Comprehensive Psychology: History, Brain, and Learning Theories
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
What is psychology?
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes.

What does behavior include in psychology?
All overt or outward actions and reactions, such as talking and movement.
What are mental processes in psychology?
All internal, covert activities of the mind, including emotions and memory.
What are the four goals of psychology?
Description, Prediction, Explanation, and Control of behavior.
What does the goal of description in psychology entail?
Providing a systematic and unbiased account of behavior.
How does psychology aim to predict behavior?
By identifying the conditions associated with the behavior.
What is the purpose of explanation in psychology?
To understand why and how behavior occurs by identifying the conditions that produce it.
What does control in psychology refer to?
Applying knowledge to change or improve behavior.
When did psychology become a scientific field?
In 1879 at a laboratory in Leipzig, Germany.
Who is considered the Father of Psychology?
Wilhelm Wundt.
What is Objective Introspection?
A method developed by Wundt where students report their reactions to stimuli to identify elements of consciousness.
What is Structuralism in psychology?
A focus on the contents of the mind, aiming to identify its basic elements, associated with Edward B. Titchener.
What is Functionalism in psychology?
A focus on the activities of the mind and how they help us adapt, associated with William James.
What is the Gestalt perspective?
The idea that the whole experience is greater than the sum of its parts, emphasizing simultaneous processing of information.

Who developed behaviorism?
John B. Watson.
What is the main focus of behaviorism?
Studying only observable behavior in a systematic and objective manner.
What does the psychodynamic approach in therapy focus on?
Surfacing unconscious needs and conflicts to help clients make informed decisions.

What is the role of a behaviorist therapist?
To modify behavior by removing rewards and creating new reward systems.
What does a humanist therapist emphasize?
Developing a sense of worth and allowing clients to make their own choices.
What is the focus of cognitive therapy?
Training clients to identify and refute irrational beliefs.
What is the biopsychological approach in therapy?
Using medication to help regulate biological factors such as serotonin levels.
What do socio-cultural psychologists advise regarding media exposure?
To minimize exposure to unrealistic ideals of beauty portrayed in media.
What is the focus of evolutionary psychologists?
Explaining behaviors rather than changing them.
What is the difference between clinical psychologists and psychiatrists?
Clinical psychologists assess and treat psychological problems without prescribing medication, while psychiatrists are licensed doctors who can prescribe medication.
What do counseling psychologists focus on?
Helping individuals with adjustment problems rather than severe psychological disorders.
How do psychologists and psychiatrists typically collaborate?
Psychologists may refer clients to psychiatrists for medication, while psychiatrists may refer clients to psychologists for therapy.
What is the primary role of Psychometricians?
They conduct psychological assessments and integrate test results to provide a holistic evaluation of an individual's capabilities and personality.
What qualifications are needed to take the Psychometrician's licensure exam in the Philippines?
A bachelor's degree in Psychology is required.
What degree is necessary to qualify for the Psychologist's Exam in the Philippines?
A master's degree in Psychology.
What does Industrial/Organizational Psychology focus on?
It examines the relationships between people and their work environments, aiming to increase productivity and assist in personnel selection.
What is the focus of Developmental Psychology?
It studies intellectual, social, and emotional development throughout the lifespan.
What topics do social psychologists study?
They study how beliefs, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others, including topics like attitude formation, aggression, prejudice, and interpersonal attraction.
What is the first step in the scientific method?
Start with a question that can be answered with observable and measurable data.
What is a hypothesis?
A tentative answer or explanation for observed behavior, based on a theory.
What is confirmation bias?
The tendency to notice only information that agrees with one's worldview, leading to selective perception.
What is the purpose of sharing research findings?
To contribute to the growth and development of science.
What is naturalistic observation?
A research method where behavior is observed in its natural setting without interference.
What is participant observation?
A research method where the researcher becomes part of the group being studied.
What is a case study?
An in-depth study of an individual or group with unique characteristics, often involving multiple research methods.
What is the strength of surveys in psychological research?
Surveys can generalize findings from a sample to a larger population if the sample is representative.
What is random sampling?
A process that gives everyone in a population an equal chance of being part of the sample.
What does a correlation measure?
The relationship between two or more variables.
What does a correlation coefficient indicate?
It shows the direction and strength of the relationship between variables, ranging from +1.00 to -1.00.
