CSLC 1- CH.1
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Sociolinguistics
The investigation of the relation of language to social systems, ideas, and behaviors.
linguistic anthropology
The study of how language, mind, and culture interact to produce people’s beliefs and worldviews.
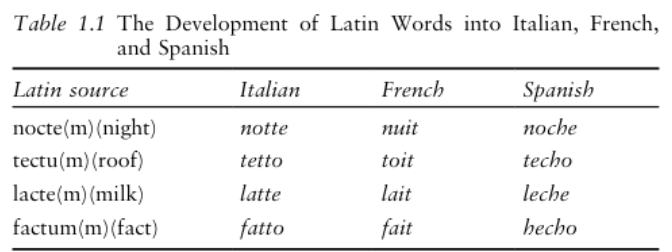
1) Cognates
Words having the same linguistic root or origin. They often have similar meanings in different languages.
2) Typological
Involves classifying languages according to how they construct their words.
Types of Synthetic Languages:
Agglutinative or Synthetic Languages: Typically use so-called morphemes, or elements that are combined to make up words.
Examples: Turkish
Opposite: Isolating Languages.
Example: Chinese
3) Fusion Languages
Combine multiple grammatical meanings into a single morpheme, making it harder to separate distinct grammatical markers.
Ex: Hablo = I Speak
Opposite: Isolating Languages.
Features of All Languages
1) Languages have finite-set of distinctive sound units and grammatical units for construction of words.
Phonemes = distinctive sound units
Morphemes = grammatical units
2) Languages have set of rules for combining morphemes to larger units of meaning (phrases/sentences/texts).
Constitute the syntax (rules and structures that govern how words are arranged) of a language.
3) Languages have a set of meaning-bearing units (words/phrases/etc.) called lexicon, which allow communication.
Lexicon = Encompasses not just words, but also their meanings, usage, and relationships with one another.
4) Languages have writing symbols (pictographs/alphabet).
5) Languages has resources to create new words, ideas, or concepts.
Constantly changing and evolving.
6) Language allow human to communicate in different contexts.
7) Language allow people to preserve knowledge.
8) Language allows meaningful social interaction.
9) Language are variable → splitting to dialects.
Bilingualism
Ability of an individual, or society, to speak two languages to varying degrees.
Primary Bilingualism
Spontaneous childhood acquisition of two languages.
Secondary Bilingualism
Anyone who acquires a second language later in life.
Chomsky’s Universal Grammar (In human brain)
Blueprint from which all specific languages are built, making up the set of principles that are available to all children and from which they can construct their specific grammar.
Ferdinand de Saussure’s Structuralism
Structuralism: Analyzes language as a system of interrelated elements.
Diachronic = How languages change over time.
Synchronic = Study of languages at a specific point.
Approach:
Sociolinguistics: Focus on parole and not langue.
langue is the system of language, and parole is how the system is used in practice.
Edward Sapir
Developed the first typological systems for classifying languages.
Took into consideration the number of morphemes used in word formation and the degree of synthesis in the formation process.
EXAMPLE:
Goodness (From Good) = Less Synthesized
Depth (From Deep) = More Synthesized
Was among the first to argue that a change in the order of words in a sentence, or omitting any words from it, reflects different concepts.
Linguistic Relativity Hypothesis (Whorfian Hypothesis)
The view that different societies encode into their languages those concepts they feel are important and necessary to them; but these, in turn, influence how they come to perceive reality.
Sociolinguistic Methodology
Interviews
conducted interviews and then analyze the data with statistics. The fusion of statistical and interview techniques is common in sociolinguistic methodology.
Fieldwork
Conducted in a natural social environment or in a specific context, rather than in an artificial way.
Ethnography
Gather the relevant information by living among a group of people, observing their communication habits, and annotating their observations.
Data Collection
Merging Sociolinguistics and Anthropology
Linguistic Competence (Langue) and Linguistic Performance (Parole)
LC = System of language itself.
LP = The ability to use it for some purpose.
Communicative Competence
The ability to use language meaningfully.
Discourse
Characterized by key words that appear frequently in conversations.
EXAMPLE: “Schools, corporations, universities, politicians, the media, and other collectivities all develop discourse styles that determine how members speak to one another and thus understand the world”
Pragmatics
Studies how context influences the interpretation of meaning in language.
Variation
A main focus of sociolinguistics is variation—how a language varies in social and regional situations and environments.
Dialect variation implies the existence of a norm, which is essentially a code against which the dialects can be defined.
Social Dialects (Sociolects)
Dialect: Regional or ethnic varieties of a language.
Social Dialect: Variants that vary according to social contexts.
Mutual Intelligibility
This means essentially that if speakers understand one another, then they likely speak dialects of the same language; if they do not, then they are probably speaking different languages.
Markedness
Links grammar and lexicon to social perceptions.
In the area of vocabulary it implies that certain lexemes are marked for gender, class, ethnicity, or some other social variable.
Internet Linguistics
The theoretical and methodological tools of sociolinguistics and linguistic anthropology are especially powerful today for studying language use in the new digital media, showing commonalities and differences between computer-mediated communication (CMC) and face-to-face (F2F) communication.
Multimodality
the use of a combination of modes of communication—writing, audio, images, animation, etc.
Discursive → can be deconstructed (ex. Text)
Presentational → Holistic (ex. Painting)
CMC
Computer-mediated communication
Synchronus and Asynchronus CMC
SC: Occurs, when the interlocutors are aware of the communication as an ongoing one.
AC: Occurs when the intended receiver is not necessarily aware that a message has occurred.
Informational Messages
Example: Wikipedia
Conversational Messages
Example: Facebook