Biology 1 - Lifestyle, Health, and Risk
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
what is a monosaccharide?
a single sugar molecule (glucose, galactose, fructose)
what is a disaccharide?
two chemically reacted monosaccharides
what is a polysaccharide?
a complex carbohydrate made up of multiple monosaccharides
why is glucose a hexose monosaccharide?
because it has 6 carbon atoms
how is alpha glucose different to beta glucose?
alpha glucose has a hydroxyl group on the first carbon positioned down, while beta glucose has it positioned up
how do monomers become polymers?
condensation (monomer-dimer-polymer)
what is the pattern of OHs in an alpha glucose
ddud (down down up down)
what is the pattern of OHs in a beta glucose?
udud (up down up down)
how do glucose molecules bond
condensation (removal of 1 water molecule)
what kind of bond do glucose molecules make?
glycosidic bonds
how do beta glucose molecules bond?
every other molecule rotates to match up the water molecules
which carbons bond when glucose molecules bond?
carbon 1 and carbon 4
what shape do alpha glucose molecules make when they bond?
coil
what two monosaccharides make up maltose?
two alpha glucoses
what two monosaccharides make up lactose?
one beta glucose and one galactose
what two monosaccharides make up sucrose?
one alpha glucose and one fructose
4 characteristics of amylose?
alpha glucoses, 1-4 bonds, coil shape, energy store
4 characteristics of amylopectin?
alpha glucoses, 1-4 and 1-6 bonds, branched, energy reserve
4 characteristics of glycogen?
alpha glucose, 1-4 and 1-6 bonds, very branched, energy reserve
3 characteristics of cellulose?
beta glucoses, forms straight lines, 1-4 and 1-6 bonds
how can polysaccharides be split?
hydrolysis
what is a triglyceride?
a lipid
what is a triglyceride made of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what bonds are used in a triglyceride?
ester bonds
what is the difference between saturated and unsaturated lipids in terms of bonding?
saturated lipids dont have any double bonds (between carbon atoms) but unsaturated have 1, polyunsaturated have more than 1
what is a lipoprotein?
a molecule made of lipids and proteins
what is a high density lipoprotein (characteristics)?
mainly protein, transports cholesterol from body tissue, to reduce total blood cholesterol
what is a low density lipoprotein (characteristics)?
mainly lipid, transports cholesterol from liver to blood, to increase total blood cholesterol
what can increased blood cholesterol lead to?
cardiovascular disease (CVD)
why can water be helpful in a cell?
temperature regulation, no rapid temperature changes, keep a stable environment
what bonds does water use to bond to itself?
hydrogen bonds
what does it mean for a molecule to be polar/dipolar?
uneven distribution of electrons leads to an area of negative or positive charge
what is the cardiac cycle?
atrial systole, ventricular systole, cardiac diastole
what does systole mean?
contraction
what does diastole mean?
relaxation
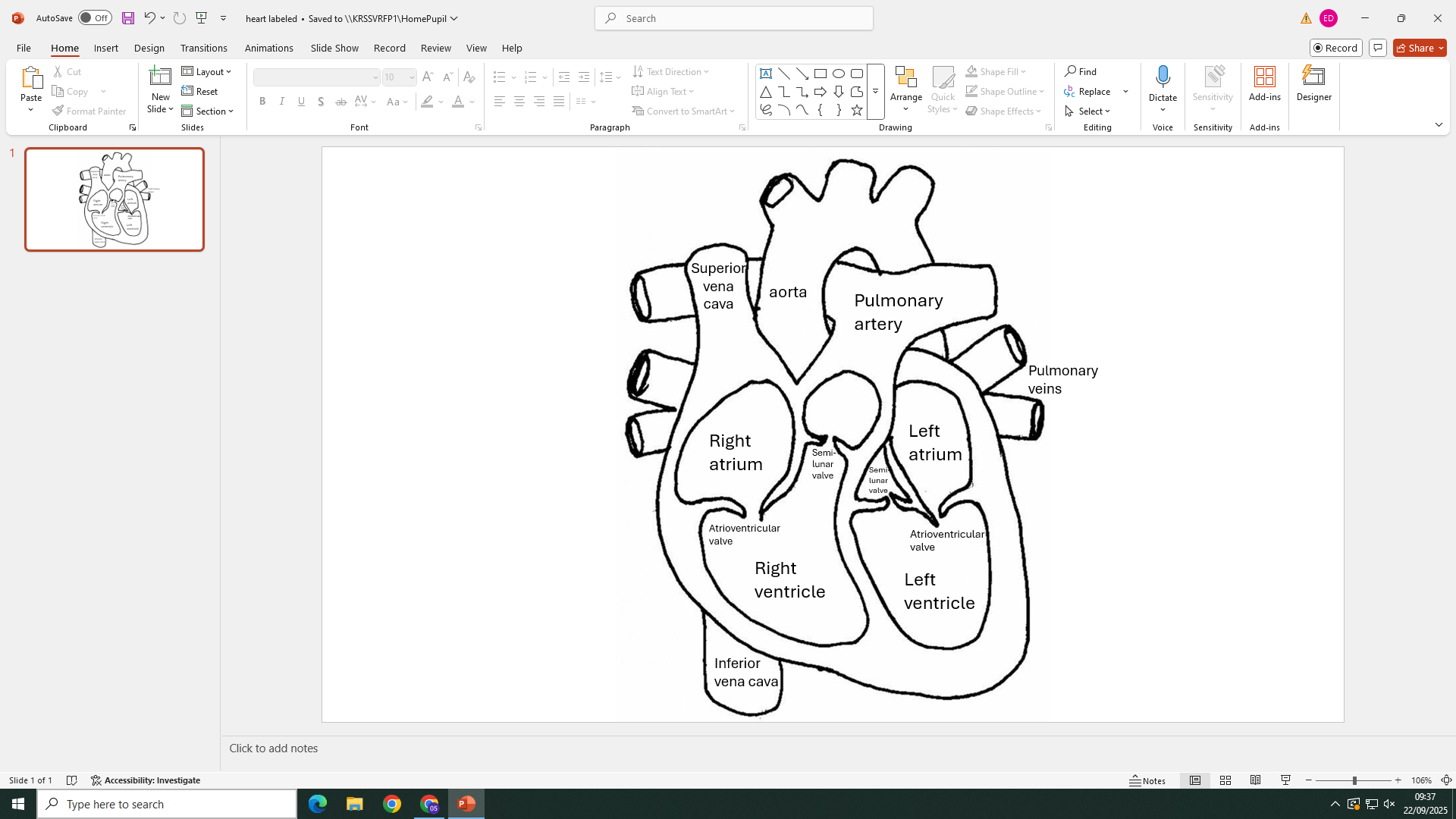
label this heart
structure of an artery + function
thick/muscular/elastic wall, inner lining (endothelium) is folded for expansion, carries blood from heart to rest of body
structure of veins + function