What is the main limitation of correlation?
Correlation does not prove causation.
What is the purpose of an experiment in psychology?
To determine the cause of a behavior by manipulating an independent variable while controlling other variables.
What is the independent variable (IV)?
The variable that is manipulated in an experiment.
What is the dependent variable (DV)?
The behavior that is measured in an experiment to assess the effect of the independent variable.
What is the experimental group?
The group that is exposed to the independent variable in an experiment.
What is the control group?
The group that receives no treatment or a treatment that should have no effect, used for comparison.
What is random assignment in experiments?
A method used to assign participants to groups, ensuring each has an equal chance of being in either the experimental or control group.
What are confounding variables?
Participant characteristics that may influence the dependent variable, which researchers aim to control.
What is the placebo effect?
When a participant's expectations influence their behavior rather than the independent variable.
What is a single-blind study?
A study where participants do not know which treatment they receive, reducing the influence of expectations.
What is the experimenter effect?
When the experimenter's expectations influence the participants' responses.
What is a double-blind study?
A study where both participants and experimenters do not know which condition each participant belongs to.
What is a quasi-experimental study?
A study that may resemble a real experiment but lacks either manipulation of the independent variable or random assignment.
What is the significance of random assignment in experiments?
It ensures that different groups are formed without bias, allowing for valid comparisons.
What are the four major ethical principles in research with human participants?
1. Scientific soundness, 2. Respect for persons, 3. Non-maleficence and beneficence, 4. Justice.
What does 'scientific soundness' require in research?
Adequate justification for the research, necessity of human participants, rigorous procedures, and researcher competence.
