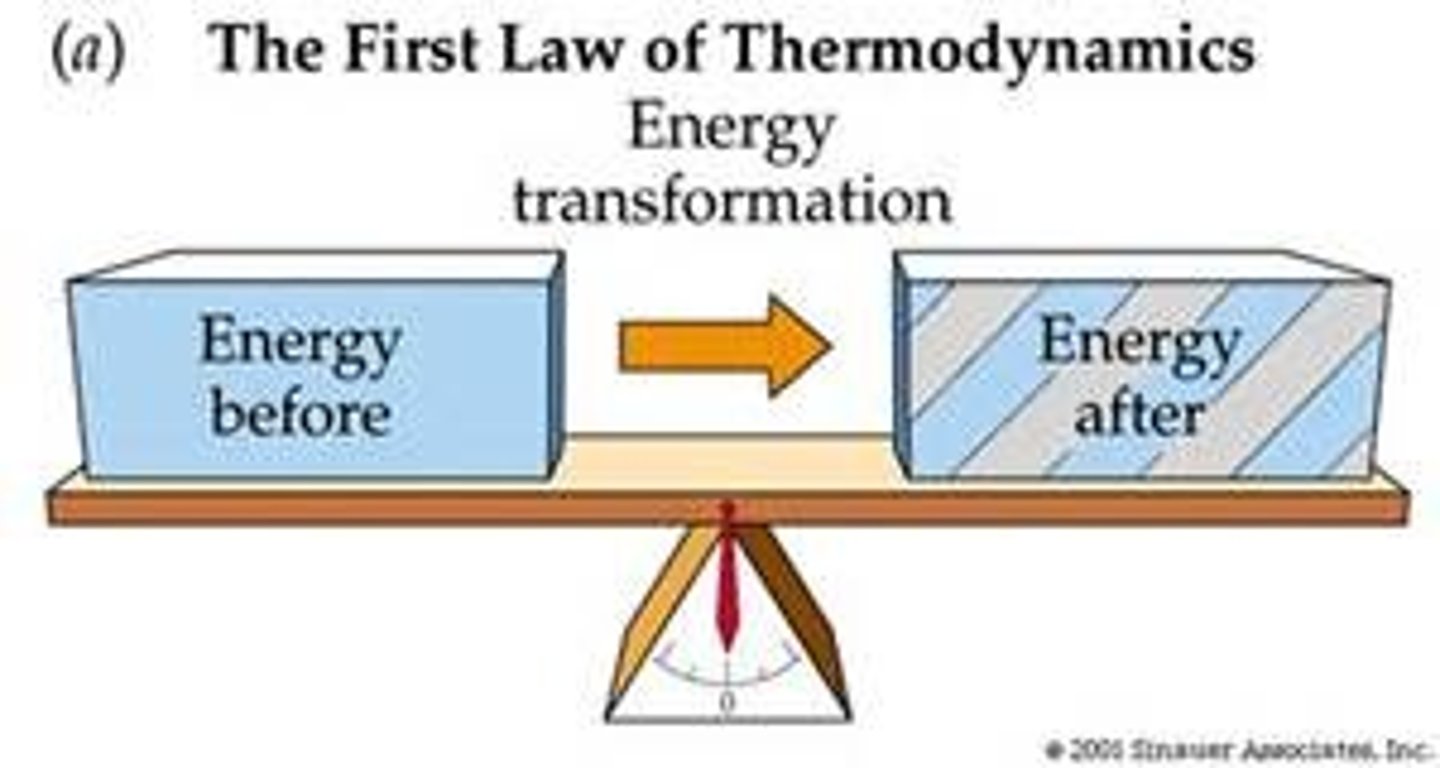
2nd law of thermodynamics
heat will flow from hotter to colder objects
standard state elements formation
any element in its standard state, as a standard enthalpy of formation of 0
matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
energy
the potential/capacity to produce change
