PNS EFFERENT
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
which motor efferent division is voluntary and which is involuntary and what are their effectors?
Somatic NS is voluntary + goes to skeletal muscles
ANS is involuntary + goes everywhere (cardiac + smooth muscle, + glands)
What interesting things does ANS do?
1. Support somatic reactions
2. Mediate emotional states
3. Adjust/Regulate homeostatic body states
How does ANS support somatic reactions? Give example
- supports increased metabolic demand
- you cannot run w/out the support of ANS using/increasing your HR, BP, etc
How does ANS mediate emotional states? Give example
- rage = red face
- blushing cheeks
How does ANS adjust or regulate homeostatic body states? give example
ANS cools us down when warm, if we are cold then peripheral vessels vasoconstrict,
What does dual innervation mean?
it means that a body organ receives neural innervation from both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Has mostly opposite effects
what organs in our body are not dually innervated?
- Skin (sweat, adrenal glands, etc bc PNS does not control sweat)
- Adrenal glands (bc they're an extension of sympathetic NS)
Cranialsacral refers to ___________ where as thoracolumbar refers to _________
cranialsacral = Parasympathetic innervates from cranial + sacral
thoracolumbar = sympathetic innervates from thoracic and lumbar
Parasympathetic division promotes maintenance activities and conserves body energy: GIVE EXAMPLES
- lowers BP, HR, Resp Rate,
- Pupils constrict
- Excites digestive tract
- GI tract activity is high
- dominant for small intestine
sympathetic division mobilizes body during activity: GIVE EXAMPLES
- Increases HR, BP, RR,
- Bronchioles dilate to breathe better
- pupil dilation
- liver releases glucose to blood
- blood flow is shunted to skeletal musc+heart
what things do the somatic and ANS systems differ in?
effectors, efferent pathways and their NTs, and target organ responses to NTs
the SOMATIC EFFERENT pathway goes from CNS --> Skeletal Muscle. Why is that?
We have a singular somatic motor fiber that is thick and heavily myelinated w/ schwann cell going straight to muscle/effector
how does the ANS EFFERENT pathway differ from the somatic one?
ANS pathway is a two neuron chain, takes 2 neurons to get to the effectors.
- 1st neuron is preganglionic neuron
- 2nd neuron is postganglionic neuron
describe the pre-ganglionic neuron
- it is still in the CNS, has a thin and lightly myelinated axon, synapses to 2nd neuron
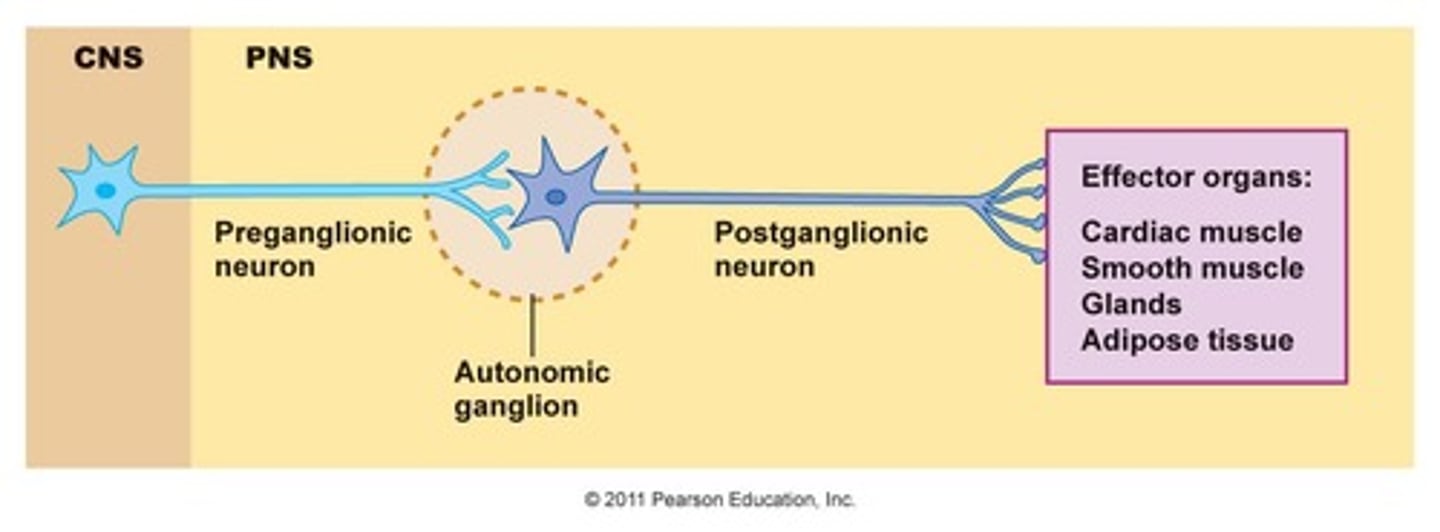
describe a post-ganglionic neuron?
- in PNS, has an unmyelinated axon that extends to effectors
Somatic neurons in somatic NS only release 1 neurotransmitter, what is that NT and its effects?
Somatic motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh) and its effects are excitatory/stimulatory
ANS takes two neurons to get to an effector, what NT can each neuron release and what are its effects?
the preganglionic fiber releases ACh, and the postganglionic fiber releases NE (norepinephrine) or also ACh which depends if its for sympathetic or parasympathetic
- effects can be stimulatory or inhibitory
the neurons that release ACH, and the receptors that bind to ACh, are called ____________
Cholinergic
Adrenaline is another word for Norepinephrine, fibers that secrete NE and receptors that NE bind to are called ___________
Adrenergic
There are 2 types of cholinergic receptors that bind ACh, what are they?
1. Nicotinic: ligand gated, nicotine binds as if it were ACh
2. Muscarinic: stimulates metabolism
cholinergic receptors are named after what?
named after drugs that bind to them and mimic ACh effects
effects of ACh at nicotinic receptors is always
stimulatory/excitatory
effects of ACh at muscarinic receptors ..
- can be inhibitory or excitatory
- depends on target organ receptor type
what are the two types of adrenergic receptors?
alpha and beta
effects of NE depend on...
on subclass of receptors on target organ
describe the adrenergic receptor types and its effects:
B1: excitatory associate w/ heart
B2: inhibitory associate w/ lungs
A1: excitatory associate w/ blood vessels