Anatomy Lab Exam 3 Back and Spine
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
axial and appendicular
What are the two divisions of the Skeleton?
skull, vertebral column, ribs and sternum (houses and protects vital organs!)
What does the Axial skeleton consist of?
1. shoulder girdle 2. pelvic girdle 3.UE 4.LE
What does the Appendicular skeleton consist of?
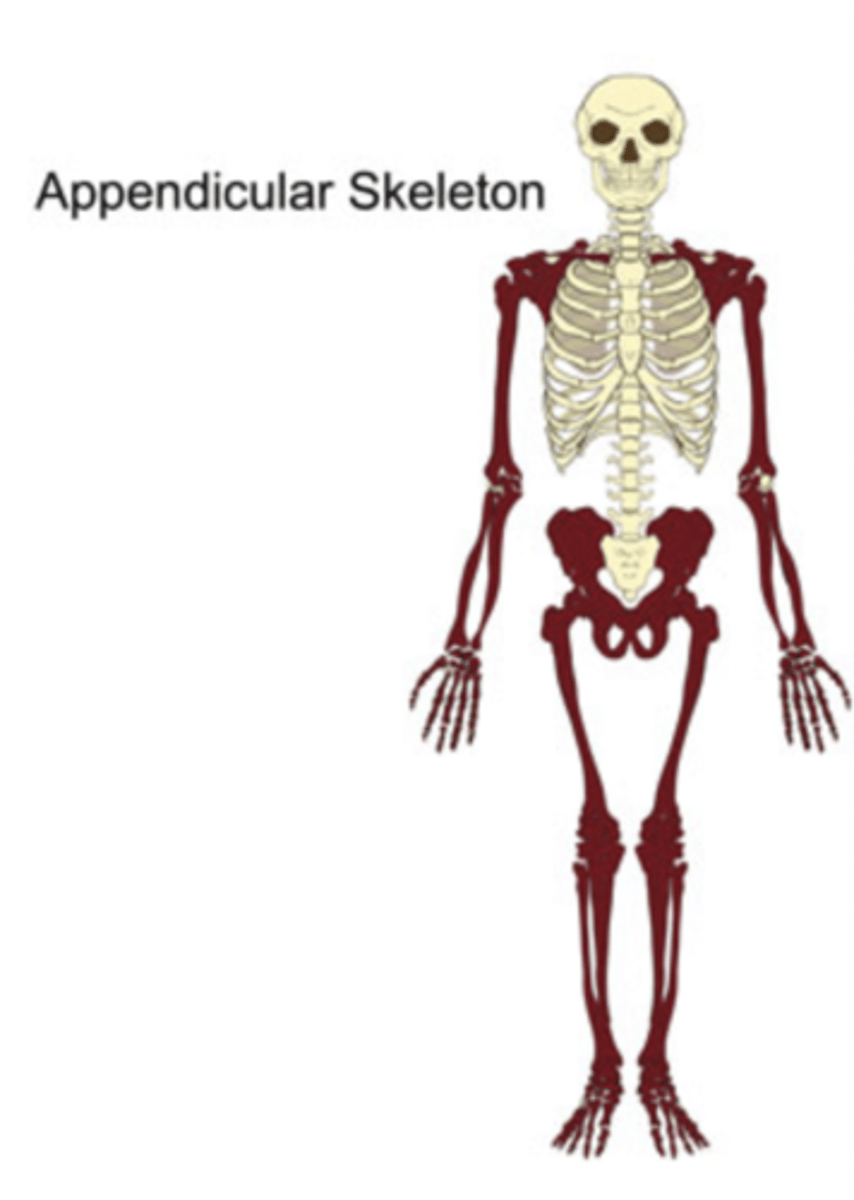
spinal cord and supports head and rib cage.
The Vertebral Column houses ______ and supports ______ and_____
7
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
Cervical vertebrae
These vertebrae support head and passage important arteries to head
12 Thoracic
How many thoracic vertebrae are there ?
Thoracic
These vertebrae articulate with and support ribs and rib cage
5 Lumbar
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
Lumbar vertebrae
These vertebrae support head, trunk and UE; provide attachment for muscles that move trunk and UE
5 Sacral vertebrae that are fused together
How many sacral vertebrae are there and what is special about them?
Sacral
There vertebrae articulate with hips and transfer weight from upper body to LE
3-5 Cocccygeal
This is known to be vestigial in humans
discs
Fibrocatilagenous ____ connect vertebral bodies
facets between adjacent vertebrae
Two superior and Two inferior processes form freely movable joints known as ____ between ____ vertebrae
Intervetebral foramen
These foramen are formed by articulations between vertebrae in the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae where the spinal roots are housed
Transverse foramen
These foramen are found in the cervical spine where they are within the body of the vertebra and house the vertebral arteries
6 articulations, 2 slightly movable (discs) and 4 freely movable (facets)
Each vertebrae has at least ___ articulations; two _____ _____ and 4 _____ ______ .
costal facets
The thoracic vertebra have two extra freely movable articulations called
1. Atlanto-occipital joint 2. Atlantoaxial joint 3. Sacroiliac joint (SIJ)
What are the 3 Special articulations of Vertebral column
Atlanto-occipital joint
This joint articulation atlas with occipital condyles skull
Atlantoaxial joint (C1= Atlas C2 = Axis)
This joint articulates with C1-C2 and is known as the
Sacroiliac joint (SIJ)
This joint articulates the sacrum with ilium
Intervertebral Discs
This is a fibroelastic carilagenous plates firmly attached to adjacent vertebral bodies
annulus fibrosis and nucleous pulposis.
