Blood, Tissue Fluid & Lymph
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is blood?
Fluid that transports substances around the circulatory system
What does blood carry?
-Glucose
-Oxygen
-Amino acids
-Hormones
-Mineral ions
What is blood composed of?
-Plasma
-Erythrocytes
-White blood cells
-Platelets
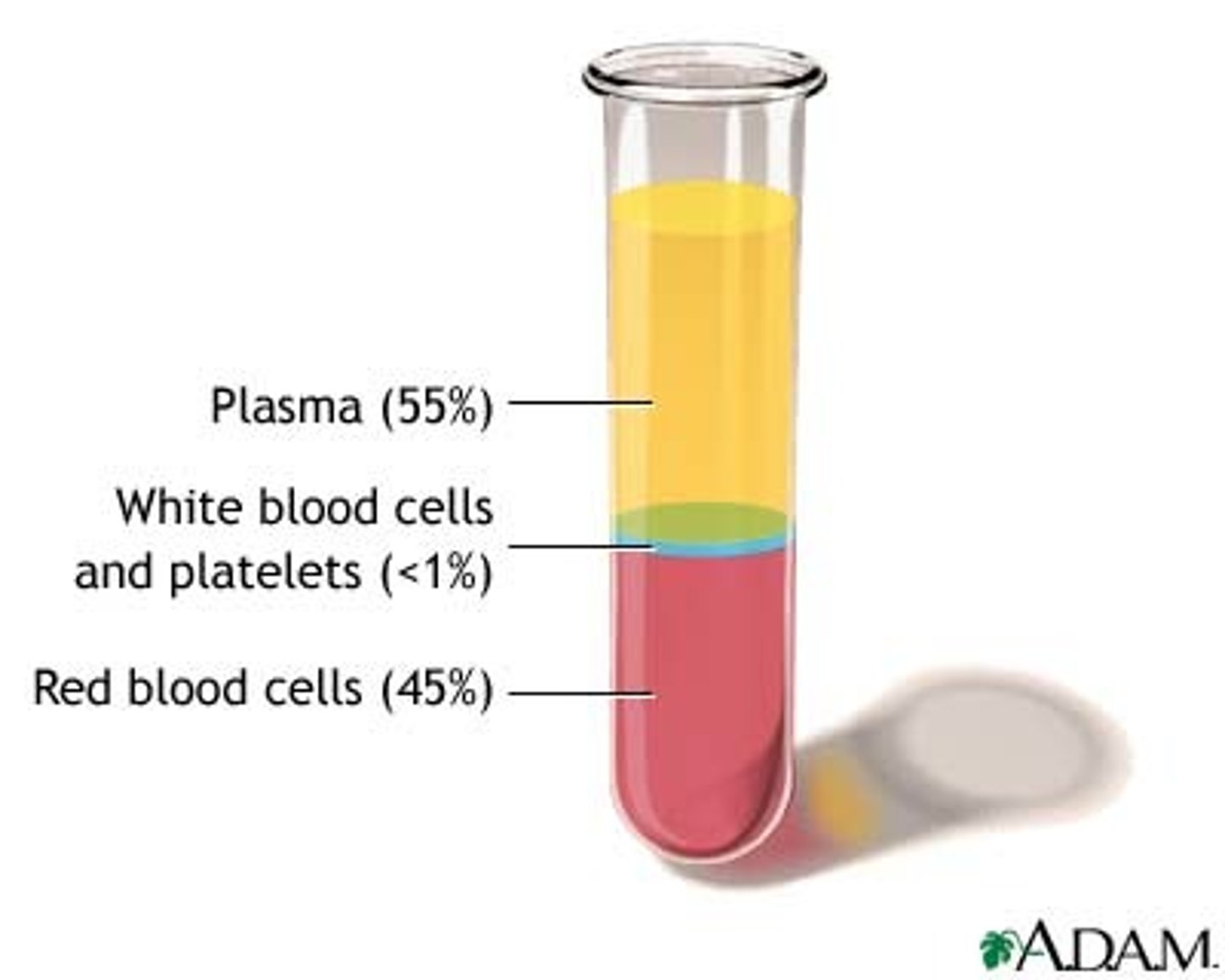
What is plasma and what is it's function?
