Biology- Chapter 2: Eukaryotic Cell Structure
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
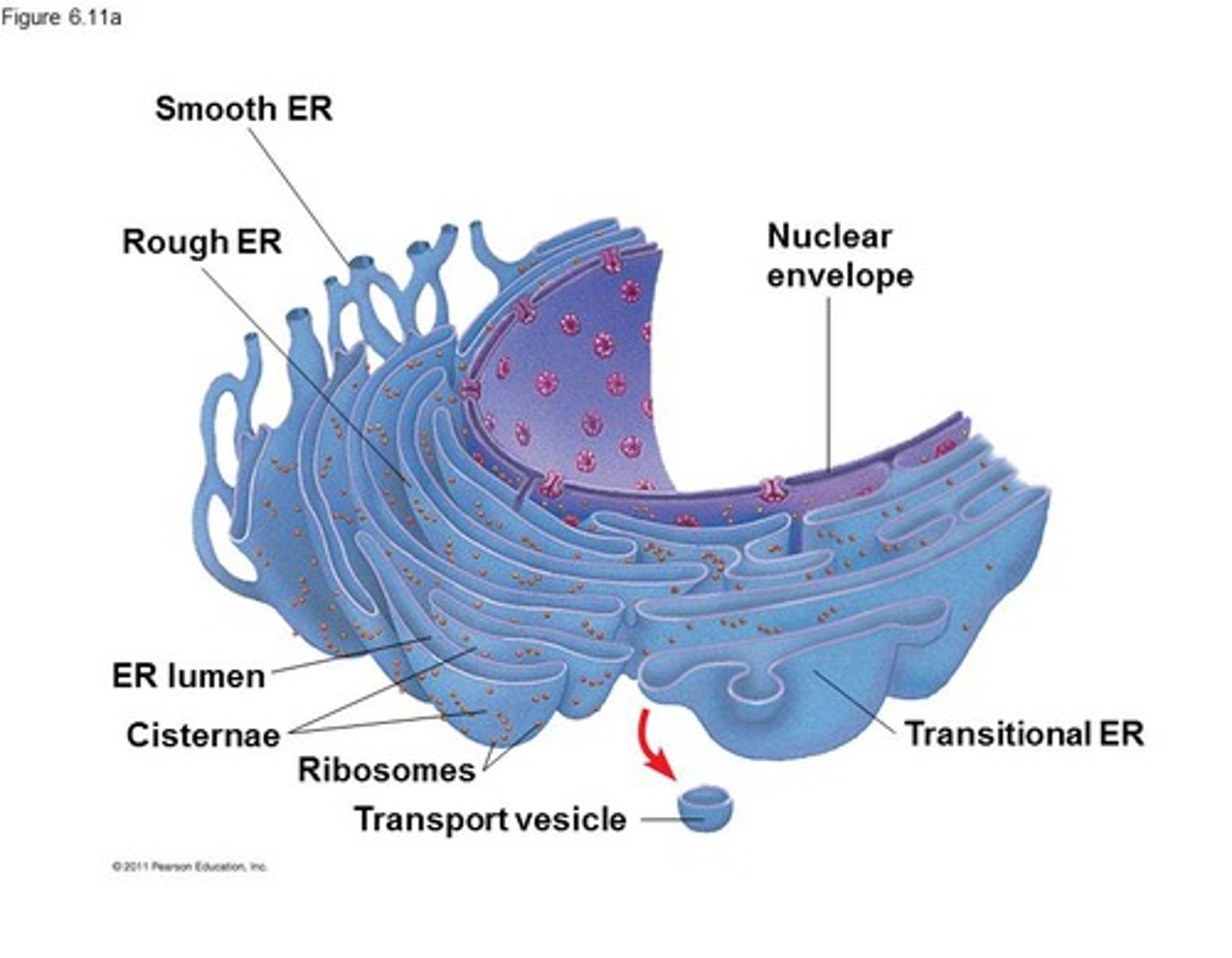
Features of endoplasmic reticulum?
Network of membranes enclosing flattened sacs (cisternae)
Connected to outer membrane of nucleus
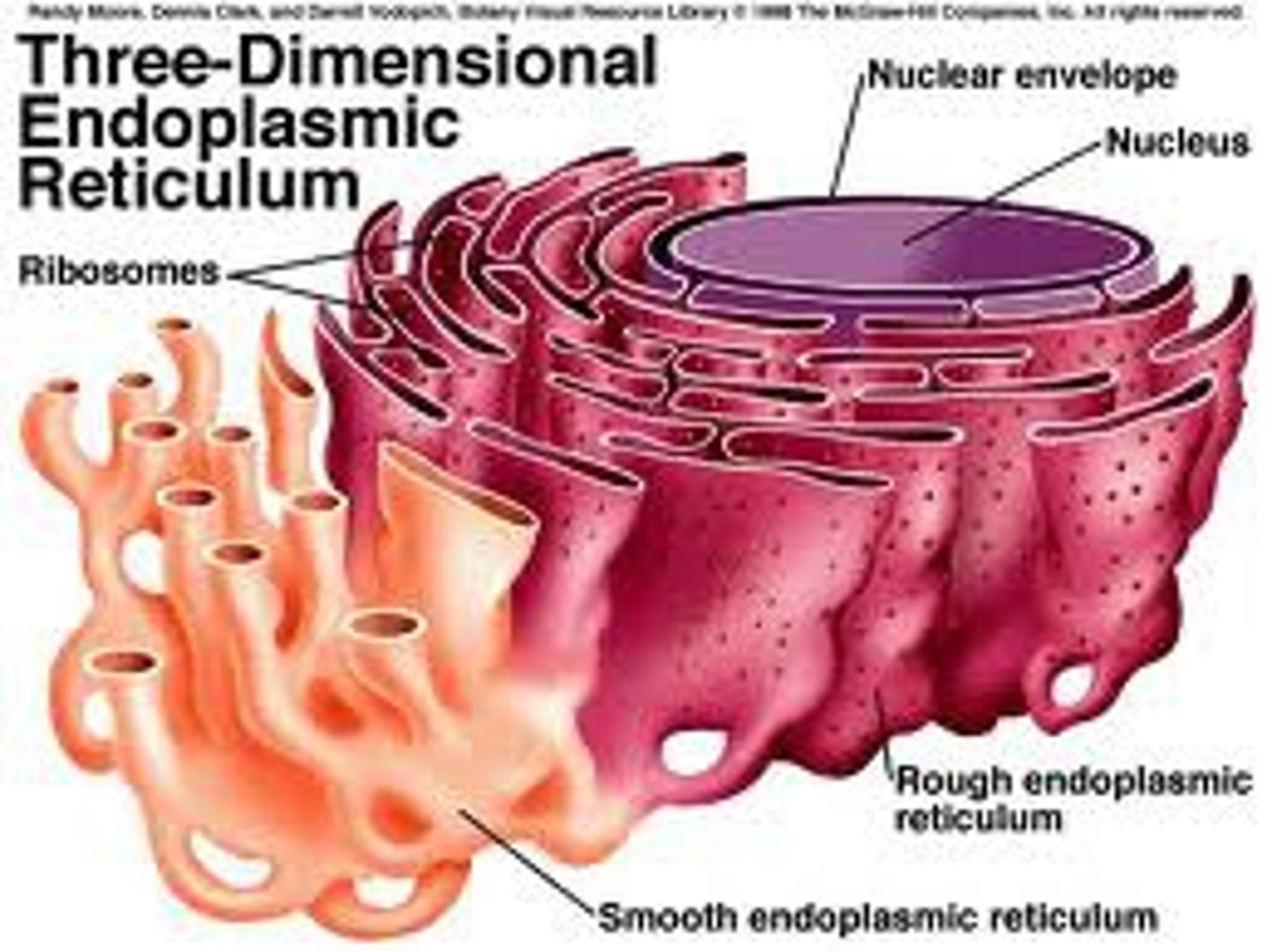
What is the Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum and its function?
