U4 APES Earth systems & Resources
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Planet formations
Planet formed 4.6 billion years ago
Heavier elements (Iron & Nickel sank
toward the center)
Lighter elements like silicon & oxygen
floated to the top
Some gases left the solid part &
became part of the atmosphere
Earths Core
innermost zone of the planet
(nickel & iron) inner core is solid.
Outer core is liquid. The interaction between
the two form magnetic field
Mantle
above core. Contains magma where
convention currents occur. The spongy
material movement drive plate tectonics
Crust
outermost layers of the planet;
thinnest layer contains basement rock of
ocean & continents.
Lithosphere
The brittle outermost layer of the Earth
Asthenosphere
Outer part of the mantle (Semi-molten, Flexible rock)
Crust (continental)
Mostly granite, Si, O
Crust (Oceanic)
Mostly Basaltic, Fe & Mg
Convection
Convection in the Earth happens in the mantle, the layer beneath the crust. It involves hot rock rising and cooler rock sinking, creating convection currents.
Hot spots
Places where molten material from the mantle reach the lithosphere
Continental Drift
Continental drift is the theory that the Earth's continents were once connected as a single supercontinent called Pangaea, and over millions of years, they slowly moved apart to their current positions.
Theory of Plate tectonics
The theory of plate tectonics explains how the Earth’s outer shell (the lithosphere) is divided into large, rigid plates that move over the semi-fluid asthenosphere below. These movements are responsible for many geological phenomena like earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountain ranges.
Divergent Plate boundaries
When plates move apart from one another
Convergent Plate boundaries
When the plates move towards one another
Transform Fault Boundaries
Plates Move sideways past eachother
Volcano formation
As a plate moves over a hot spot, rising magma forms a volcano
Faults
A fault is a crack or fracture in the Earth’s lithosphere where two blocks of rock have moved relative to each other. Faults are created by stress and are often the cause of earthquakes.
Earthquakes
occurs when the rocks across of the lithosphere unexpedly rupture along a fault
Soil
Soil is the top layer of Earth’s surface where plants grow. It’s made up of a mixture of minerals, organic matter (like decayed plants and animals), air, and water.
Soil formation
Soil formation begins
when bedrock is broken
by physical, chemical, &
biological processes
called weathering
Soil components
Pore space 50% (air/water)
Soil Space 50% (Mineral matter & Organic Matter)
Soil Properties (Texture)
Clay, Sand, & Silt
(Ex. If a soil sample contains: (Silty Clay)
30% clay
10% sand
60% silt
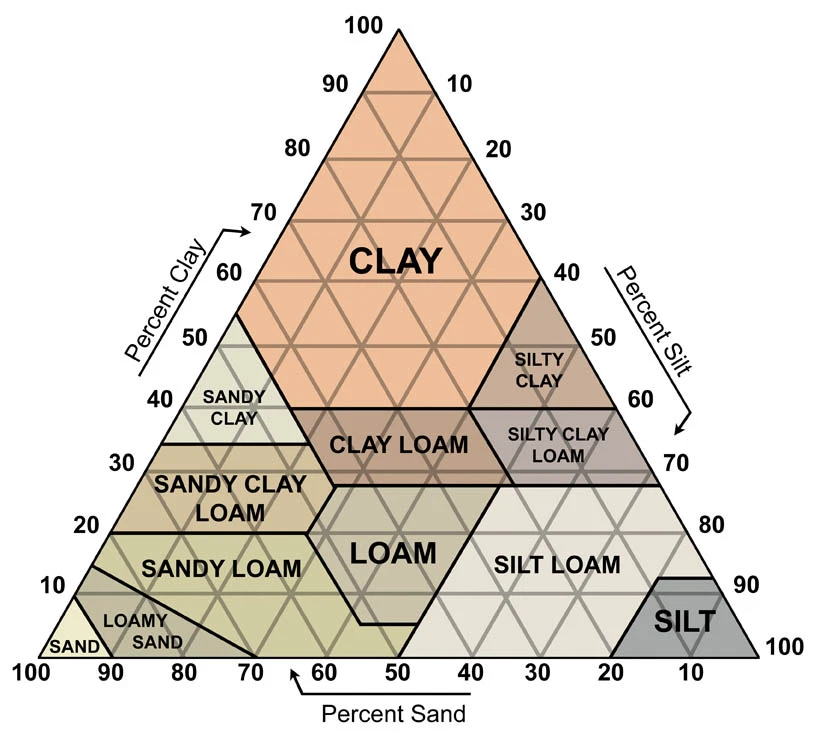
Soil Texture
Largest → Smallest
Sand → Silt → Clay
Sand = easily seen
silt = size of flour
clay = electronic microscope
O horizon
composed of organic detritus in various
stages of decomposition.
A horizon
topsoil, a zone of organic material &
minerals that have been mixed together.
E horizon
Zone of leaching, found in some acidic soils
under the O horizon or, less often, the A horizon.
B horizon
primarily of mineral material with very little
organic matter.
C horizon
least-weathered soil horizon, always
beneath the B horizon, & similar to the parent material.
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is when a body of water becomes overly rich in nutrients (like nitrogen and phosphorus), often due to runoff from fertilizers, sewage, or animal waste.
Desert soil
Soil: Very dry, sandy, and low in organic matter.
May have salts from evaporation.
Poor for farming without irrigation.
Grass land soil
Soil: Deep and nutrient-rich, especially in temperate grasslands (like prairies).
Great for growing crops—often used in agriculture.
Lots of roots from grasses add organic material.