The Intervertebral Discs are composed of outer cartilaginous ring called the _____ _____ and inner gelatinous _____ ____
Anterior Longitudinal ligament (ALL)
This ligaments runs from skull to sacrum along anterior border of vertebral bodies limiting hyperextension
Posterior Longitudinal ligament (PLL)
This ligament runs from skull to sacrum along posterior border of vertebral bodies limiting hyperflexion. Lies in the vertebral canal anterior to the spinal cord.
Ossification of the PLL
Abnormal calcification of the PLL can start within months of birth and affects ability to move arms and legs
1. sensory and/or motor dysfunction in limbs 2. bladder dysfunction 3. abnormal reflexes 4. clumsiness 5. spastic gait
Symptoms of ossification of the PLL include
Ligamentum flava
This ligament connects adjacent vertebral lamina helps form the roof of the vertebral canal.
Ligamentum flava
Hypertrophy of this ligament can result in spinal stenosis
Interspinal ligament
This ligament connects adjacent vertebral processes
Supraspinal ligament
This ligament is from sacrum to head
1. Interspinal ligament 2. Supraspinal ligament
These 2 ligaments helps limit hyperflexion, join to form nuchal ligament in cervical spine
12 thoracic vertebrae
The twelve ribs articulate posteriorly with _____ on each side of the thorax
First 7 ribs
These ribs are considered "true ribs" and articulate anteriorly with the sternum
Ribs 8-12
The ribs are considered false ribs (vertebrocohondral ribs)
floating ribs (vertebral ribs)
Ribs 11 and 12 are considered
1. head 2. Inferior facet 3. superior facet
A typical rib is composed of a wedge shaped ____, with a large ____ ___ for articulation with its vertebrae and a small _____ ____ for articulation with the vertebra above
short neck
The head is connected to the shaft or body of the rib by the
tubercle that articulates with a transverse process.
The neck extends from the head to a ______ that articulates with a _____ ____ of the ribs vertebra
costal groove
Along the inferior border of the rib is the ____ ____ which accommodates the intercostal vein, artery and nerve.
vein, artery and nerve
The costal groove contains intercostal
Sternum
The bone is a flat bone composed of the manubrium, body and xiphoid process
clavicles
The superior border of the sternum has two clavicular notches for articulation with the
first seven costal cartilages
Seven facets along each side of the sternum articulate with the
1. Trapezius 2. Rhomboids 3. lattissimus dorsi
What are the superficial muscles of the back
1. splenius capitis 2. splenius cervicis
What are the superficial muscles of the neck
deep to trapezius and medial to levator scapulae.
The splenius capitis and splenius cervicis are found deep to the _______ and medial to the ______ ____
Erector Spinae group (aka sacrospinalis);
What are the intermediate back muscles
I Love Sugar 1. iliocostalis 2. Longissimus 3. Spinalis
What are the 3 muscles included in the Erector Spinae muscles?
Erector Spinae muscles
The muscles are responsible for extension and lateral flexion of the vertebral column
1. Transversospinalis 2. rotatores 3. multifidus 4. semispinalis
What are the deep back muscles
Deep back muscles
These back muscles are responsible for extension, lateral flexion and rotation of the vertebral column
spinal cord and brain
Meninges contain protective CT that protect the ______ and _______
1. dura 2. arachnoid 3. pia
What are the 3 layers of meninges from most superficial to deep
epidural space
The dura of the cord is separated from the vertebral canal by the
barely separated
The arachnoid membrane and dura are ____ ____ by a minimal amount of fluid
subarachnoid space
The pia and arachnoid are separated by a large
CSF
The large subarachnoid space houses _____. This space is contiguous with the subarachnoid space of the brain
spinal cord
The pia mater is intimately attached to the tissues of the
denticulate ligament.
A fibrous band of pia mater called the _____ _____ extends the entire length of the cord and separates the dorsal and ventral roots of the cord. The base of each projection of the ligament attaches to the cord and apex attached to the dura mater. Twenty one pairs of ligaments anchor the cord laterally
lamina
Ligamentum flavum connects adjacent vertebral ____
posterior to vertebral bodies and anterior to spinal cord
The Posterior Longitudinal ligament (PLL) is _____ to the vertebral bodies and ____ to the spinal cord
lateral
Intervetebral discs are just _____ to the PLL
Conus Medullaris
This is considered the end of spinal cord proper
Cauda Equina
The is a collection of spinal nerves below L2
Filum terminale
This eminates from the conus medullaris and is a thin layer of pia mater
Lumbar cistern
This is a large subarachnoid space that lies between L2 and S2 and houses the filum terminale and cauda equine
Dorsal which is posterior and carries Afferent root.. DAS or "arrives through the back door"
Which nerve roots carry sensory innervations?
Ventral which is anterior and carries Efferent roots... VEM or "Exits through the front door"
Which nerve roots carry motor innervations?
Cervical vertebrae
What vertebrae has this distinctive characteristic of having transverse foramina and Bifid spinous process.
Thoracic Vertebrae
What vertebrae has this distinctive characteristic of having costal facets and Spine-like spinous processes
Lumbar Vertebrae
What vertebrae has this distinctive characteristic of have massive vertebral body, mammilary process for multifidus origin, rounded, short spinous process