Part of the endoplasmic reticulum
Function: Lipid and carbohydrate synthesis and storage ; drug detoxification
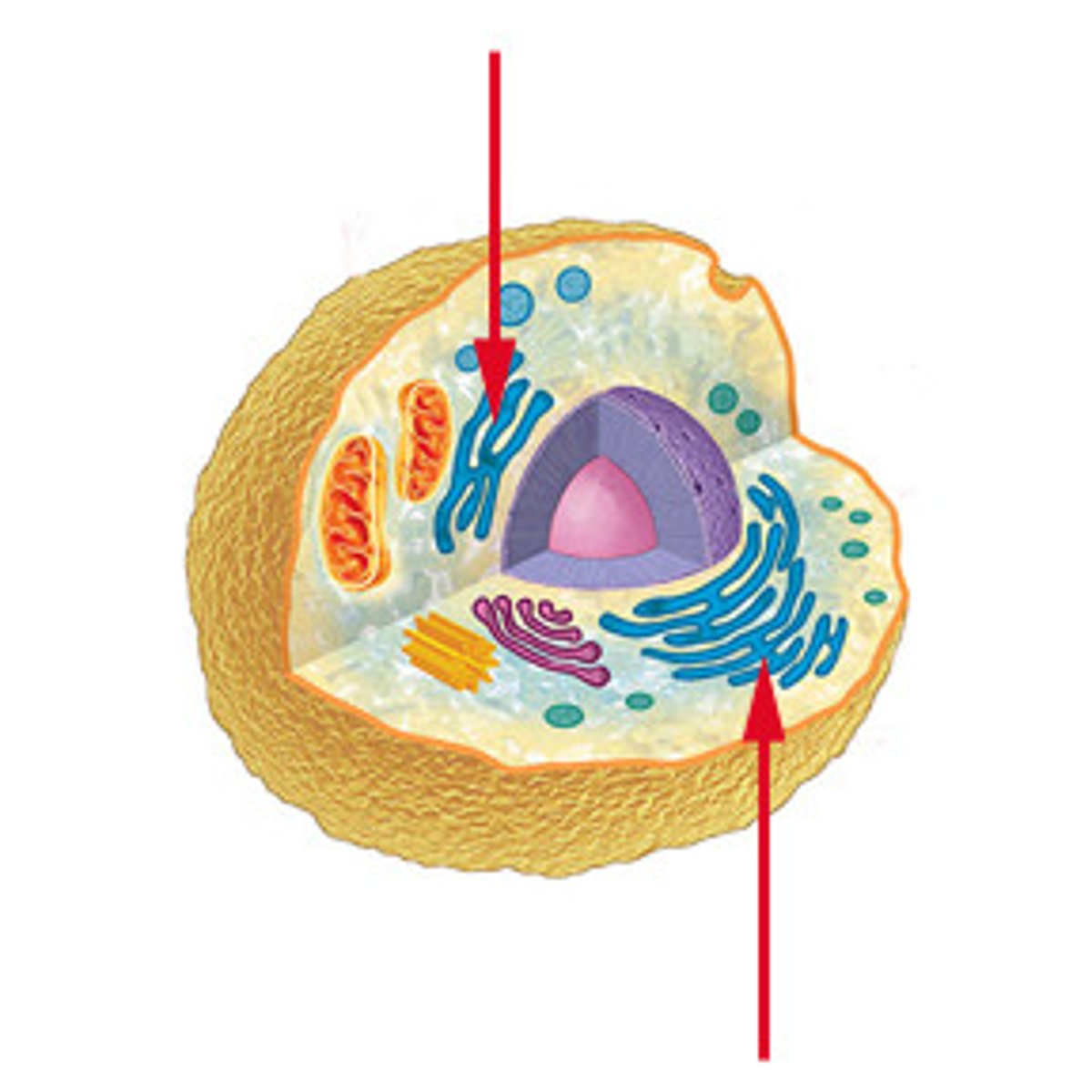
What is the Rough endoplasmic reticulum and its function?
Is part of the endoplasmic reticulum ; ribosomes bound to its surface
Function: Synthesises and transports proteins
What is the cytoskeleton?
A network of fibres present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
What are microfilaments and what is its function?
Part of the cytoskeleton - are contractile fibres made of actin
Function: Responsible for cell movement & cell contraction during cytokinesis
What are microtubules and what is its function?
Part of cytoskeleton - are globular proteins that polymerise to form tubes)
Function: Determines shape of cells, acts as tracks for cell movement
Is what spindle fibres are made of
What are intermediate fibres/filaments and what is its function?
