axial skeleton A&P lab
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
bones in the body
206
axial bones
80
appendicular bones
126
bone classifications
flat, long, short, sesamoid, irregular
flat bone examples
sternum, ribs, skull bones
long bones examples
femur, radius, tibia, fibula
short bone examples
carpal bones and tarsal bones
sesamoid bones examples
patella
irregular bone examples
vertebrae, hyoid, ethmoid, zygomatic, mandible
bone markings
the various ridges, grooves, depressions, and other features found on the surfaces of bones
projections
raised areas on the surface of the bone
depressions
hollow or recessed area on the surface of a bone
spongy bone (cancellous)
a porous bone tissue located primarily in the ends of long bones, the flat bones of the skull, and the pelvis
compact bone
the hard, dense outer layer of bones that provides strength, structural support, and protection
hydroxyapatite
primary bone mineral giving strength, rigidity, and hardness
red marrow
site of red blood cell production
yellow marrow
filled with adipose
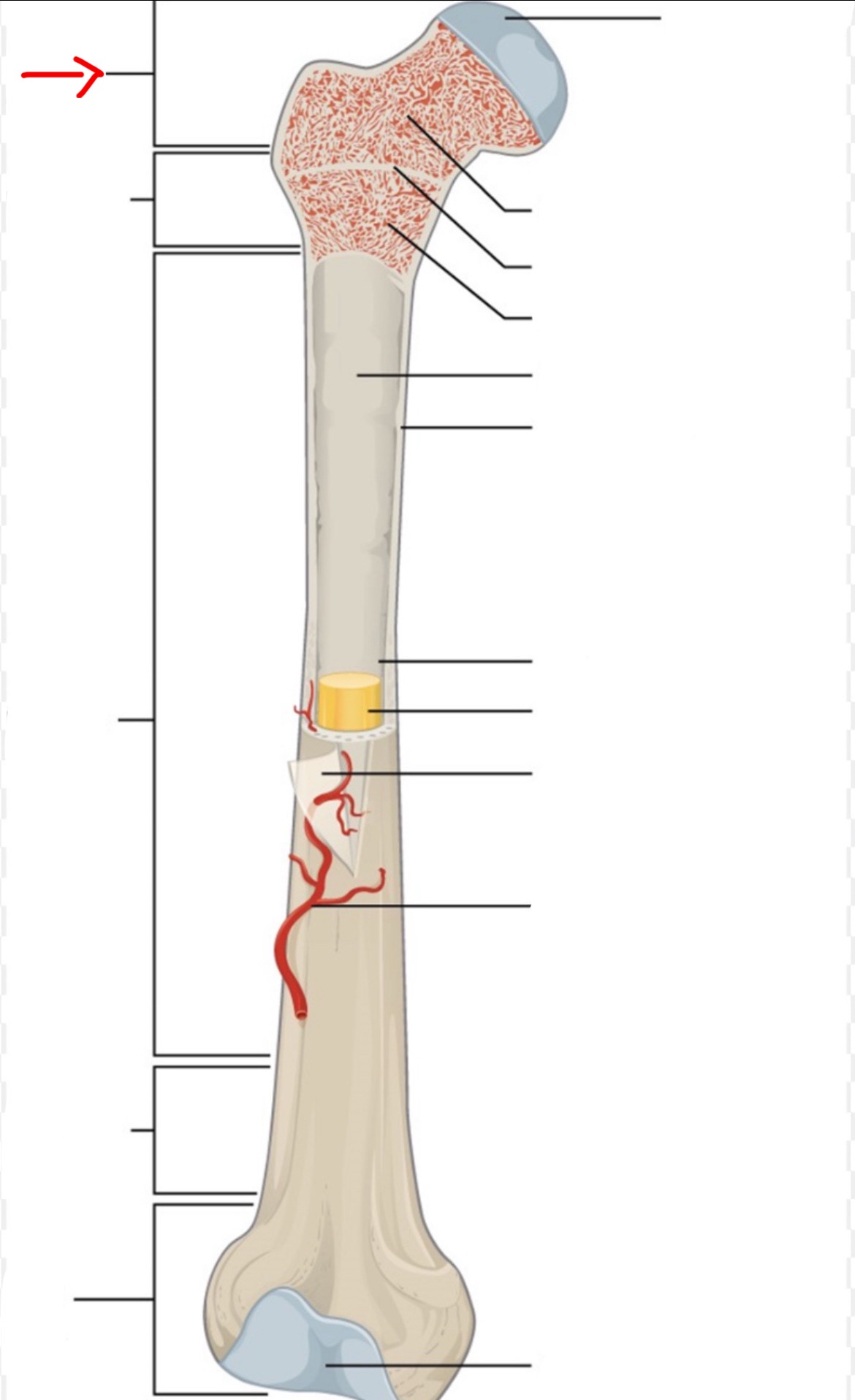
proximal epiphysis
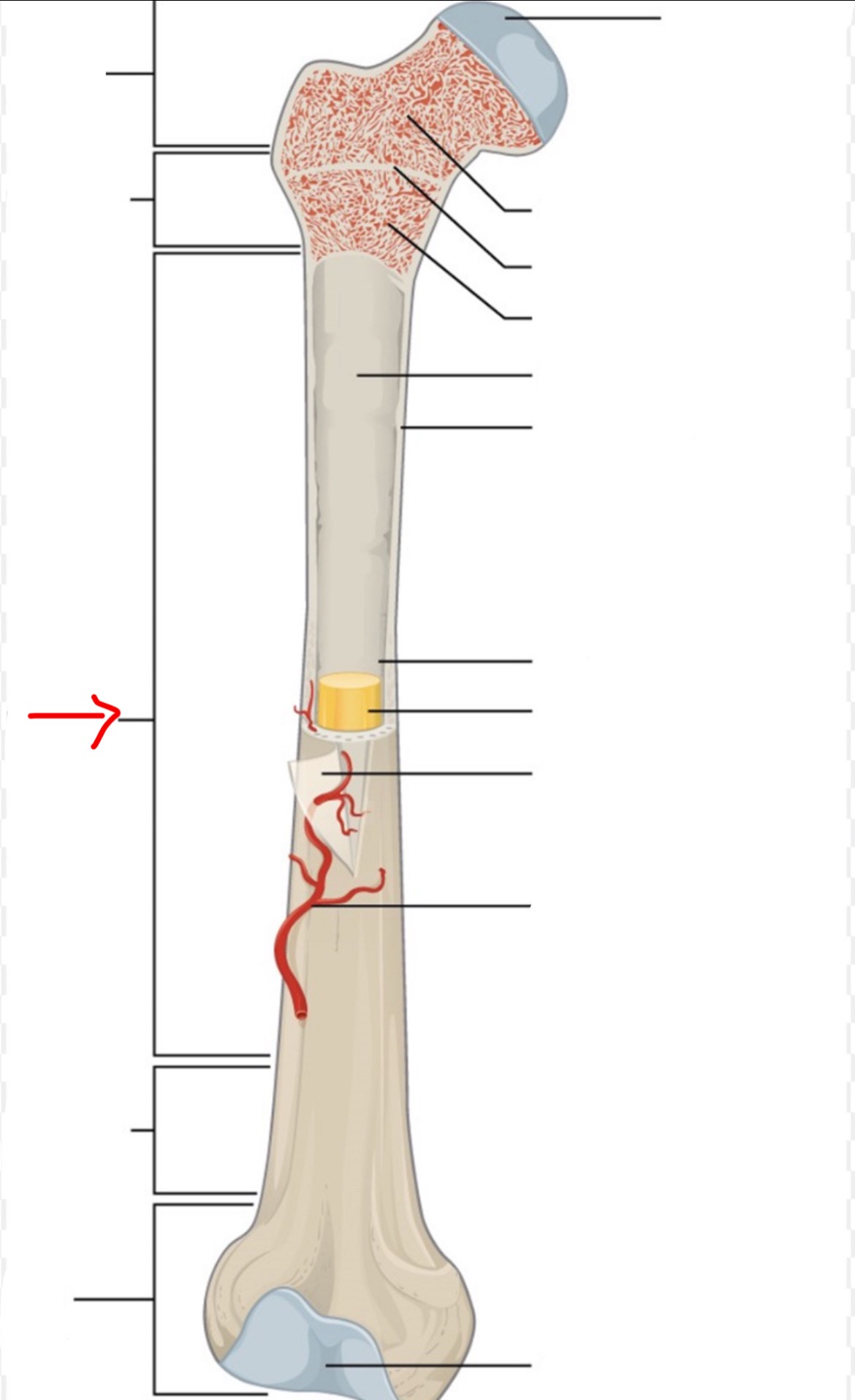
diaphysis
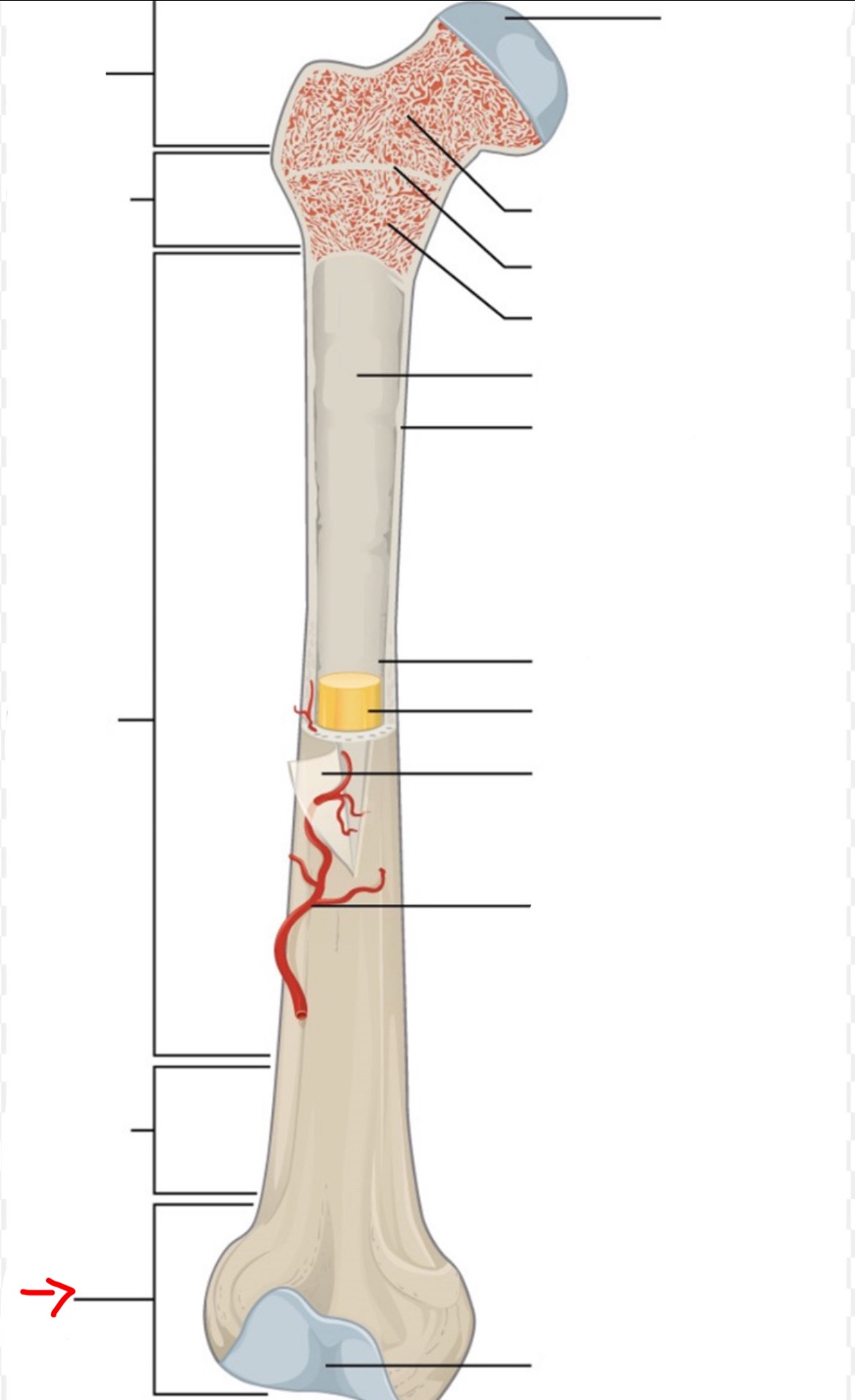
distal epiphysis
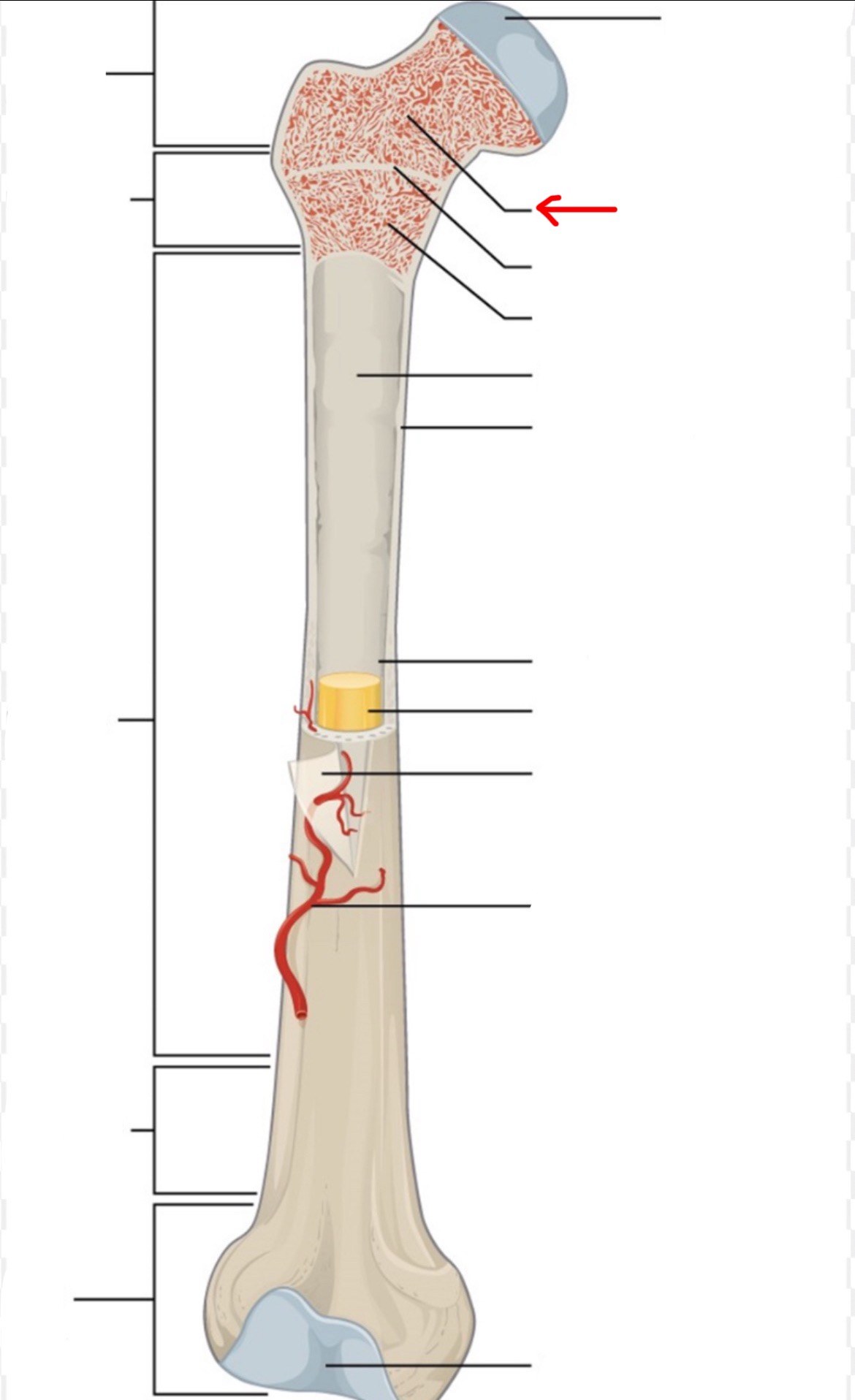
spongy bone
