Gen chem 2 equilibrium
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
When K >> 1
Product favored reaction. Rxn proceeds forward at equilibrium there is a lot of product and very little reactant.
When K << 1
Reactant favored reaction. Rxn proceeds backward at equilibrium there is a lot of reactant and very little product.
What does K mean?
K is the measure of how far a reaction will proceed in the direction it has been written.
Large K means that
at EQUILIBRIUM you have lots of product and not much reactant
A very large value of K (10^8): Rxn runs to comple on [products] > [reactants] The equilibrium lies toward the product side
Small K means that
at EQUILIBRIUM the concentration of products is smaller than the concentration of reactants.
A very small value of K (10^-12): Rxn effec vely doesn’t happen [reactants] > [products] The equilibrium lies toward the reactant side
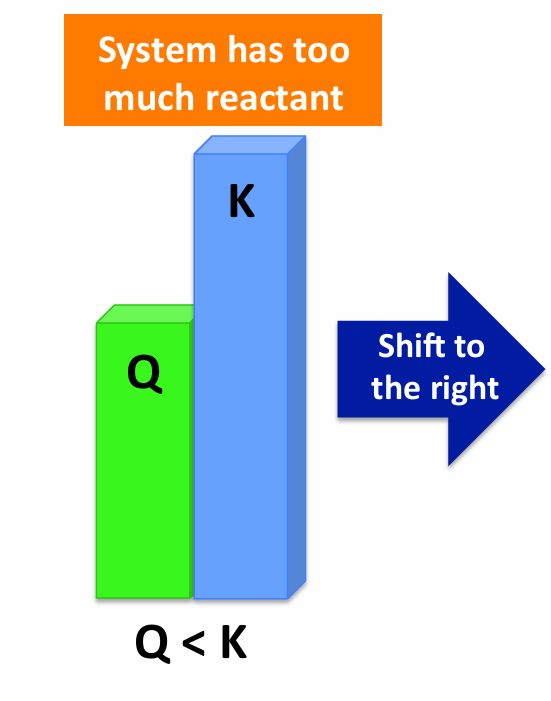
If Q < K
