IMED1001 - Cellular Physiology II
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Types of Tissue
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
Nervous Tissue
- specialised for communication by electrical and chemical signals
- Neurons (nerve cells) detect stimuli and transmit messages
- Neuroglia protect and assist neurons.
- CNS: oligodendrocytes (myelin)
- PNS: Schwann cells (myelin)
Types of Muscular Tissue
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
Function of Simple/Pseudostratified Epithelial Tissue
- Diffusion/filtration/secretion (e.g alveoli, blood and lymph vessels)
- Secretion/absorption (e.g ducts/glands/renal tubules)
- Mucus secretion (trachea, upper respiratory tract)
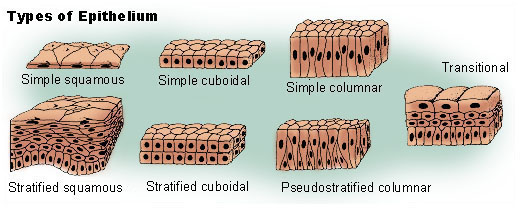
Function of Stratified Epithelial tissue
- Mechanical Protection (oesophagus, mouth, vagina)
- Secretion/protection (ducts of glands)
- Stretchyness (bladder, urethra)

Connective Tissue
Three basic components:
- cells
- protein fibres (collagen = strong, elastin = stretchy)
- ground substance (GS) (attracts water-modulates viscosity)
Types of Connective Tissue
- Connective Tissue Proper (Loose and Dense): Loose ones are more ground substances, less fibres. Dense ones have more fibres, less ground substance, e.g ligaments and tendons
- Supporting Connective Tissue (Cartilage and Bone): Cartilage are firm semisolid and contain variable amount of fibres. Bone is solid and calcified (collagen with calcium and salt added)