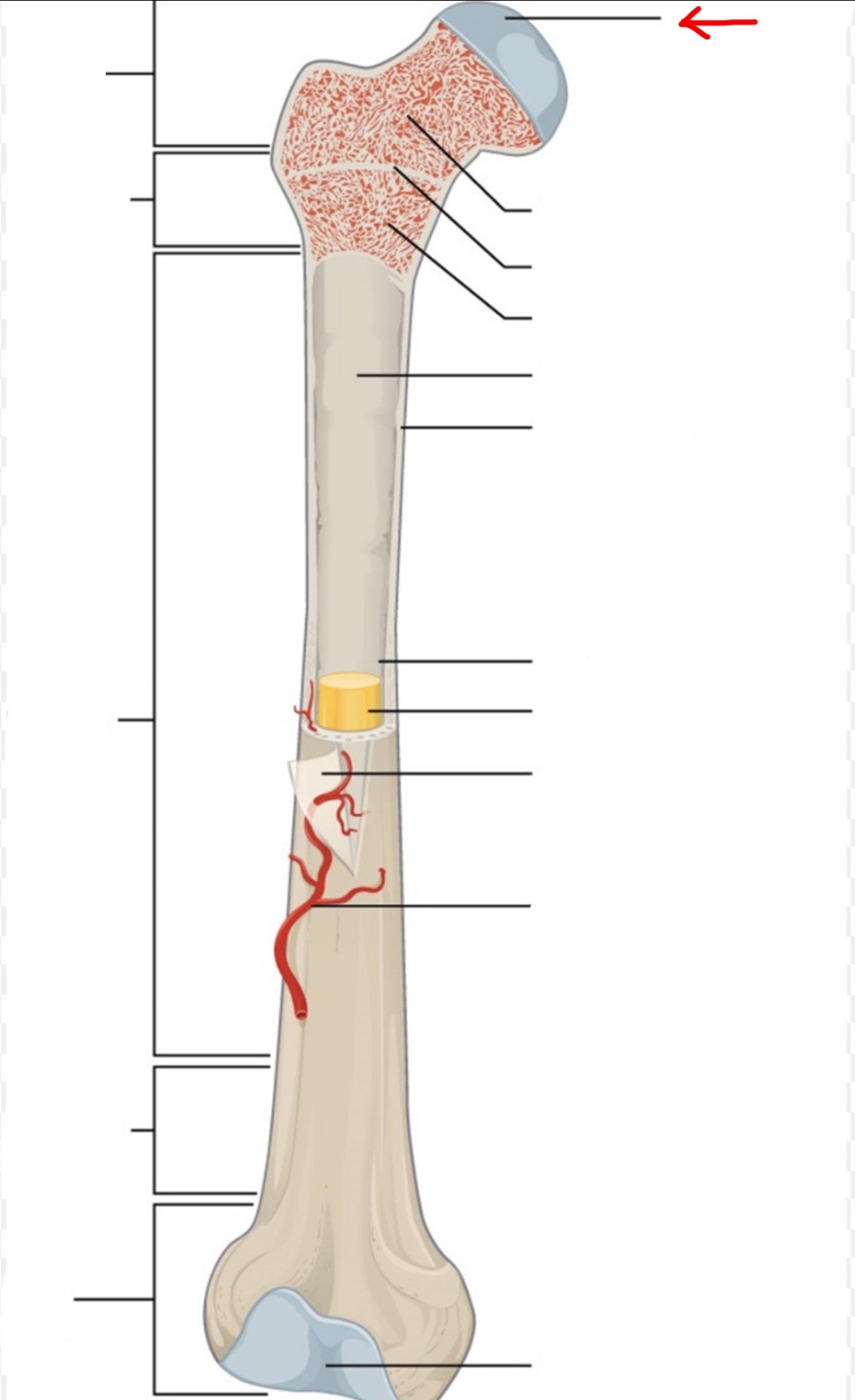
articular cartilage
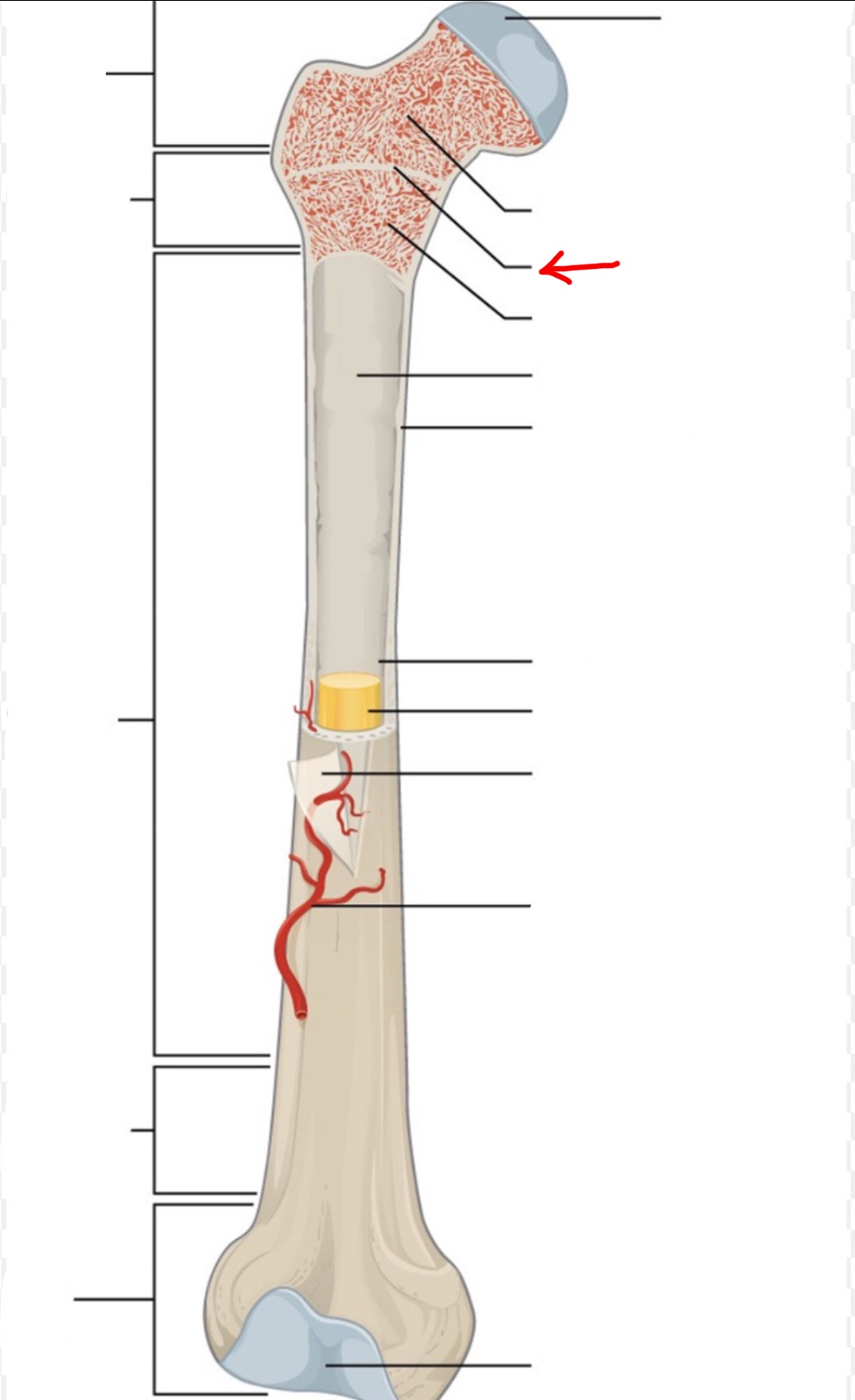
epiphyseal line
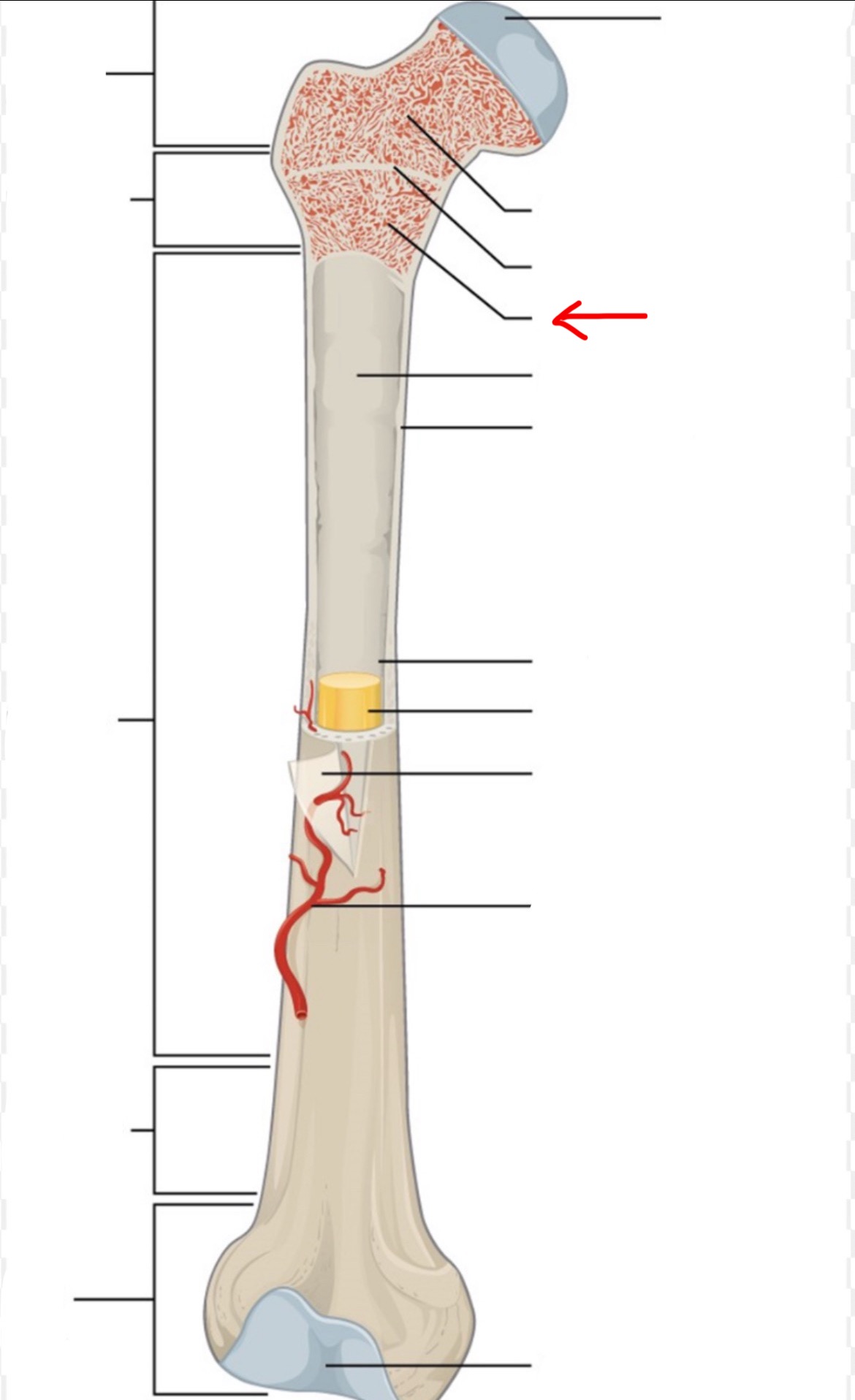
red bone marrow
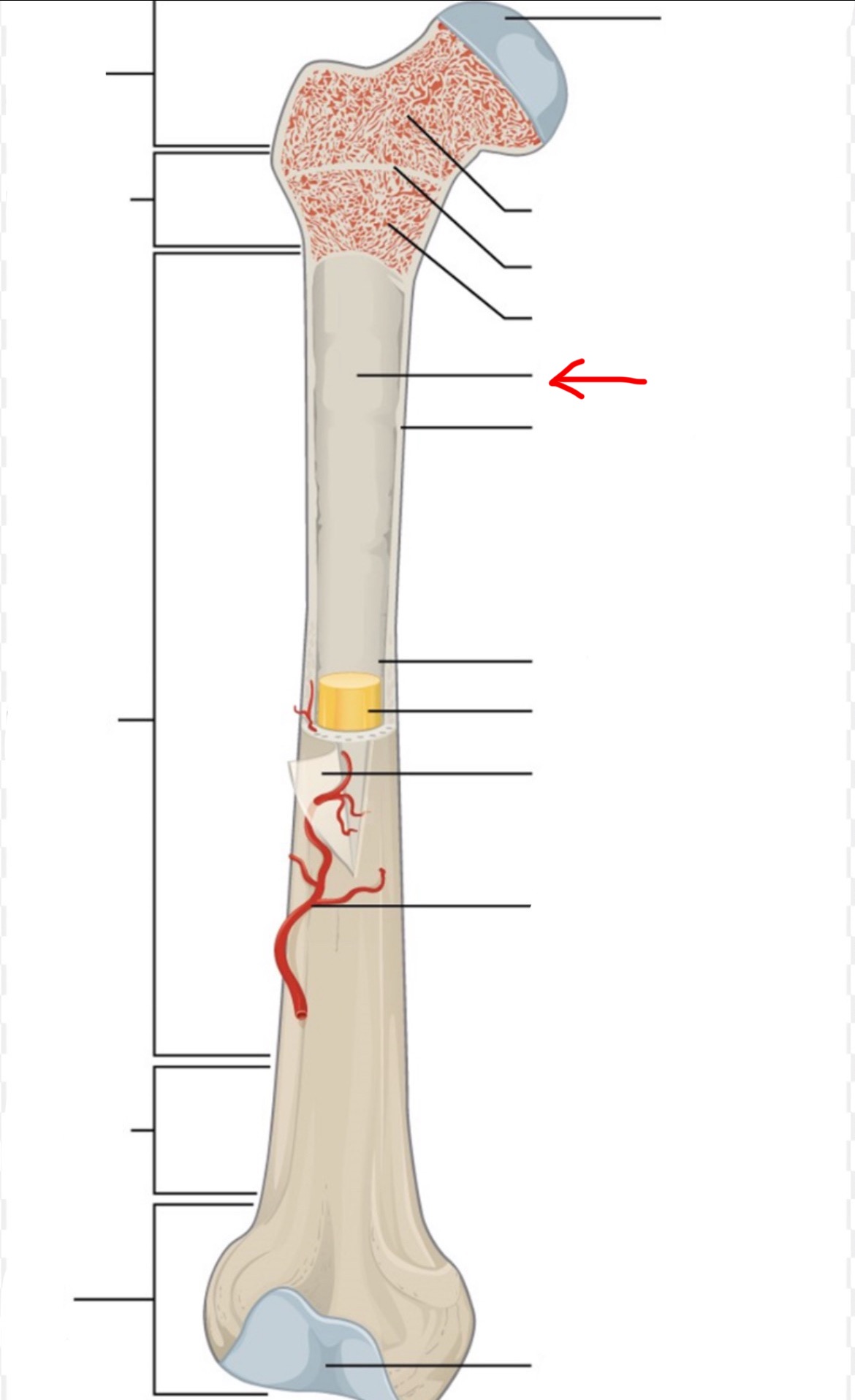
endosteum
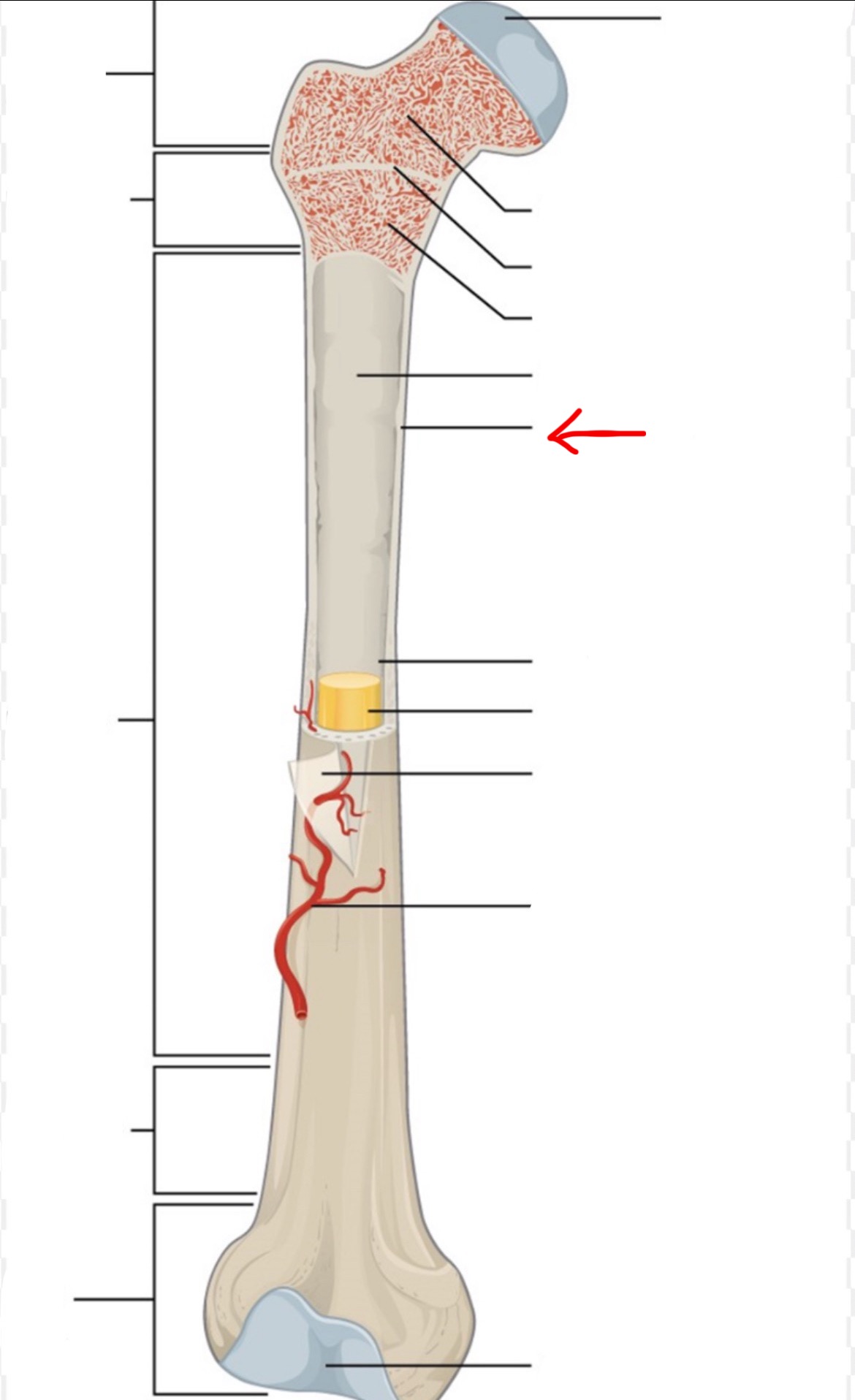
compact bone
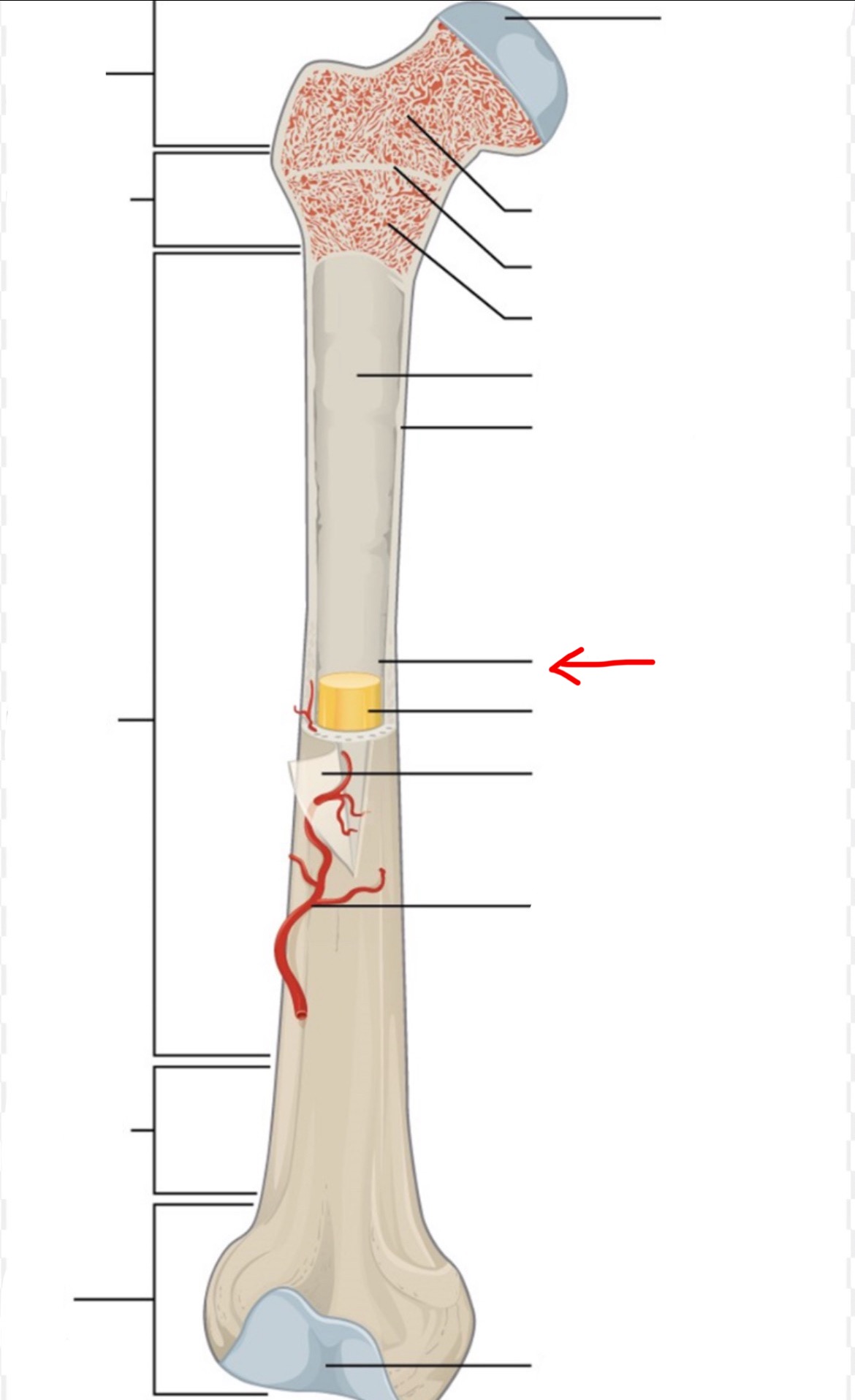
medullary cavity
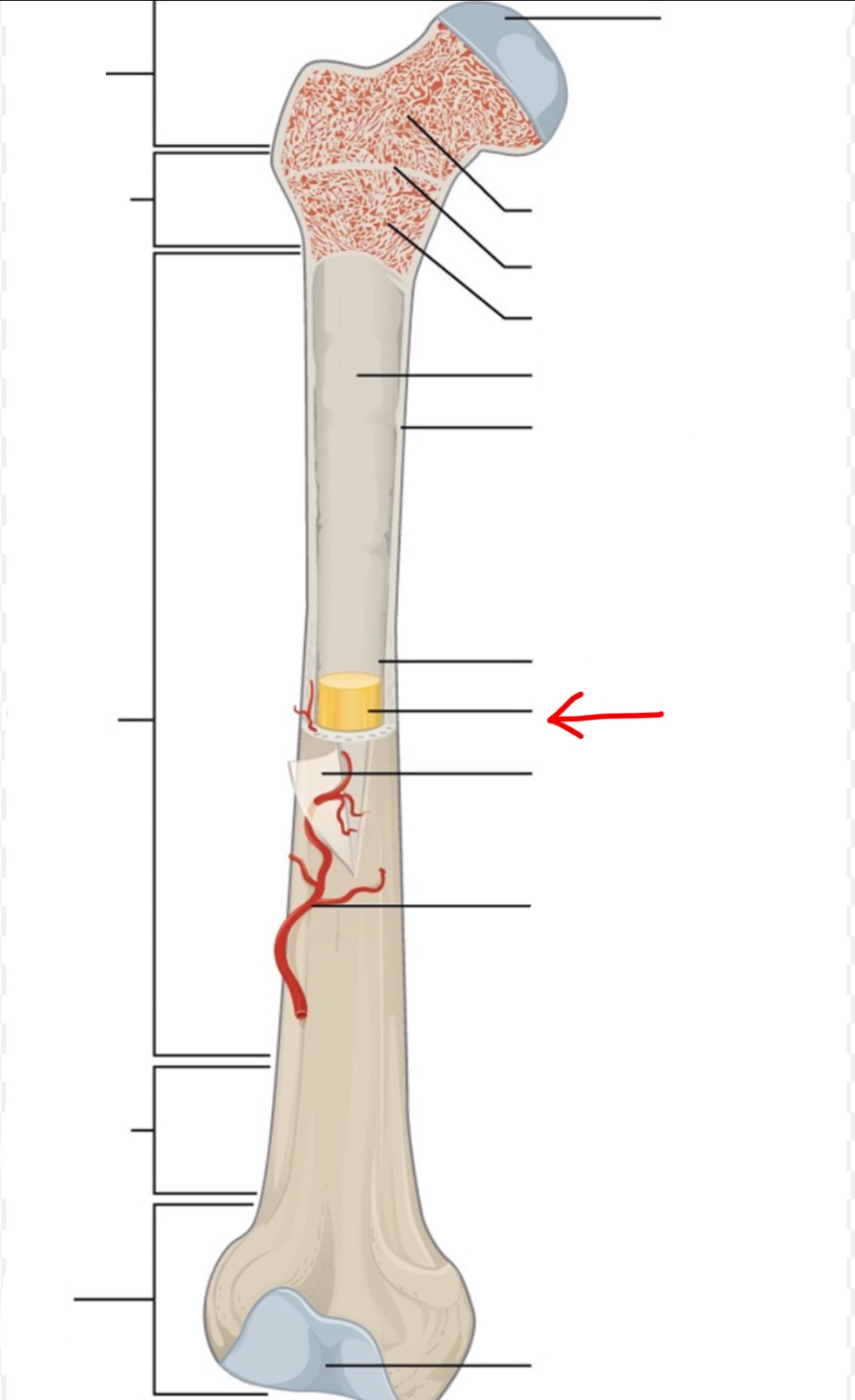
yellow bone marrow
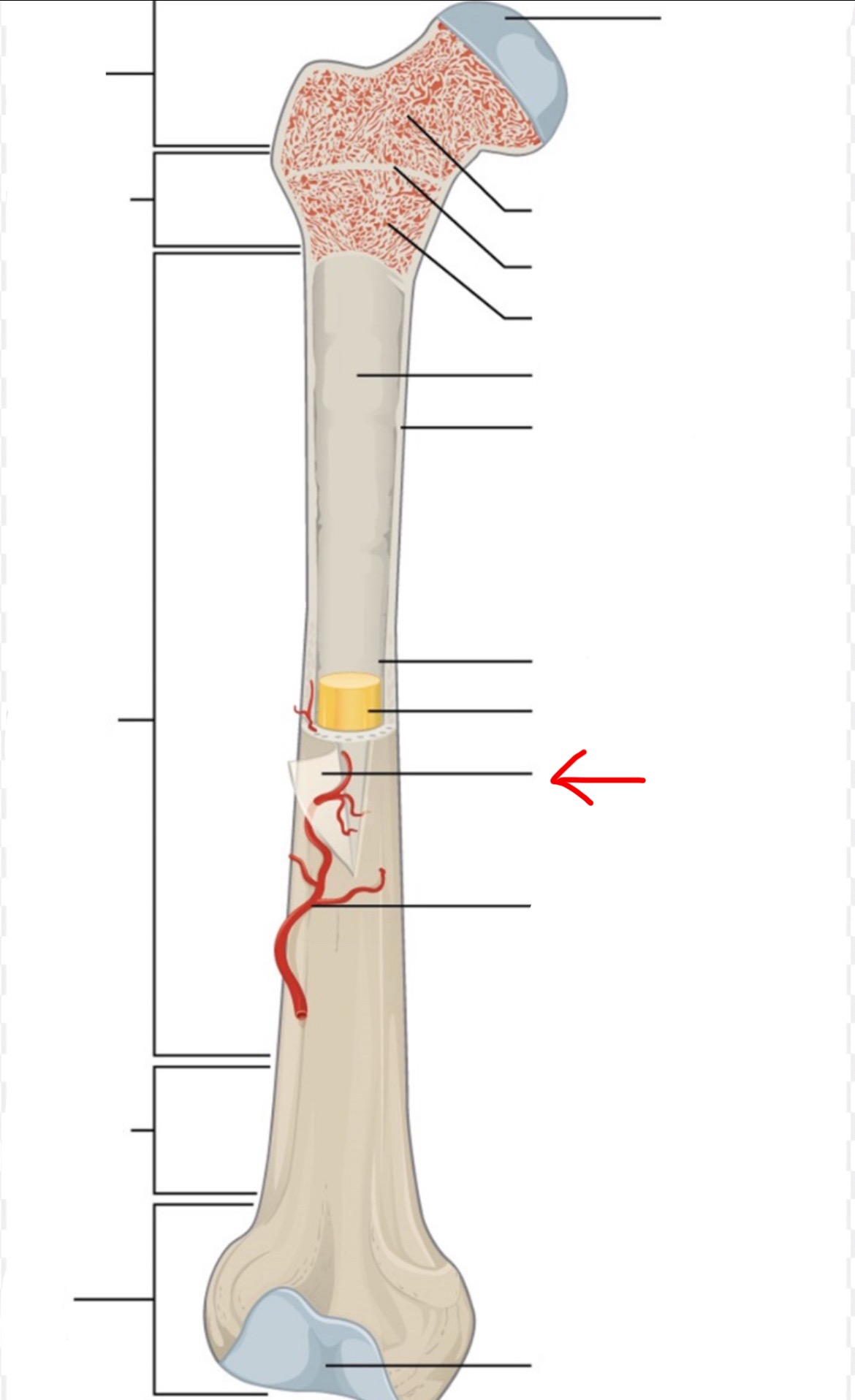
periosteum
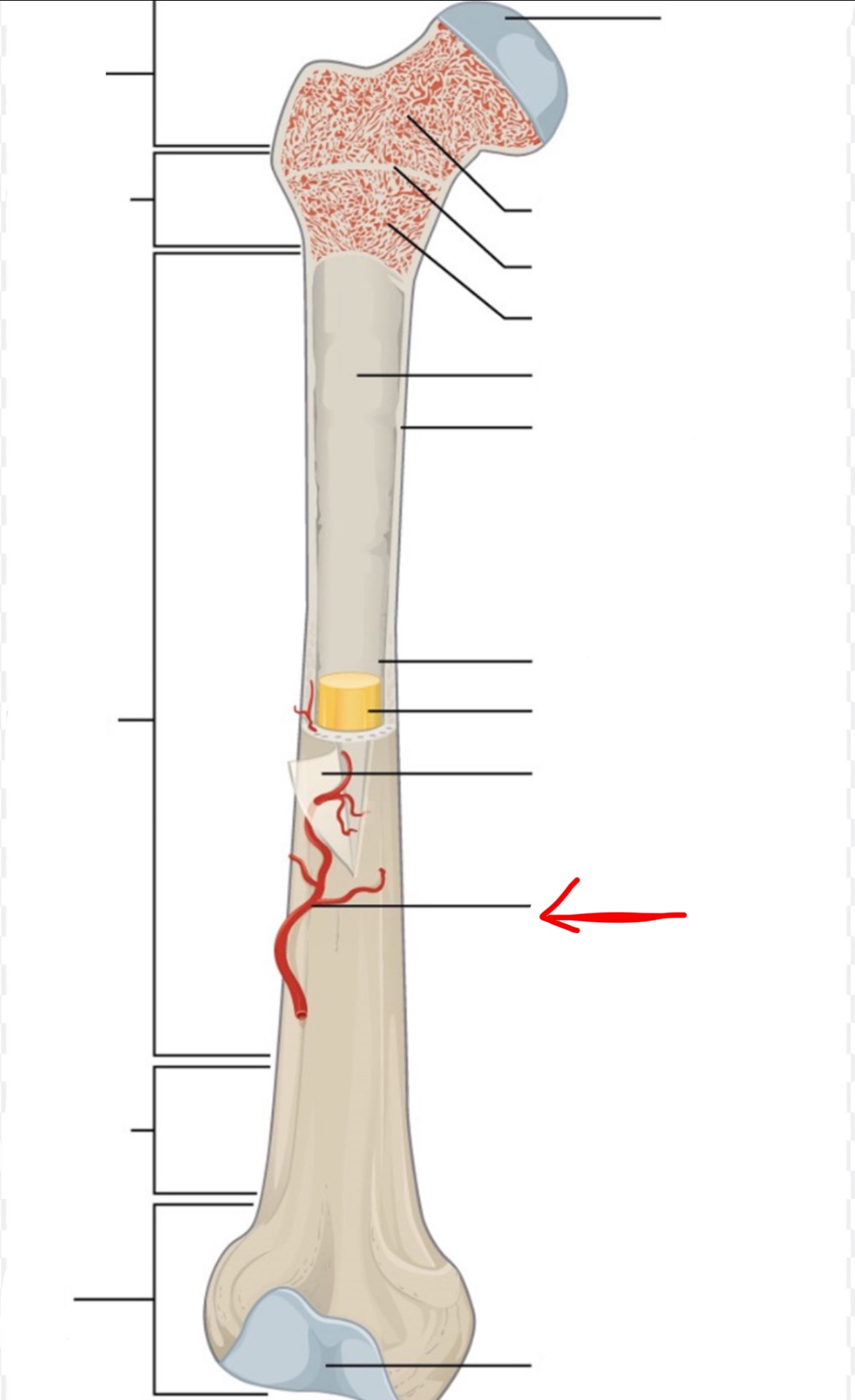
nutrient artery
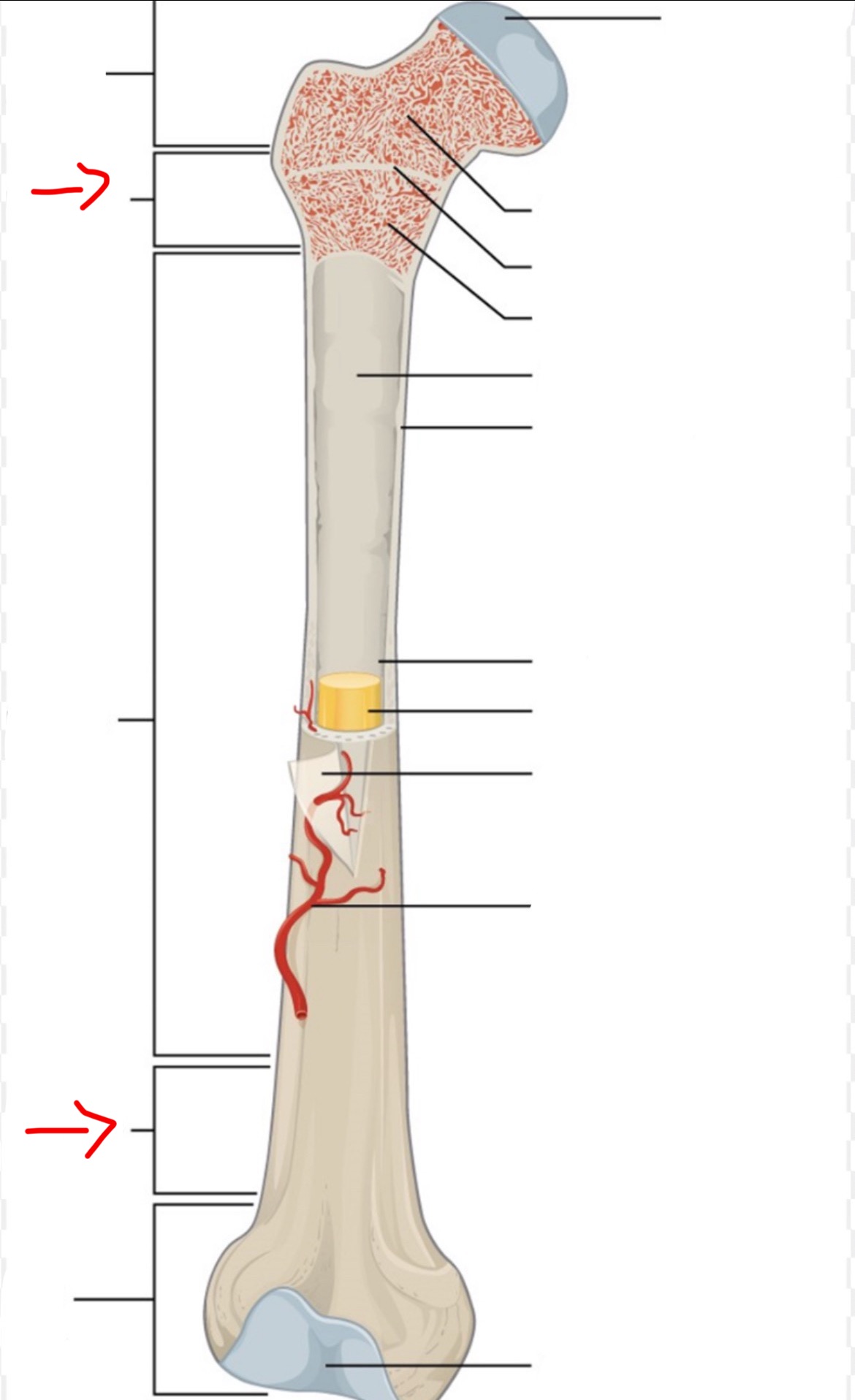
metaphysis
osteon
basic structural unit of bone tissue
central canal
contains nerves and vasculature