-Liquid part of the blood mainly made of water, which carries the components of the blood
What is the function of blood?(4)
-Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide from respiring tissues
-Transports digested food from the small intestine
-Transports hormones
-Transports food molecules from storage molecules
What is tissue fluid?
-Fluid surrounding cells in tissues, made of substances that have left the blood plasma
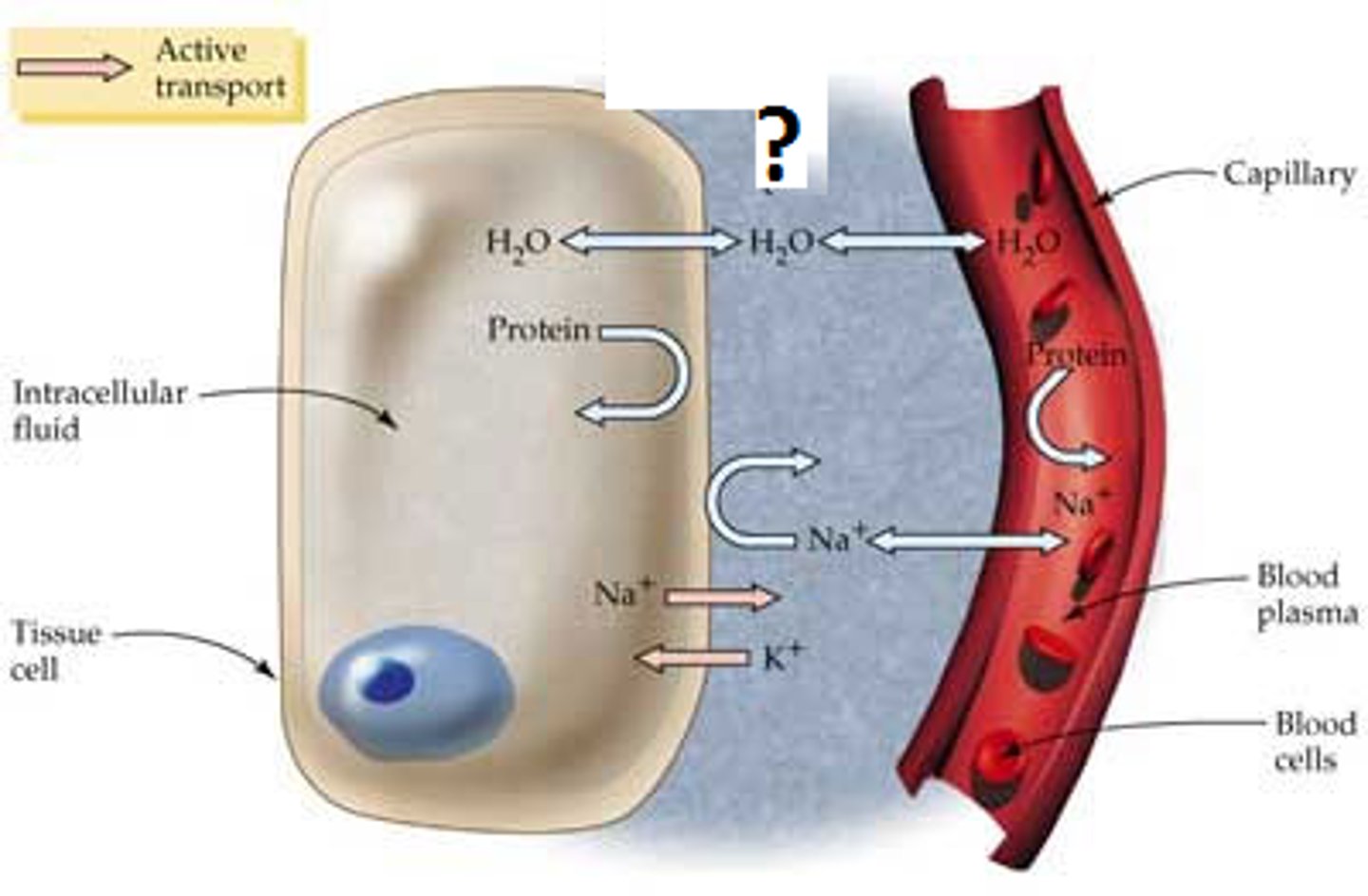
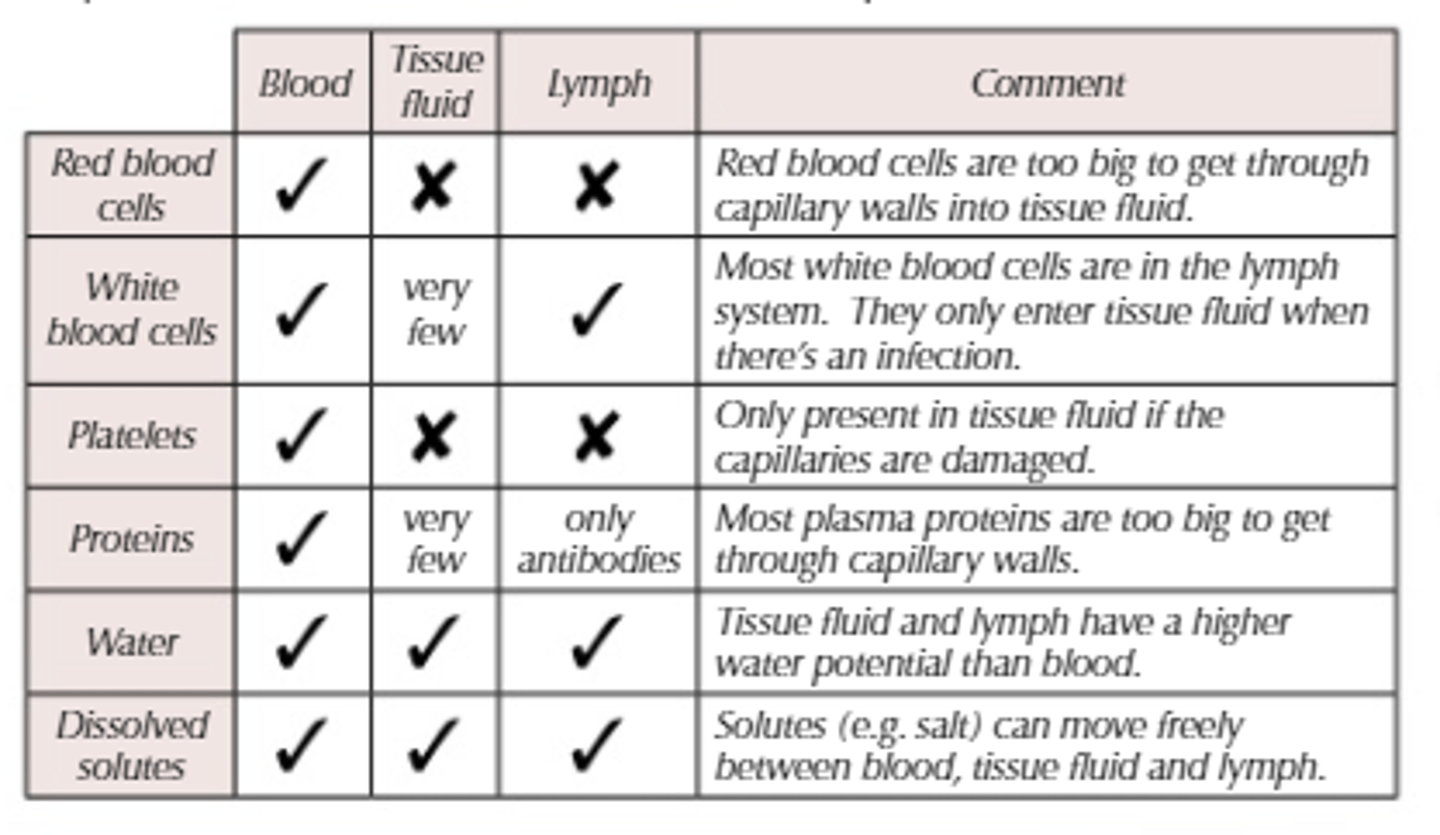
What is the similarities and differences between the composition of tissue fluid and plasma?