- Fluid Connective Tissue (Blood): ground substance, 45% cells, 55% plasma
How cells hold together with eachother (3 of them)
- Tight Junctions: very very close
- Desmosomes: very very strong
- Gap Junctions: Pass through
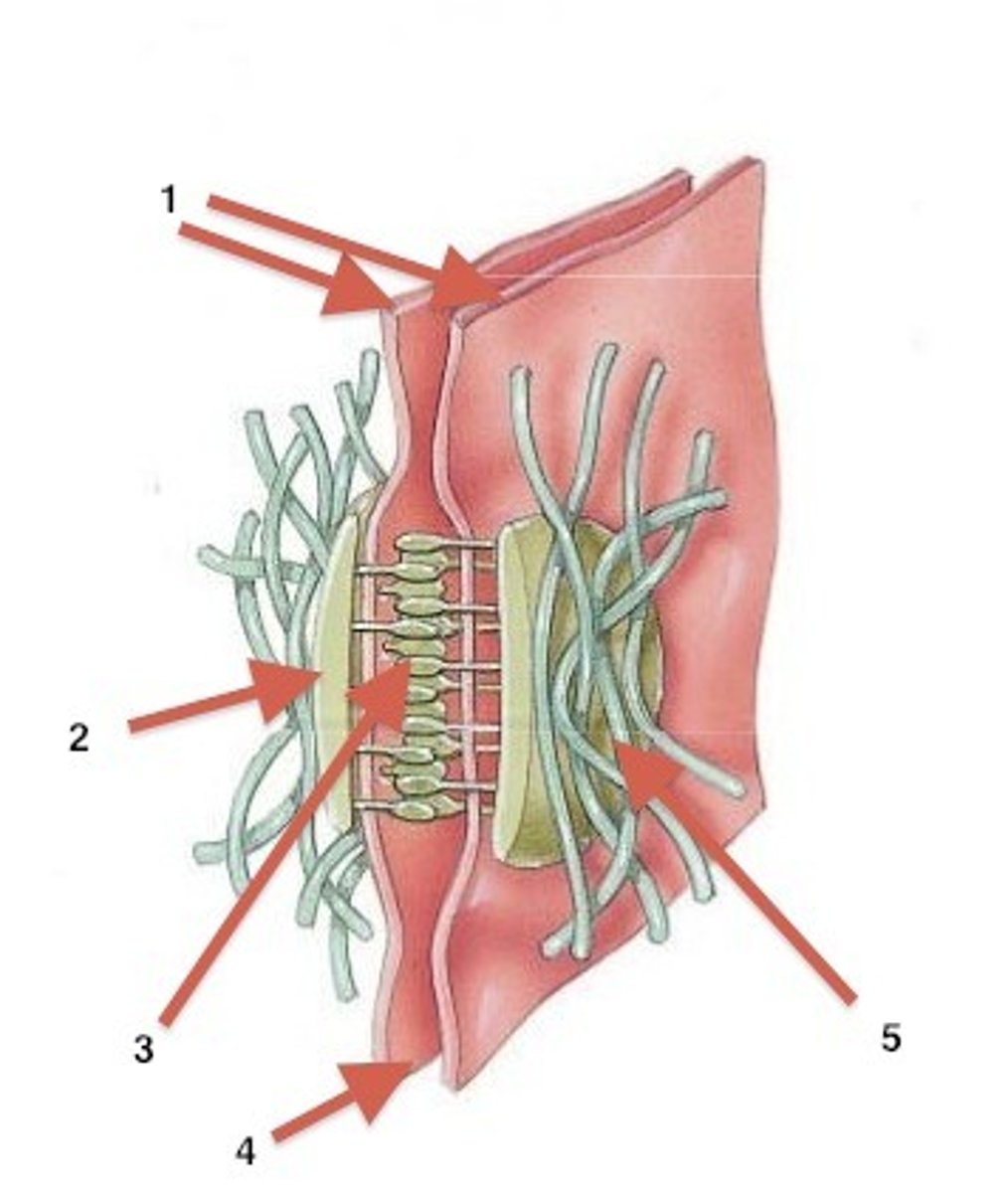
Tight Junctions
- plasma membranes of two adjacent cells are linked by cell adhesion proteins (claudins)
- seals gap between cells (nothing can pass between cells) (forces substances to go through cells, not around them)
- tight but not strong
- e.g stomach - tight junctions prevent digestive juices from seeping between epithelial cells
- TAKE IMAGE FROM SLIDE 20 OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY 2
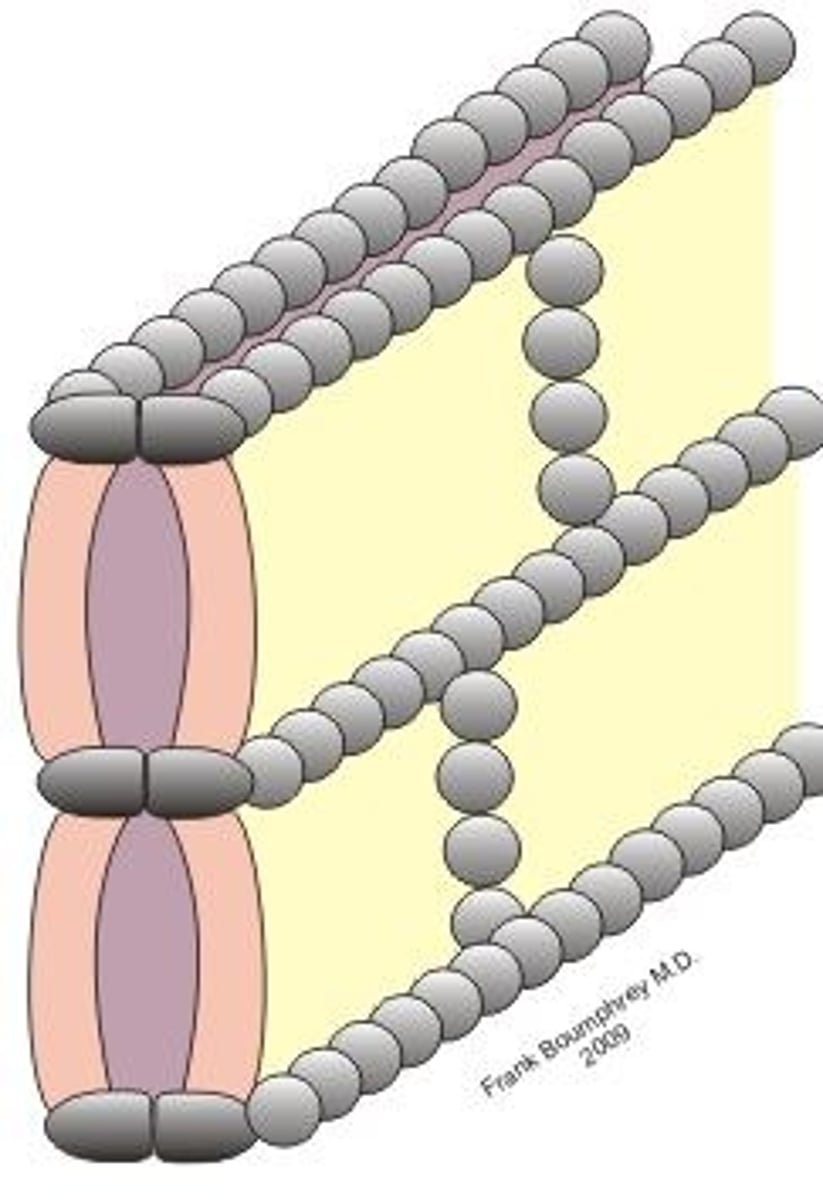
Desmosomes
- Super strong - holds cells together, resist mechanical stress
- cadherins proteins attach to the cytoskeleton (anchor cytoskeleton (intermediate filaments) to membrane plaque
- cannot prevent substances going between cells
- We also have Hemidesmosomes (half desmosomes anchor cells to the underlying basement membrane and prevents epithelia from being peeled away from underlying tissues)
- TAKE IMG FROM SLIDE 21 OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY 2
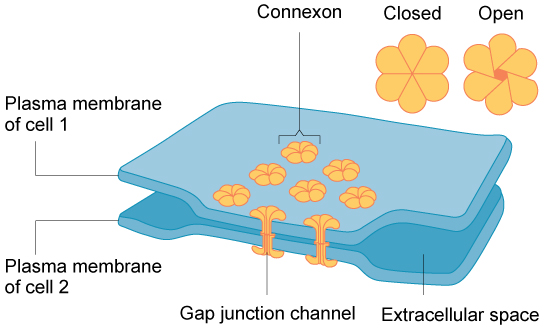
Gap Junctions
- allows things to pass from one cell to the next
- formed by connexons (ring of proteins that spans the membranes of 2 adjacent cells. Each connexon = 6 transmembrane proteins (called connexins))