concentric lamellae
layered circles that surround the central canal
lacuna
pockets in concentric lamellae
osteocytes
cells within lacunae that make bone
canaliculi
connect lacunae to central canal to receive nutrients
epiphyseal plate
made of cartilage and open for bone growth
epiphyseal line
made of bone marks and ends bone growth
growing bone
diaphysis is growing not the epiphysis
hayline cartilage
most abundant, flexible, makes up growth plate, covers articulating surfaces
fibrocartilage
stiff and tough, absorbs shock, found in intervertebral discs
elastic cartilage
least abundant, most flexible, found in ear and epiglottis
true ribs
7 pairs
false ribs
5 pairs
floating ribs
2 pairs
cervical vertebrae
7
thoracic vertebrae
12
lumbar vertebrae
5
sacrum
5 fused
coccyx
3-5 fused
number of ribs
24 ribs
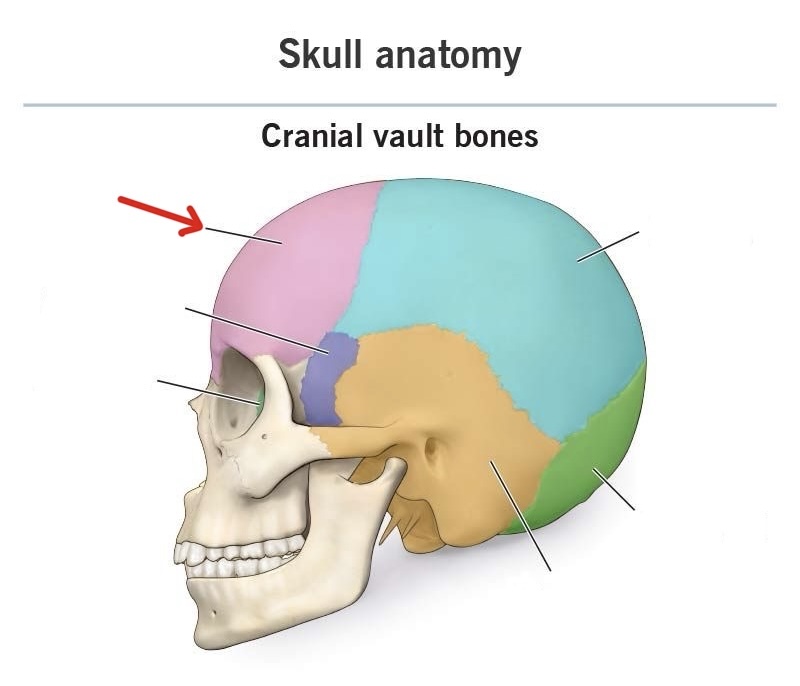
frontal
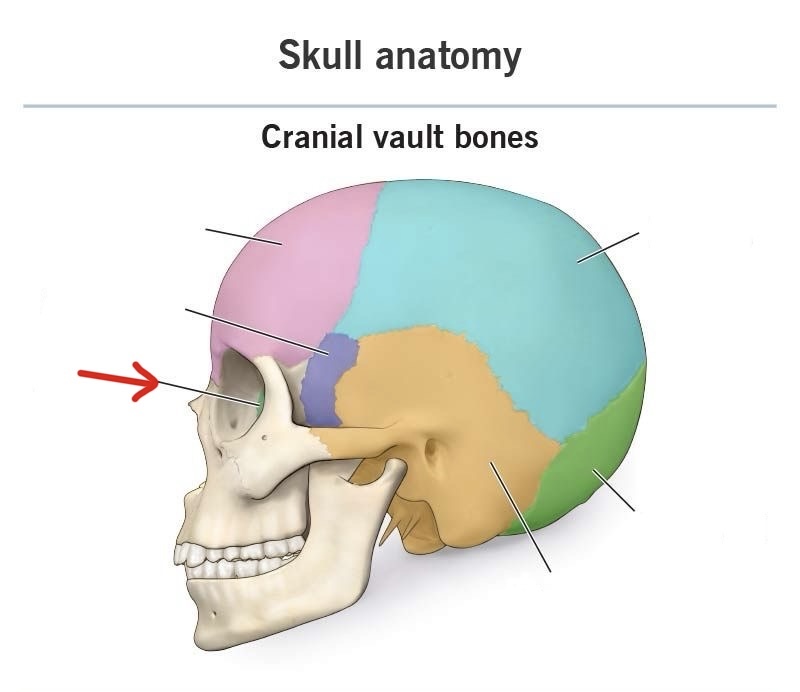
ethmoid
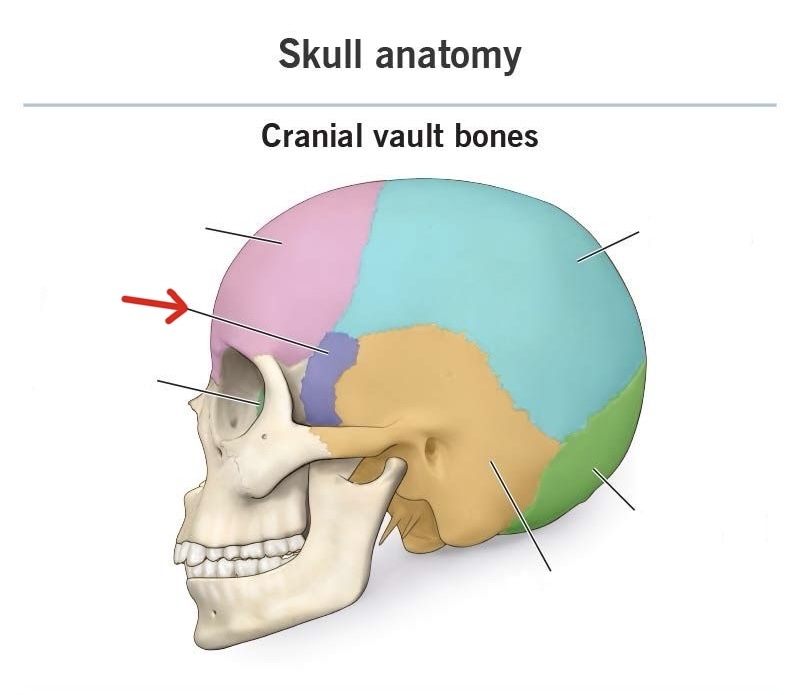
sphenoid
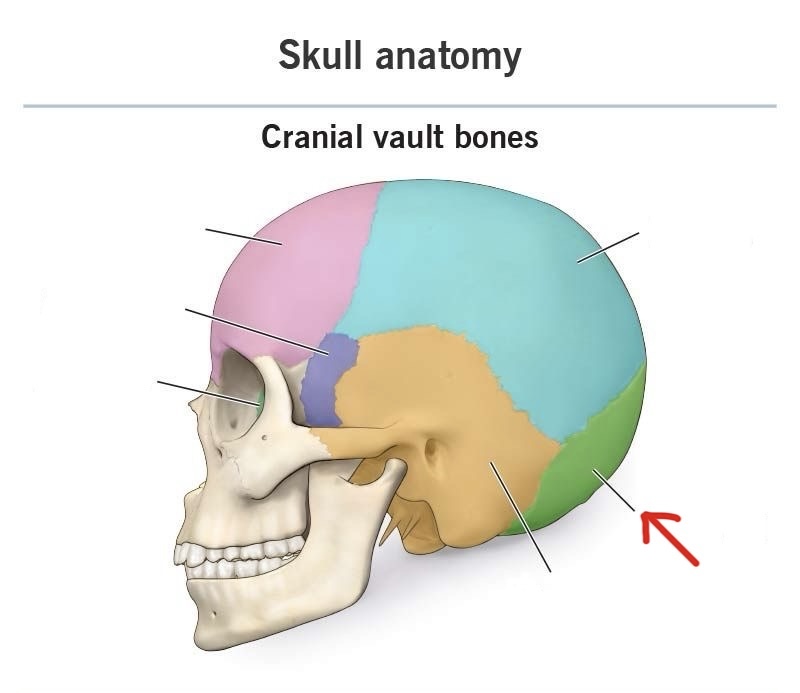
temporal
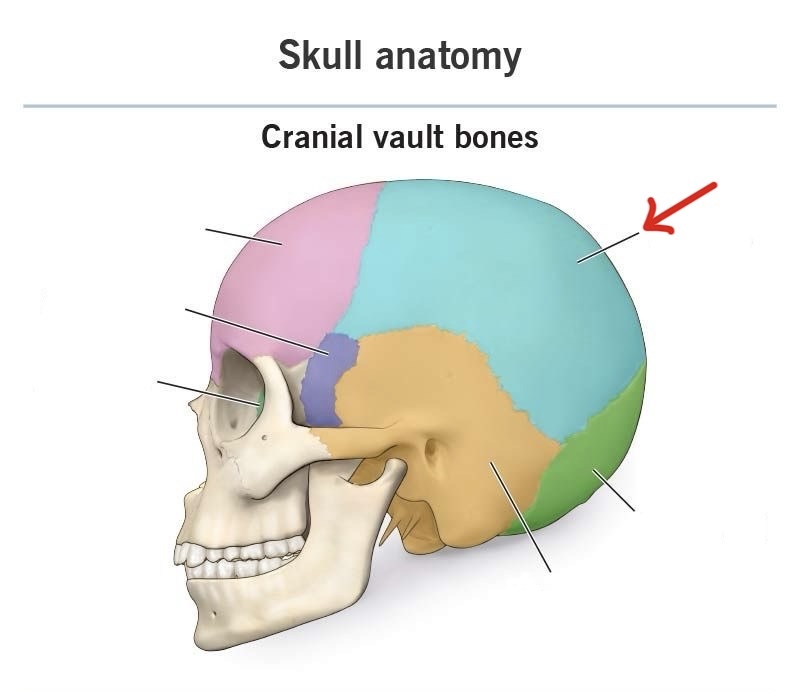
parietal
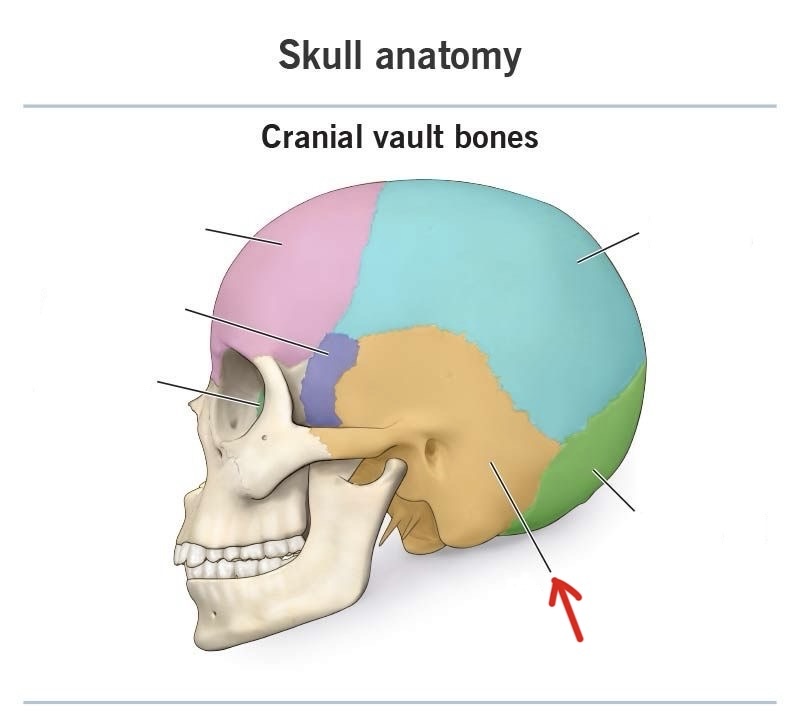
occipital
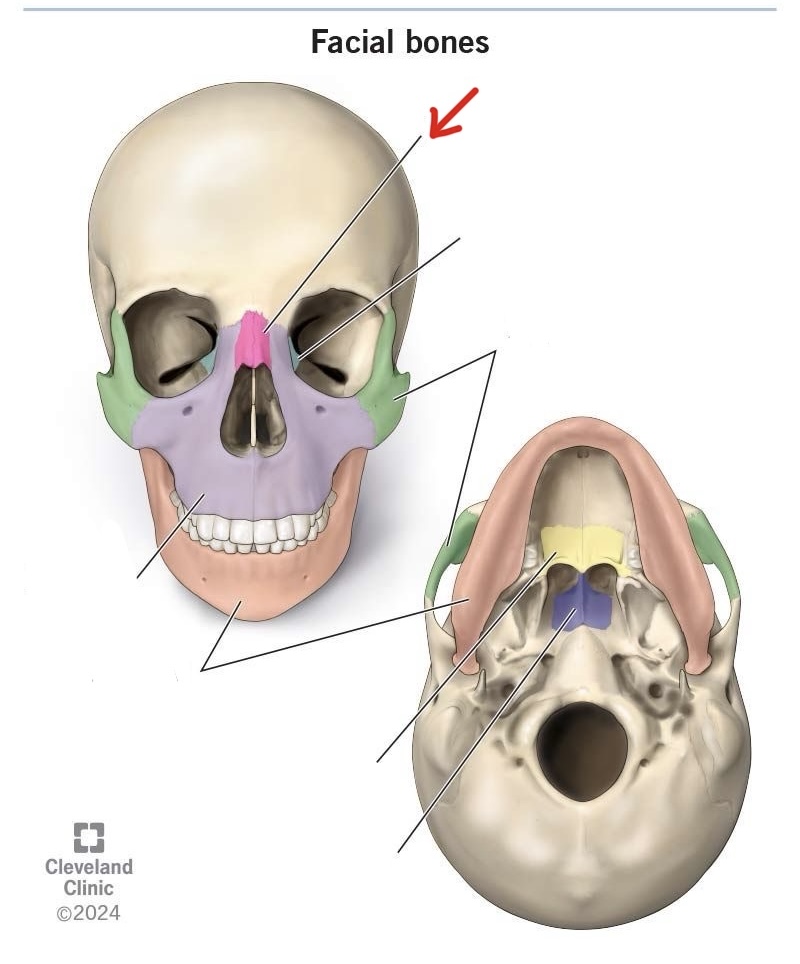
nasal bone
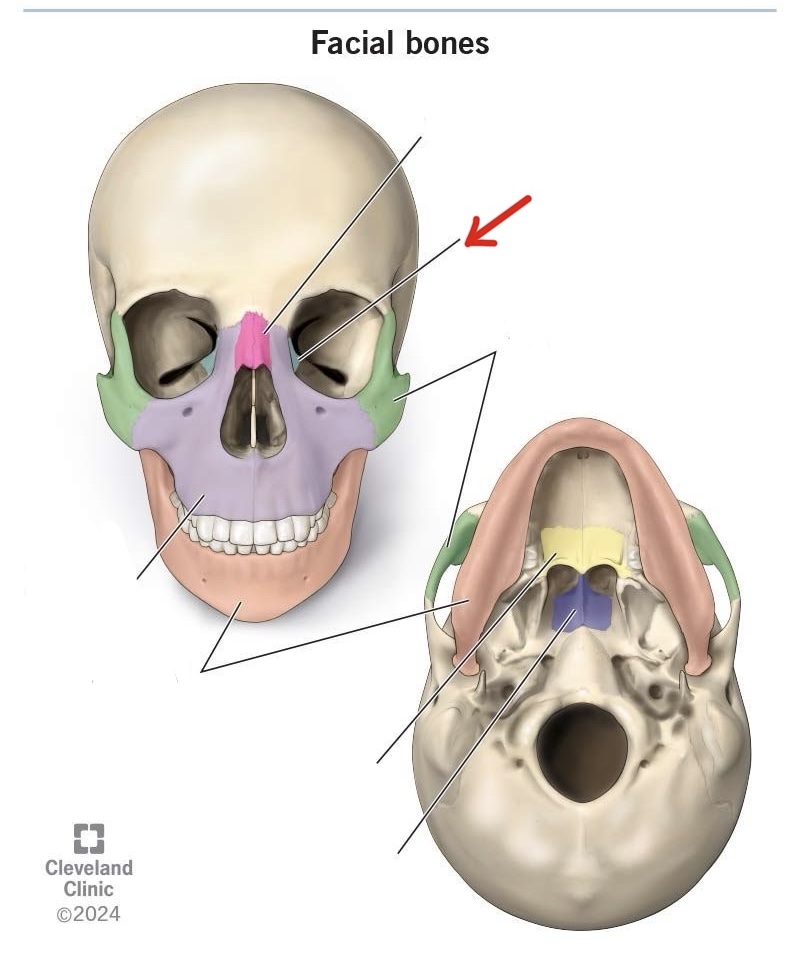
lacrimal bone
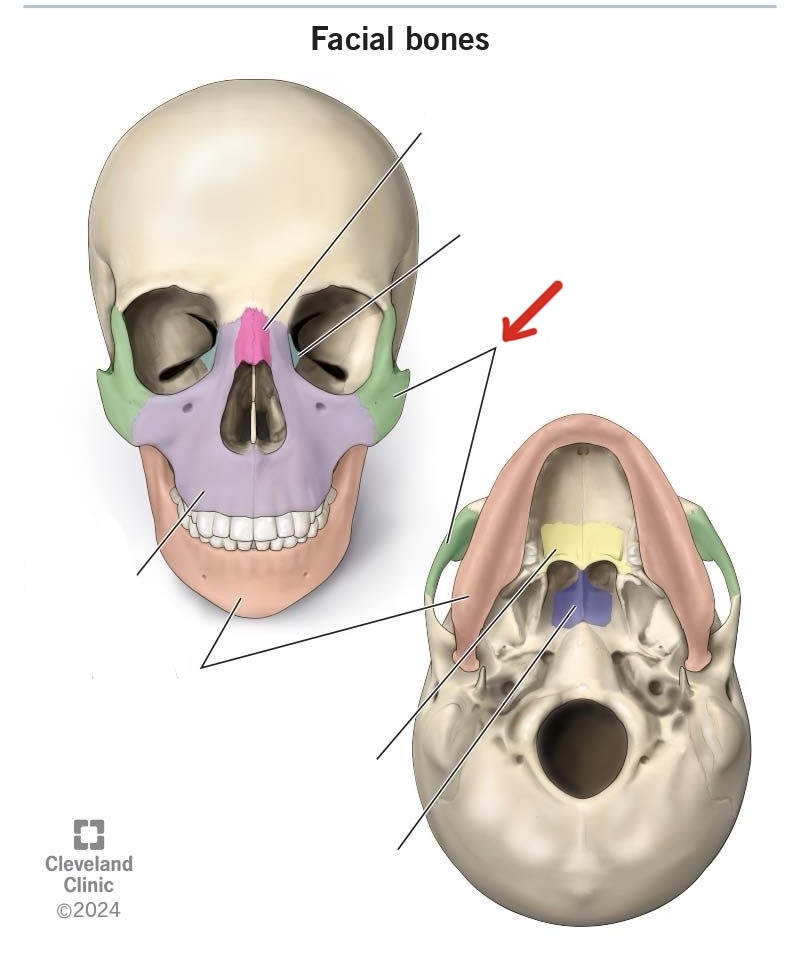
zygomatic bone