-Very similar composition to plasma
BUT:
-No erythrocytes
-Fewer proteins
-Fewer White Blood Cells
What is the function of tissue fluid?
-Site of diffusion between blood and body cells
-Body cells take up nutrients from the tissue fluid, and also excrete waste products into it

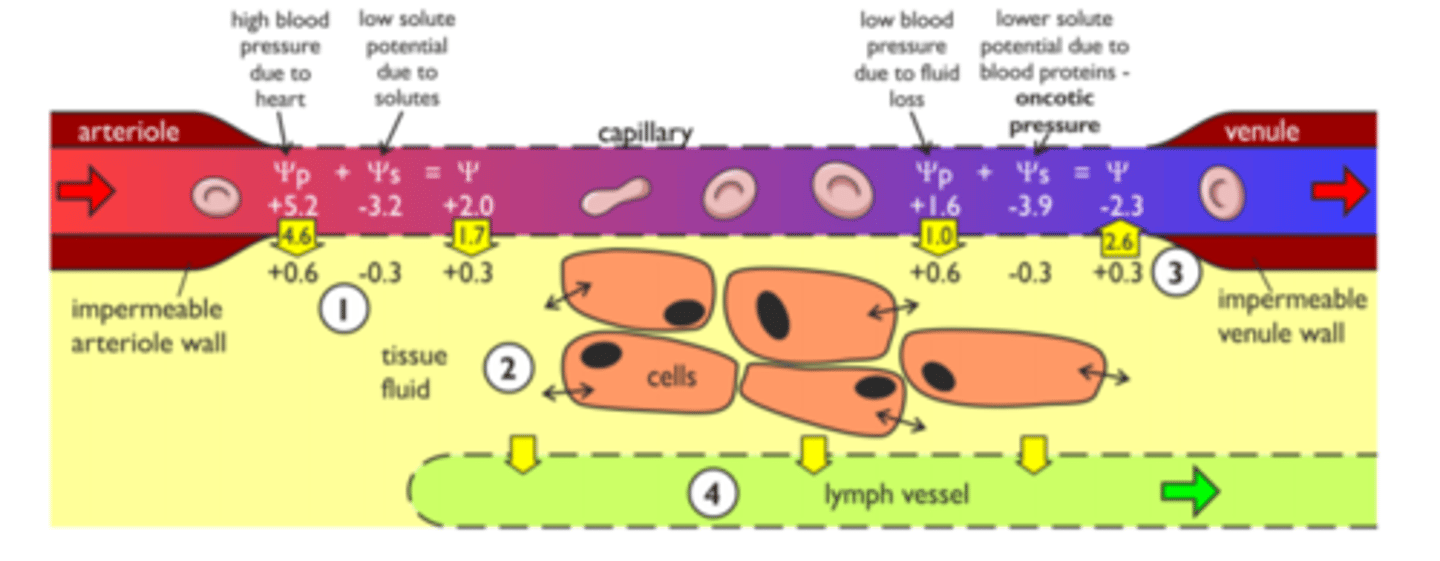
What is pressure filtration?
Movement of plasma through capillary walls into the tissue fluid surrounding the cells.