Part of the cytoskeleton
Function: Gives mechanical strength to cells, helps to maintain integrity
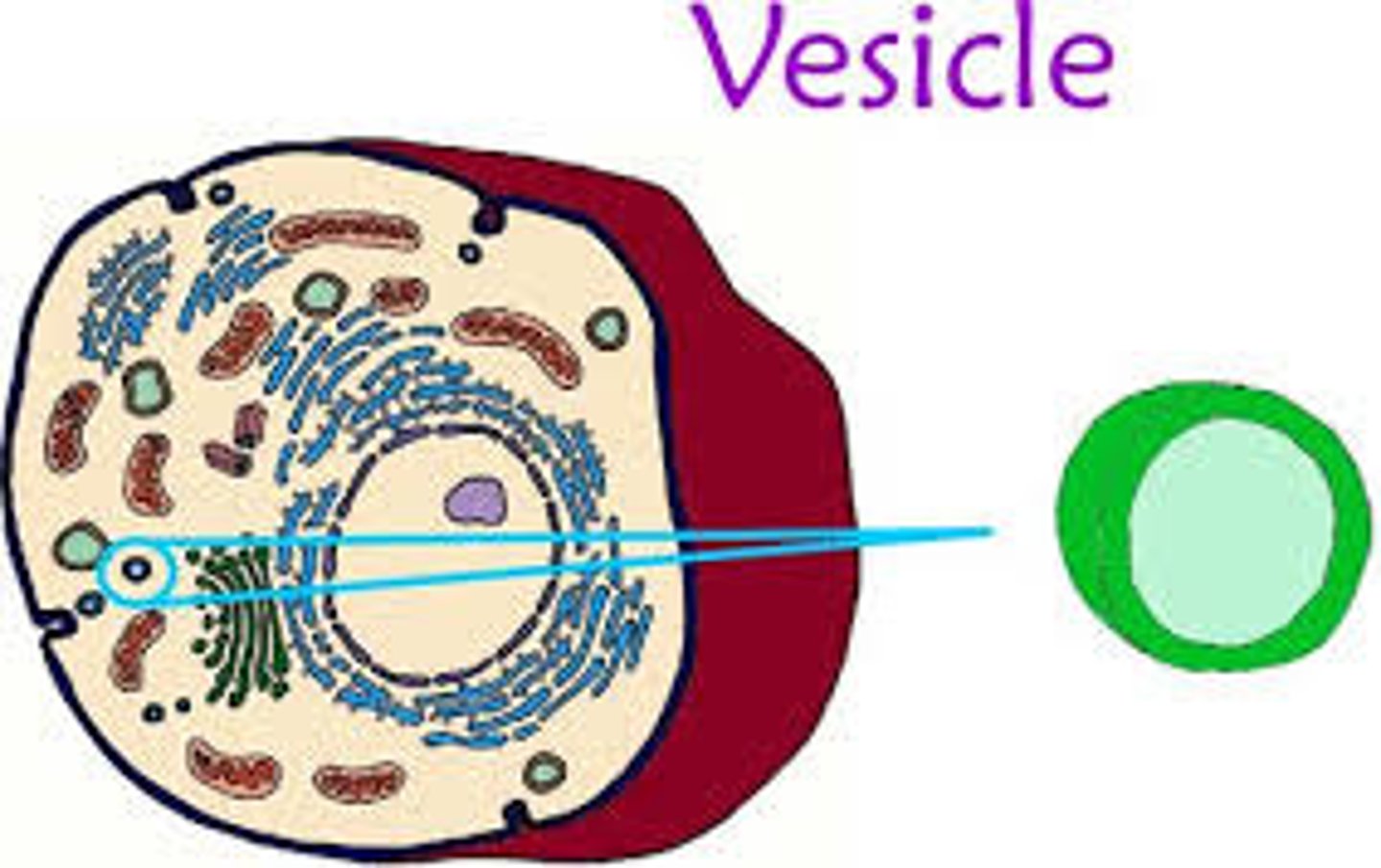
Features of vesicles and its function?
Consists of a single membrane filled with fluid
Function: Transport substances inside the cell
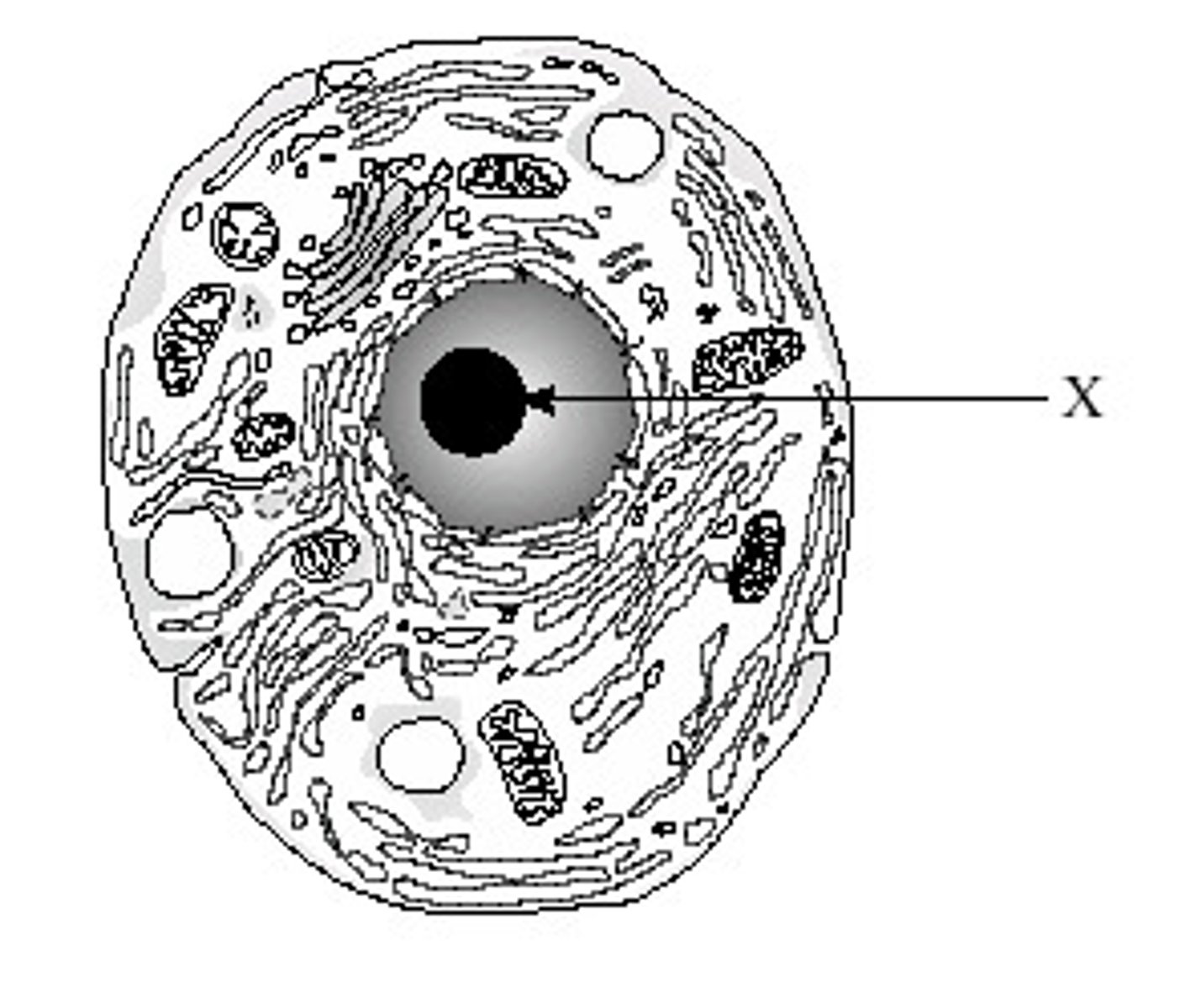
Features of nucleolus and its function?