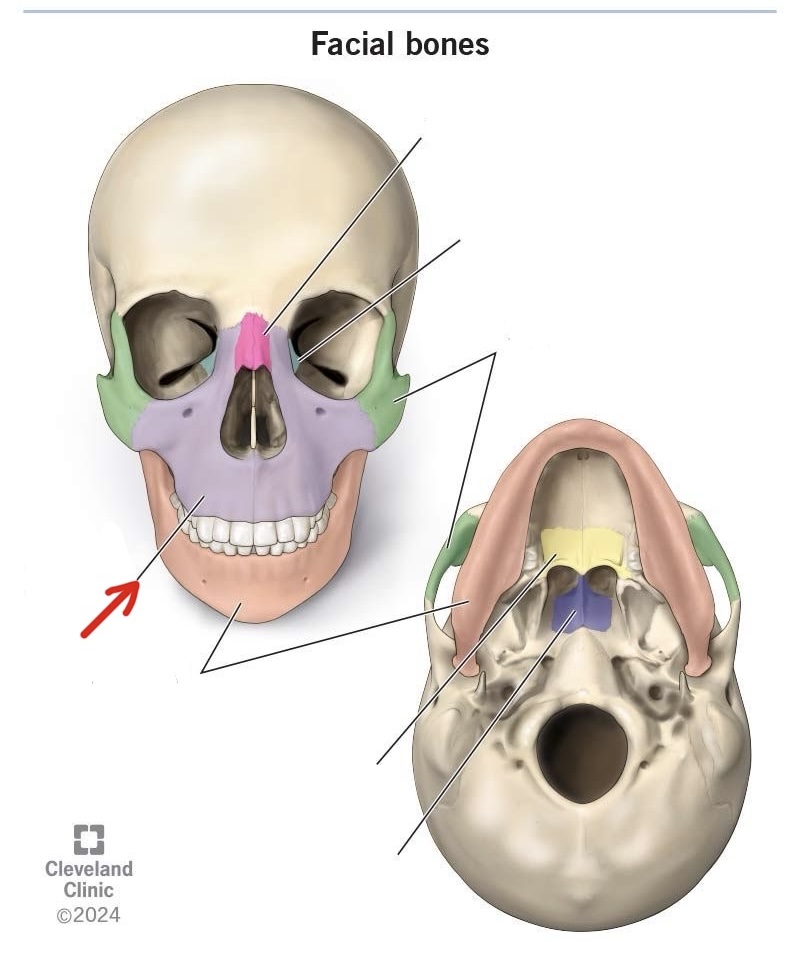
maxilla
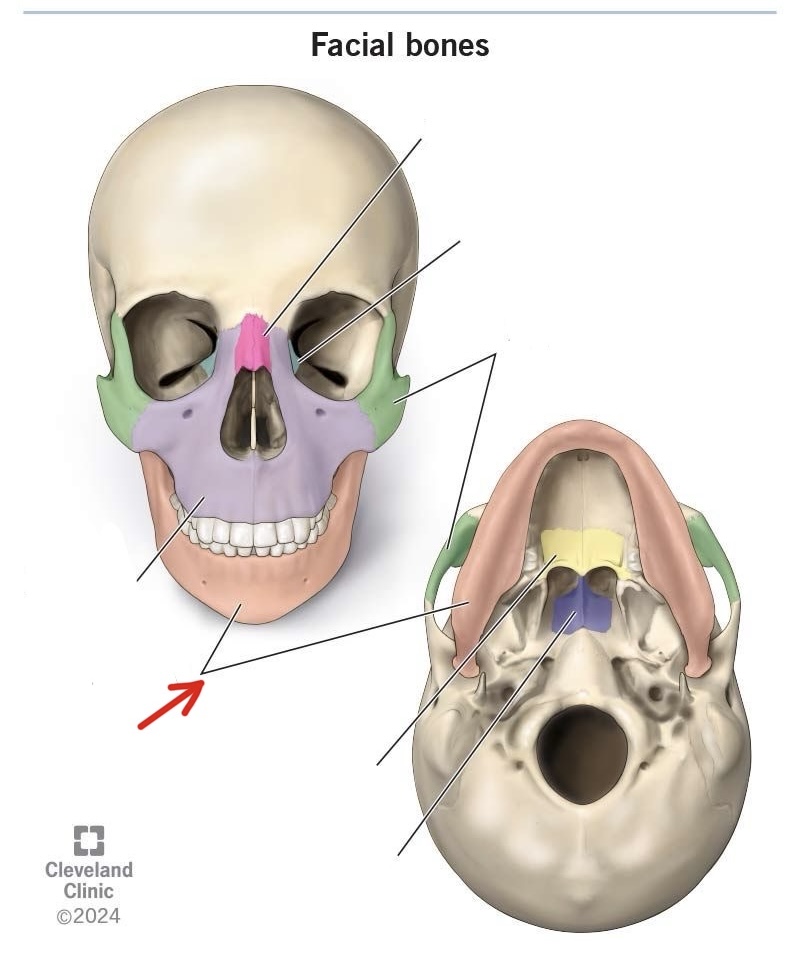
mandible
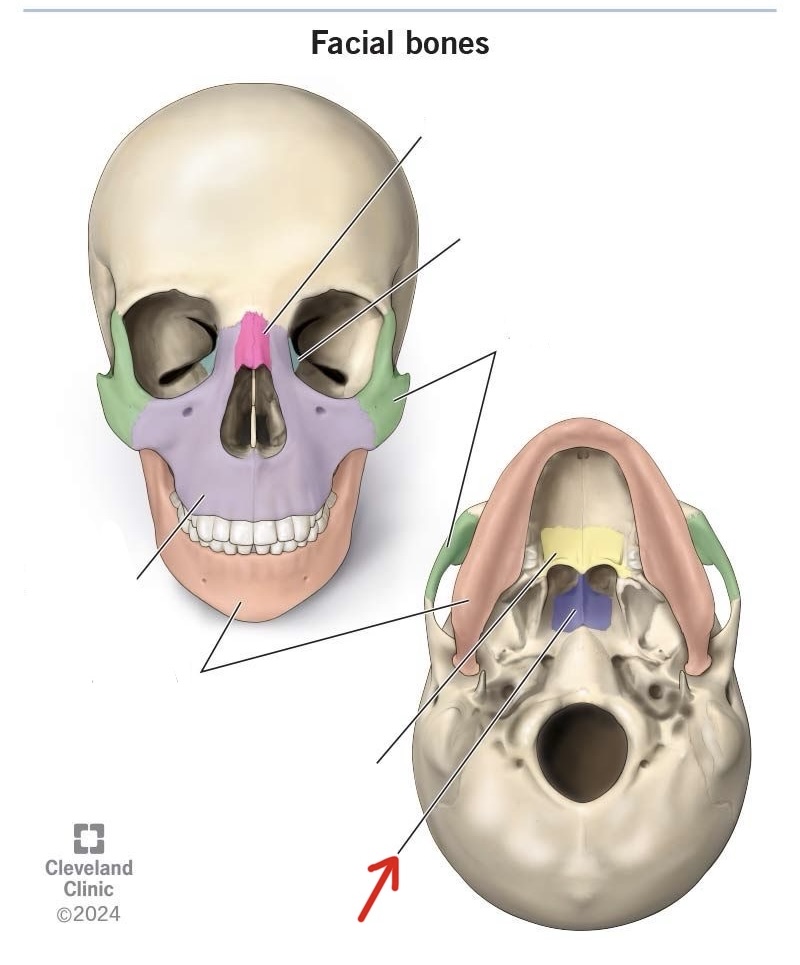
vomer
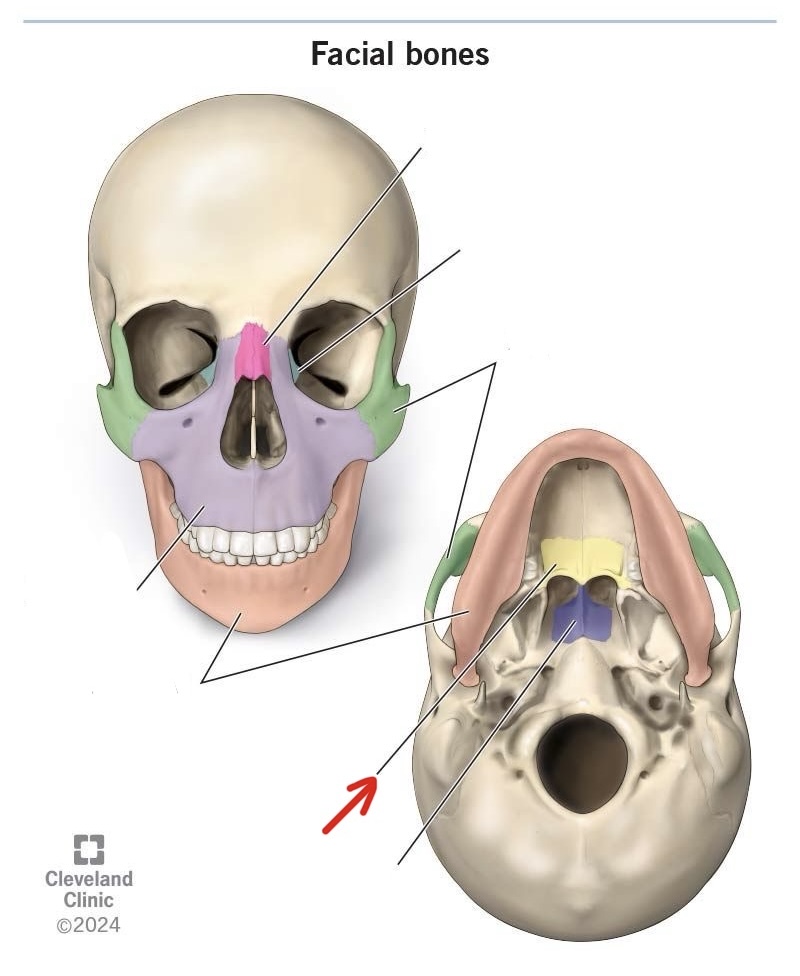
palatine
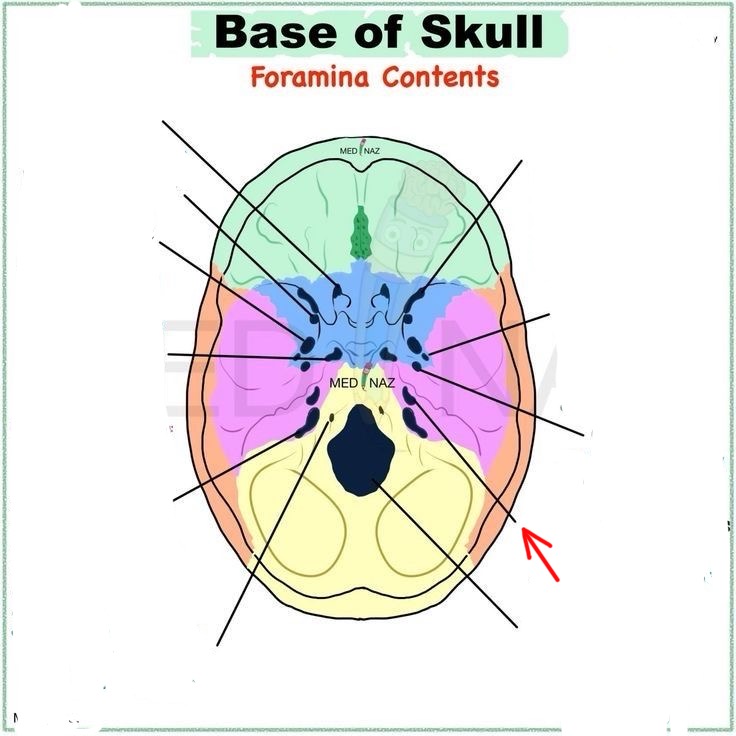
internal acoustic meatus
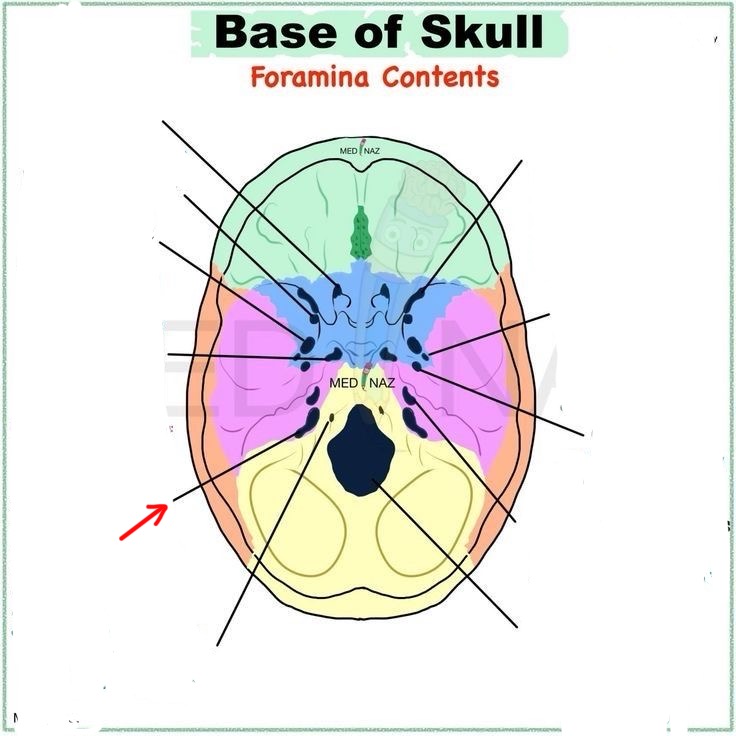
jugular foramen
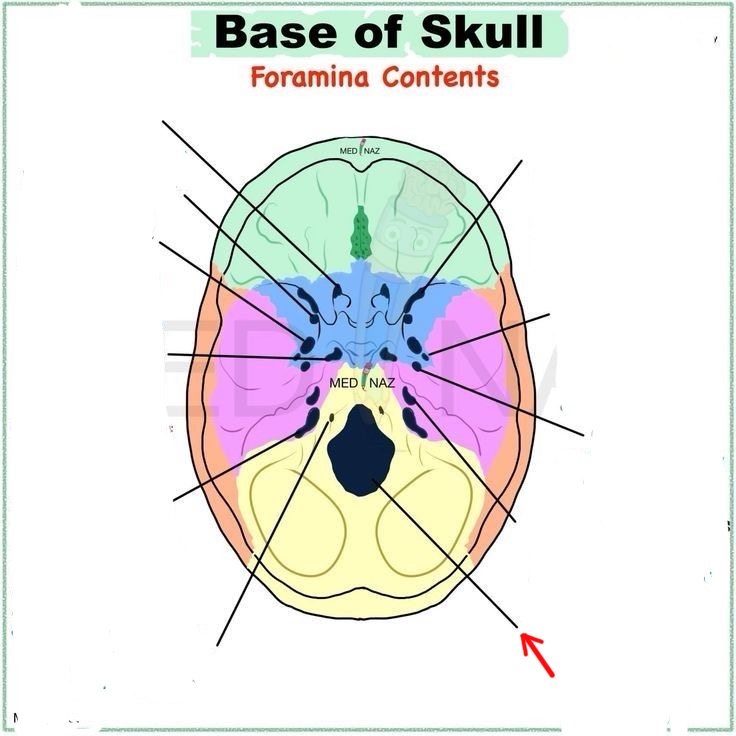
foramen magnum
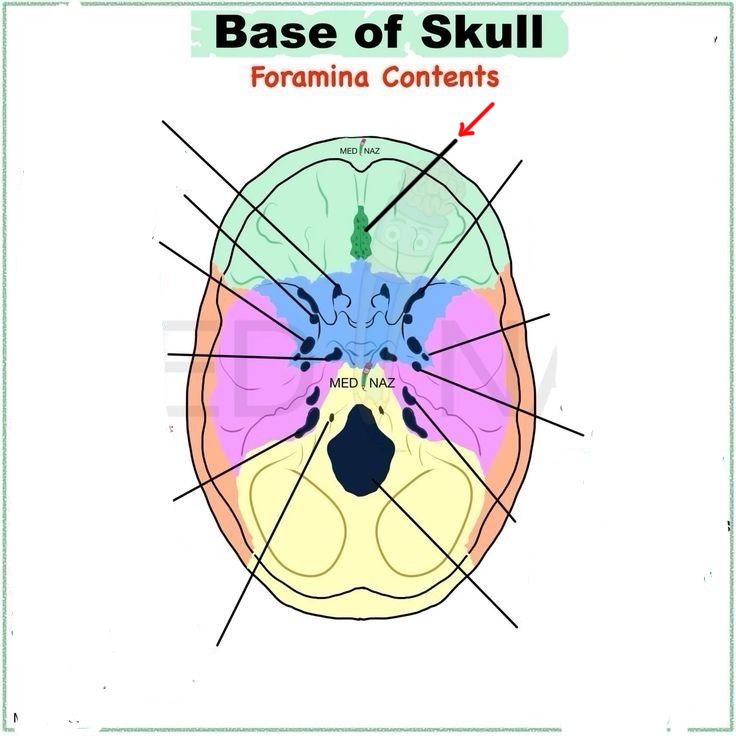
cribriform foramina
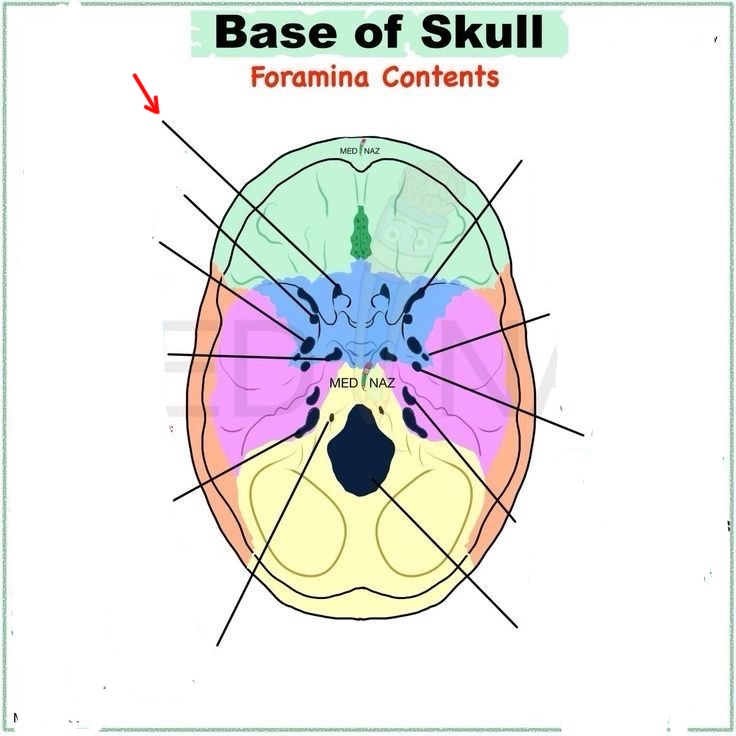
optic canal
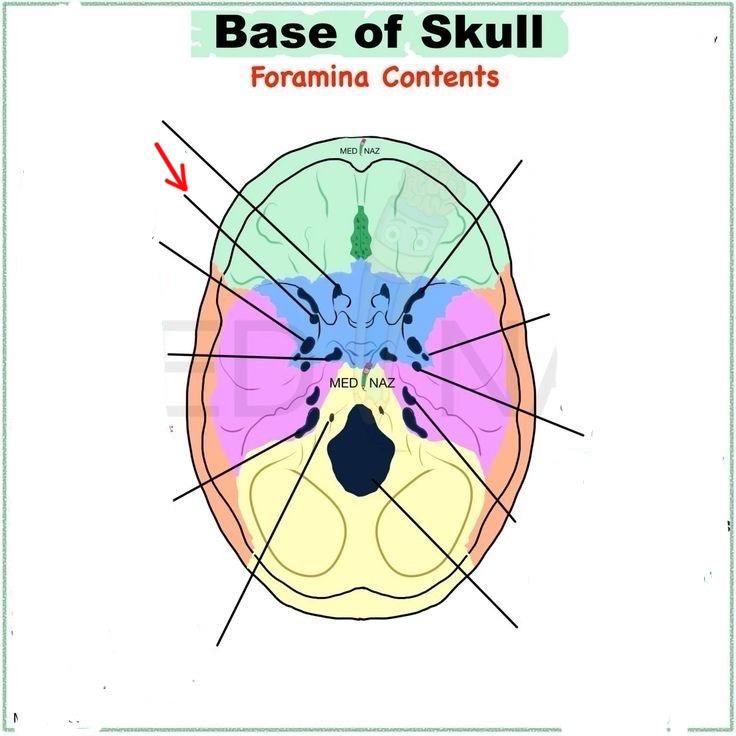
foramen rotundum
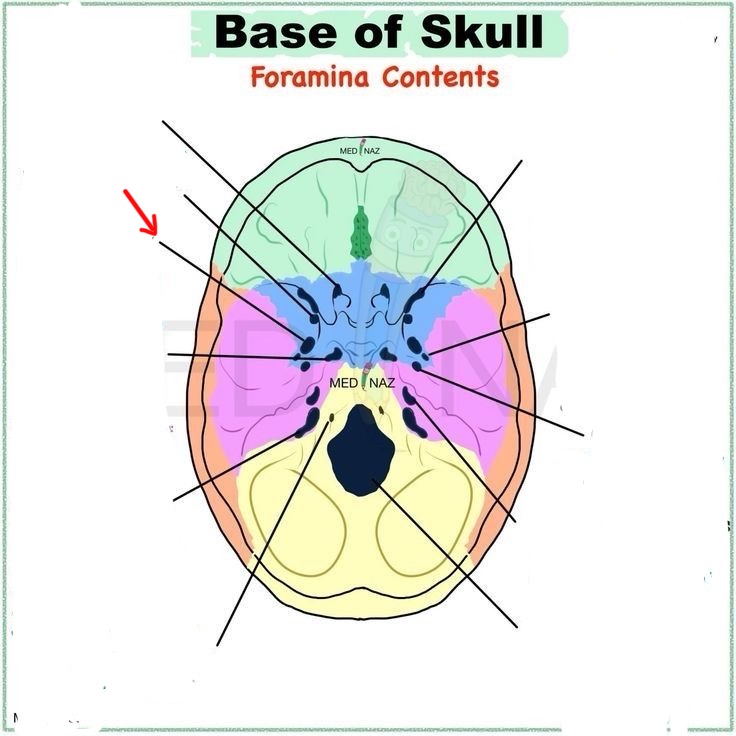
foramen ovale
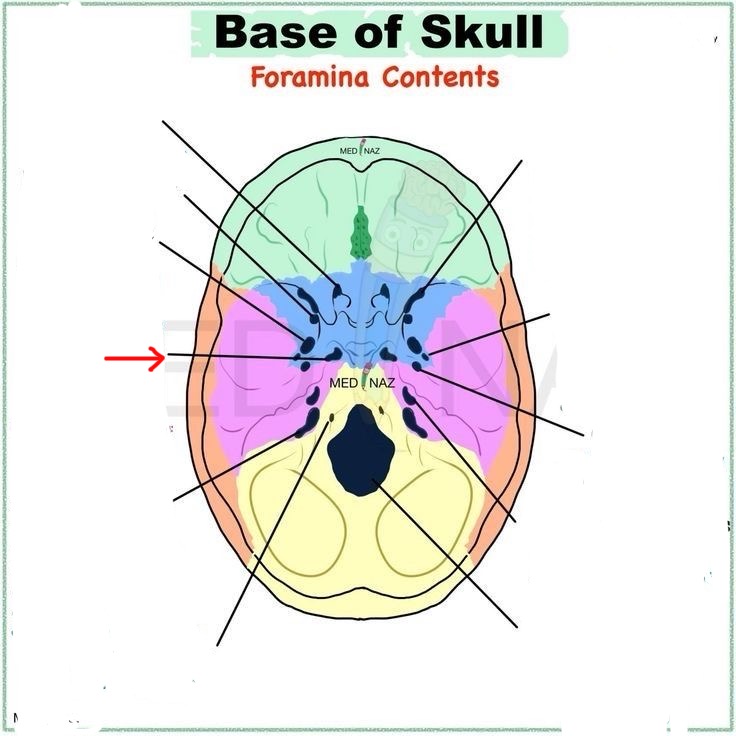