What does 'respect for persons' mean in research ethics?
Upholding participants' autonomy by informing them about the study's nature, purpose, risks, and benefits.
What is non-maleficence and beneficence in research ethics?
Minimizing risks and ensuring they are reasonable compared to the anticipated benefits.
What does justice refer to in the context of research ethics?
Ensuring fair compensation and equal sharing of benefits and burdens among participants.
What is a neuron?
The basic building block of the nervous system that receives and sends messages.
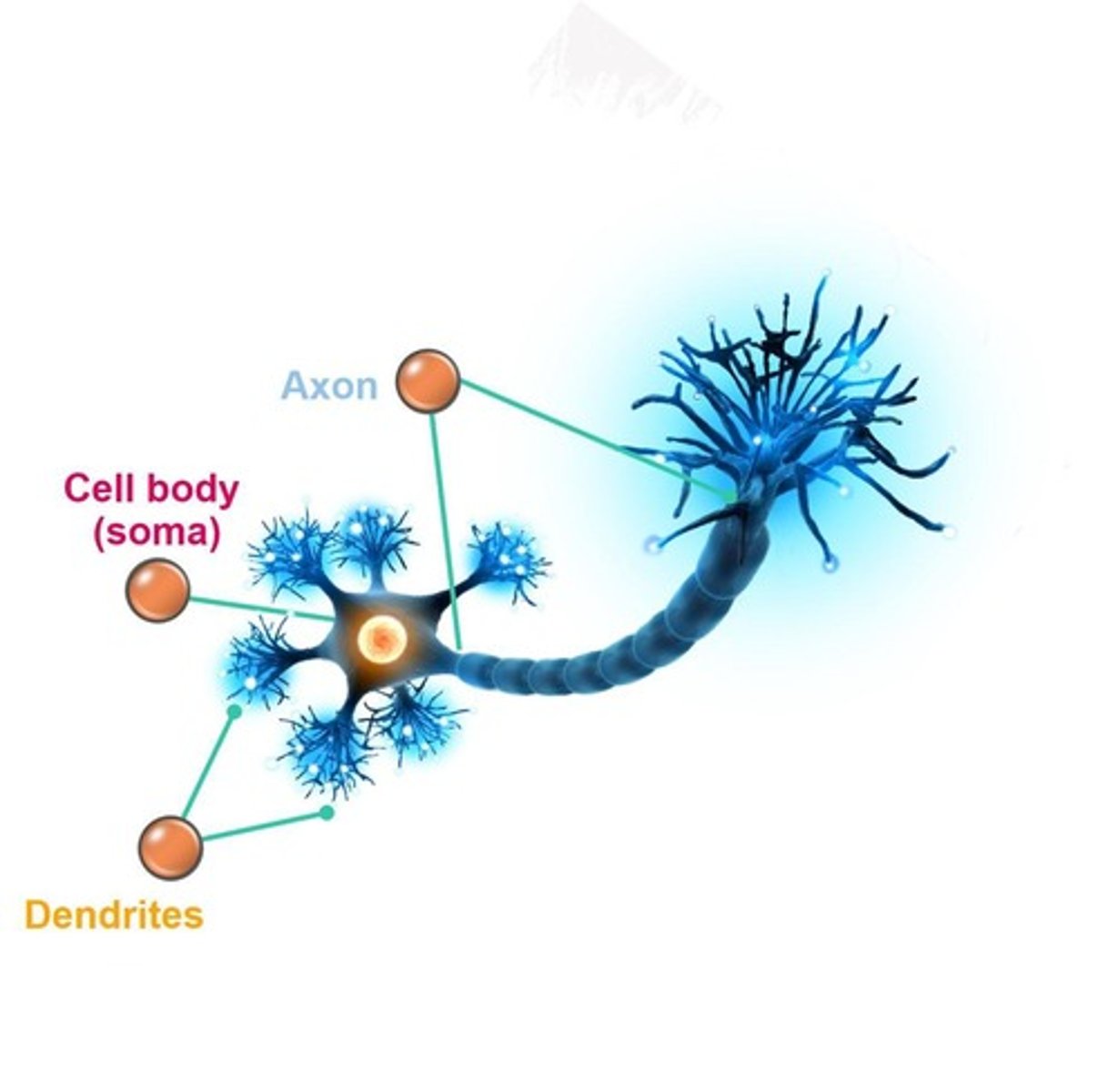
What are the three basic parts of a neuron?
Soma (cell body), axon, and dendrites.
What is the function of the soma in a neuron?
It maintains the life of the cell.
What role do dendrites play in a neuron?
They receive messages from other neurons.
What is the function of the axon in a neuron?
It sends messages to other cells.
What percentage of the brain is made up of neurons?
Only 10-20% of the brain is made of neurons.
What are glial cells?
Cells that provide support, nutrients, and protection to neurons.
What are the two types of glial cells?
Oligodendrocytes (in the brain and spinal cord) and Schwann cells (in the rest of the body).
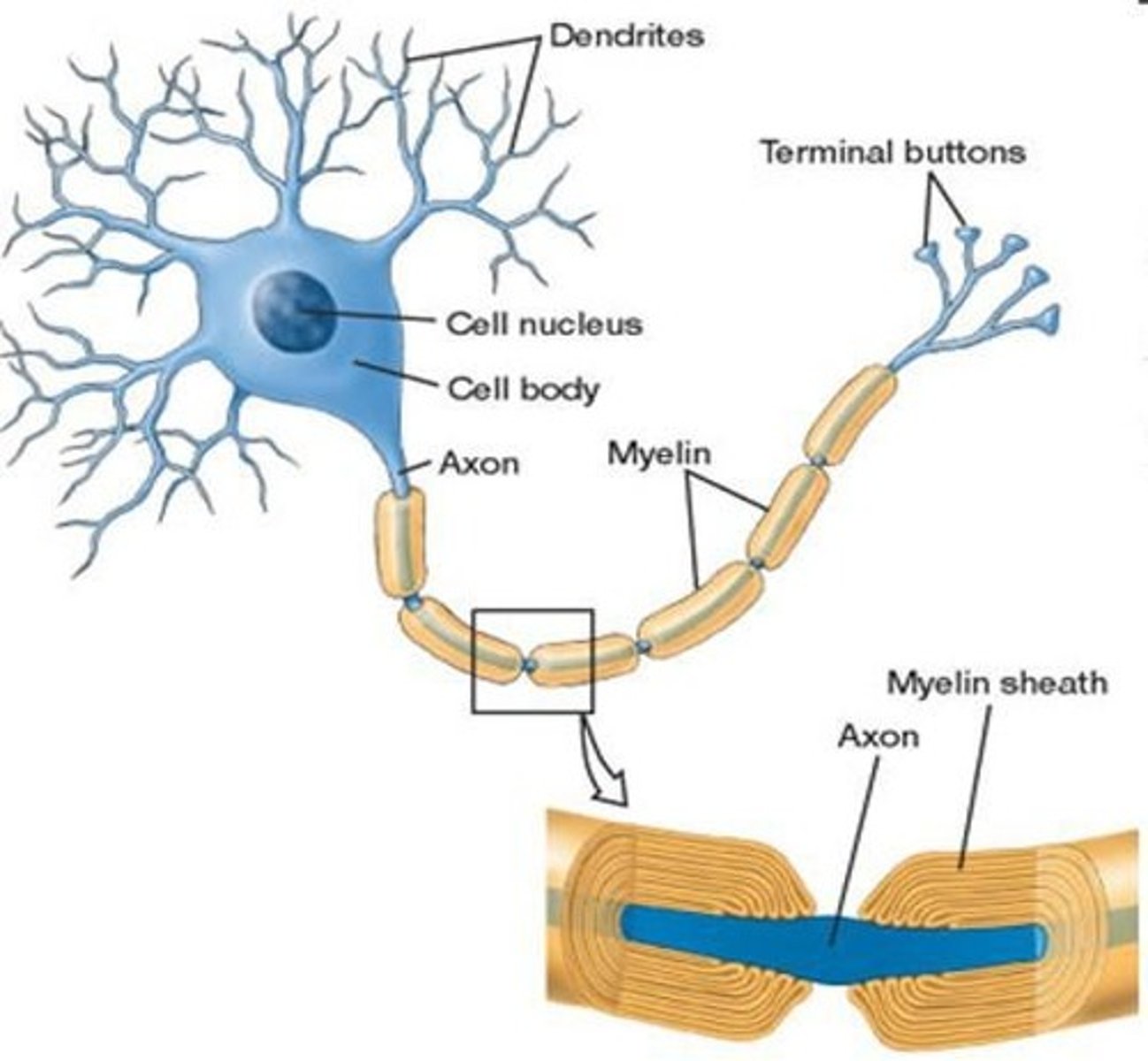
What is the primary function of myelin?
To insulate axons and speed up neural impulses.
What is saltatory conduction?
The process where neural impulses jump between nodes of Ranvier, speeding up transmission.
What can happen if axons are unmyelinated?
They can cause seizures and permanent damage to the axon.
What is synaptic transmission?
The process of communication between neurons involving generating, sending, and receiving messages.
What is the role of ions in generating a neural impulse?
Charged particles inside and outside the neuron create the electrical signals necessary for communication.
What is the function of the semipermeable cell membrane in a neuron?
It allows smaller molecules to pass in and out while restricting larger molecules.
What is the charge of ions inside a resting neuron?
Mostly negative.