Feature: Centre of nucleus
Made of proteins and RNA
Function: To produce rRNA to make ribosomes for protein synthesis
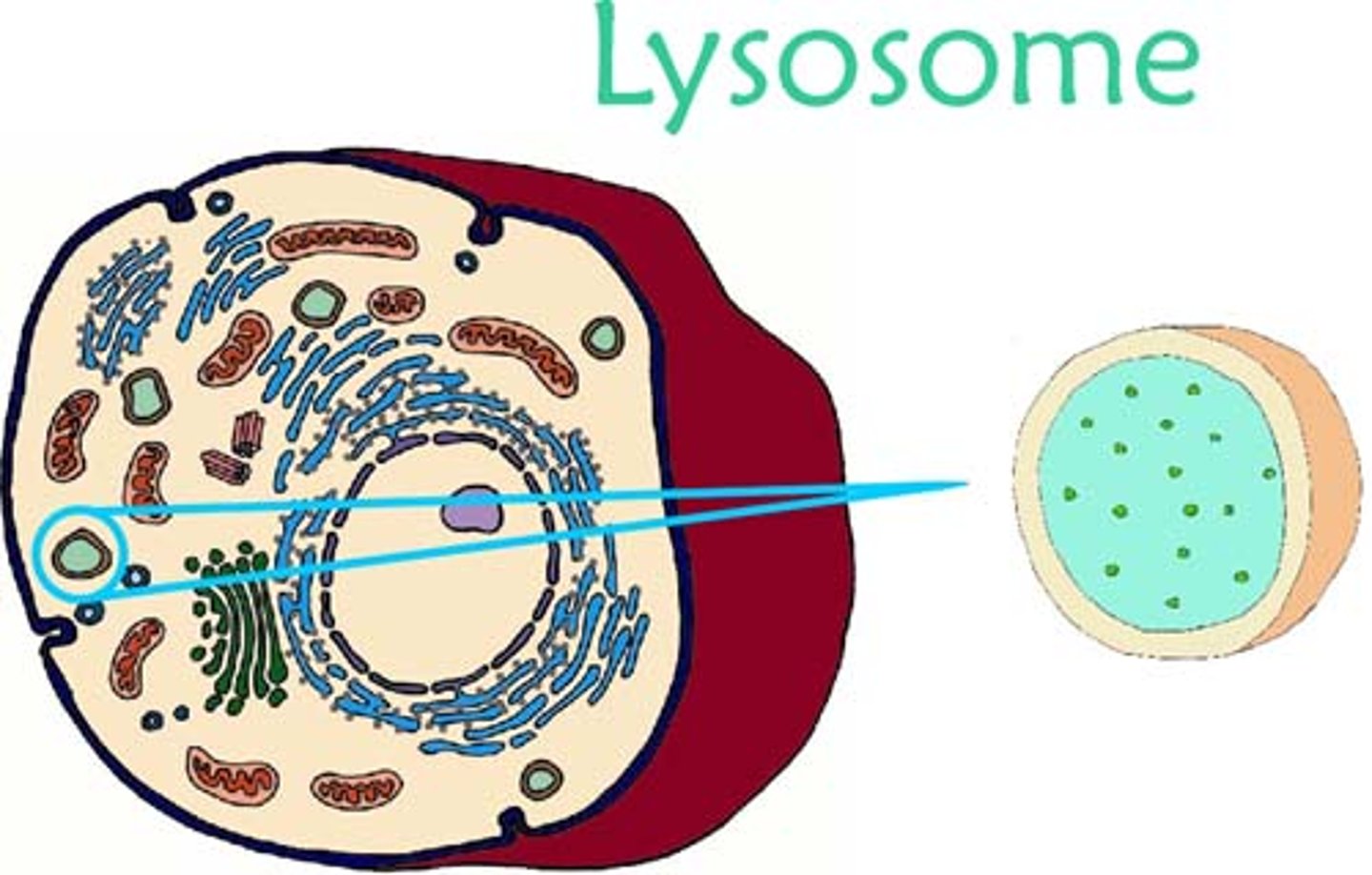
Features of Lysosomes and its function?