foramen lacerum
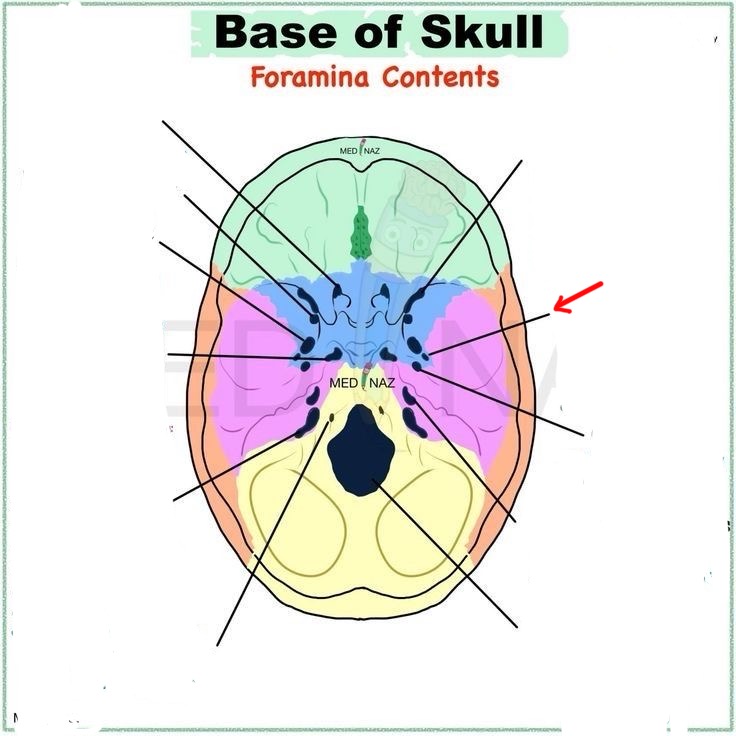
foramen spinosum
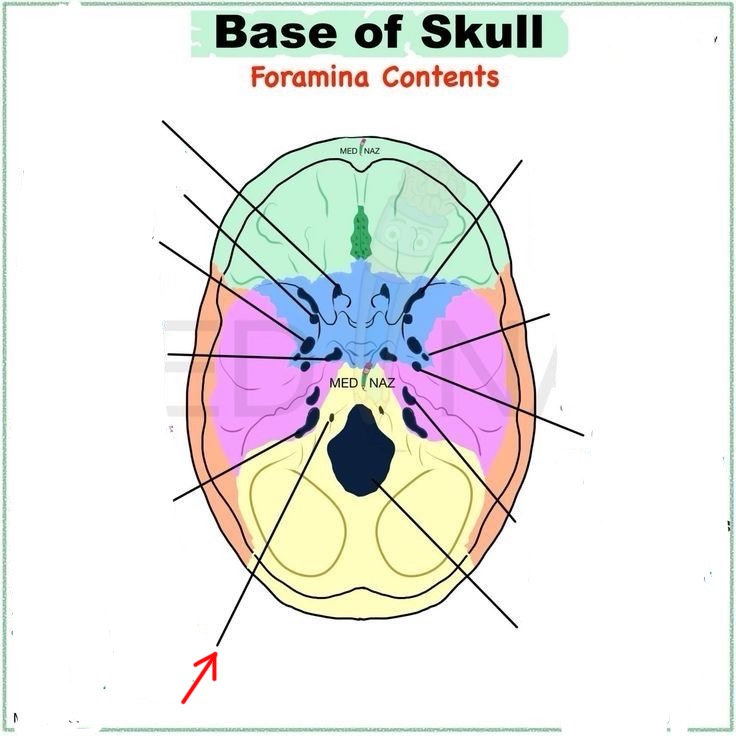
hypoglossal canal
hyoid
“floats” at the C3 vertebrae level, doesn’t articulate to other bones
cornu
horn
cervical vertebrae shape
concave
thoracic vertebrae shape
convex
lumbar vertebrae shape
concave
sacral vertebrae shape
convex
atlas
C1, holds the head
axis
C2, head rotation rubs against C1
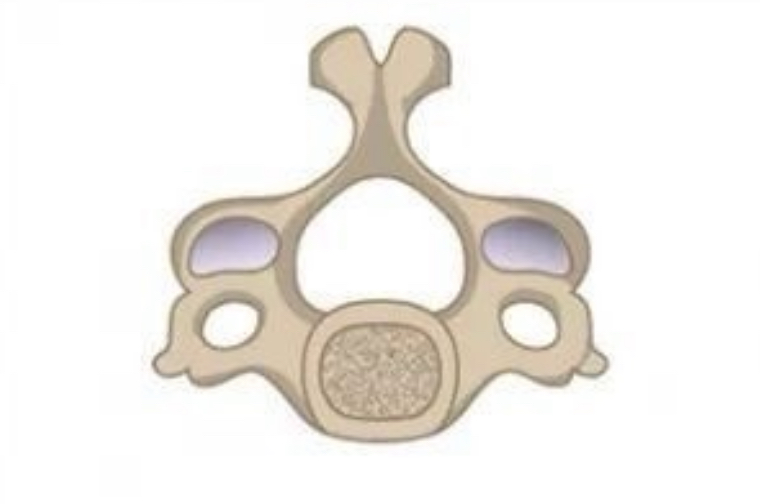
cervical vertebrae
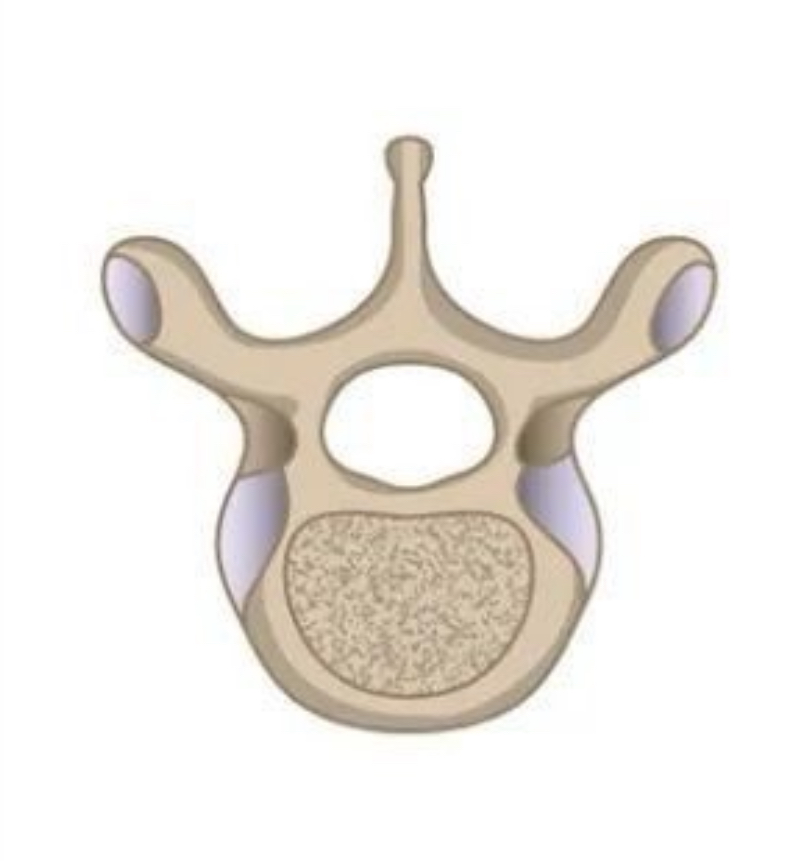
thoracic vertebrae
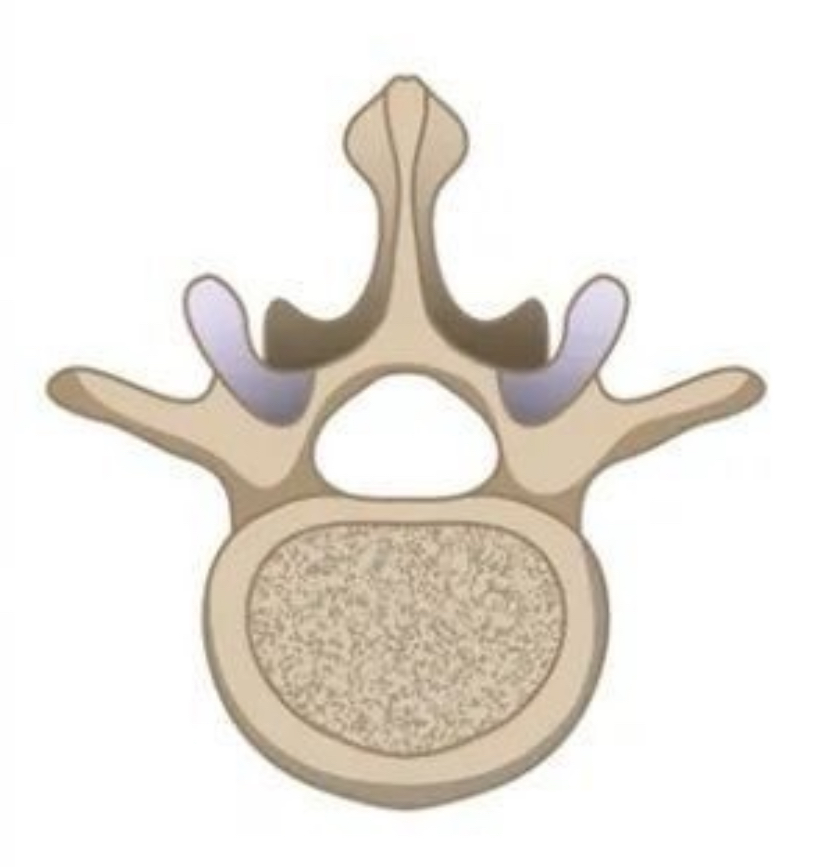
lumbar vertebrae
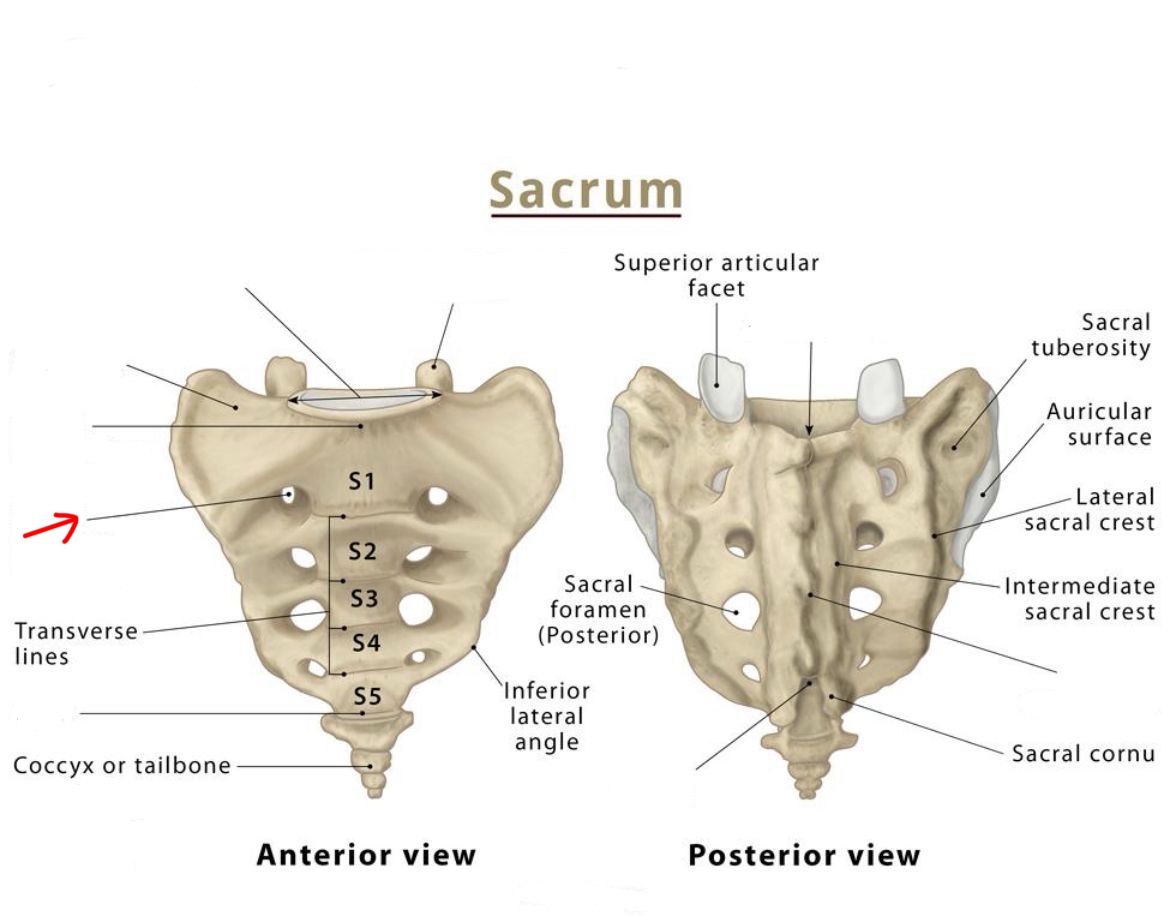
Sacral foramina