Reaction proceeds forward (RIGHT)
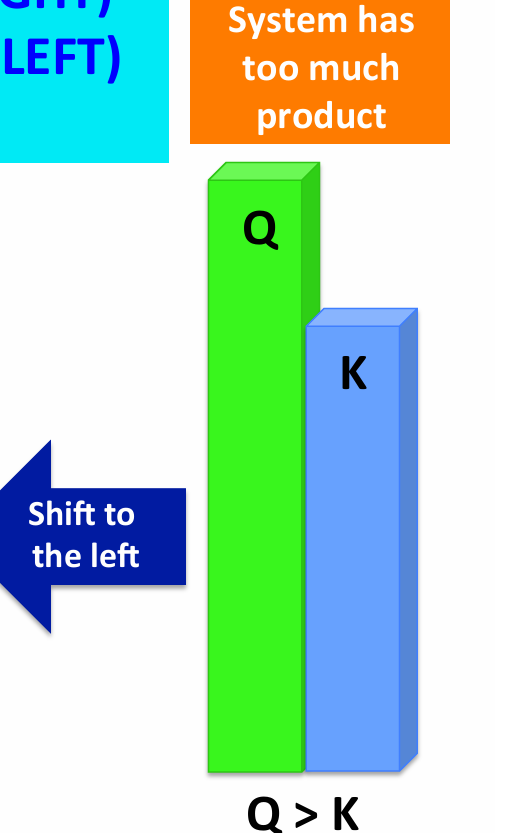
If Q > K
Reaction proceeds backwards (LEFT)
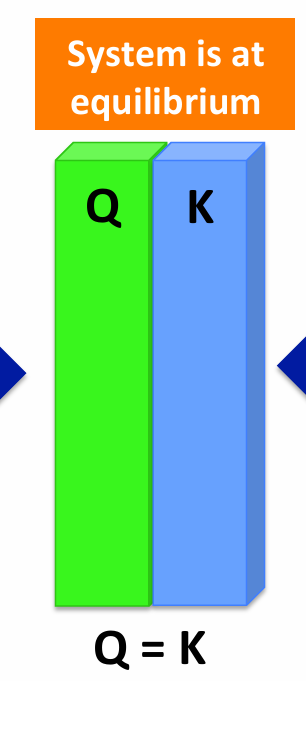
If Q = K
Reaction is at equilibrium
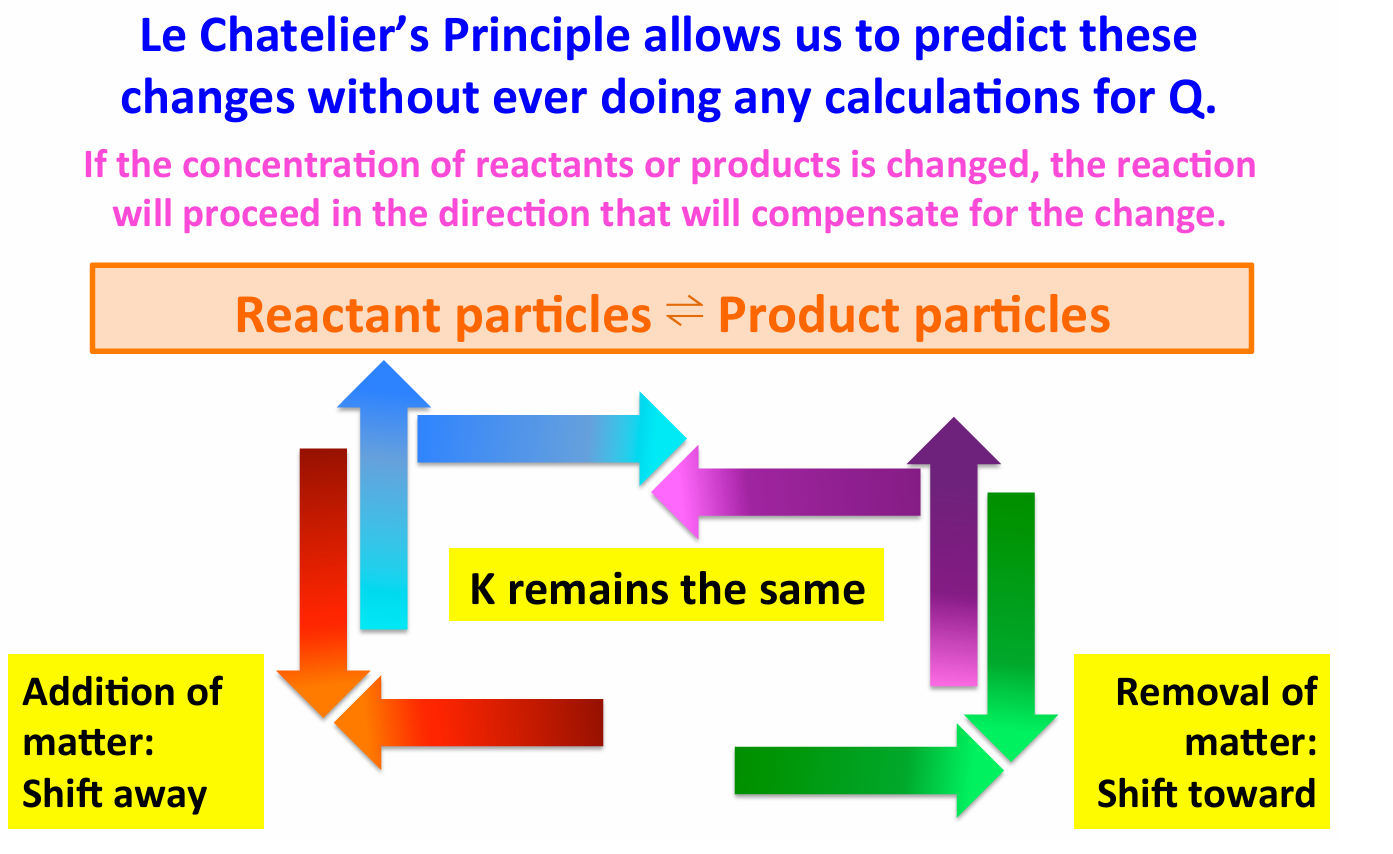
If we remove reactant from the system
There is now less reactant than there was at equilibrium The equilibrium will shift to the LEFT, towards reactants, to make more of the reactant
If we remove product from the system
There is now less product than there was at equilibrium The equilibrium will shift to the RIGHT towards products, to make more of the product
If some ammonia gas is added to the system
The equilibrium position will shift to the left.
If some solid NH4Cl is added to the system
The equilibrium position won’t shift, and K remains unchanged (pure solids are not included)
ΔH < 0
This reaction releases heat - EXOTHERMIC! Heat can be thought of as a product in an exothermic rxn.