Feature: Specialised forms of vesicles
Fluid contains lots of hydrolytic enzymes
Function: Breaks down waste material in cells , & pathogens when ingested by phagocytic cells
Helps with apoptosis
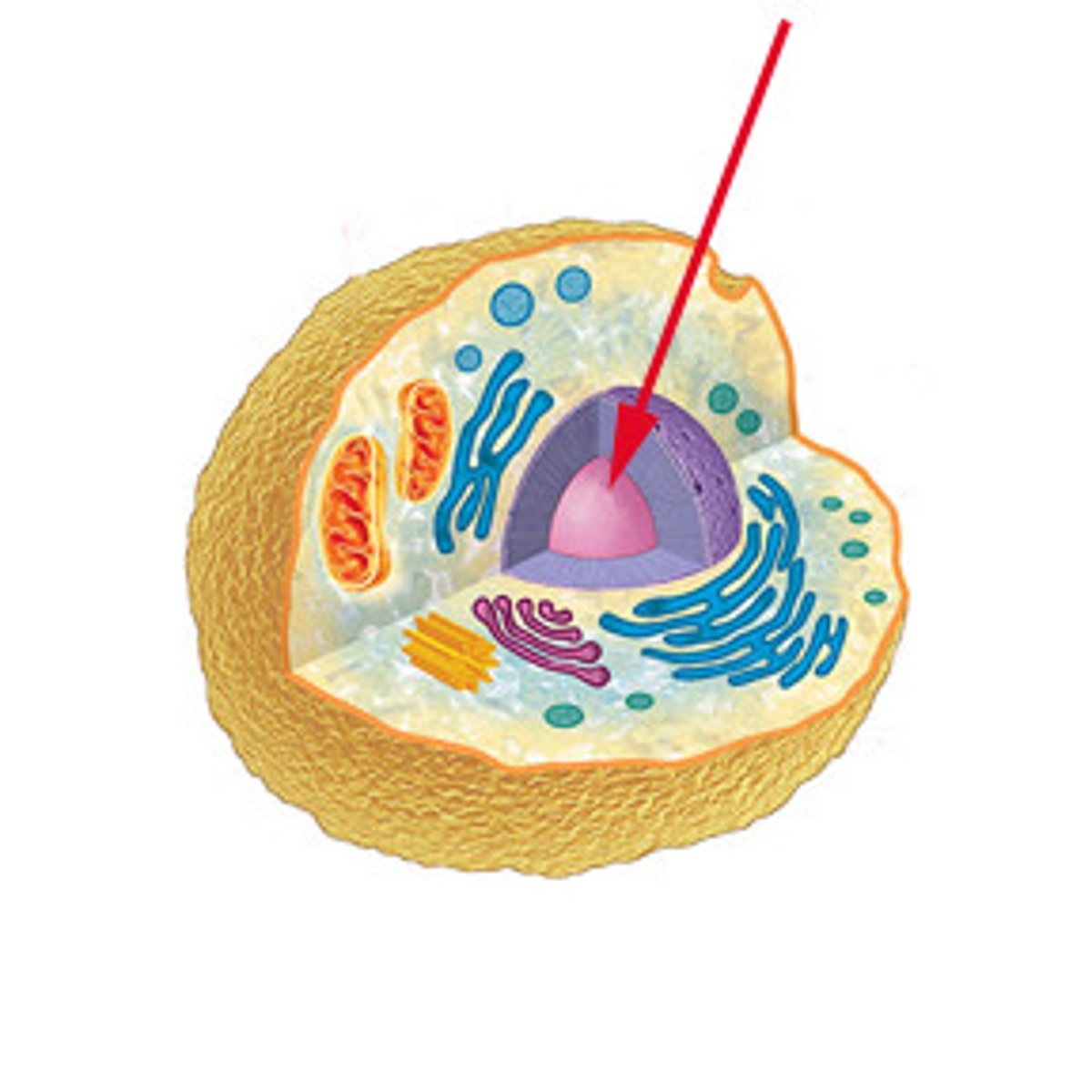
Nucleus' features and functions
Feature: Contains DNA
Function: Directs synthesis of protein, so controls metabolic activities
Feature: DNA contained within double membrane aka nuclear envelope
Feature: Nuclear pores with N.E.
Function: Allows mRNA out and nucleotides in
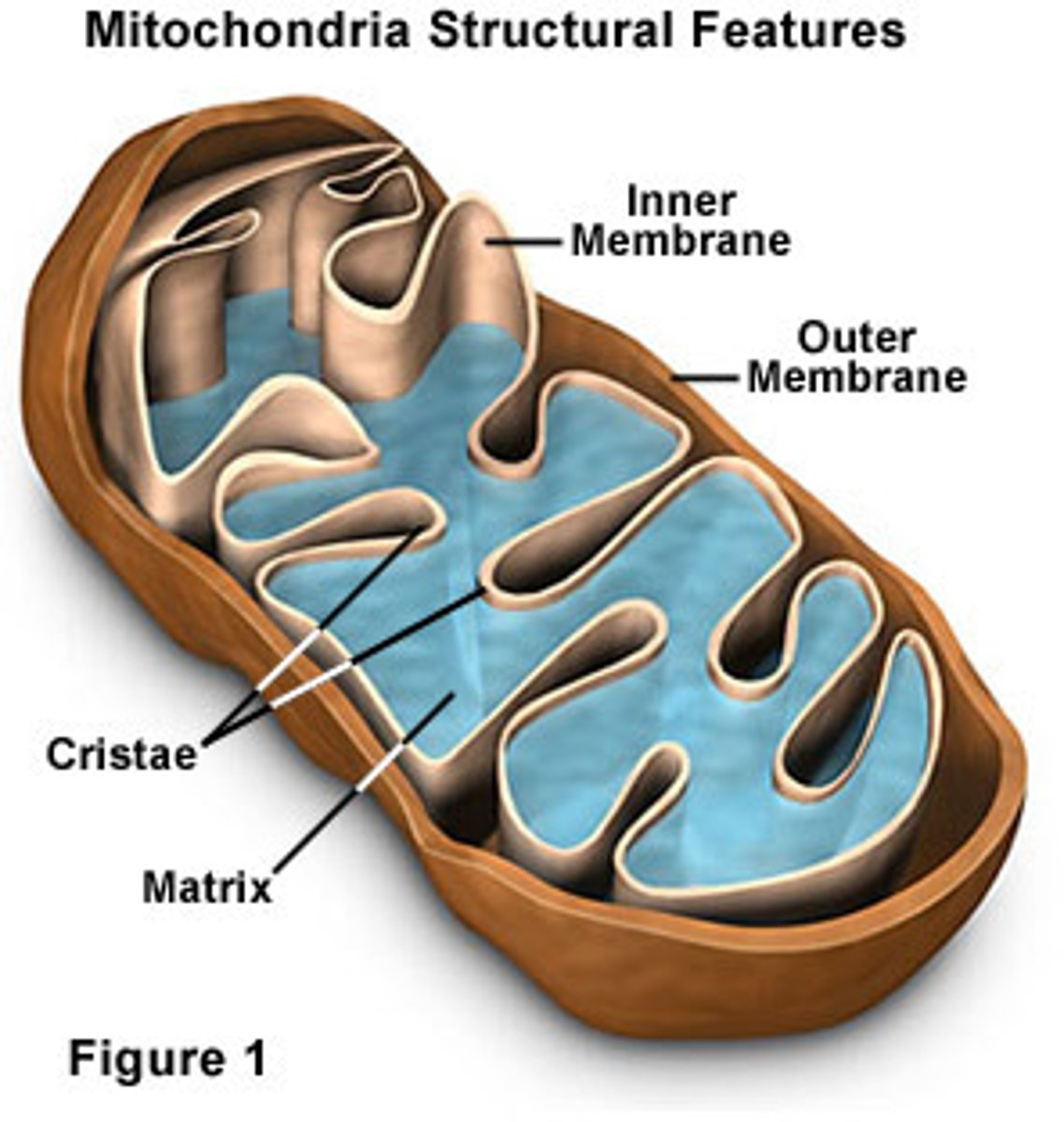
Mitochondria's features and functions
Feature: Highly folded inner membrane (CRISTAE), contains enzymes used in aerobic resp.