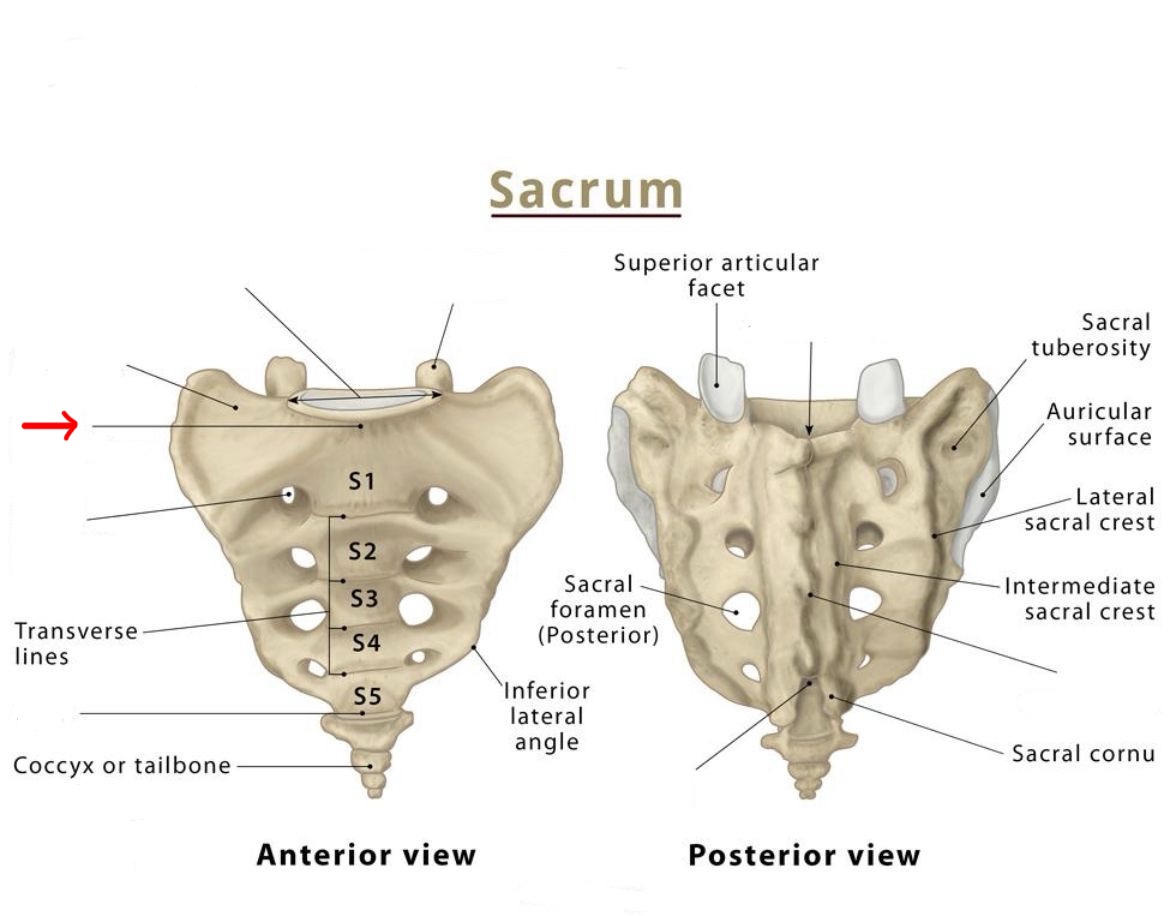
sacral promontory
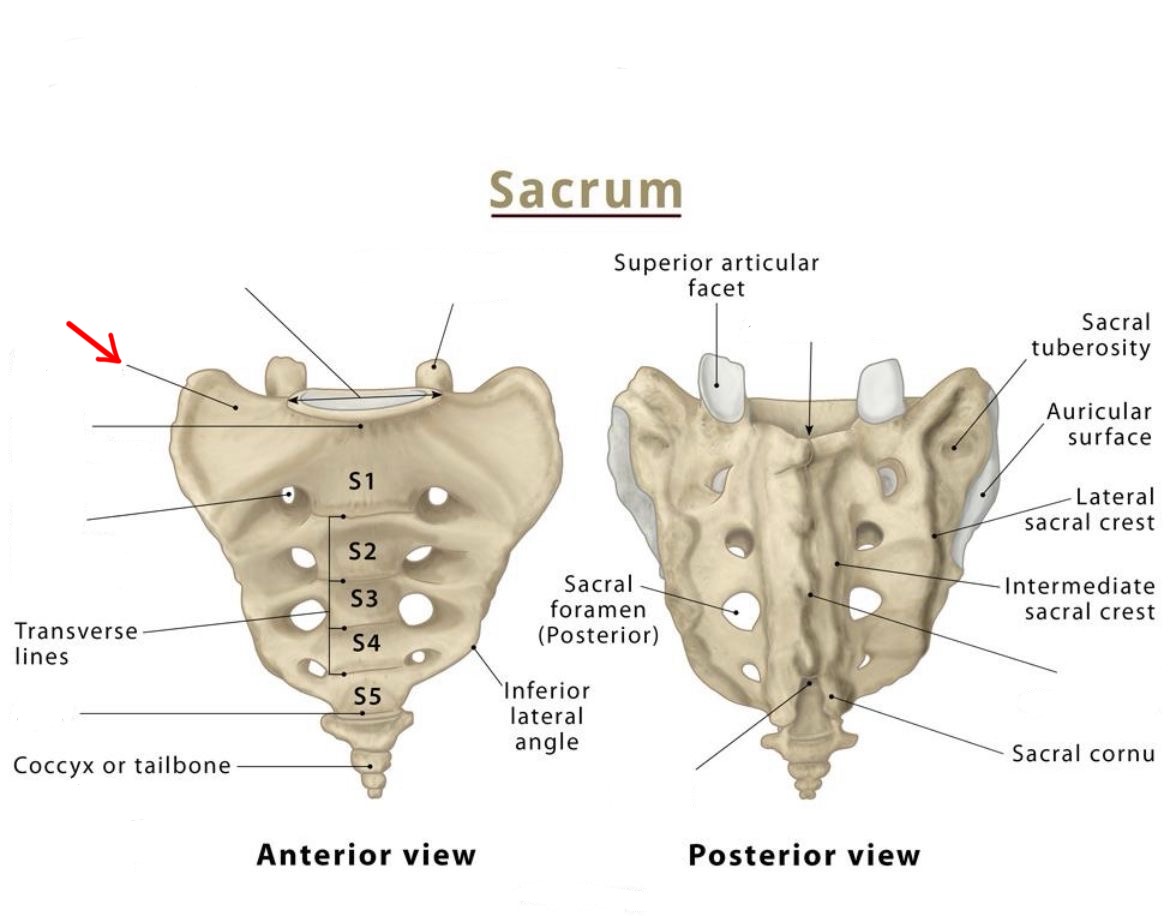
ala
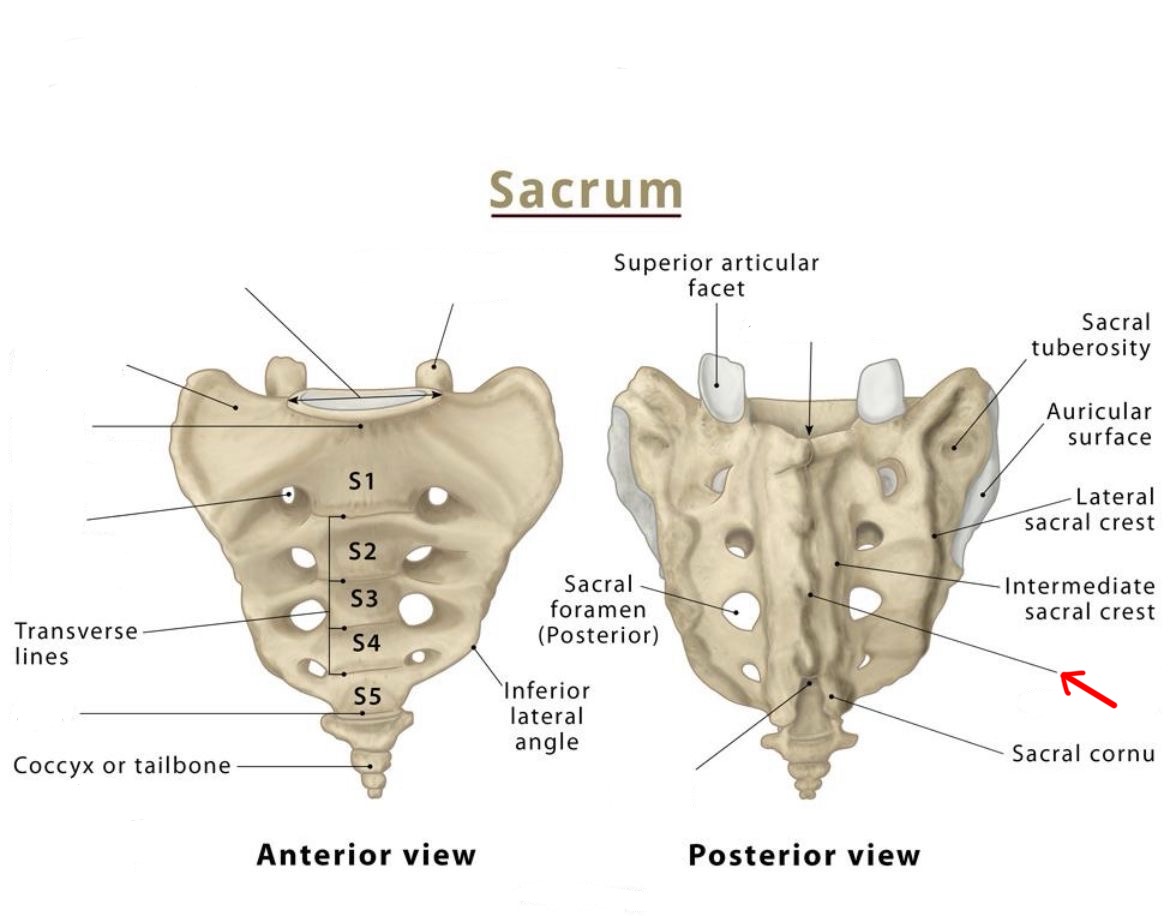
sacral crest
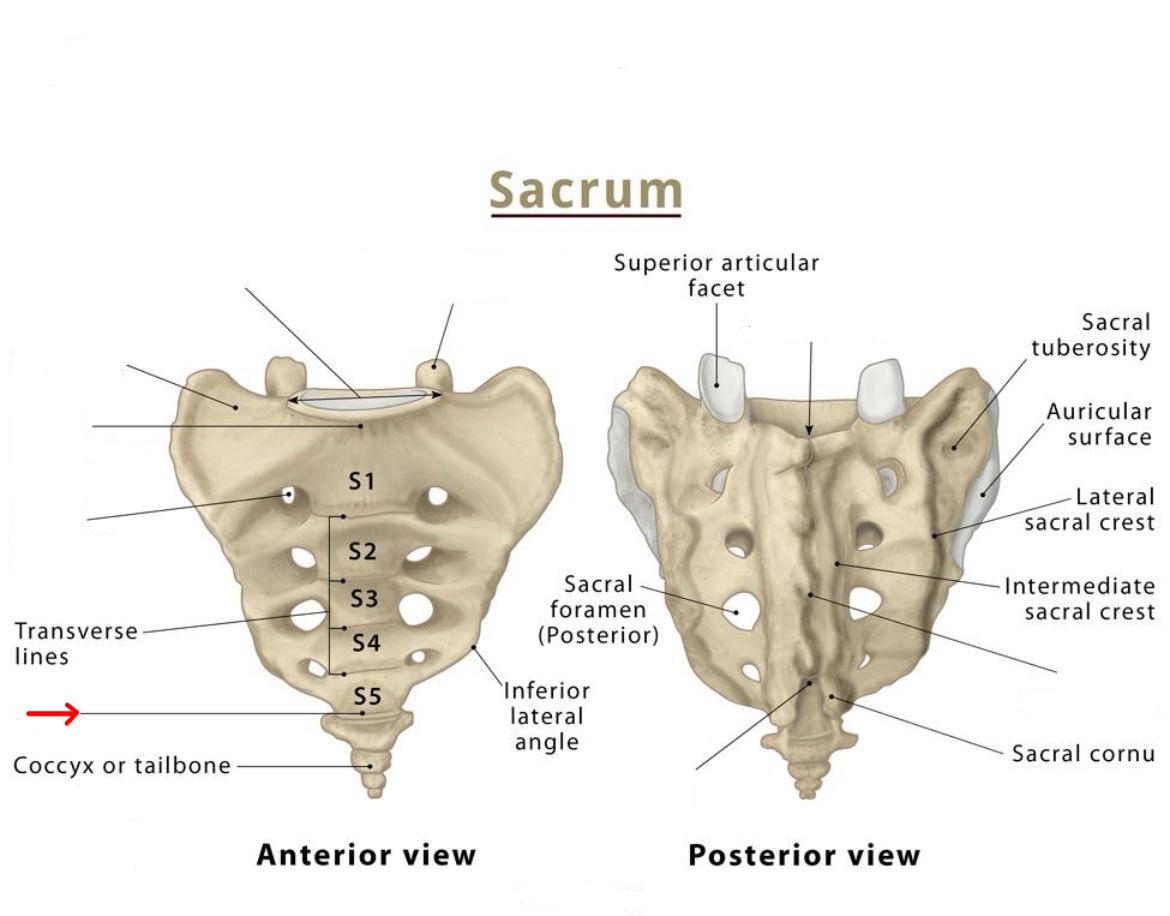
apex
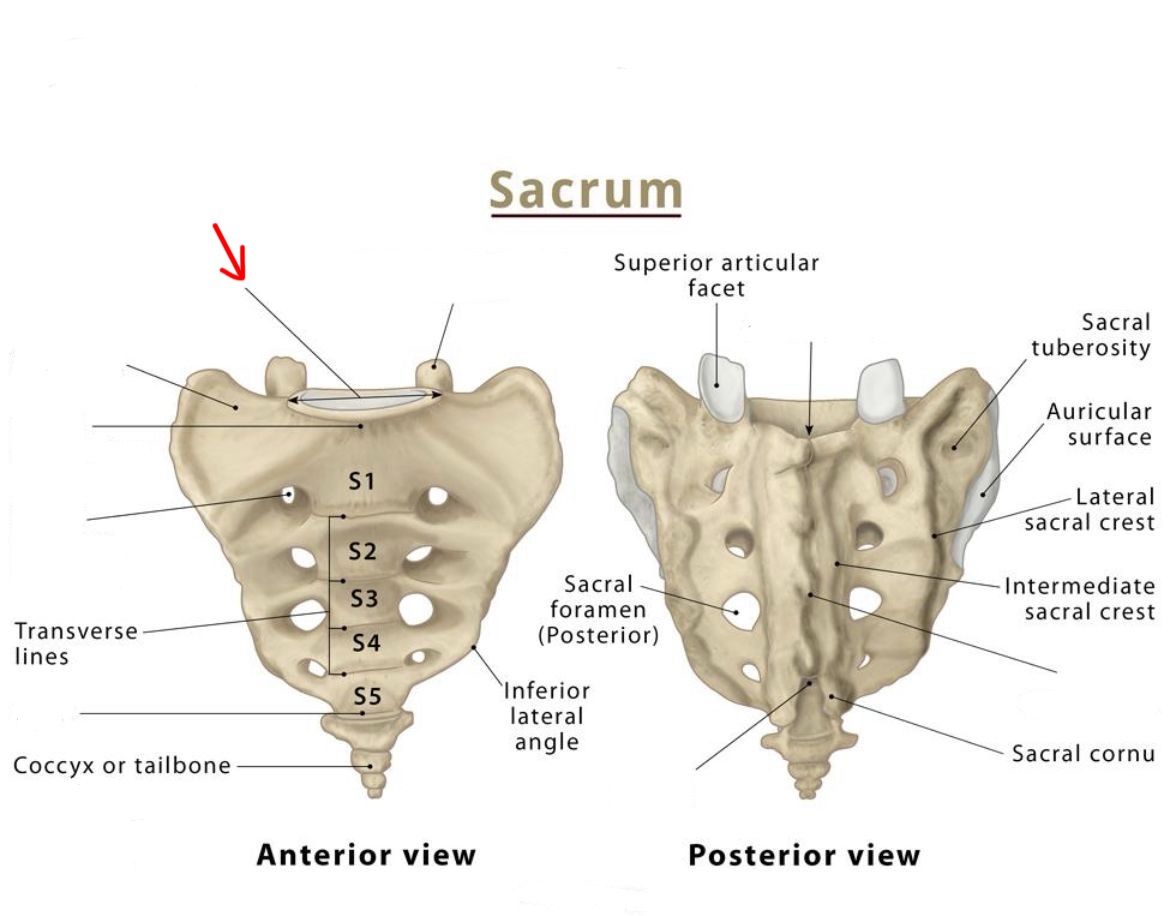
base
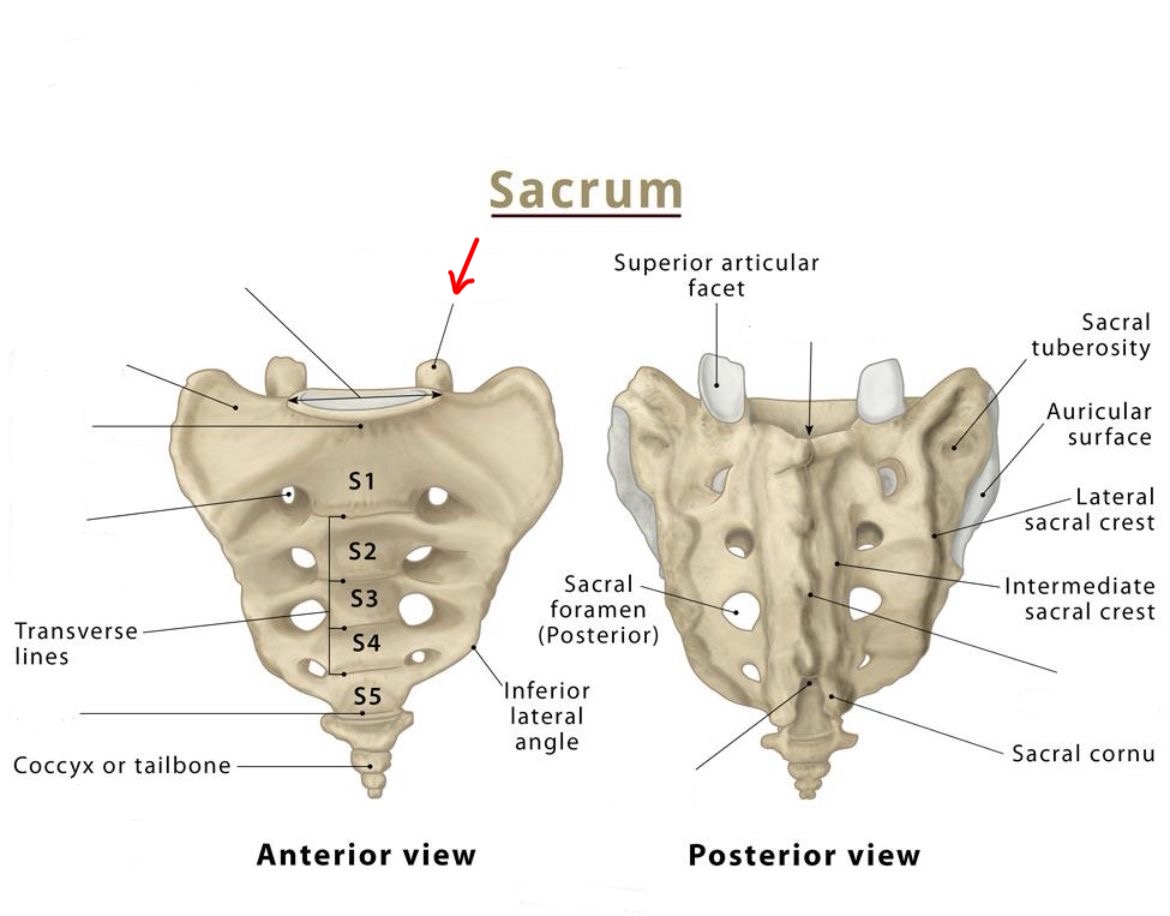
superior articular process
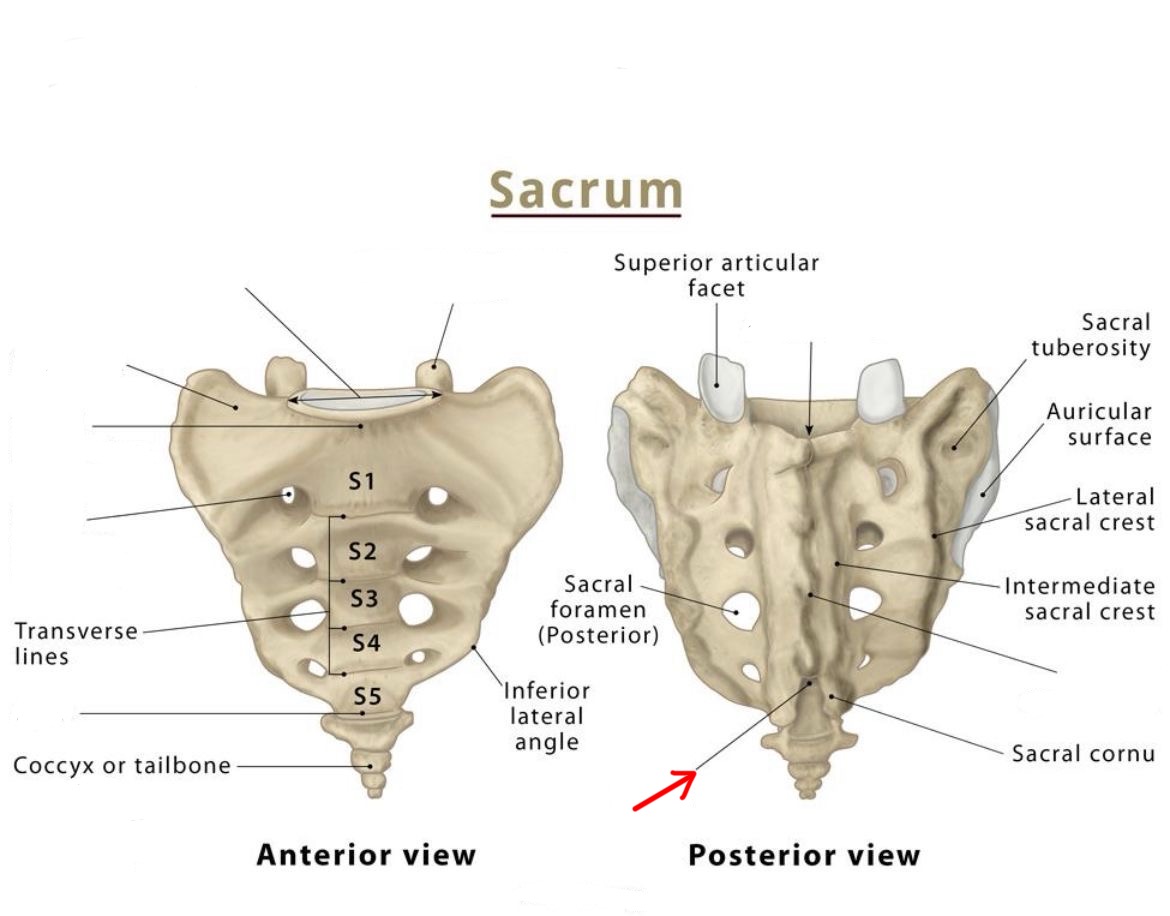
sacral hiatus
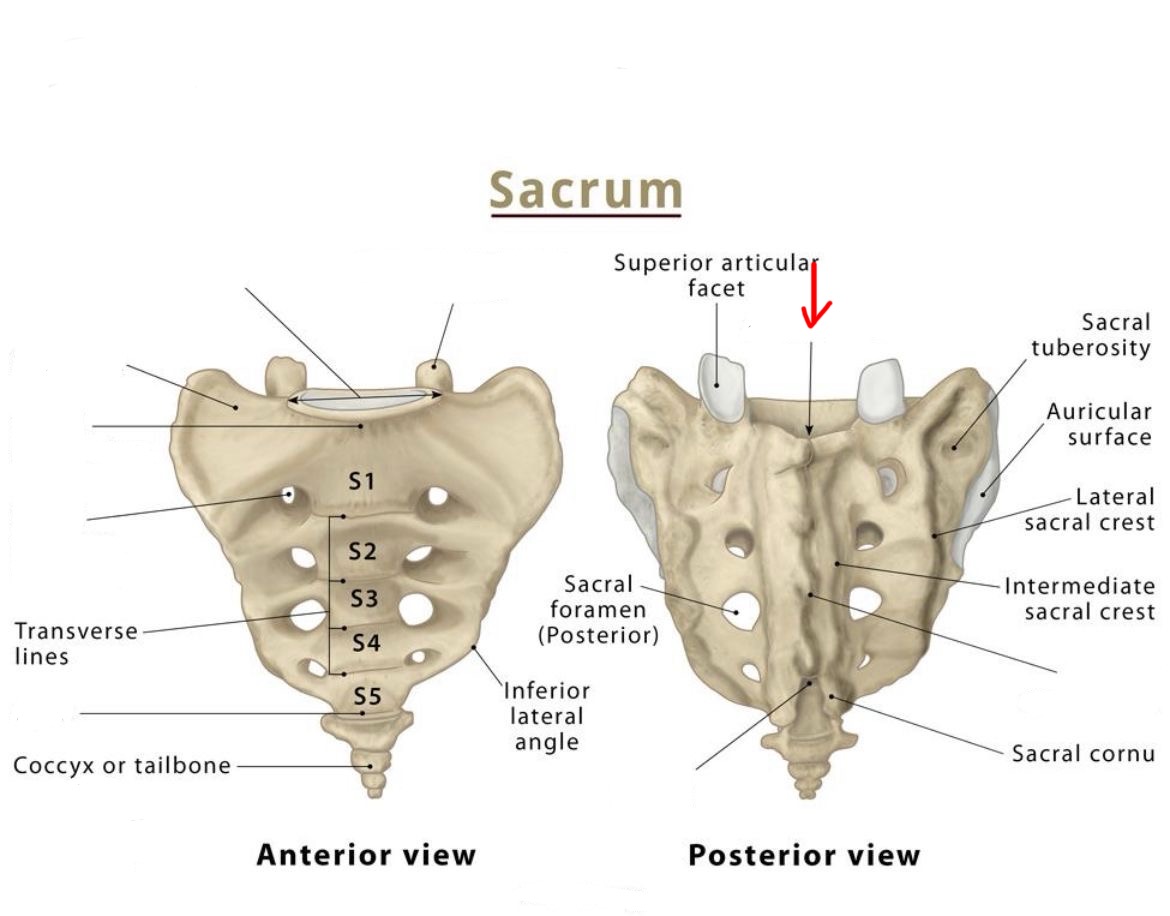
sacral canal
scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature, s shape
kyphosis
exaggerated thoracic curvature, hunchback
lordosis
exaggerated lumbar curvature, common in pregnant women
sternum
3 fused bones
manubruim