What happens if we increase the temperature of the reaction? The Equilibrium will shift to consume the added heat! Equilibrium shifts toward the reactants
What happens if we decrease the temperature of the reaction? The Equilibrium will shift to produce more heat! Equilibrium shifts toward the products
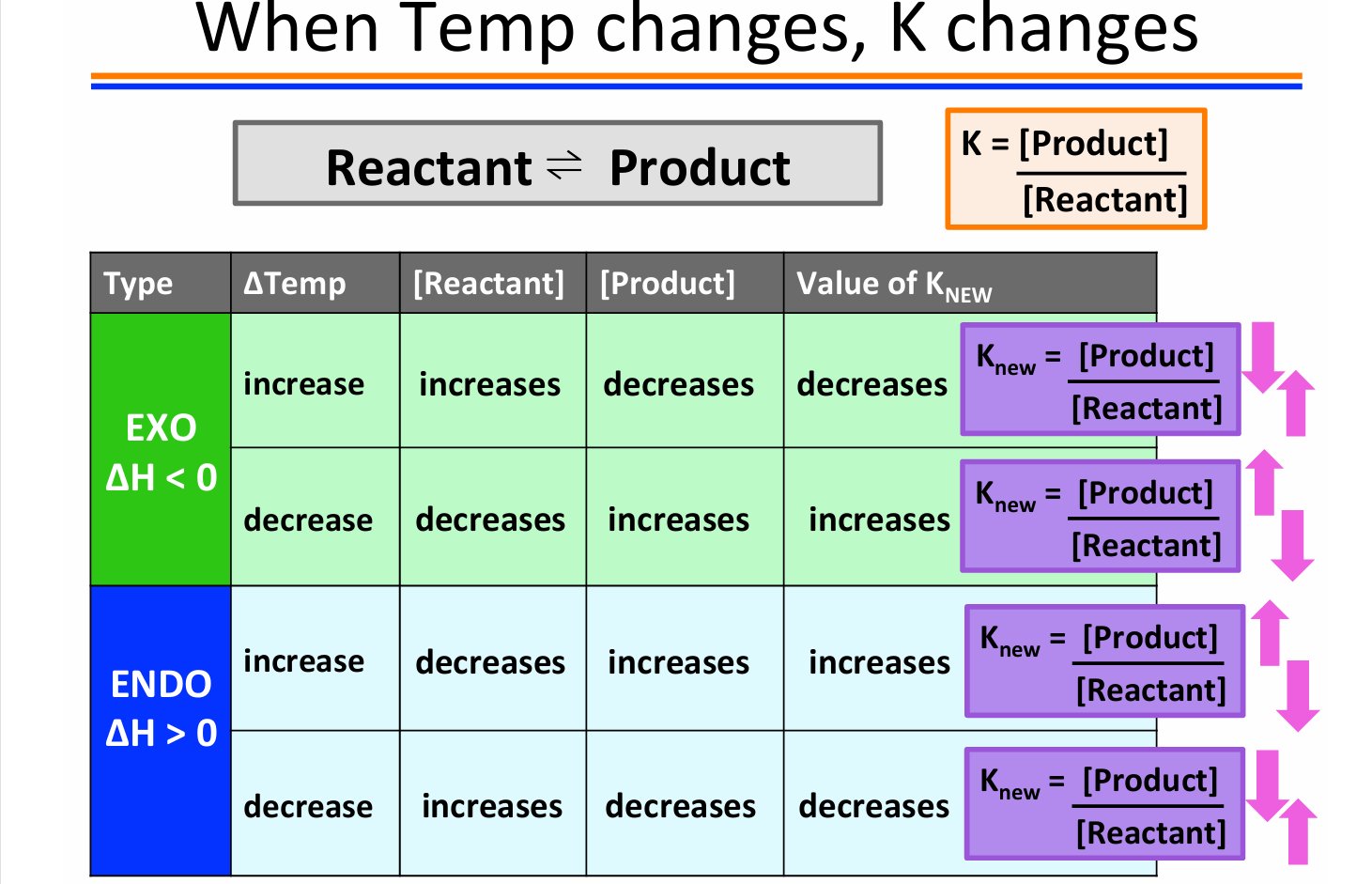
ΔH > 0
This reac on absorbs heat - ENDOTHERMIC Heat can be thought of as a reactant in an endothermic rxn.
What happens if we increase the temperature of the reaction? The Equilibrium will shift to consume the added heat! Equilibrium shifts toward the products
What happens if we decrease the temperature of the reaction? The Equilibrium will shift to produce more heat! Equilibrium shifts toward the reactants
Heat is a reactant
Consider the endothermic reaction: heat + C(s) + CO2(g) ⇌ 2CO(g) If such a system at equilibrium is heated, equilibrium will ________ , and
shift to the right; the value of K increases
When temp increases rxn shifts right and more CO is produced K increases
In general, for exothermic reactions
K decreases when the temperature is raised. When temp increases rxn shifts left and more reactant is produced K decreases
Heat is a product
Daltons Law of Partial Pressures
For this mixture of gases in a closed container: Ptotal = pN2 + pO2 + pNO2
Volume and pressure are related
For systems that contain a gas: What happens when we stress the system by changing the volume? We change the pressure
Increase volume: Decrease pressure
Decrease volume: Increase pressure
Equilibrium shifts toward the side with more moles
(increases pressure)
Equilibrium shifts toward the side with less moles
(decreases pressure)
3 moles gaseous reactant : 2 moles gaseous product
From 3 moles to 2 moles (decreasing pressure) When volume is decreased this reaction shifts to the RIGHT
From 2 moles to 3 moles (increasing pressure)
When volume is increased this reaction shifts to the LEFT
K changes only
when T changes
Addition of a noble gas (group 8)
Adding the noble gas changes the overall pressure of the system, but it does not interact with the other gases in the system. The noble gas does not affect the par al pressures (or concentrations) of the reactants or the products. There will be NO SHIFT in equilibrium and no change in K
For endothermic reactions
K increases when temperature increases
For exothermic reactions
K decreases when temperature increases.