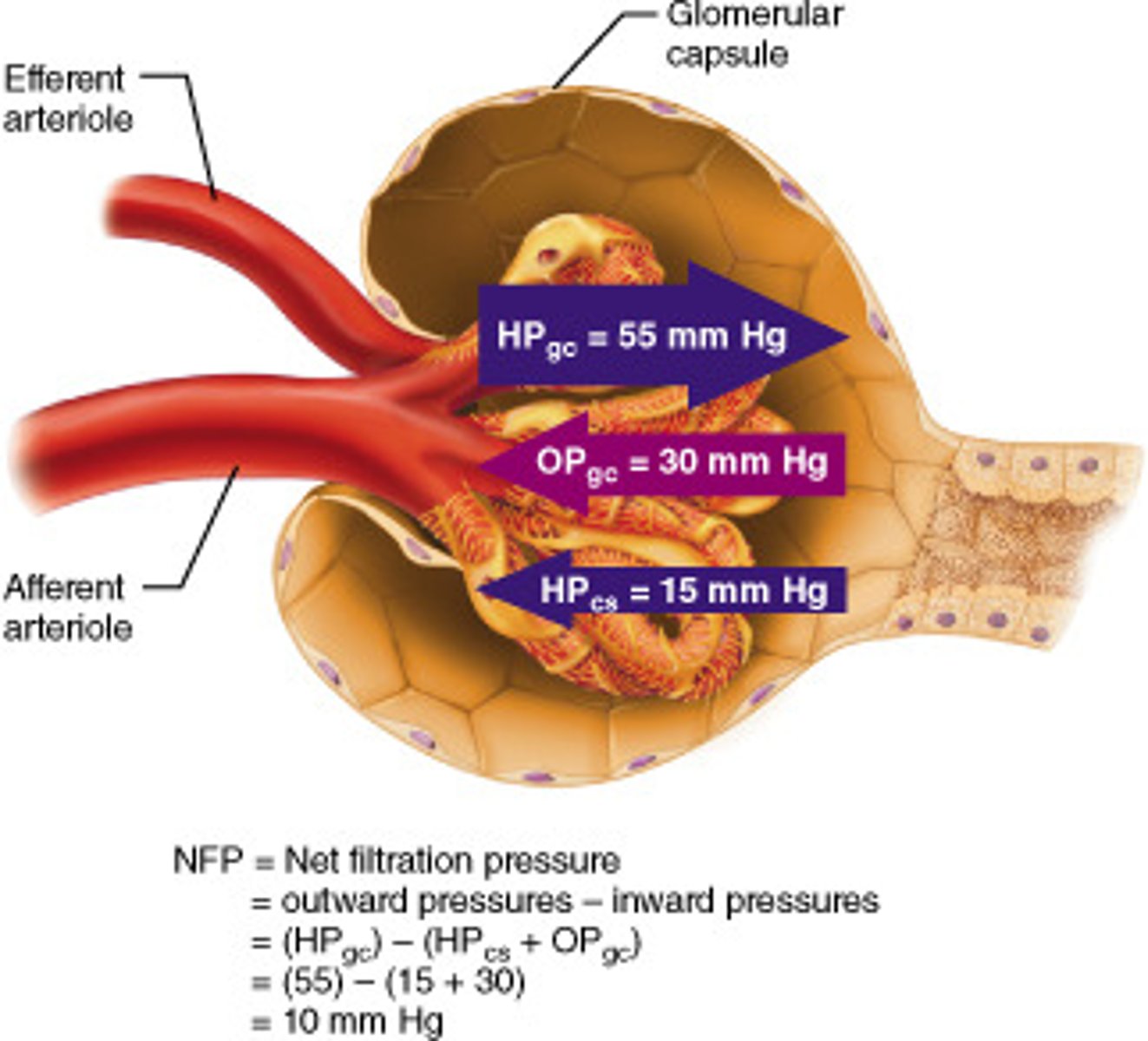
What is hydrostatic pressure?