- Creates a pore connecting cytoplasms (allows direct communication between cells (shared cytoplasm). Ions, nutrients and other small solutes pass between cells. Located in cardiac and smooth muscle
- no ligand or receptor
- physical contact between cells involved
- connected 2 cytoplasms
- allows free passage for molecules/ions
IMG PRESENT
Cellular Communication
- most commonly involves a signal (ligand) produced by one cell that is receieved by a receptor on another cell
- Cellular Communication can be direct or via extracellular fluid
- Direct: juxtacrine (1) and gap junctions (3)
- via Extracellular fluid (ECF): Autocrine (2), Paracrine (4), Endocrine (5) and Neuronal (6)
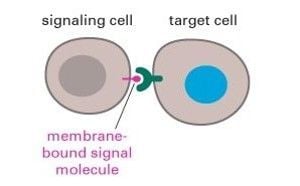
Juxtacrine Cell Communication
- Physical contact between cells involved
- Transmembrane proteins and phospholipids
- receptor bound to one cell; ligand bound to the other - signal cannot diffuse away (notch signalling - neurons)
Autocrine Cell Communication
- cell signalling to itself
- signal molecule release into ECF
- short distances (usually less then 20 micrometres)
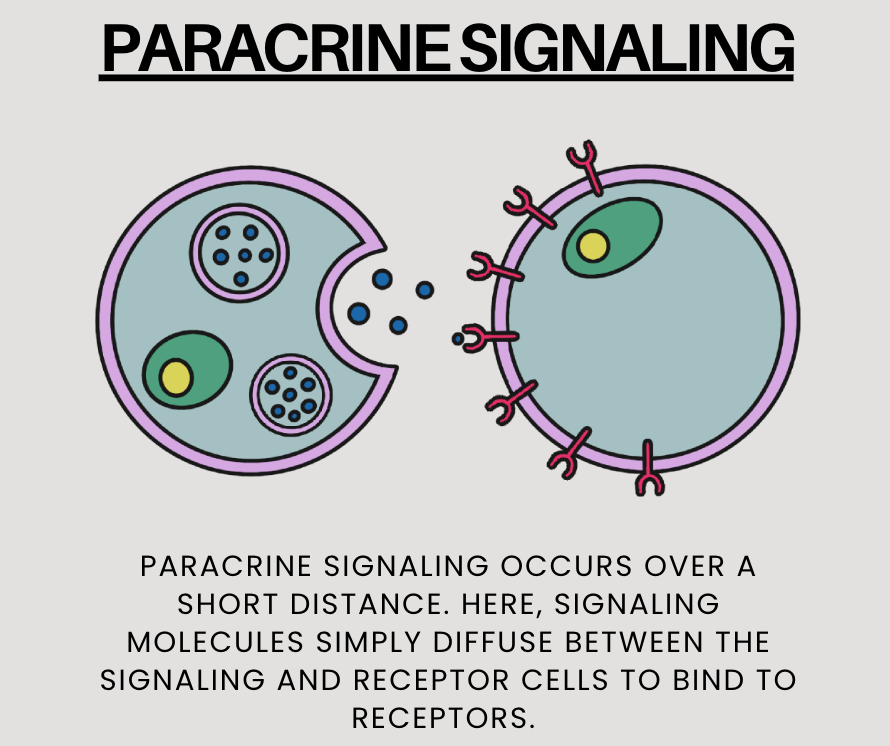
Paracrine Cell Communication
- other cells, not in physical contact
- signalling molecule release into ECF
- acts on nearby cells - short distances
Endocrine Communication
- long distances
- transport via bloodstream
- hormones bind to receptor (e.g insulin)
Neural Communication
- long distance
- target = nerve, muscle and gland
- noradrenaline, acetylcholine, many others