Function: In cristae final stages of aerobic resp. occurs
Feature: Fluid interior (MATRIX)
Function: Contains mtDNA which can produce more enzymes & reproduce themselves
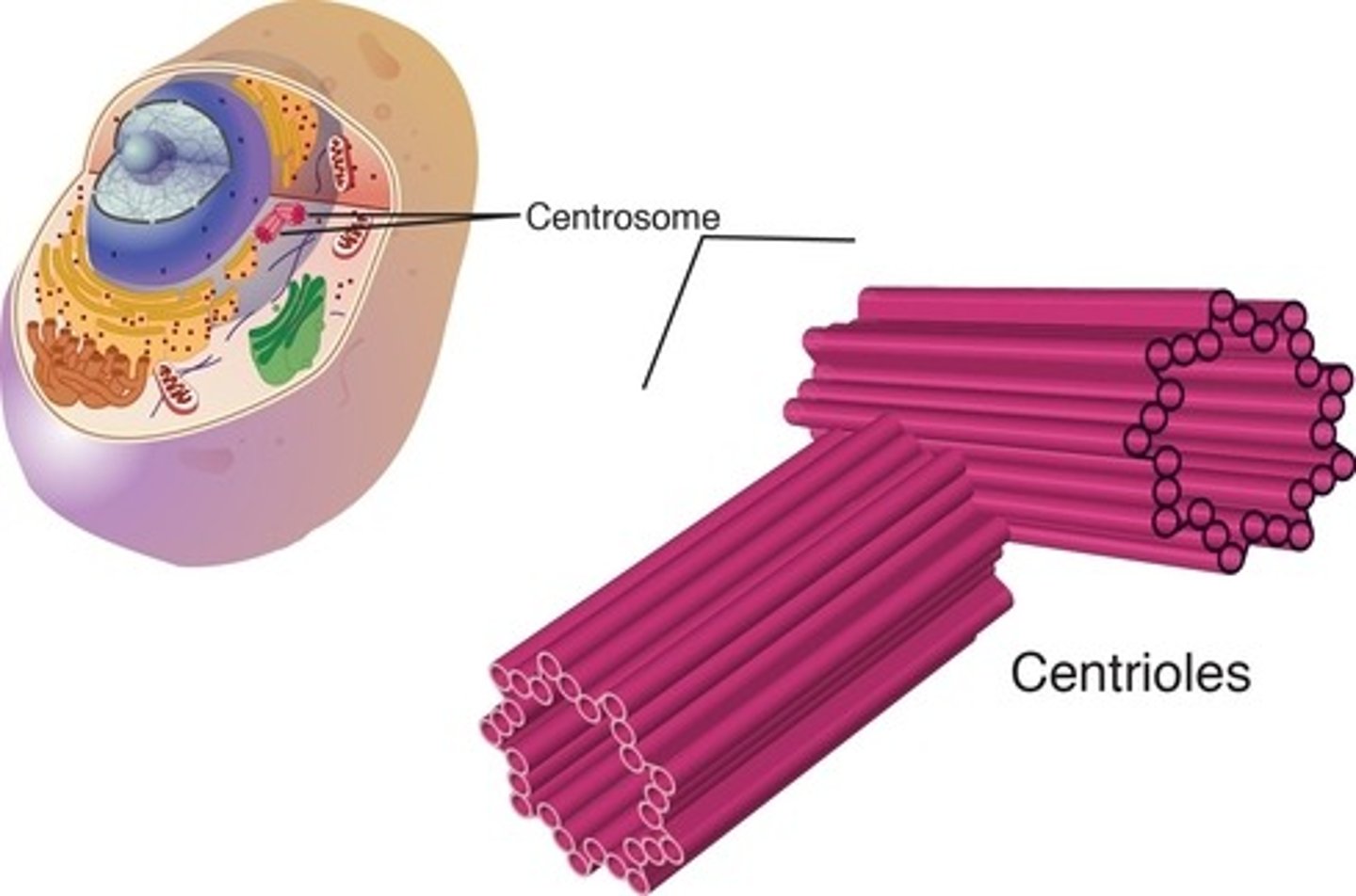
Centrioles' features and functions
Feature: Made of microtubules ; 2 associated centrioles form centrosome
Function: Makes and organizes spindle fibers in cell division
Function: W. structures like flagella and cilia, determine positioning of them
Flagella's features and functions
Feature: Long, few & protrude from some cell types, whip-like
Function: Causes cell movement