What is the charge of ions outside a resting neuron?
Mostly positive.
What must happen to initiate an electrical impulse in a neuron?
Negative ions must exit and positive ions must enter the neuron.
What triggers the opening of sodium channels in a neuron?
A command received from another neuron.
What happens when sodium channels open in a resting neuron?
Positive sodium ions flow into the neuron, making the inside more positive.
What is created when the charges inside a neuron are reversed?
An action potential, which is an electrical neural impulse.
How does the action potential travel down the axon?
It triggers the opening of sodium channels sequentially along the axon.
What prevents all channels from opening simultaneously in a neuron?
The organized nature of the brain ensures that channels open one by one.
What is the axon terminal?
The end of the axon where neurotransmitters are released.
What are synaptic knobs?
Swollen knobs at the axon terminal that contain synaptic vesicles.
What do synaptic vesicles contain?
Neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit messages to other neurons.
What is the synapse?
The gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released.
What happens when neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the next neuron?
They can either trigger an action potential or keep the neuron at resting potential.
What are the two processes for cleaning up excess neurotransmitters in the synapse?
Reuptake and enzyme degradation.
What is reuptake?
The process of neurotransmitters being taken back into the synaptic vesicles.
What is enzyme degradation?
The breakdown of excess neurotransmitters into simpler molecules by enzymes.
What are excitatory neurotransmitters?
Chemicals that cause the receiving cell to fire.
What are inhibitory neurotransmitters?
Chemicals that cause the receiving cell to stop firing.
How do neurons determine whether to fire or not?
They add up all 'fire' messages and subtract 'rest' messages; if the result reaches a threshold, they fire.
What is the all-or-none principle in neuronal firing?
A neuron either fires at full strength or does not fire at all.
