SKINS AND MEMBRANES
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Cutaneous membrane
Mucous membrane
Serous membrane
3 types Epithelial membranes
Cutaneous membrane = skin
A dry membrane
Outermost protective boundary
MUCOUS MEMBRANE
Lines all body cavities that open to the exterior body surface
SEROUS MEMBRANE
Surface simple squamous epithelium
Underlying areolar connective tissue
Peritoneum (Abdominal cavity)
Pleura (Around the lungs)
Pericardium (Around the heart)
Specific serous membranes (ABDOMINAL CAVITY, LUNGS, HEART)
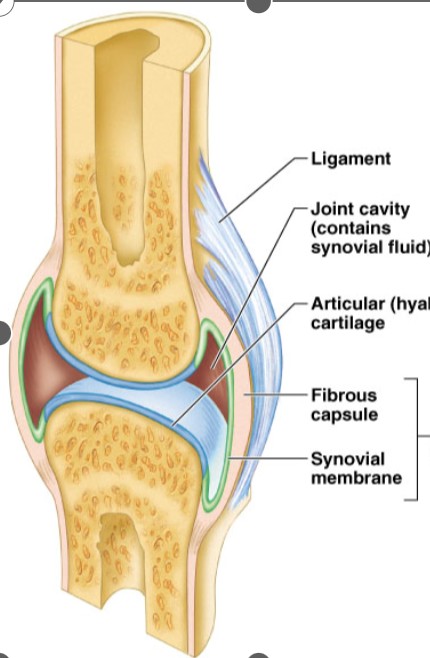
Connective tissue
Synovial membrane
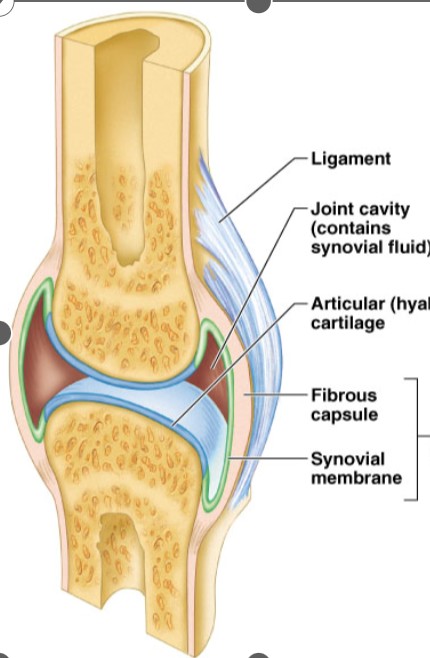
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Skin (cutaneous membrane)
Skin derivatives
- Sweat glands
- Oil glands
- Hairs
- Nails
Mechanical damage
Chemical damage
Bacterial damage
Thermal damage
Ultraviolet radiation
Desiccation
SKIN FUNCTIONS, Protects deeper tissues from:
Epidermis – outer layer
Stratified squamous epithelium, outer layer of?
Stratum basale (Cells undergoing mitosis Lies next to dermis)
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucidum (Occurs only in thick skin)
Stratum corneum (Shingle-like dead cells)
Layer of Epidermis
STRATUM BASALE
Cells undergoing mitosis, Lies next to dermis
MELANIN
Pigment produced by melanocytes
Color is yellow to brown to black Melanocytes are mostly in the stratum basale
Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetic and exposure to sunlight
MELANIN
Yellow, brown or black pigments
Carotene
Orange-yellow pigment from some vegetables
Hemoglobin
Red coloring from blood cells in dermis capillaries
Oxygen content determines the extent of red coloring
CYANOSIS
Low oxygen content creates a bluish appearance
DERMIS
Dense connective tissue, Has connective tissue, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, and other structures.
PAPILLARY LAYER
RETICULAR LAYER
2 LAYERS OF DERMIS
PAPILLARY LAYER
Projections called dermal papillae
Pain receptors
Capillary loops
RETICULAR LAYER
Blood vessels
Glands
Nerve receptors
HYPODERMIS
Deep to dermis
Not part of the skin
Anchors skin to underlying organs
Composed mostly of adipose tissue
Sebaceous glands
Sweat glands
2 types of glands
Sebaceous glands
Produce oil
Lubricant for skin
Kills bacteria
Most with ducts that empty into hair follicles
Glands are activated at puberty
Sweat glands
Widely distributed in skin
Two types (Eccrine, Apocrine)
(Eccrine, Apocrine)
Two types of sweat glands
ECCRINE SWEAT GLANDS
Open via duct to pore on skin surface
Apocrine sweat gland
Ducts empty into hair follicles
HAIR
Consists of hard keratinized epithelial cells
Melanocytes provide pigment for ____ color
Central medulla → Cortex → Cuticle
Hair Anatomy
NAILS
Scale-like modifications of the epidermis
Heavily keratinized
First-degree burns
Only epidermis is damaged
Skin is red and swollen
Second degree burns
Epidermis and upper dermis are damaged
Skin is red with blisters
Third-degree burns
Destroys entire skin layer Burn is gray-white or black
CANCER
abnormal cell mass
Benign Does not spread (encapsulated)
Malignant Metastasized (moves) to other parts of the body
Two types of skin cancer
A = Asymmetry Two sides of pigmented mole do not match
B = Border irregularity Borders of mole are not smooth
C = Color Different colors in pigmented area
D = Diameter Spot is larger then 6 mm in diameter
ABCD Rule
Melanocytes
Melanin, Pigment produced by?