Function: Used as a sensory organelle detecting chemical changes in cell's environment (some cells)
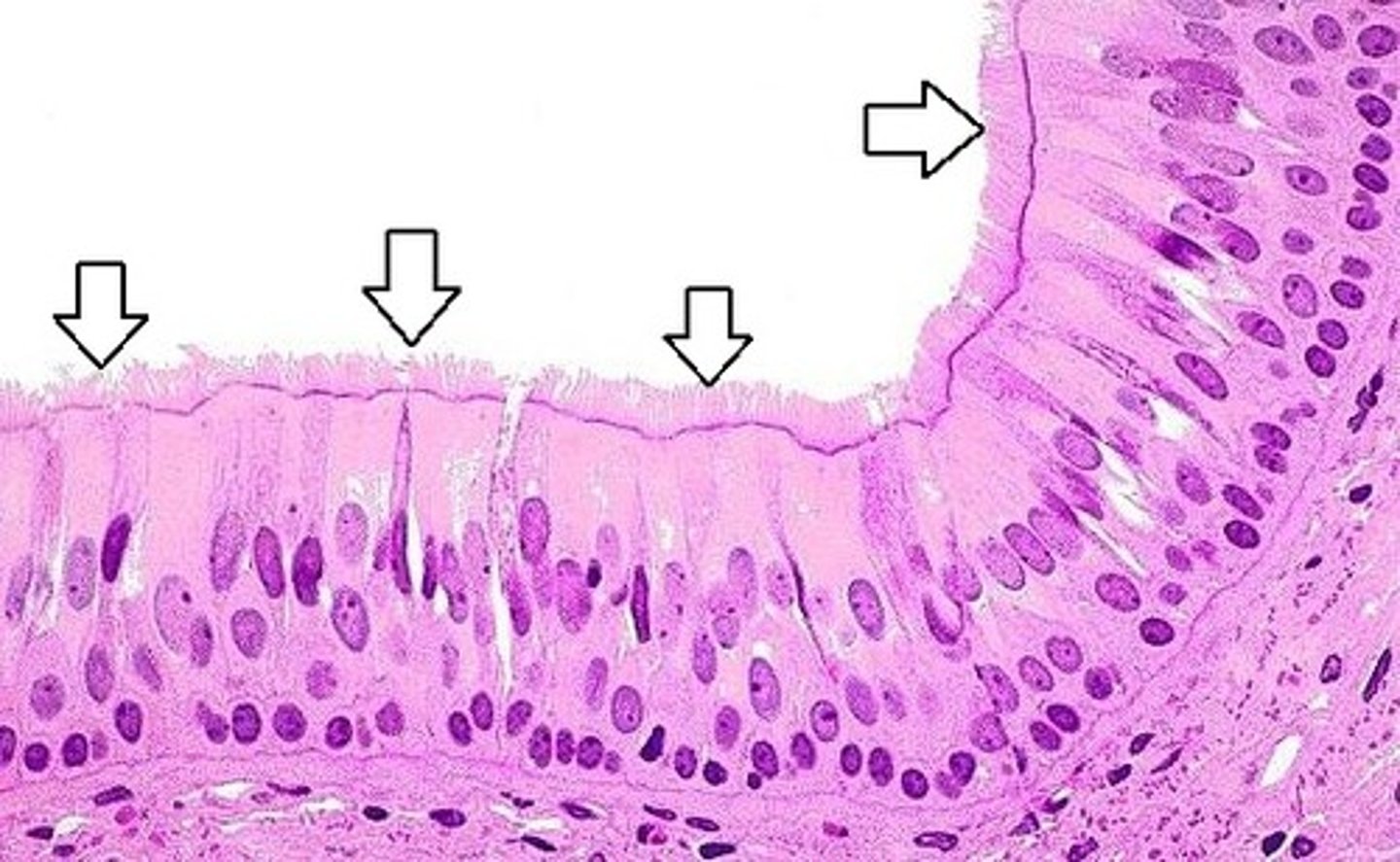
Cilia features and functions
Feature: Short & many
Function: Stationary - have important function in sensory organs
Feature: Contain 2 central microtubules surrounded by 9 pairs of microtubules (9+2 wheel arrangement)
Function: Mobile - beat rhythmically (pairs of parallel microtubules slide over each other, cilia move)
Ribosome's feature and function
Feature: Made of 2 subunits of RNA
Function: Where peptide chains are synthesized (proteins)
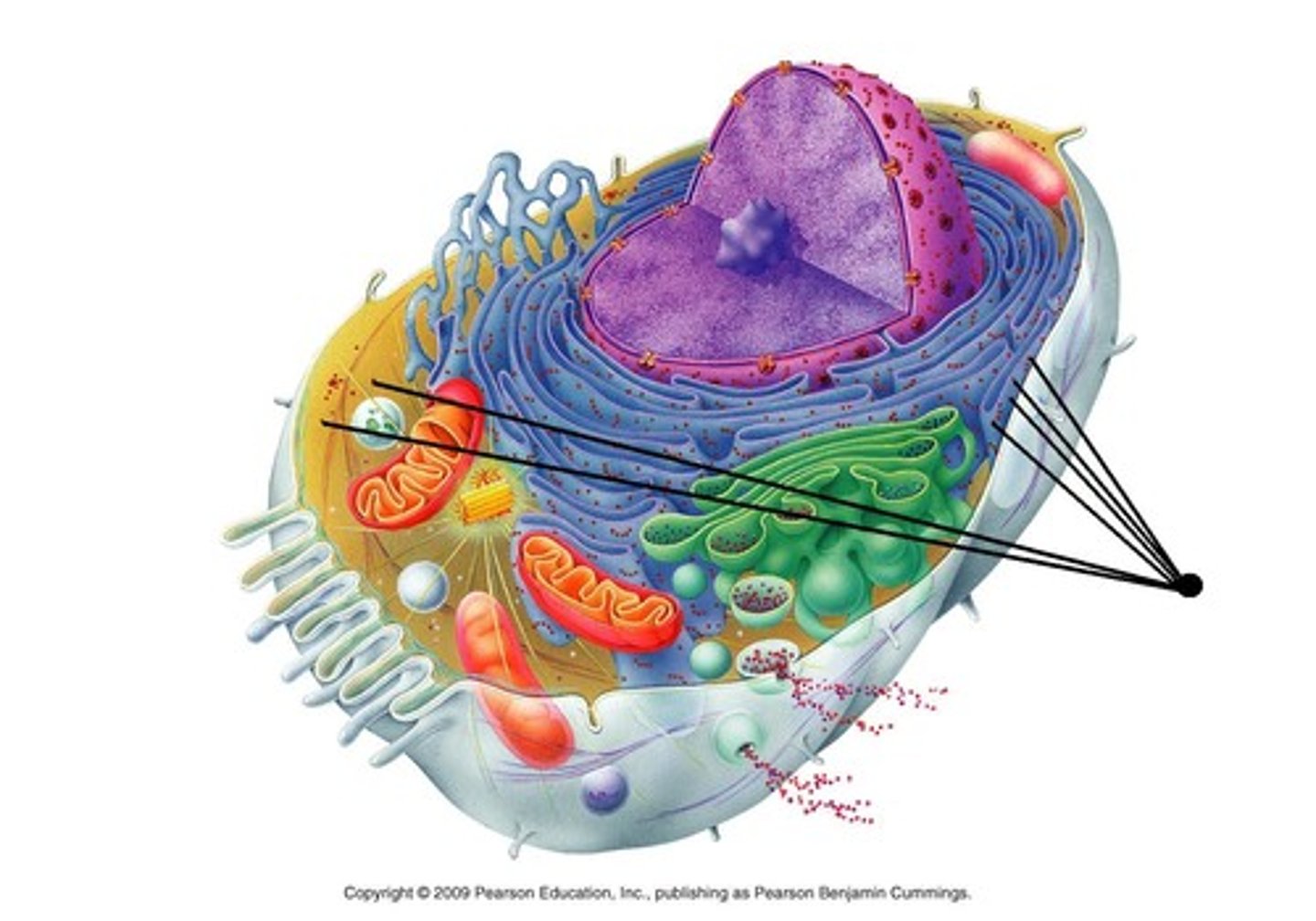
Golgi apparatus features and function
