Tectonic Hazards
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
what are examples of intraplate eathquakes?
2011 Mineral, Virginia and 1812 New Madrid
where do hotspot volcanoes occur?
over magma plumes in the asthenosphere eg Hawaii and Iceland
properties of a continental plate?
thicker, less dense, mainly made of granite
what is mantle convection?
Mantle convection is the slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the interior of the Earth to the surface.
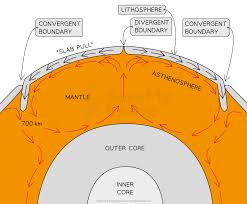
what are long, narrow depressions in the ocean floor with depths of over 6km and up to 11km
Deep sea trenches
example of a deep sea trench
Marina trench
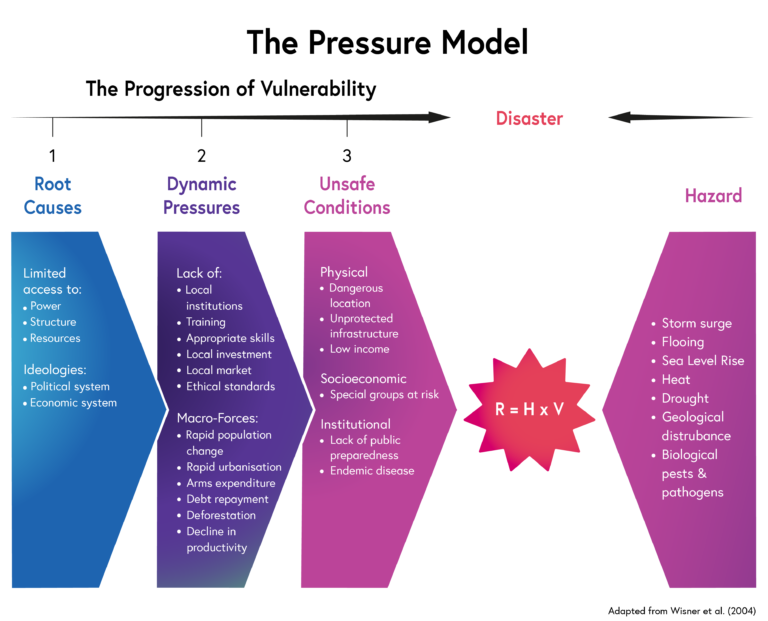
Main sectors in the Pressure model of the PAR model
Root causes - (resources, decision making and governance), Dynamic pressures -(education, urbanisation and population change) causing Unsafe conditions - poor quality housing and infrastructure, poverty
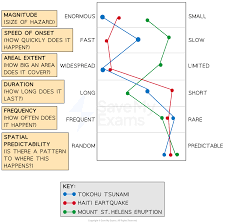
measuring - Magnitude, Speed of onset, Areal extent, Duration, Frequency, Spatial predictability