-Pressure from the surge of blood every time the heart contracts
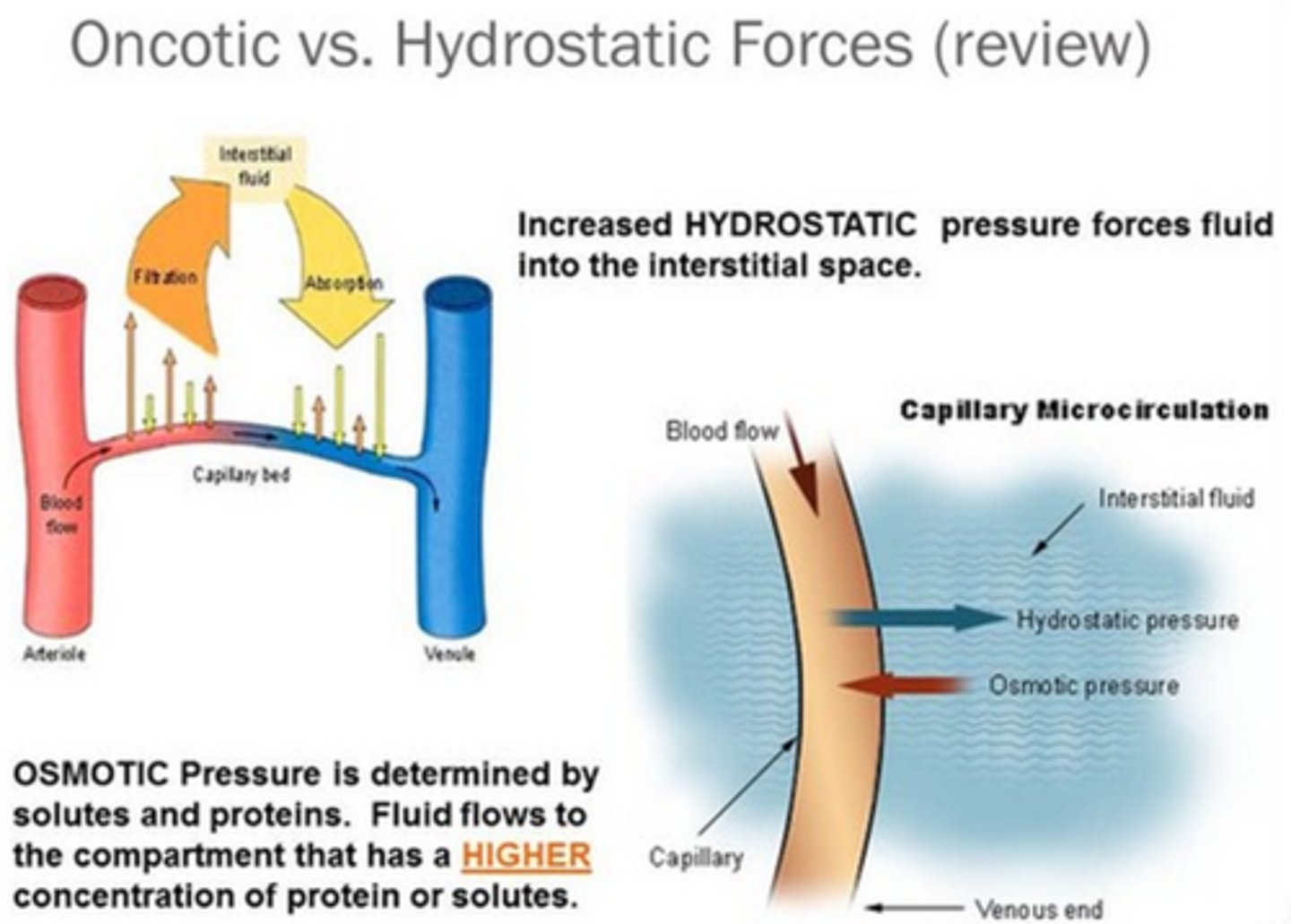
What is oncotic pressure?
Tendency of water to move into the blood by osmosis
-Higher oncotic pressure = Higher solute concentration = Lower water potential

At the capillary bed near the arteries, why is fluid forced out from the capillaries into the tissue fluid?
-Hydrostatic pressure in capillaries greater than oncotic pressure in the tissue fluid, so water is forced out via osmosis
How do plasma proteins contribute to the osmotic effect?
-The plasma in the proteins provide a higher solute potential, so there's a lower water potential in the blood
Why does water re-enter the capillaries near the venule end?
-There is a lower water potential due to fluid leaving, so as oncotic pressure is higher than the hydrostatic pressure in the tissue fluid, water moves back in via osmosis
There is usually an excess of tissue fluid leftover after it leaves for the bloodstream. What happens to the tissue fluid?