thinner/less elastic walls, larger lumen (space), contains valves, carries blood back to the heart
structure of capillaries + function
one cell thick walls (speeds up diffusion), where metabolic exchange happens
what are the events that lead to atherosclerosis?
damage to the endothelium, WBCs create fatty streaks, over time it hardens to become an atheroma, this restricts blood flow in the artery, hardening of arteries = atherosclerosis
how is a blood clot formed?
thromboplastin released from damaged blood vessel, thrombloplastin + calcium trigger prothrombin to convert to thrombin, thrombin triggers fibrinogen to fibrin (insoluble fibres), these then tangle together to form a mesh where platelets get trapped, this is a blood clot
what is thrombosis?
blood clotting
how can thrombosis lead to CVD?
heart attack, stroke, deep vein thrombosis
what factors can lead to CVD?
age, diet, inactivity, gender, genetics, high blood pressure, smoking
what is a saturated lipid?
mainly found in animal fats (butter etc), they have no double bonds between the carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon tails (each carbon is joined to at least 2 hydrogen atoms - the lipid is ‘saturated’ with hydrogen)
what is an unsaturated lipid?
mainly found in plants (olive oil etc), one or more double bond between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon tails, therefore a kinked chain
what are statins?
drugs that reduce blood cholesterol by reducing the amount of ‘bad’ LDL cholesterol produced in the liver (treatment for CVD)
what are antihypertensives?
drugs with beta-blockers (reduce strength of the heartbeat) and vasodilators (widen blood vessels) and they contain diuretics (reduce sodium = less water reabsorbed) all to reduce blood volume therefore reduce blood pressure
what are anticoagulants?
drugs to reduce blood clotting
what are platelet inhibitory drugs?
type of anticoagulant that prevents platelets clumping together to clot
how do monosaccharides join to form disaccharides?
through condensation reactions forming glycosidic bonds
how does energy imbalance lead to weight gain?
if energy intake is higher than energy output, excess energy turns into fat reserves
how can energy imbalance lead to weight loss?
if energy intake is lower than energy output, it will turn fat reserves into energy
how can mono/di/polysaccharides store energy?
compact, large, insoluble
name two obesity indicators
BMI, waist-to-hip ratio
what is an energy budget?
the amount of energy taken in by an organism and the amount of energy used up (input - output = budget)
what are the potential ethical issues regarding the use of invertebrates in research?
they can’t give consent and may experience pain, unethical to cause distress or suffering to any living organism (though some people believe it’s more acceptable to perform experiments on invertebrates than vertebrates because they have a less sophisticated nervous system
why do many animals have a heart and circulation?
all cells need energy, most get it from aerobic respiration which uses glucose and oxygen so the body needs a way to deliver these to all its cells (diffusion would be too slow in a multicellular organism so mass transport system is needed)