Feature: Network of flattened membranes (cisternae)
Function: Modifies proteins & packages them in vesicles for transport
Feature: Doesn't contain ribosomes
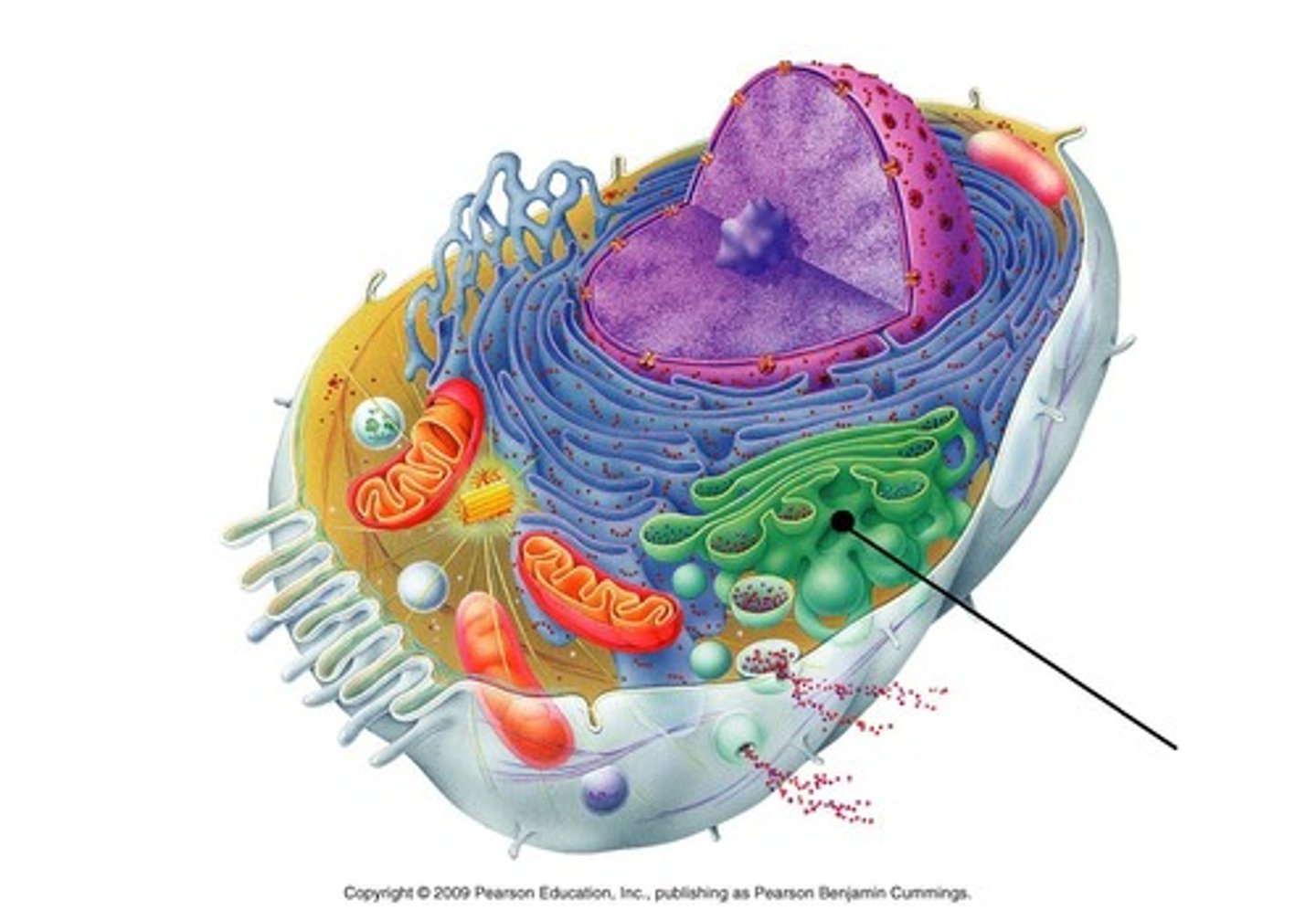
What type of vesicles will the G.A. package the modified protein in?
Secretory if leaving
Lysosomes to stay
Plasma membrane
Feature: Phospholipid bilayer w. proteins, cholesterol and carb chains
Function: Protein and carb chains act as receptors in cell signaling
Feature: Create a partially impermeable membrane
Function: keeps useful things in & waste out
Function: Compartmentalization
Function: Allows metabolic reactions to occur