-Returned to the blood through the lymphatic system
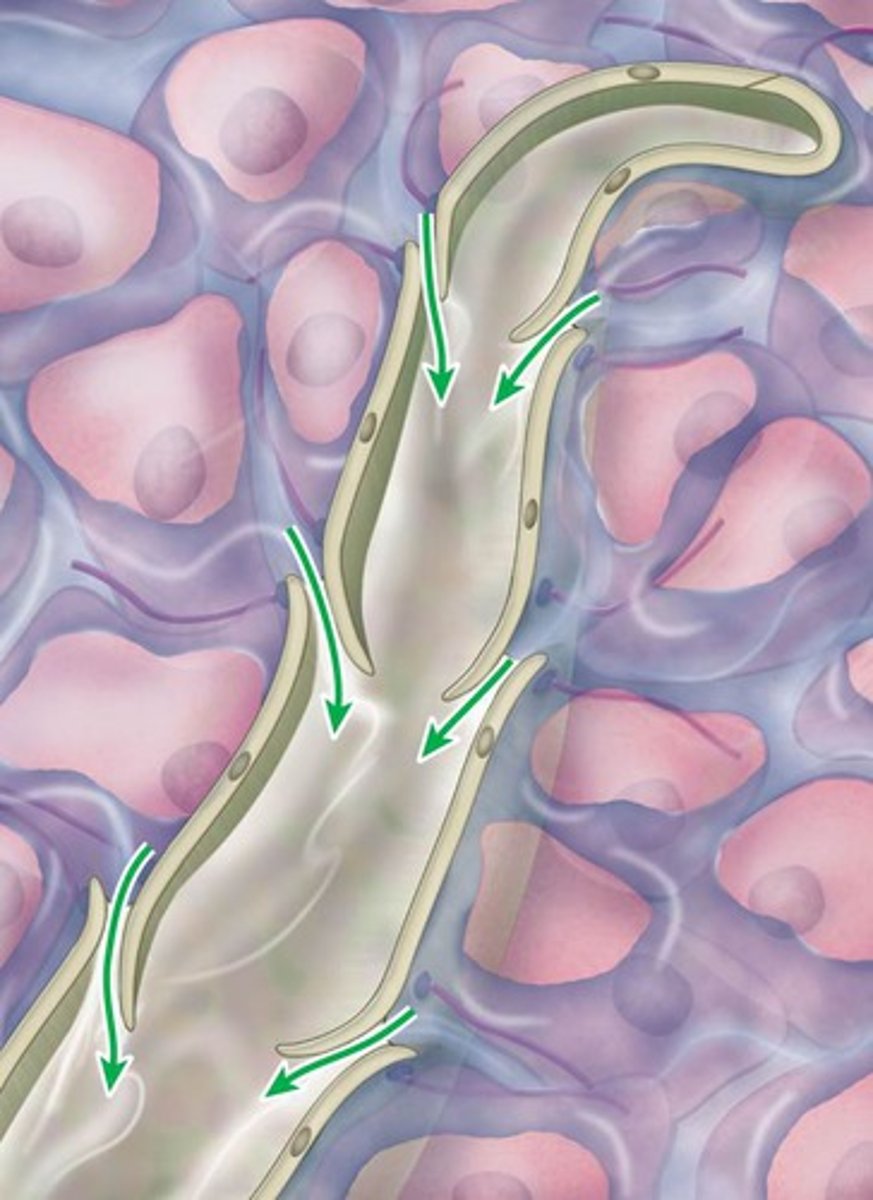
What vessels do the excess tissue fluid drain into?
Lymph capillaries, in which the fluid is then called Lymph.
What is the composition of Lymph?
-Similar to plasma and tissue fluid but with less oxygen and fewer nutrients and more fatty acids.
-As well as more Lymphocytes
What structures do lymph vessels pass by and what do they do?
-Lymph nodes, which are a build up of lymphocytes to intercept and filter pathogens before returning to the blood