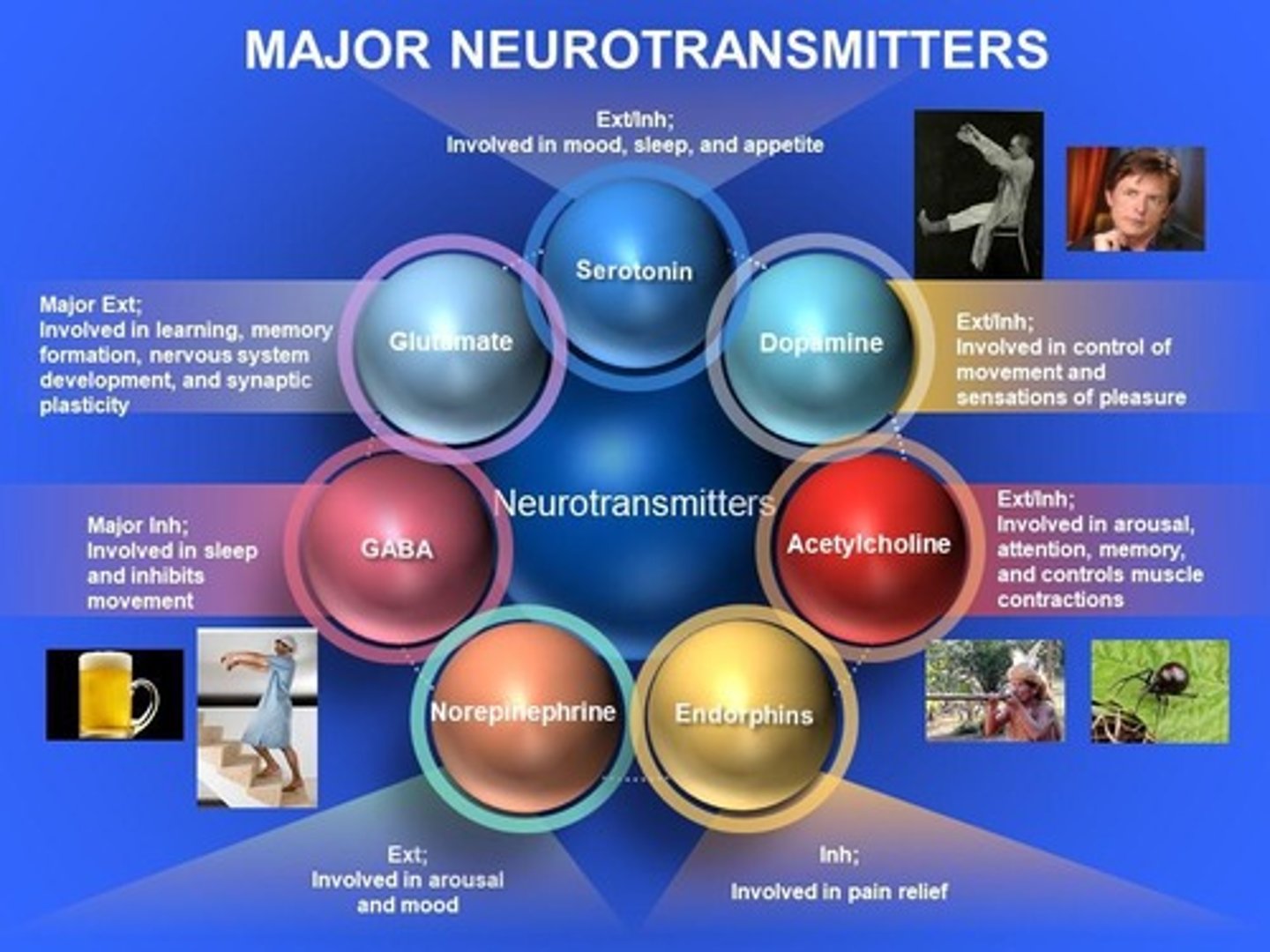
What role does acetylcholine play in the nervous system?
It is involved in memory, arousal, attention, and muscle contractions, acting as both excitatory and inhibitory.
What is glutamate's role in the nervous system?
It is the major excitatory neurotransmitter, important for learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity.
What role does GABA play in the brain?
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter, involved in sleep and inhibiting movement.
What condition is associated with low levels of GABA?
Somnambulism (sleepwalking) may occur due to low levels of GABA, allowing muscles to act out dreams.